UVa 122 Trees on the level(二叉树层序遍历)
Trees are fundamental in many branches of computer science. Current state-of-the art parallel computers such as Thinking Machines’ CM-5 are based on fat trees. Quad- and octal-trees are fundamental to many algorithms in computer graphics.
This problem involves building and traversing binary trees.
Given a sequence of binary trees, you are to write a program that prints a level-order traversal of each tree. In this problem each node of a binary tree contains a positive integer and all binary trees have have fewer than 256 nodes.
In a level-order traversal of a tree, the data in all nodes at a given level are printed in left-to-right order and all nodes at level k are printed before all nodes at level k+1.
For example, a level order traversal of the tree
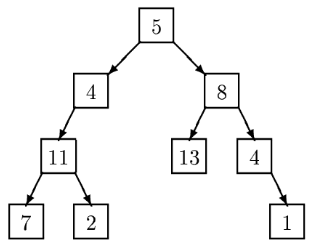
is: 5, 4, 8, 11, 13, 4, 7, 2, 1.
In this problem a binary tree is specified by a sequence of pairs (n,s) where n is the value at the node whose path from the root is given by the string s. A path is given be a sequence of L’s and R’s where L indicates a left branch and R indicates a right branch. In the tree diagrammed above, the node containing 13 is specified by (13,RL), and the node containing 2 is specified by (2,LLR). The root node is specified by (5,) where the empty string indicates the path from the root to itself. A binary tree is considered to be completely specified if every node on all root-to-node paths in the tree is given a value exactly once.
Input
The input is a sequence of binary trees specified as described above. Each tree in a sequence consists of several pairs (n,s) as described above separated by whitespace. The last entry in each tree is (). No whitespace appears between left and right parentheses.
All nodes contain a positive integer. Every tree in the input will consist of at least one node and no more than 256 nodes. Input is terminated by end-of-file.
Output
For each completely specified binary tree in the input file, the level order traversal of that tree should be printed. If a tree is not completely specified, i.e., some node in the tree is NOT given a value or a node is given a value more than once, then the string “not complete” should be printed.
Sample Input
(11,LL) (7,LLL) (8,R)
(5,) (4,L) (13,RL) (2,LLR) (1,RRR) (4,RR) ()
(3,L) (4,R) ()
Sample Output
5 4 8 11 13 4 7 2 1
not complete
题意
把给你的所有结点转成一棵树,并按层次遍历输出
题解
用链表的就不多说了,贴个数组的
代码
- #include<bits/stdc++.h>
- using namespace std;
- int Left[],Right[],V[],failed,cnt;
- vector<int> vec;
- void addnode(int v,char *s)
- {
- int n=strlen(s);//s[0]=','后的一个字符
- int u=;
- for(int i=;i<n;i++)
- {
- if(s[i]=='L')
- {
- if(Left[u]==-)
- {
- ++cnt;
- Left[cnt]=Right[cnt]=V[cnt]=-;
- Left[u]=cnt;
- }
- u=Left[u];
- }
- else if(s[i]=='R')
- {
- if(Right[u]==-)
- {
- ++cnt;
- Left[cnt]=Right[cnt]=V[cnt]=-;
- Right[u]=cnt;
- }
- u=Right[u];
- }
- else break;
- }
- if(V[u]!=-)failed=;//节点值已经存在
- V[u]=v;
- }
- int bfs()
- {
- vec.clear();
- queue<int> qu;
- qu.push();
- while(!qu.empty())
- {
- int top=qu.front();qu.pop();
- if(V[top]==-)return ;//节点没有赋值
- vec.push_back(V[top]);
- if(Left[top]!=-)qu.push(Left[top]);
- if(Right[top]!=-)qu.push(Right[top]);
- }
- return ;
- }
- int read()
- {
- int v;
- char s[];
- Left[]=Right[]=V[]=-;//0为根节点
- failed=;
- cnt=;
- for(;;)
- {
- if(scanf("%s",s)!=)return ;
- if(!strcmp(s,"()"))break;
- sscanf(&s[],"%d",&v);//从s[1]开始读一个数字
- addnode(v,strchr(s,',')+);
- }
- return ;
- }
- int main()
- {
- while(read())
- {
- if(failed==||bfs()==)
- printf("not complete\n");
- else
- for(int i=;i<vec.size();i++)
- printf("%d%c",vec[i],i==vec.size()-?'\n':' ');
- }
- return ;
- }
UVa 122 Trees on the level(二叉树层序遍历)的更多相关文章
- UVA.122 Trees on the level(二叉树 BFS)
UVA.122 Trees on the level(二叉树 BFS) 题意分析 给出节点的关系,按照层序遍历一次输出节点的值,若树不完整,则输出not complete 代码总览 #include ...
- UVa 122 Trees on the level (动态建树 && 层序遍历二叉树)
题意 :输入一棵二叉树,你的任务是按从上到下.从左到右的顺序输出各个结点的值.每个结 点都按照从根结点到它的移动序列给出(L表示左,R表示右).在输入中,每个结点的左 括号和右括号之间没有空格,相邻 ...
- UVA 122 -- Trees on the level (二叉树 BFS)
Trees on the level UVA - 122 解题思路: 首先要解决读数据问题,根据题意,当输入为“()”时,结束该组数据读入,当没有字符串时,整个输入结束.因此可以专门编写一个rea ...
- UVa 122 Trees on the level(链式二叉树的建立和层次遍历)
题目链接: https://cn.vjudge.net/problem/UVA-122 /* 问题 给出每个节点的权值和路线,输出该二叉树的层次遍历序列. 解题思路 根据输入构建链式二叉树,再用广度优 ...
- UVA - 122 Trees on the level (二叉树的层次遍历)
题意:给定结点值和从根结点到该结点的路径,若根到某个叶结点路径上有的结点输入中未给出或给出超过一次,则not complete,否则层次遍历输出所有结点. 分析:先建树,建树的过程中,沿途结点都申请了 ...
- uva 122 trees on the level——yhx
题目如下:Given a sequence of binary trees, you are to write a program that prints a level-order traversa ...
- UVa 122 Trees on the level
题目的意思: 输入很多个节点,包括路径和数值,但是不一定这些全部可以构成一棵树,问题就是判断所给的能否构成一棵树,且没有多余. 网上其他大神已经给出了题目意思:比如我一直很喜欢的小白菜又菜的博客 说一 ...
- 【LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现】【107-Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II(二叉树层序遍历II)】
[107-Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II(二叉树层序遍历II)] [LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现][全部题目文件夹索引] 原题 Given a ...
- [LeetCode] 107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II 二叉树层序遍历 II
Given a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left ...
随机推荐
- URL中文乱码及特殊字符处理
一.中文乱码 IE高版本(应该是9以上,不确定),在get方式请求中中文传到后台容易出现乱码问题.解决方法如下: 1.第一种,换成post方式 如果可以得话换成post方式就可以.如果采用表单或者aj ...
- mobile-net v2 学习记录。我是菜鸡!
声明:只是自己写博客总结下,不保证正确性,我的理解很可能是错的.. 首先,mobile net V1的主要特点是: 1.深度可分离卷积.用depth-wise convolution来分层过滤特征,再 ...
- 建立一个php 基础类
在些PHP文件的时候,一般首先都是要先写一下基础类: 主要包括以下几个方面: 1.服务器的链接:包括主机,用户名,密码 2.数据库的选择:要操作哪个数据库 3.字符集的设置:设置什么样的编码 4.查询 ...
- MySQL5.7 并行复制配置
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/langdashu/p/6125621.html [MySQL] 号称永久解决了复制延迟问题的并行复制,MySQL5.7 一.缘由: 某天看到主从 ...
- Array.Resize(ref arry, size);
数组原来的内容不变,后面添加新的空间. 内部操作应该是:重新分配了一块空间,然后将旧的内容拷过去
- How to Pronounce Work vs. Walk
How to Pronounce Work vs. Walk Share Tweet Share Tagged With: Comparison If you’re confused about th ...
- Java 分页与原理(上)
Java web 实习需要用到分页技术 所以现在学习一下 做个记录 方便以后查阅 分类:传统分页技术 下拉式分页技术 起始位置(0)开始 查询(10条记录)
- CMake Error at cmake/OpenCVUtils.cmake
CMake Error at cmake/OpenCVUtils.cmake:1047 (message): Failed to download . Status= Call Stack (most ...
- 随机数模块 random模块(1)
1.取随机小数 import random print(random.random()) # (0,1) print(random.uniform(2,3)) # (n,m) 2.取随机整数 impo ...
- win10虚拟桌面;一不小心按错了突然只剩下桌面,启动的程序都没了
先说如何关闭虚拟桌面:ctrl+win+F4(万一你还没看到怎么关闭虚拟桌面,就创建并调整到虚拟桌面,会很懵的,因为你启动的所有程序全部都突然消失了,只剩下开机的桌面了): win10有个功能,虚拟桌 ...
