AtCoder ABC 130F Minimum Bounding Box
题目链接:https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc130/tasks/abc130_f
题目大意
给定地图上 N 个点的坐标和移动方向,它们会以每秒 1 个单位的速度移动,设 Ans(t) 为在 t 时刻,$(x_{max} - x_{min}) * (y_{max} - y_{min})$的值,求 Ans(t) 的最小值。(最小值可能不是一个整数)
分析
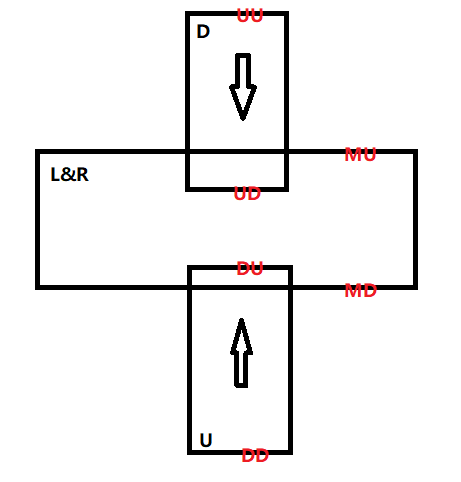
其中,UU 代表往下移动的点中 Y 坐标最大值,UD 代表往下移动的点中 Y 坐标最小值,其余同理。
我们发现,影响$(y_{max} - y_{min})$就是这 6 个值,当它们某两个值重合时就有可能改变答案。
X 坐标方向上也是同理,只要旋转一下即可。
当我们把 X 和 Y 坐标上对应的 6 个值都算出来的时候,把它们两两组合,暴力枚举所有可能时刻,就能求出最终答案。
代码如下
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; #define INIT() ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
#define Rep(i,n) for (int i = 0; i < (n); ++i)
#define For(i,s,t) for (int i = (s); i <= (t); ++i)
#define rFor(i,t,s) for (int i = (t); i >= (s); --i)
#define ForLL(i, s, t) for (LL i = LL(s); i <= LL(t); ++i)
#define rForLL(i, t, s) for (LL i = LL(t); i >= LL(s); --i)
#define foreach(i,c) for (__typeof(c.begin()) i = c.begin(); i != c.end(); ++i)
#define rforeach(i,c) for (__typeof(c.rbegin()) i = c.rbegin(); i != c.rend(); ++i) #define pr(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << " "
#define prln(x) cout << #x << " = " << x << endl #define LOWBIT(x) ((x)&(-x)) #define ALL(x) x.begin(),x.end()
#define INS(x) inserter(x,x.begin())
#define UNIQUE(x) x.erase(unique(x.begin(), x.end()), x.end())
#define REMOVE(x, c) x.erase(remove(x.begin(), x.end(), c), x.end()); // 删去 x 中所有 c
#define TOLOWER(x) transform(x.begin(), x.end(), x.begin(),::tolower);
#define TOUPPER(x) transform(x.begin(), x.end(), x.begin(),::toupper); #define ms0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define msI(a) memset(a,inf,sizeof(a))
#define msM(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a)) #define MP make_pair
#define PB push_back
#define ft first
#define sd second template<typename T1, typename T2>
istream &operator>>(istream &in, pair<T1, T2> &p) {
in >> p.first >> p.second;
return in;
} template<typename T>
istream &operator>>(istream &in, vector<T> &v) {
for (auto &x: v)
in >> x;
return in;
} template<typename T1, typename T2>
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out, const std::pair<T1, T2> &p) {
out << "[" << p.first << ", " << p.second << "]" << "\n";
return out;
} inline int gc(){
static const int BUF = 1e7;
static char buf[BUF], *bg = buf + BUF, *ed = bg; if(bg == ed) fread(bg = buf, , BUF, stdin);
return *bg++;
} inline int ri(){
int x = , f = , c = gc();
for(; c<||c>; f = c=='-'?-:f, c=gc());
for(; c>&&c<; x = x* + c - , c=gc());
return x*f;
} template<class T>
inline string toString(T x) {
ostringstream sout;
sout << x;
return sout.str();
} inline int toInt(string s) {
int v;
istringstream sin(s);
sin >> v;
return v;
} //min <= aim <= max
template<typename T>
inline bool BETWEEN(const T aim, const T min, const T max) {
return min <= aim && aim <= max;
} typedef long long LL;
typedef unsigned long long uLL;
typedef pair< double, double > PDD;
typedef pair< int, int > PII;
typedef pair< int, PII > PIPII;
typedef pair< string, int > PSI;
typedef pair< int, PSI > PIPSI;
typedef set< int > SI;
typedef set< PII > SPII;
typedef vector< int > VI;
typedef vector< double > VD;
typedef vector< VI > VVI;
typedef vector< SI > VSI;
typedef vector< PII > VPII;
typedef map< int, int > MII;
typedef map< int, string > MIS;
typedef map< int, PII > MIPII;
typedef map< PII, int > MPIII;
typedef map< string, int > MSI;
typedef map< string, string > MSS;
typedef map< PII, string > MPIIS;
typedef map< PII, PII > MPIIPII;
typedef multimap< int, int > MMII;
typedef multimap< string, int > MMSI;
//typedef unordered_map< int, int > uMII;
typedef pair< LL, LL > PLL;
typedef vector< LL > VL;
typedef vector< VL > VVL;
typedef priority_queue< int > PQIMax;
typedef priority_queue< int, VI, greater< int > > PQIMin;
const double EPS = 1e-;
const LL inf = 0x7fffffff;
const LL infLL = 0x7fffffffffffffffLL;
const LL mod = 1e9 + ;
const int maxN = 1e5 + ;
const LL ONE = ;
const LL evenBits = 0xaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa;
const LL oddBits = 0x5555555555555555; #define UU A[0]
#define UD A[1]
#define MU A[2]
#define MD A[3]
#define DU A[4]
#define DD A[5] struct State{
double A[] = {-inf, inf, -inf, inf, -inf, inf};
double _max = -inf, _min = inf; State operator+ (const double &x) const {
State ret = *this;
if(fabs(ret.UU) < 1e9) ret.UU -= x;
if(fabs(ret.UD) < 1e9) ret.UD -= x;
if(fabs(ret.DU) < 1e9) ret.DU += x;
if(fabs(ret.DD) < 1e9) ret.DD += x; Rep(i, ) {
if(fabs(ret.A[i]) < 1e9) {
ret._max = max(ret._max, ret.A[i]);
ret._min = min(ret._min, ret.A[i]);
}
}
return ret;
}
}; int N;
State X, Y;
double ans = infLL;
set< double > T; // 记录关键时间节点 int main(){
//freopen("MyOutput.txt","w",stdout);
//freopen("input.txt","r",stdin);
//INIT();
cin >> N;
Rep(i, N) {
double x, y;
string d;
cin >> x >> y >> d; if(d[] == 'U') {
Y.DU = max(Y.DU, y);
Y.DD = min(Y.DD, y); X.MU = max(X.MU, x);
X.MD = min(X.MD, x);
}
if(d[] == 'D') {
Y.UU = max(Y.UU, y);
Y.UD = min(Y.UD, y); X.MU = max(X.MU, x);
X.MD = min(X.MD, x);
}
if(d[] == 'R') {
X.DU = max(X.DU, x);
X.DD = min(X.DD, x); Y.MU = max(Y.MU, y);
Y.MD = min(Y.MD, y);
}
if(d[] == 'L') {
X.UU = max(X.UU, x);
X.UD = min(X.UD, x); Y.MU = max(Y.MU, y);
Y.MD = min(Y.MD, y);
}
} Rep(i, ) {
Rep(j, ) {
T.insert(fabs(X.A[i] - X.A[j]));
T.insert(fabs(X.A[i] - X.A[j]) / );
T.insert(fabs(Y.A[i] - Y.A[j]));
T.insert(fabs(Y.A[i] - Y.A[j]) / );
T.insert(fabs(X.A[i] - Y.A[j]));
T.insert(fabs(X.A[i] - Y.A[j]) / );
}
} foreach(i, T) {
if(*i > 1e9) break;
State tmpX = X + *i;
State tmpY = Y + *i; ans = min(ans, (tmpX._max - tmpX._min) * (tmpY._max - tmpY._min));
} printf("%.10f\n", ans);
return ;
}
AtCoder ABC 130F Minimum Bounding Box的更多相关文章
- ABC130 Task F. Minimum Bounding Box
题目链接 题解 最小的 bounding box 一定可以在四个时间段的最左端点和最右端点之间取到. 举例言之,设四个时间段分别是 (2, 5), (7, 10), (4, 9), ( 10, 20) ...
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 130 F Minimum Bounding Box 三分法求极值(WA)
题意:给n个点的起始坐标以及他们的行走方向,每一单位时间每个点往它的方向移动一单位.问最小能包围所有点的矩形. 解法:看到题目求极值,想了想好像可以用三分法求极值,虽然我也不能证明面积是个单峰函数. ...
- 3D空间中的AABB(轴向平行包围盒, Aixe align bounding box)的求法
引言 在前面的一篇文章中讲述了怎样通过模型的顶点来求的模型的包围球,而且还讲述了基本包围体除了包围球之外,还有AABB包围盒.在这一章,将讲述怎样依据模型的坐标求得它的AABB盒. 表示方法 AABB ...
- Latex 中插入图片no bounding box 解决方案
在windows下,用latex插入格式为jpg,png等图片会出现no bounding box 的编译错误,此时有两个解决办法: 1.将图片转换为eps格式的图片 \usepackage{grap ...
- bounding box的简单理解
1. 小吐槽 OverFeat是我看的第一篇深度学习目标检测paper,因为它是第一次用深度学习来做定位.目标检测问题.可是,很难懂...那个bounding box写得也太简单了吧.虽然,很努力地想 ...
- 论文阅读笔记四十七:Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression(CVPR2019)
论文原址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1902.09630.pdf github:https://github.com/generalized-iou 摘要 在目标检测的评测体系中,I ...
- 第二十六节,滑动窗口和 Bounding Box 预测
上节,我们学习了如何通过卷积网络实现滑动窗口对象检测算法,但效率很低.这节我们讲讲如何在卷积层上应用这个算法. 为了构建滑动窗口的卷积应用,首先要知道如何把神经网络的全连接层转化成卷积层.我们先讲解这 ...
- maya cmds pymel polyEvaluate 获取 bounding box
maya cmds pymel polyEvaluate 获取 bounding box cmds.polyEvaluate(bc = 1) #模型 cmds.polyEvaluate(bc2 = ...
- Torch 两个矩形框重叠面积的计算 (IoU between tow bounding box)
Torch 两个矩形框重叠面积的计算 (IoU between tow bounding box) function DecideOberlap(BBox_x1, BBox_y1, BBox_x2, ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ 3159: 决战 解题报告
BZOJ 3159: 决战 1 sec 512MB 题意: 给你一颗\(n\)个点,初始点权为\(0\)的有跟树,要求支持 Increase x y w 将路径\(x\)到\(y\)所有点点权加上\( ...
- bzoj4403题解
[参考代码] #pragma GCC optimize(2) #include <cstdlib> #define function(type) __attribute__((optimi ...
- 如何扫描统计全国Telnet默认口令
如何扫描统计全国Telnet默认口令 zrools2016-01-21共339474人围观 ,发现 23 个不明物体系统安全终端安全 本文原创作者:zrools 本文中介绍的工具.技术带有一定的攻击性 ...
- 选择排序-Python & Java
选择排序:1.找出最小的数值放在第一位2.找出剩余数据中最小的数值放在第二位,以此类推,直到最后一个数值 算法的时间复杂度为:O(n) ''' 选择排序: 1.找出最小的数值放在第一位 2.找出剩余数 ...
- Java8 时间调节器
TemporalAdjuster 是做日期数学计算.例如,要获得“本月第二个星期六”或“下周二”. 让我们来看看他们的操作. 选择使用任何编辑器创建以下java程序在 C:/> JAVA Jav ...
- 解压lzma格式的img文件报“Filename has an unknown suffix, skipping”怎么办
1 确认img文件是什么压缩格式 file 文件名 2 报标题错误怎么办? mv initrd.img initrd.img.xz xz -d initrd.img.xz cpio -ivd < ...
- [POI2011]IMP-Party
题目 不难发现\(\frac{2}{3}n-\frac{1}{3}n=\frac{1}{3}n\)(雾 一个团要求点之间两两有边,于是我们枚举两个点,如果这两个点之间没有边相连,那么就删掉这两个点,由 ...
- 众所周知,static修饰的成员只实例化一次,而string类型每次赋值都会重新创建一个实例,那么用static修饰string呢?
string 类型每次实例化都会重新创建一个实例: 解释:string 类型重载了运算符 “=” ,每次 “=” 操作都是一次 “new”. static 修饰符的成员只实例化一次?? 解释:这个说法 ...
- javascript基础入门之js中的结构分支与循环语句
javascript基础入门之js中的结构分支与循环语句 程序的结构①顺序结构:自上而下:②选择(分支)结构:多条路径,根据不同的条件,只执行其中一个:③循环结构:重复某些代码④配合特定的语句实现选择 ...
- LNMP部署
部署企业LNMP架构 源码包:nginx-* ; mysql-* ; php-* ; boost-* ; zend-loader-php5.6-linux-* ;yum软件: pcre-devel z ...
