Data Management Technology(2) -- Data Model
1.Data Model
Model
- Is the abstraction of real world
- Reveal the essence of objects, help people to locate and resolve problems
Data Model
- A data model explicitly determines the structure of data, and defines the operation that can be imposed, in order to represent the characteristic of the world
- Data model is the core and fundamental of database
- Data model determines the function and performance of database
- There exists different data models
- From different level, or different point of view
- The evolution of data model promotes the database progress
- Conceptual model
- documents and organizes the data for communication between functional and technical people
- Logical model
- describes data semantics, data relationships, data constraints and data operation in database
- Physical model
- describes how data is organized in storage device
Different level of abstraction
2.Conceptual Model - ER Model
- Is the most popular conceptual model
- Gives us a language to specify
- what information the db must hold
- what are the relationships among components of that information
- View the world as a collection of entities
Basic stuff
Entities and Attributes
(1)Entities
- real-world objects distinguishable from other objects
- described using a set of attributes
- Example: specific person, company, event, plant
(2)Attributes属性
- each has an atomic domain: string, integers, reals, etc.
- An entity is represented by a set of attributes, that is descriptive properties
possessed by all members of an entity set. - Domain – the set of permitted values for each attribute. Value types: Integer, String, Real,… etc.
- Attribute types:
- Simple and composite attributes.
- Single-valued and multi-valued attributes
- Example: multivalued attribute: phone_numbers
- Derived attributes
- Can be computed from other attributes
- Example: age, given date_of_birth
(3)Entity set
- a collection of similar entities
- Example: set of all persons, companies, trees, holidays
Relations
A mathematical definition: –if A, B are sets, then a relation R is a subset of A × B
The degree of relationship
- Binary relationship
- Ternary relationship
- Unitary relationship
Relationship Attribute
- An attribute can also be property of a relationship.
- Modeled as a mathematical set
- Binary and multiway relationships
- Converting a multiway one into many binary ones
- Constraints on the degree of the relationship
- many-one, one-one, many-many
- Attributes of relationships
- not necessary, but useful
Multiway Relationships
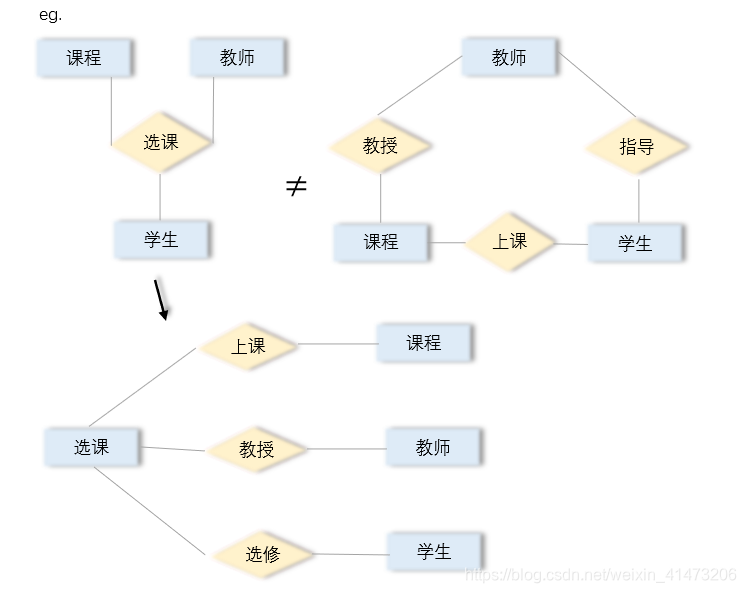 左:只有一个关系:选课(课程,教师,学生)
左:只有一个关系:选课(课程,教师,学生)
右:有三个关系:教授(课程,教师);上课(课程,学生);指导(教师,学生)
Arrows in Multiway Relationships:—>means can be determined by others
Mapping Cardinality Constraints
Express the number of entities to which another entity can be associated via a relationship set.
Most useful in describing binary relationship sets.
For a binary relationship set the mapping cardinality must be one of the following types:
- One to one (<—->)
- One to many (<––>)
- Many to one (—->) (–M——1–)
- Many to many (—-) (–M—–N–)
Some elements in A and B may not be mapped to any elements in the other set
Roles in Relationships
need an entity set twice in one relationship
Entity sets of a relationship need not be distinct
Roles are indicated in E-R diagrams by labeling the lines that connect diamonds to rectangles.
Role labels are optional, and are used to clarify semantics of the relationship
Constraints约束
A constraint = an assertion about the database that must be true at all times
Part of the database schema
Very important in database design
- Give more semantics to the data
- help us better understand it
- Allow us to refer to entities (e.g, using keys)
- Enable efficient storage, data lookup, etc.
Modeling Constraints
Finding constraints is part of the modeling process.
Commonly used constraints:
*Keys: resident identification card number uniquely identifies a person.
Single-value constraints: a person can have only one father.
*Referential integrity constraints: if you work for a company, it must exist in the database.
*Domain constraints: peoples’ ages are between 0 and 150.
General constraints: all others (at most 50 students enroll in a class)
Keys in E/R Diagrams
A super key of an entity set is a set of one or more attributes whose values uniquely determine each entity.
A candidate key of an entity set is a minimal super key
Although several candidate keys may exist, one of the candidate keys is selected to be the primary key.
Every entity set must have a key
So that the entity can be identified
A key can consist of more than one attribute
There can be more than one key for an entity set
one key will be designated as primary key
ER Modeling Principle
Design Techniques
- be faithful
- KISS (keep it simple and stupid)
- Avoid redundancy.
- Limit the use of weak entity sets.
- Don’t use an entity set when an attribute will do.
Avoiding Redundancy
- Redundancy occurs when we say the same thing in two different ways.
- Redundancy wastes space and (more importantly) encourages inconsistency.
- The two instances of the same fact may become inconsistent if we change one and forget to change the other, related version.
Entity Sets Versus Attributes
- An entity set should satisfy at least one of the following conditions:
- It is more than the name of something; it has at least one nonkey attribute.
- It is the “many” in a many-one or many-many relationship.
3.Logical Model - Relational Model
Logical Data Model (LDM)
Represent the abstract information structure of business domain
Unambiguous, formalized definition on the model
Implemented in DBMS, adjusted to achieve efficiency on computing system.
Three elements of logical data model:
- Data structure
- Data operation
- Data constraints
The evolution of LDM
物理模型[–>文件模型–>层次模型–>网状模型–>关系模型(most popular LDM)–>XML模型/面向对象模型–>]概念模型
Structure of Relational Model
Relational Database
Database that adopts relational model
Database Modeling & Implementation
Ideas
->Database Model (E/R, ODL)( Diagrams (E/R))
->Relational Schema(Tables: column names: attributes rows: tuples)
->Physical storage(Complex file organization and index structures.)
ER Model vs. Relational Model
Both are used to model data
ER model has many concepts
- entities, relations, attributes, etc.
- well-suited for capturing the app. requirements
- not well-suited for computer implementation
- (does not even have operations on its structures)
Relational model
- has just a single concept: relation
- world is represented with a collection of tables
- well-suited for efficient manipulations on computers
Schema vs. instance
Analogy with programming languages:
- Schema = type
- Instance = value
Important distinction:
- Database Schema = stable over long periods of time
- Database Instance = changes constantly, as data is inserted/updated/deleted
Schema图示
- Corresponds to the programming language concept of type definition
- E.g. Java
- String movie = “Spider man”;
The Schema of a Relation:
- Relation name plus attribute names
- E.g. Product(Name, Price, Category, Manufacturer)
- In practice we add the domain for each attribute
The Schema of a Database
- A set of relation schemas
- E.g. Product(Name, Price, Category, Manufacturer), Vendor(Name, Address, Phone), . . . . . . .
Instance实例
- Corresponds to the programming-language concept of the value of a variable
- E.g. Java
- String movie = “Spider man”;
Relational schema = R(A1,…,Ak):
- Instance = relation with k attributes (of “type” R)
- values of corresponding domains
Database schema = R1(…), R2(…), …, Rn(…)
- Instance = n relations, of types R 1, R 2, …, Rn
Updates
The database maintains a current database state.
Updates to the data:
1) add a tuple
2) delete a tuple
3) modify an attribute in a tuple
Updates to the data happen very frequently.
Cartesian product笛卡尔积
- D1 = {a, b}
- D2 = {c, d}
- D3 = {e, f, g}
D1XD2XD3 = {(a, c, e), (a, c,
f), (a, c, g), (a, d, e), (a, d, f), (a, d, g), (b, c, e), (b, c, f),
(b, c, g), (b, d, e), (b, d, f), (b, d, g)}
由定义可以看出,笛卡尔积也是一个集合,其中:
- 元素中的每一个di叫做一个分量(Component),来自相应的域(di∈Di)
- 每一个元素(d1,d2,d3,…,dn)叫做一个n元组(n-tuple),简称元组(Tuple)。但元组不是di的集合,元组的每个分量(di)是按序排列的。如:
(1,2,3)≠(2,3,1)≠(1,3,2);
而集合中的元素是没有排序次序的,如(1,2,3)=(2,3,1)=(1,3,2)。
Mathematical Definitions of Relations
Relation is the subset of Cartesian product
Relation keeps the meaningful tuple in the Cartesian product
Relation has FINITE tuples(关系有有限元组)
Relation vs. Cartesian product
Relation as table
Rows = tuples
Columns = components
Names of columns = attributes
Relation name + set of attribute names= schema
REL (A 1,A 2,…,An)
Set theoretic
Domain — set of values: like a data type
Cartesian product: D1 X D2 X … X Dn
n-tuples (V1,V2,…,Vn)
Relation=subset of Cartesian product of one or more domains
FINITE only; empty set allowed
Tuples(元组) = members of a relation inst.
Arity (元)= number of domains
Components (分量)= values in a tuple
Domains(域) — corresp. with attributes
Cardinality(基数)= max number of tuples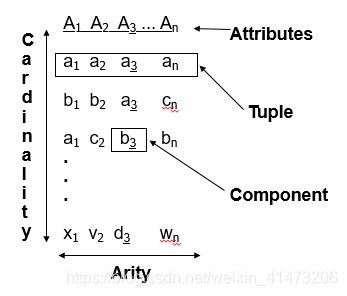 #### Database
#### Database
A database consists of multiple relations
Information about an enterprise is broken up into parts, with each relation storing one part of the information
account : stores information about accounts
depositor : stores information about which customer owns which account
customer : stores information about customers
Relation’s features
Tuples with same value are not allowed
Relations are Unordered
- Order of tuples is irrelevant (tuples may be stored in an arbitrary order)
- Order of Attributes is also irrelevant
Attribute values must comply with domain constraint
- 同一属性名下的各个属性值必须来自同一个域,是同一类型的数据
Each attribute must has a different name
Different attributes can use a same domain
Attribute values are required to be atomic; that is, indivisible(不可再分的)
- E.g. the value of an attribute can be an account number, but cannot be a set of account numbers
- Also the attribute can’t be a composite one
translating from ER to relational model
Basic cases
- Relationships to Relations: entity set E = relation with attributes of E
- Relationships to Relations: relationship R = relation with attributes being keys of related entity sets + attributes of R
- watch out for attribute name conflicts
Special cases
- many-one, one-one relations: combining two relations
- It is OK to combine the relation for an entity-set E with the relation R for a many-one relationship from E to another entity set.
- 多对一的时候将关系合并到多的一方的E中
- Example: Drinkers(name, addr) and Favorite(drinker, beer) combine to make Drinker1(name, addr, favoriteBeer).
- One-One relationship: Any side is okay
- It is OK to combine the relation for an entity-set E with the relation R for a many-one relationship from E to another entity set.
- translating weak entity sets
Constraints of Relational Model
Integrity Constraints
Purpose: prevent semantic inconsistencies in data(防止数据中的语义不一致)
predicates on the database
must always be true (that is, checked whenever database gets updated)
Main types of IC’s:
Domain Integrity Constraints(1 table)
- Attach constraints to values of attributes
- Enhances types system
- Also checks the Null value
- It is possible for tuples to have a null value, denoted by null, for some of their attributes
- null signifies an unknown value or that a value does not exist.
- e.g., values of age must less than 120
Entity Integrity Constraints(1 table)
- Defined by Primary Key
- A primary key is a combination of columns which uniquely specify a row
- A primary key cannot allow null values. (You cannot define a primary key on columns that allow nulls.)
- Each table can have at most one primary key.
- e.g., 2 acts can’t share the same act_no
Referential Integrity constraints ( 2 tables)
- e.g., b_names associated w/ loans must be names of real branches
Unique Key Constraints
A unique key
can uniquely identify each row in a table. That is, no two distinct rows
in a table can have the same value (or combination of values) in those
columns constrained by unique key.
A unique key can allow null values. (You can define a unique key on columns that allow nulls.)
Each table can have multiple unique keys
Referential Integrity Constraints
Referential integrity
is a property of data which, when satisfied, requires every value of
one attribute (column) of a relation (table) to exist as a value of
another attribute in a different (or the same) relation (table).
For referential integrity to hold in a relational database, any field in a table that is declared a foreign key can contain only values from a parent table’s primary key or a candidate key
Unary relation referencing
Relational-Algebra-Operations
Querying the Database
Goal: specify what we want from our database
Could write in C++/Java, but bad idea
Instead use high-level query languages:
Theoretical: Relational Algebra, Datalog
Practical: SQL
Relational algebra: a basic set of operations on relations that provide the basic principles.
Motivation: The Stack
To use the “stack” data structure in my program, I need to know
- what a stack looks like
- what (useful) operations I can perform on a stack
- PUSH and POP
Next, I look for an implementation of stack
- browse the Web
- find many of them
- choose one, say LEDA(an open source algorithm library)
LEDA already implement PUSH and POP
It also gives me a simple language L, in which to define a stack and call PUSH and POP
- S = init_stack(int);
- S.push(3); S.push(5);
- int x = S.pop();
Can also define an expression of operations on stacks
- T = init_stack(int);
- T.push(S.pop());
To summarize, I know
- definition of stack
- its operations (PUSH, POP): that is, a stack algebra
- an implementation called LEDA, which tells me how to call PUSH and POP in a language L
- I can use these implementations to manipulate stacks
- LEDA hides the implementation details
- LEDA optimizes implementation of PUSH and POP
Algebra
Mathematical system consisting of:
- Operands (运算对象)— variables or values from which new values can be constructed.
- Operators (运算符)— symbols denoting procedures that construct new values from given values.
Relational Algebra
An algebra whose operands are relations or variables that represent relations.
Operators are designed to do the most common things that we need to do with relations in a database.
- The result is an algebra that can be used as a query language for relations.
Operators: relations as input, new relation as output
Five basic RA operations:
- Basic Set Operations
- union, difference (no intersection, no complement)
- Selection
- Projection
- Cartesian Product
Derived operations:
- Intersection, complement
- Joins (natural, equi-join, theta join, semi-join)
Five Basic RA Operations
Set Operations
Binary operations
- Union
- difference
Unary operations
- Selection
- Projection
Cartesian Product
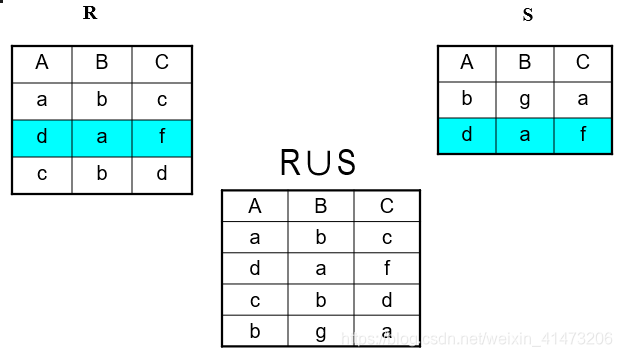
Set Operations: Union
Union: all tuples in R1 or R2
No duplicate tuples
Notation: R1 U R2
R1, R2 must have the same schema
R1 U R2 has the same schema as R1, R2
Example:
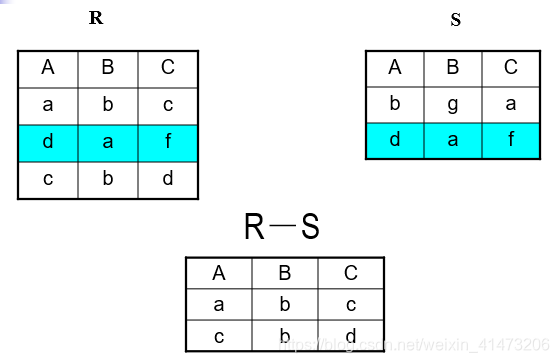
 ##### Set Operations: Difference
##### Set Operations: Difference
Difference: all tuples in R1 and not in R2
Notation: R1 – R2
R1, R2 must have the same schema
R1 - R2 has the same schema as R1, R2
Example:
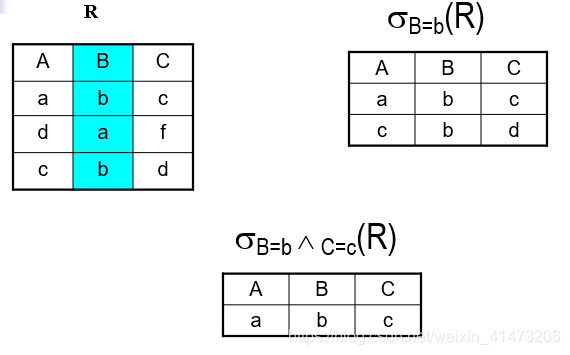
Selection选择运算
Returns all tuples which satisfy a condition
Notation: σc(R)\sigma_{c}(R)σc(R)
c is a condition: =, <, >, and, or, not
Output schema: same as input schema
 ##### Projection投影运算
##### Projection投影运算
Unary operation: returns certain columns
Notation: ΠA1,…,An(R)\Pi_{A1,…,An} (R)ΠA1,…,An(R)
Input schema R(B1,…,Bm)
Condition: {A1, …, An}包含于{B1, …, Bm}
Output schema S(A1,…,An)
no duplicate elimination
Cartesian Product
Each tuple in R1 with each tuple in R2
Notation: R1 x R2
Input schemas R1(A1,…,An), R2(B1,…,Bm)
Output schema is S(A1, …, An, B1, …, Bm*)*
Notation: R1 x R2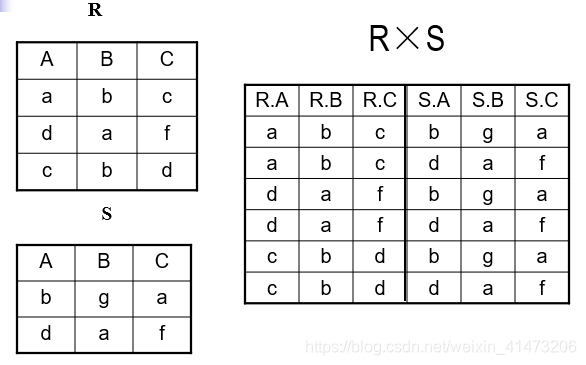
Derived RA Operations
 1) Intersection
1) Intersection
2) Most importantly: Join
3) Division
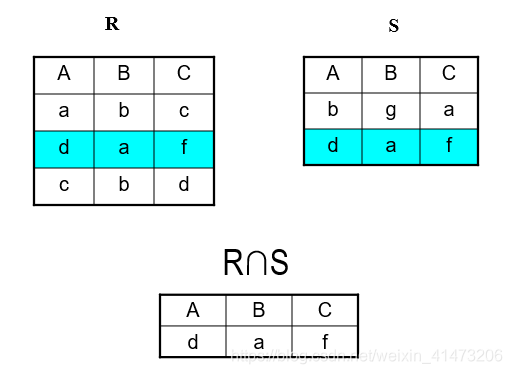
Set Operations: Intersection
Difference: all tuples both in R1 and in R2
Notation: R1∩R2
R1, R2 must have the same schema
R1∩R2 has the same schema as R1, R2
Intersection is derived: R1∩R2 = R1 – (R1 – R2)
Joins连接
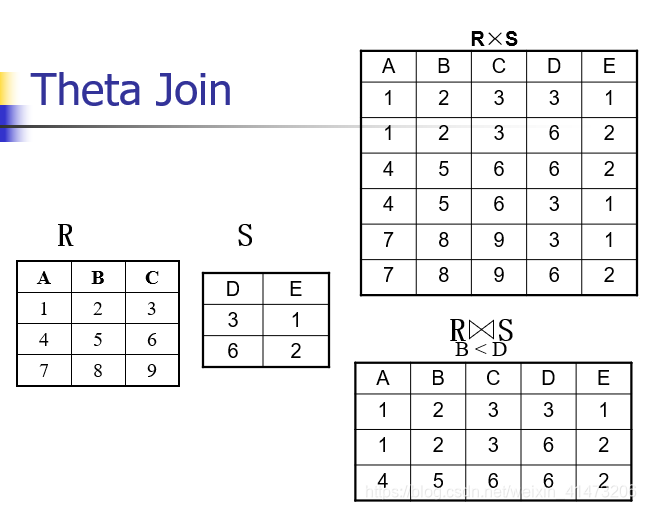
Theta join
A join that involves a predicate
Notation: R1|X|cR2 where c is a condition
Input schemas: R1(A1,…,An), R2(B1,…,Bm)
Output schema: S(A1,…,An,B1,…,Bm)
Derived operator:R1∣X∣cR2=σc(R1xR2)R1|X|_cR2 = \sigma_c(R1 x R2)R1∣X∣cR2=σc(R1xR2)
Natural join
A frequent type of join connects two relations by:
Equating attributes of the same name, and
Projecting out one copy of each pair of equated attributes.
Called natural join.
Denoted R3 := R1 JOIN R2.
Notation: R1|X|R2
Input Schema: R1(A1, …, An), R2(B1, …, Bm)
Output Schema: S(C1,…,Cp)
Where {C1, …, Cp} = {A1, …, An} U {B1, …, Bm}
Meaning: combine all pairs of tuples in R1 and R2 that agree on the attributes:
{A1,…,An}|X|{B1,…, Bm} (called the join attributes)
Equivalent to a cross product followed by selection
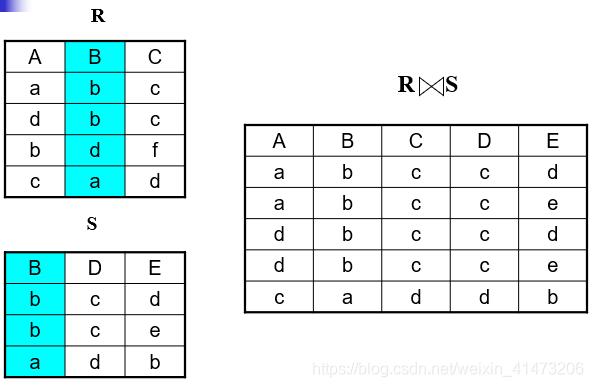
Equi-join
Most frequently used in practice: R1|X|A=B_{A=B}A=BR2
Natural join is a particular case of equi-join
A lot of research on how to do it efficiently
Outer join
An extension of the join operation that avoids loss of information.
Computes the join and then adds
tuples form one relation that does not match tuples in the other
relation to the result of the join.
Uses null values to signify the unmatched values
Subtypes: left outer joins, right outer joins, and full outer joins
- 左外连接 = 自然连接 + 左侧表中失配的元组。
- 右外连接 = 自然连接 + 右侧表中失配的元组。
- 全外连接 = 自然连接 + 两侧表中失配的元组。
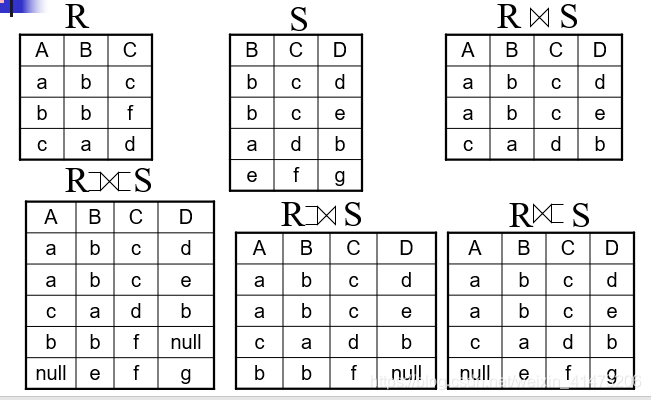
etc.
Division(除运算)
R(X,Y)是被除关系
S(Y)是除关系
商关系由R中某些X属性值构成,其中的任一X值所对应的一组Y值都包含除关系S。
除运算常用于包含语义“至少…”的语义的查询或运算
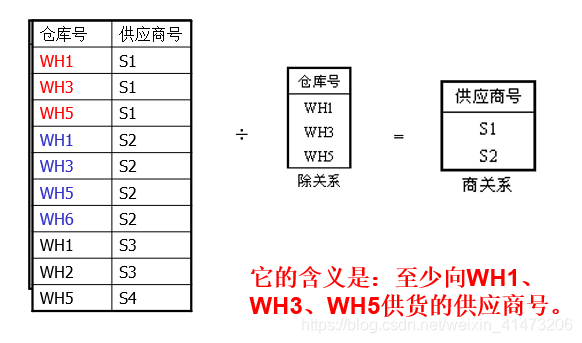
Complex Query
- σ\sigmaσ选择运算->|X|自然连接运算->Π\PiΠ投影运算
Exercise


Data Management Technology(2) -- Data Model的更多相关文章
- Data Management Technology(1) -- Introduction
1.Database concepts (1)Data & Information Information Is any kind of event that affects the stat ...
- Data Management Technology(5) -- Recovery
Recovery Types of Failures Wrong data entry Prevent by having constraints in the database Fix with d ...
- Data Management Technology(3) -- SQL
SQL is a very-high-level language, in which the programmer is able to avoid specifying a lot of data ...
- Data Management Technology(4) -- 关系数据库理论
规范化问题的提出 在规范化理论出现以前,层次和网状数据库的设计只是遵循其模型本身固有的原则,而无具体的理论依据可言,因而带有盲目性,可能在以后的运行和使用中发生许多预想不到的问题. 在关系数据库系统中 ...
- Data Management and Data Management Tools
Data Management ObjectivesBy the end o this module, you should understand the fundamentals of data m ...
- MySQL vs. MongoDB: Choosing a Data Management Solution
原文地址:http://www.javacodegeeks.com/2015/07/mysql-vs-mongodb.html 1. Introduction It would be fair to ...
- [Windows Azure] Data Management and Business Analytics
http://www.windowsazure.com/en-us/develop/net/fundamentals/cloud-storage/ Managing and analyzing dat ...
- 场景3 Data Management
场景3 Data Management 数据管理 性能优化 OLTP OLAP 物化视图 :表的快照 传输表空间 :异构平台的数据迁移 星型转换 :事实表 OLTP : 在线事务处理 1. trans ...
- Lifetime-Based Memory Management for Distributed Data Processing Systems
Lifetime-Based Memory Management for Distributed Data Processing Systems (Deca:Decompose and Analyze ...
随机推荐
- Flutter学习笔记(28)--使用第三方jar包
如需转载,请注明出处:Flutter学习笔记(28)--使用第三方jar包 1.打开一个Flutter项目,点击编码窗口右上角的Open for Editing in Android Studio,这 ...
- Win10系统重做
一.准备工作: 1.电脑(台式电脑.笔记本电脑): 2.U盘(内存大于4G): 3.软碟通(UltraISO):下载地址:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1tpCiIyIwK_7LaL ...
- 关于List和String有意思的几个应用
关于List和String有意思的几个应用 1. List:all_equal 功能:验证列表中的所有元素是否是都一样的. 解析:该技巧是使用[1:] 和 [:-1] 来比较所给定列表中的所有元素 ...
- 【转载】Docker registry仓库历史镜像批量清理
前言 在jenkins CI/CD流水线中以自动打包并push镜像的方式运行了一段时间之后, docker registry中堆积的历史镜像数量极多,磁盘空间告急,为此,有必要定期做镜像的清理,并释放 ...
- C#中类的实例化过程
创建某个类型的第一个实例时,所进行的操作顺序为:1.静态变量设置为02.执行静态变量初始化器3.执行基类的静态构造函数4.执行静态构造函数5.实例变量设置为06.执行衯变量初始化器7.执行基类中合适的 ...
- forEach和map的区别,简单写了IE低版本的原形封装
今天有点'不务正业',旧的没有写完又开新的,没办法 -0- 今天遇到这个特感兴趣嘛入正题了 forEach 和 map 的区别 参考:http://blog.csdn.net/boysky0015/a ...
- react学习之弹出层
react的弹出层不同于以往的DOM编程,我们知道,在DOM中,弹出层事件绑定在对应的节点上即可,但是在react中,往往只能实现父子之间的传递控制,显然,弹出层的层级不符合此关系. 在这里我们需要使 ...
- deducmsV5.7 在{dede:datalist}标签中runphp无效的解决办法
问题: 后台数据是dede:datalist标签展示中,中间有isshow - 是否展示的字段,数据库里存的是0/1:我本来想用{dede:field.isshow runphp='yes'}来着,可 ...
- PWA学习笔记(二)
设计与体验 APP Shell: 1.应用从显示内容上可粗略划分为内容部分和外壳部分,App Shell 就是外壳部分,即页面的基本结构 2.它不仅包括用户能看到的页面框架部分,还包括用户看不到的代码 ...
- 好程序员web前端分享前端学习路线自学如何找到工作
好程序员web前端分享前端学习路线自学如何找到工作,自学能不能学会WEB前端并且找到WEB前端开发岗位的工作取决于自身条件,如果基础好,自律性强那么将会容易很多,还有就是自学最难克服的并不是知识点,而 ...
