NLP标注工具brat 配置文件说明
快速搭建brat
通过docker:
docker run --name=brat -d -p 38080:80 -e BRAT_USERNAME=brat -e BRAT_PASSWORD=brat -e BRAT_EMAIL=brat@example.com cassj/brat
启动会拉取镜像,耐心等待,然后打开IP:38080,使用brat,brat登录
braf 的四类配置文件
the configuration of an annotation project is controlled by four files:
- annotation.conf: 标记类型 configuration
- visual.conf: annotation显示配置
- tools.conf: annotation工具配置
- kb_shortcuts.conf: 键盘快捷键 keyboard shortcut tool configuration
annotation.conf
标记配置文件
# 实体类型
[entities]
# 每行一个实体类型
Protein
Simple_chemical
Complex
Organism
# 事件
[events]
# 事件名称 参数名称:参数类型
Gene_expression Theme:Protein
Binding Theme+:Protein
Positive_regulation Theme:<EVENT>|Protein, Cause?:<EVENT>|Protein
Negative_regulation Theme:<EVENT>|Protein, Cause?:<EVENT>|Protein
# 关系
[relations]
# 关系名称 关系的属性,syntax ARG:TYPE (where ARG are, by convention, Arg1 and Arg2)
Part-of Arg1:Protein, Arg2:Complex
Member-of Arg1:Protein, Arg2:Complex
# TODO: Should these really be called "Equivalent" instead of "Equiv"?
Equiv Arg1:Protein, Arg2:Protein, <REL-TYPE>:symmetric-transitive
Equiv Arg1:Simple_chemical, Arg2:Simple_chemical, <REL-TYPE>:symmetric-transitive
Equiv Arg1:Organism, Arg2:Organism, <REL-TYPE>:symmetric-transitive
# 属性定义
[attributes]
# 名称 参数
Negation Arg:<EVENT>
Confidence Arg:<EVENT>, Value:Possible|Likely|Certain
Visual configuration (visual.conf)
可视化configuration包含两部分
- [labels]
- [drawing]
The [labels] 定义标记类型UI上如何显示:
Simple_chemical | Simple chemical | Chemical
标记类型 | 全称 | 显示文字
使用"|"隔开,第一部分是里定义的
The [drawing] 用于定义显示样式,比如定义标记的颜色等
[labels]
Simple_chemical | Simple chemical | Chemical
Protein | Protein
Complex | Complex
Organism | Organism
Gene_expression | Gene expression | Expression | Expr
Binding | Binding
Regulation | Regulation
Positive_regulation | Positive regulation | +Regulation
Negative_regulation | Negative regulation | -Regulation
Phosphorylation | Phosphorylation | Phos
Equiv | Equiv
Theme | Theme
Cause | Cause
Participant | Participant
[drawing]
SPAN_DEFAULT fgColor:black, bgColor:lightgreen, borderColor:darken
ARC_DEFAULT color:black, arrowHead:triangle-5
ATTRIBUTE_DEFAULT glyph:*
Protein bgColor:#7fa2ff
Simple_chemical bgColor:#8fcfff
Complex bgColor:#8f97ff
Organism bgColor:#ffccaa
Positive_regulation bgColor:#e0ff00
Regulation bgColor:#ffff00
Negative_regulation bgColor:#ffe000
Cause color:#007700
Equiv dashArray:3-3, arrowHead:none
Negation box:crossed, glyph:<NONE>, dashArray:<NONE>
Confidence dashArray:3-6|3-3|-, glyph:<NONE>
工具栏配置 (tools.conf)
The annotation tool configuration file, tools.conf, is divided into the following sections:
- [options]
- [search]
- [normalization]
- [annotators]
- [disambiguators]
These sections are all optional: an empty file is a vali
Option configuration ([options] section)
[options] 用来配置服务端如何处理分词、分局、验证、日志等:
Tokens tokenizer:VALUE, whereVALUE=whitespace: split by whitespace characters in source text (only)ptblike: emulate Penn Treebank tokenizationmecab: perform Japanese tokenization using MeCab
Sentences splitter:VALUE, whereVALUE=regex: regular expression-based sentence splittingnewline: split by newline characters in source text (only)
Validation validate:VALUE, whereVALUE=all: perform full validationnone: don't perform any validation
Annotation-log logfile:VALUE, whereVALUE=<NONE>: no annotation loggingNAME: log into file NAME (e.g. "/home/brat/work/annotation.log")
For example, the following [options] section gives the default brat configuration before v1.3:
|
| [options] | |
|---|---|
| Tokens | tokenizer:whitespace |
| Sentences | splitter:regex |
| Validation | validate:none |
| Annotation-log | logfile: |
The following [options] section enables Japanese tokenization using MeCab, sentence splitting only by newlines, full validation, and annotation logging into the given file. (In setting Annotation-log logfile, remember to make sure the web server has appropriate write permissions to the file.)
|
| [options] | |
|---|---|
| Tokens | tokenizer:mecab |
| Sentences | splitter:newline |
| Validation | validate:all |
| Annotation-log | logfile:/home/brat/work/annotation.log |
Normalization DB configuration ([normalization] section)
The [normalization] section defines the normalization resources that are available. For information on setting up normalization DBs, see the brat normalization documentation.
Each line in the [normalization] section has the following syntax:
DBNAME DB:DBPATH, <URL>:HOMEURL, <URLBASE>:ENTRYURL
Here, DB, <URL>, <URLBASE> and <PATH> are literal strings (they should appear as written here), while "DBNAME", "DBPATH", "HOMEURL" and "ENTRYURL" should be replaced with specific values appropriate for the database being configured:
DBNAME: sets the database name (e.g. "Wiki", "GO"). The name can be otherwise freely selected, but should not contain characters other than alphanumeric ("a"-"z", "A"-"Z", "0"-"9"), hyphen ("-") and underscore ("_"). This name will be used both in the brat UI and in the annotation file to identify the DB.DBPATH(optional): provides the file system path to the normalization DB data on the server, relative to the brat server root. IfDBPATHisn't set, the system assumes the DB can be found in the default location under the givenDBNAME.HOMEURL: sets the URL for the home page of the normalization resource (e.g. "http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/"). Used both to identify the resource more specifically thanDBNAMEand to provide a link in the annotation UI for accessing the resource.URLBASE(optional): sets a URL template (e.g. "http://en.wikipedia.org/?curid=%s") that can be filled in to generate a direct link in the annotation UI to an entry in the normalization resource. The value should contain the characters "%s" as a placeholder that will be replaced with the ID of the entry.
The following example shows examples of configured normalization DBs.
|
| [normalization] | |
|---|---|
| Wiki | DB:dbs/wiki, :http://en.wikipedia.org, :http://en.wikipedia.org/?curid=%s |
| UniProt | :http://www.uniprot.org/, :http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/%s |
The first line sets configuration for a database called "Wiki", found as "dbs/wiki" in the brat server directory, and the second for a DB called "UniProt", found in the default location for a DB with this name.
搜索配置 ([search] section)
The [search] 用来配置在线搜索,这样选中一个词语后,可以点击搜索链接进行搜索。
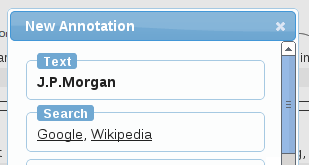
Each line in the [search] section contains the name used in the user interface for the search service, and a single key:value pair. The key should have the special value "" and its value should be the URL URL of the search service with the string to query for replaced by "%s".
The following example shows a simple [search] section.
|
| [search] | |
|---|---|
| :http://www.google.com/search?q=%s | |
| Wikipedia | :http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/%s |
When selecting a span or editing an annotation, these search options will then be shown in the brat annotation dialog.
Annotation tool configuration ([annotators] section)
The [annotators] section defines automatic annotation services that can be invoked from brat.
Each line in the [annotators] section contains a unique name for the service and key:value pairs defining the way it is presented in the user interface and the URL of the web service for the tool. Values should be given for "tool", "model" and "" (the first two are used for the user interface only).
The following example shows a simple [annotators] section.
|
| [annotators] | |
|---|---|
| SNER-CoNLL | tool:Stanford_NER, model:CoNLL, :http://example.com:80/tagger/ |
Disambiguation tool configuration ([disambiguators] section)
The [disambiguators] section defines automatic semantic class (annotation type) disambiguation services that can be invoked from brat.
Each line in the [disambiguators] section contains a unique name for the service and key:value pairs defining the way it is presented in the user interface and the URL of the web service for the tool. Values should be given for "tool", "model" and "" (the first two are used for the user interface only).
The following example shows a simple [disambiguators] section.
|
| [disambiguators] | |
|---|---|
| simsem-MUC | tool:simsem, model:MUC, :http://example.com:80/simsem/%s |
As for search, the string to query for is identified by "%s" in the URL.
来看一个demo:
[options]
# Possible values for validate:
# - all: perform full validation
# - none: don't perform any validation
Validation validate:all
# Possible values for tokenizer
# - ptblike: emulate Penn Treebank tokenization
# - mecab: perform Japanese tokenization using MeCab
# - whitespace: split by whitespace characters in source text (only)
Tokens tokenizer:whitespace
# Possible values for splitter:
# - regex : regular expression-based sentence splitting
# - newline: split by newline characters in source text (only)
Sentences splitter:newline
# Possible values for logfile:
# - <NONE> : no annotation logging
# - NAME : log into file NAME (e.g. "/home/brat/annotation.log")
Annotation-log logfile:<NONE>
[search]
# Search option configuration. Configured queries will be available in
# text span annotation dialogs. When selected on the UI, these open
# the given URL ("<URL>") with the string "%s" replaced with the
# selected text span.
Google <URL>:http://www.google.com/search?q=%s
Wikipedia <URL>:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Special:Search?search=%s
UniProt <URL>:http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/?sort=score&query=%s
EntrezGene <URL>:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?term=%s
GeneOntology <URL>:http://amigo.geneontology.org/cgi-bin/amigo/search.cgi?search_query=%s&action=new-search&search_constraint=term
ALC <URL>:http://eow.alc.co.jp/%s
[annotators]
# Automatic annotation service configuration. The values of "tool" and
# "model" are required for the UI, and "<URL>" should be filled with
# the URL of the web service. See the brat documentation for more
# information.
# Examples:
# Random tool:Random, model:Random, <URL>:http://localhost:47111/
# Stanford-CoNLL-MUC tool:Stanford_NER, model:CoNLL+MUC, <URL>:http://127.0.0.1:47111/
# NERtagger-GENIA tool:NERtagger, model:GENIA, <URL>:http://example.com:8080/tagger/
[disambiguators]
# Automatic semantic disambiguation service configuration. The values
# of "tool" and "model" are required for the UI, and "<URL>" should be
# filled with the URL of the web service. See the brat documentation
# for more information.
# Example:
# simsem-GENIA tool:simsem, model:GENIA, <URL>:http://example.com:8080/tagger/%s
[normalization]
# Configuration for normalization against external resources. The
# resource name (first field of each line) should match that of a
# normalization DB on the brat server (see tools/norm_db_init.py),
# "<URL>" should be filled with the URL of the resource (preferably
# one providing a serach interface), and "<URLBASE>" should be a
# string containing "%s" that, when replacing "%s" with an ID in
# the external resource, becomes a link to a page representing
# the entry corresponding to the ID in that resource.
# Example
#UniProt <URL>:http://www.uniprot.org/, <URLBASE>:http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/%s
#GO <URL>:http://www.geneontology.org/, <URLBASE>:http://amigo.geneontology.org/cgi-bin/amigo/term_details?term=GO:%s
#FMA <URL>:http://fme.biostr.washington.edu/FME/index.html, <URLBASE>:http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ontology-lookup/browse.do?ontName=FMA&termId=FMA:%s
快捷键
选中标记后,键盘上按快捷键,可以快速切换选项
P Protein
S Simple_chemical
X Complex
O Organism
C Cause
T Theme
作者:Jadepeng
出处:jqpeng的技术记事本--http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoqi
您的支持是对博主最大的鼓励,感谢您的认真阅读。
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
NLP标注工具brat 配置文件说明的更多相关文章
- 用深度学习做命名实体识别(二):文本标注工具brat
本篇文章,将带你一步步的安装文本标注工具brat. brat是一个文本标注工具,可以标注实体,事件.关系.属性等,只支持在linux下安装,其使用需要webserver,官方给出的教程使用的是Apac ...
- 自然语言处理标注工具——Brat(安装、测试、使用)
一.Brat标注工具安装 1.安装条件: (1)运行于Linux系统(window系统下虚拟机内linux系统安装也可以) (2)目前brat最新版本(v1.3p1)仅支持python2版本运行使用( ...
- NLP+VS︱深度学习数据集标注工具、方法摘录,欢迎补充~~
~~因为不太会使用opencv.matlab工具,所以在找一些比较简单的工具. . . 一.NLP标注工具BRAT BRAT是一个基于web的文本标注工具,主要用于对文本的结构化标注,用BRAT生成的 ...
- 推荐 | 中文文本标注工具Chinese-Annotator(转载)
自然语言处理的大部分任务是监督学习问题.序列标注问题如中文分词.命名实体识别,分类问题如关系识别.情感分析.意图分析等,均需要标注数据进行模型训练.深度学习大行其道的今天,基于深度学习的 NLP 模型 ...
- [分享] 封装工具ES4配置文件解释
[分享] 封装工具ES4配置文件解释 LiQiang 发表于 2015-2-3 14:41:21 https://www.itsk.com/thread-346132-1-4.html [分享] 封装 ...
- 开源图像标注工具labelme的安装使用及汉化
一 LabelMe简介 labelme是麻省理工(MIT)的计算机科学和人工智能实验室(CSAIL)研发的图像标注工具,人们可以使用该工具创建定制化标注任务或执行图像标注,项目源代码已经开源. 项目开 ...
- PDF文件如何标注,怎么使用PDF标注工具
我们在使用文件的时候需要给文件的部分添加标注,能够更加直观的了解文件,但是有很多小伙伴们对于PDF文件怎么添加标注都不知道,也不知道PDF标注工具要怎么使用,那么下面就跟大家分享一下怎么使用PDF标注 ...
- 深度学习标注工具 LabelMe 的使用教程(Windows 版本)
深度学习标注工具 LabelMe 的使用教程(Windows 版本) 2018-11-21 20:12:53 精灵标注助手:http://www.jinglingbiaozhu.com/ LabelM ...
- CocoStuff—基于Deeplab训练数据的标定工具【三、标注工具的使用】
一.说明 本文为系列博客第三篇,主要展示COCO-Stuff 10K标注工具的使用过程及效果. 本文叙述的步骤默认在完成系列文章[二]的一些下载数据集.生成超像素处理文件的步骤,如果过程中有提示缺少那 ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript笔记五
1.条件分支语句 - switch语句 - 语法: switch(条件表达式){ case 表达式: 语句... break; case 表达式: 语句... break; case 表达式: 语句. ...
- linux alias(命令别名)
alias:获取定义的所有命令别名 alias NAME='COMMAND':定义别名 unalias NAME:撤销别名
- selenium webdriver学习--------iframe的处理
有时候我们在定位一个页面元素的时候发现一直定位不了,反复检查自己写的定位器没有任何问题,代 码也没有任何问题.这时你就要看一下这个页面元素是否在一个iframe中,这可能就是找不到的原因之一.如果你在 ...
- String引发的提问,我差点跪了
面试官:下面代码执行结果是什么?String t0 = "helloworld";String t1 = new String("helloworld");Sy ...
- mac安装pip
1.下载get-pip.py curl -O https://raw.github.com/pypa/pip/master/contrib/get-pip.py SaintKings-Mac-mini ...
- windows系统tomcat上开发的j2ee程序,如何适配linux系统上奔跑的websphere7
公司需要将几个windows系统tomcat中间件下开发的j2ee系统部署到linux系统websphere7中间件下去运行. 这就需要做系统的适配工作.由于时间比较久了,具体问题就不详细写了.把这个 ...
- 【开发者portal在线开发插件系列五】命令的响应,即命令结果的上报(mid的使用)
基础篇 [开发者portal在线开发插件系列一]profile和基本上下行消息 [开发者portal在线开发插件系列二]多条上下行消息(messageId的使用) 基础场景见上面两个帖子,这里单独介绍 ...
- 1.flask基础
1.flask和django的区别? flask,是一个轻量级的框架,内置了:路由/视图/模板(jinja2)/cookie/session/中间件. 可扩展强,第三方组件非常多,例如:wtforms ...
- Linux编辑器vi使用方法详细介绍(转)
vi编辑器是所有Unix及Linux系统下标准的编辑器,它的强大不逊色于任何最新的文本编辑器,这里只是简单地介绍一下它的用法和一小部分指令.由于对Unix及Linux系统的任何版本,vi编辑器是完全相 ...
- [TimLinux] JavaScript 判断 input checkbox选中的方法
1. input属性 <label> <span>选择</span> <input type="checkbox" name=" ...
