python的__future__模块
一、概述
Python的每个新版本都会增加一些新的功能,或者对原来的功能作一些改动。有些改动是不兼容旧版本的,也就是在当前版本运行正常的代码,到下一个版本运行就可能不正常了。
从Python 2.7到Python 3.x就有不兼容的一些改动,比如2.x里的字符串用'xxx'表示str,Unicode字符串用u'xxx'表示unicode,而在3.x中,所有字符串都被视为unicode。
因此,写u'xxx'和'xxx'是完全一致的,而在2.x中以'xxx'表示的str就必须写成b'xxx',以此表示“二进制字符串”。
直接把代码升级到3.x是比较冒进的,因为有大量的改动需要测试。相反,可以在2.7版本中先在一部分代码中测试一些3.x的特性,如果没有问题,再移植到3.x不迟。
Python提供了__future__模块,把下一个新版本的特性导入到当前版本,于是我们就可以在当前版本中测试一些新版本的特性。
二、源代码
个人Python环境,__future__路径:C:\ProgramData\Anaconda3\Lib\__future__.py
"""Record of phased-in incompatible language changes.
Each line is of the form:
FeatureName = "_Feature(" OptionalRelease "," MandatoryRelease ","
CompilerFlag ")"
where, normally, OptionalRelease < MandatoryRelease, and both are 5-tuples
of the same form as sys.version_info:
(PY_MAJOR_VERSION, # the 2 in 2.1.0a3; an int
PY_MINOR_VERSION, # the 1; an int
PY_MICRO_VERSION, # the 0; an int
PY_RELEASE_LEVEL, # "alpha", "beta", "candidate" or "final"; string
PY_RELEASE_SERIAL # the 3; an int
)
OptionalRelease records the first release in which
from __future__ import FeatureName
was accepted.
In the case of MandatoryReleases that have not yet occurred,
MandatoryRelease predicts the release in which the feature will become part
of the language.
Else MandatoryRelease records when the feature became part of the language;
in releases at or after that, modules no longer need
from __future__ import FeatureName
to use the feature in question, but may continue to use such imports.
MandatoryRelease may also be None, meaning that a planned feature got
dropped.
Instances of class _Feature have two corresponding methods,
.getOptionalRelease() and .getMandatoryRelease().
CompilerFlag is the (bitfield) flag that should be passed in the fourth
argument to the builtin function compile() to enable the feature in
dynamically compiled code. This flag is stored in the .compiler_flag
attribute on _Future instances. These values must match the appropriate
#defines of CO_xxx flags in Include/compile.h.
No feature line is ever to be deleted from this file.
"""
all_feature_names = [
"nested_scopes",
"generators",
"division",
"absolute_import",
"with_statement",
"print_function",
"unicode_literals",
"barry_as_FLUFL",
"generator_stop",
"annotations",
]
__all__ = ["all_feature_names"] + all_feature_names
# The CO_xxx symbols are defined here under the same names defined in
# code.h and used by compile.h, so that an editor search will find them here.
# However, they're not exported in __all__, because they don't really belong to
# this module.
CO_NESTED = 0x0010 # nested_scopes
CO_GENERATOR_ALLOWED = 0 # generators (obsolete, was 0x1000)
CO_FUTURE_DIVISION = 0x2000 # division
CO_FUTURE_ABSOLUTE_IMPORT = 0x4000 # perform absolute imports by default
CO_FUTURE_WITH_STATEMENT = 0x8000 # with statement
CO_FUTURE_PRINT_FUNCTION = 0x10000 # print function
CO_FUTURE_UNICODE_LITERALS = 0x20000 # unicode string literals
CO_FUTURE_BARRY_AS_BDFL = 0x40000
CO_FUTURE_GENERATOR_STOP = 0x80000 # StopIteration becomes RuntimeError in generators
CO_FUTURE_ANNOTATIONS = 0x100000 # annotations become strings at runtime
class _Feature:
def __init__(self, optionalRelease, mandatoryRelease, compiler_flag):
self.optional = optionalRelease
self.mandatory = mandatoryRelease
self.compiler_flag = compiler_flag
def getOptionalRelease(self):
"""Return first release in which this feature was recognized.
This is a 5-tuple, of the same form as sys.version_info.
"""
return self.optional
def getMandatoryRelease(self):
"""Return release in which this feature will become mandatory.
This is a 5-tuple, of the same form as sys.version_info, or, if
the feature was dropped, is None.
"""
return self.mandatory
def __repr__(self):
return "_Feature" + repr((self.optional,
self.mandatory,
self.compiler_flag))
nested_scopes = _Feature((2, 1, 0, "beta", 1),
(2, 2, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_NESTED)
generators = _Feature((2, 2, 0, "alpha", 1),
(2, 3, 0, "final", 0),
CO_GENERATOR_ALLOWED)
division = _Feature((2, 2, 0, "alpha", 2),
(3, 0, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_FUTURE_DIVISION)
absolute_import = _Feature((2, 5, 0, "alpha", 1),
(3, 0, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_FUTURE_ABSOLUTE_IMPORT)
with_statement = _Feature((2, 5, 0, "alpha", 1),
(2, 6, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_FUTURE_WITH_STATEMENT)
print_function = _Feature((2, 6, 0, "alpha", 2),
(3, 0, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_FUTURE_PRINT_FUNCTION)
unicode_literals = _Feature((2, 6, 0, "alpha", 2),
(3, 0, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_FUTURE_UNICODE_LITERALS)
barry_as_FLUFL = _Feature((3, 1, 0, "alpha", 2),
(3, 9, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_FUTURE_BARRY_AS_BDFL)
generator_stop = _Feature((3, 5, 0, "beta", 1),
(3, 7, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_FUTURE_GENERATOR_STOP)
annotations = _Feature((3, 7, 0, "beta", 1),
(4, 0, 0, "alpha", 0),
CO_FUTURE_ANNOTATIONS)
三、使用说明
1.division
- Python2
整数相除的结果为取整去余;浮点数相除为精确除法。
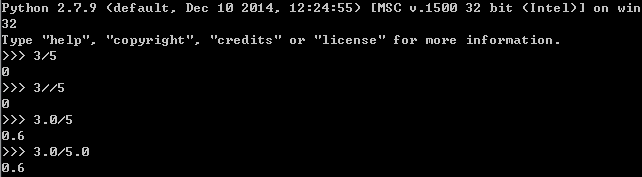
- Python3
默认为精确除法;如果需要取整时使用//,也称之为地板除。

2.print
- Python2中print为打印关键字

- Python3中print为打印函数名

3.unicode_literals
- Python2,字符串默认为str类型;添加前缀u后变为Unicode类型
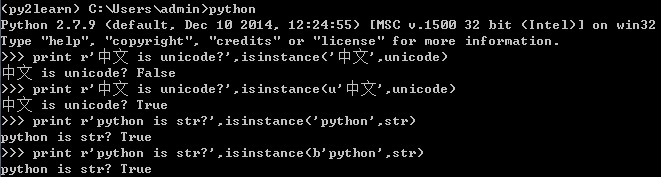
- Python3,字符串默认为Unicode类型;如果需要str类型,添加前缀b

4.absolute_import
首先需要了解相对导入、绝对导入的概念
相对导入:在不指明 package 名的情况下导入自己这个 package 的模块,比如一个 package 下有 a.py 和 b.py 两个文件,在 a.py 里 from . import b 即是相对导入 b.py
绝对导入:指明顶层 package 名,比如 import a,Python 会在 sys.path里寻找所有名为 a 的顶层模块
- Python2,支持绝对导入,
- Python3,支持相对导入、绝对导入
python的__future__模块的更多相关文章
- 【python】__future__模块
转自:http://www.jb51.net/article/65030.htm Python的每个新版本都会增加一些新的功能,或者对原来的功能作一些改动.有些改动是不兼容旧版本的,也就是在当前版本运 ...
- python模块之__future__模块
Python的每个新版本都会增加一些新的功能,或者对原来的功能作一些改动.有些改动是不兼容旧版本的,也就是在当前版本运行正常的代码,到下一个版本运行就可能不正常了.为了在低版本中可以使用高版本的新特性 ...
- python 使用__future__
Python的每个新版本都会增加一些新的功能,或者对原来的功能作一些改动.有些改动是不兼容旧版本的,也就是在当前版本运行正常的代码,到下一个版本运行就可能不正常了. 从Python 2.7到Pytho ...
- python使用__future__
Python的新版本会引入新的功能,但是,实际上这些功能在上一个老版本中就已经存在了.要“试用”某一新的特性,就可以通过导入__future__模块的某些功能来实现. 例如,Python 2.7的整数 ...
- Python进阶之模块与包
模块 .note-content {font-family: "Helvetica Neue",Arial,"Hiragino Sans GB","S ...
- Python进阶之模块
在计算机程序的开发过程中,随着程序代码越写越多,在一个文件里代码就会越来越长,越来越不容易维护. 为了编写可维护的代码,我们把很多函数分组,分别放到不同的文件里,这样,每个文件包含的代码就相对较少,很 ...
- __future__模块
Python提供了__future__模块,把下一个新版本的特性导入到当前版本,于是我们就可以在当前版本中使用一些新版本的特性,比如除法: 在Python 2.x中,对于除法有两种情况,如果是整数相除 ...
- 关于python 的 __future__
经常看到__future__: from __future__ import absolute_importfrom __future__ import print_functionfrom __fu ...
- python之platform模块
python之platform模块 ^_^第三个模块从天而降喽!! 函数列表 platform.system() 获取操作系统类型,windows.linux等 platform.platform() ...
随机推荐
- Excel上下标如何设置?
Excel表格怎么设置上下标?Excel上下标设置技巧 在21世纪的我们,平时的工作和学习中,经常会使用到一些专业的文档,比如方程式.数据的公式和科学计数等,其中均会涉及到许多的上下标符号输入以及使用 ...
- HTML和css常见问题解答2
1.将一个块级元素水平和垂直居中有几种方法?分别是什么? 四种方式: (1).要让div等块级元素水平和垂直居中,必需知道该div等块级元素的宽度和高度,然后设置位置为绝对位置,距离页面窗口左边框和上 ...
- Java内存分析工具MAT
MAT是一个强大的内存分析工具,可以快捷.有效地帮助我们找到内存泄露,减少内存消耗分析工具.内存中堆的使用情况是应用性能监测的重点,而对于堆的快照,可以dump出来进一步分析,总的来说,一般我们对于堆 ...
- [python / selenium] - 用python刷公选课是一种什么体验?
前言 看公选课还是能学到很多知识的,这里是给大家提供一个selenium的使用思路(好好学公选课,我真的看了) 思路 当观看者移动鼠标到某一范围时就会停止播放,就让selenium一直将鼠标悬停在视频 ...
- 01-Vue.js基础
一.Vue基础 1.介绍 Vue是一套用于构建用户界面的渐进式框架.Vue的核心库只关注视图层,不仅容易上手,还便于与第三方库或既有的项目整合.兼容性:Vue 不支持 IE8 及以下版本,因为 Vue ...
- .net core 拦截器的使用
.net core 拦截器的使用 实例代码:https://gitee.com/D_C_L/InterceptorTest.git 拦截器主要是将程序中的一些可以独立出去的模块进行拦截,比如幕等性,和 ...
- Slickflow.NET 开源工作流引擎高级开发(五) -- 引擎和外部事件的交互
前言:引擎组件的基本职责是负责流程流转,但是在流转过程中,除了对内部控制逻辑进行实现外,也不可避免的要去调用或者响应外部事件.本文主要描述外部事件的类型,以及调用方法过程. 1. 外部事件的类型 外部 ...
- for循环使用element的折叠面板遇到的问题-1
首先,效果是点击添加折叠面板,折叠面板的title右侧是关闭的小按钮,每次添加的面板都自动展开,其他的面板自动关闭,但其中发现一个问题是,每次点击关闭的时候,虽然上一个面板被关闭了,但他的下一个会自动 ...
- 【React Native】在原生和React Native间通信(RN调用原生)
一.从React Native中调用原生方法(原生模块) 原生模块是JS中也可以使用的Objective-C类.一般来说这样的每一个模块的实例都是在每一次通过JS bridge通信时创建的.他们可以导 ...
- Flutter Text文本
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() { runApp( App() ); } class App extends Stateless ...
