MapReduce源码刨析
MapReduce编程刨析:
Map
map函数是对一些独立元素组成的概念列表(如单词计数中每行数据形成的列表)的每一个元素进行指定的操作(如把每行数据拆分成不同单词,并把每个单词计数为1),用户可以自定义一个把数据拆分成不同单词并把单词计数为1的映射map函数),事实上每个元素都是被独立操作的,而原始列表没有被修改,因为这里创建了一个新的列表来保存新的答案。
public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> {
//设定Context传递给 {@link Mapper} 实现
public abstract class Context
implements MapContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> {
}
//在任务开始的时候调用一次 为map方法提供预处理一些内容
protected void setup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
// 对输入分片里的key/value对调用一次,进行处理。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value,
Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value);
}
//任务结尾调用一次,进行扫尾工作。
protected void cleanup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context); //对key/value进行处理。
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}
}
编写MapReduce程序时,Map都要继承Mapper类,Mapper有4种泛型:KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT。KEYIN,VALUEIN是输入数据(key,value)的值,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT是输出数据(key,value)的值。因为它们经常在节点间进行网络传输,所以继承Writable接口被封闭类的驱动。
首先run()方法执行Map作业中的setup方法,它只在作业开始的时候调用一次处理Map作业需要的一些初始化作业。
然后,通过while循环遍历context里的(key,value)对 ,对每一组需要重写map方法以满足业务需求,在map中有3个参数。分别是key,value,context。key作为输入的关键字,value为输入的值。他们是MapReduce过程用于传值的(key,value),数据的输入是一批(key,value),从源码 context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value);可以看出生成结果也是一对(key,value),然后将其写入context。
因为MapReduce 是基于集群运算的框架,因此key和value的值为了满足集群之间的网络传输的规则,需要支持序列化和反序列化,而且整个MapRedcue过程会按照key进行排序分组,因此key必须实现WritableComparable接口,保证MapReduce对数据输出的结果执行进行相应的排序操作。
最后调用cleanup方法做最后的处理。它只在MapReduce进行结束的时候执行一次进行作业的扫尾工作。
代码
public class WordCountMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//key记录的是数据的偏移位置,value是每次分片提供给我们的读取一行数据。
//Map读数据时按分片给的内容一行一行来读取的。
String[] words = value.toString().split(" "); //每一行数据拆按照“ ”拆分放入字符数组words
for (String word : words) {
context.write(new Text(word), new IntWritable(1)); //每个单词当key,并赋值1
}
}
- 第1个参数类型LongWritable:输入key类型,记录数据分片的偏移量。
- 第2个参数类型Text:输入value,对应分片中的文本数据。
- 第3个参数Text:输出key,对应map方法计算的key值。
- 第4个参数IntWritable:输出value,对应map计算的value值。
Mapper从分片后传出的上下文接收数据以LongWritable, Text为(key,value)接收,然后重写map方法,默认设置一行一行读取数据并以(key,value)的形式进行便利.最后经过context.write方法按照Mapper类中定义的输出格式(Text, IntWritable)写入上下文。给Mapper Redcuer 等支持Context传输程序使用。
Reduce
Reducer获取Mapper任务输出的已经完成的地址信息后,系统会启用复制程序,将需要的数据复制到本地存储空间,如果Mapper输出很小,会复制到Reducer的内存区域。否则会复制到磁盘上,随着复制内容的增加,Reduce作业批量地启动合并任务,执行合并操作,启动Reducer类后接收上下文地数据进行Reduce任务。
public class Reducer<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> {
// 设定Context传递给{@link Reducer}实现,即获得Context的内容
public abstract class Context
implements ReduceContext<KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT> {
}
//任务开始调用一次,为reduce方法提供预处理的一些内容
protected void setup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
//对key/value进行处理
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void reduce(KEYIN key, Iterable<VALUEIN> values, Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for(VALUEIN value: values) {//迭代获取context的数据
context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value); //将计算结果写入context
}
}
//在任务结尾调用一次进行一次扫尾工作
protected void cleanup(Context context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
}
//Reducer类的驱动方法
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKey()) {
reduce(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getValues(), context);
//如果使用备份存储,请将其重置
Iterator<VALUEIN> iter = context.getValues().iterator();
if(iter instanceof ReduceContext.ValueIterator) {
((ReduceContext.ValueIterator<VALUEIN>)iter).resetBackupStore();
}
}
} finally {
cleanup(context); //扫尾
}
}
}
任何一个Reduce任务都会继承Reducer类,有4个值分别是:KEYIN,VALUEIN,KEYOUT,VALUEOUT。
KEYIN,VALUEIN是Reducer接收来自Mapper的输出,故Writable类型要和Mapper类中的KEYOUT、VALUEIN指定输出的key/value数据类型是一 一对应的。每个Reducer类接收的数据并不是Mapper传出的数据量,而是shuffle过程分区决定的,一般一个分区对应一个Reducer类,当只有一个Reducer类时,可以接收所有分区的数据。
Reducer的结构和Mapper源码结构十分相似,run方法的驱动Reducer的任务,执行顺序时setup→while→cleanup,其中setup与clean方法分别提供了对预执行和扫尾的操作和支持。分别在Reducer任务执行前执行一次,在Reducer任务后结尾执行一次。 while (context.nextKey())判断所在的Reducer类中(一般一个Reducer类对应一个,一个分区接收一组或多组由Map任务输出的key/value对的值)相同的key及相应的值一定在一个分区。)是否有下一个分区,如果有则会把相同key对应的值放到一块传给reduce方法进行处理。reducer有KEYIN key, Iterable <.VALUEIN./> values, Context context 共3个形式参数,其中 key时whiel条件判定的key,values就是与该vaues和key相同的key的所有值,然后会根据for循环把他们写入到上下文中。
reduce方法将传过来的数据按照key进行排序。Reduce任务接收的数据来自Map任务的输出,中间经过shuffle分区、排序、分组,正式给reduce方法处理。
代码
public class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
//reduce方法重写
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int total = 0; //初始化变量为0
for (IntWritable value : values) {
total += value.get();//将相同的单词对应的值加一起
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(total));//结果写入上下文
}
}
Driver
public class WordCountDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration()); //获取环境变量
job.setJarByClass(WordCountDriver.class); //指定驱动类
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMapper.class); //指定Map类
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class); //map K
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //map v
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class); //指定reducer类
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); //reduce k
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //reduce v
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); //任务输如路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); //任务输出路径
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
首先获取Job的实例,并创建环境变量的实例conf赋值于Job的构造方法,在job作业中set方法只有作业被提交之后才起作用,之后他们将抛出一个IllegalStateException异常。通常,用户创建应用程序,通过Job描述作业各个方面,然后提交作业监视其进度。7-13行指定map和reduce的输入输出文件类型。FileInputFormat继承InputFormat类,主要完成输入路径的设置。FileOutputFormat继承OutputFormat类通过setOutputPath方法指定Job作业执行完成结果的输出路径,对于Shuffle过程默认的分区、分组、排序、如果不能满足任务要求,也可以自定义指定。
过程
检查作业提交输入输出样式的细节。
为作业计算InputSplit值。
如果需要的话,为作业的DistributedCahe建立统计信息。
复制作业的jar包和配置文件到FileSystem上的MapReduce系统目录下。
提交作业到ResourceManager并且监控它的状态。
作业Job输入
检查作业的有效性。
检查作业输入的有效性。
提供RecordReader的实现,这个RecordReadr从逻辑InputSplit中输入记录,这些记录将由Mapper处理。
作业Job输出
- 检查作业的输出,检查路径是否已经存在
- 提供一个RecordWriter的实现,用来输出作业加过,TextOutputFormat是默认的OutputFormat,输出文件被保存在FileSystem上。
Mapper输入
Mapper的输入本质上来讲是源自于HDFS上存储的数据,这些数据进入Mapper计算之前有个分片的过程,它主要将HDFS上的Block在进行map之前重新划分,生成一组记录分片长度和一个记录数据位置的数组,进而内部形成记录数组位置的值key vakye扩及然后传给Mapper计算,这里 key和value的类型由一套默认的类型机制,同时也是向用户开放的。
setInputFormatClass
public void setInputFormatClass(Class<? extends InputFormat> cls
) throws IllegalStateException {
ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
conf.setClass(INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR, cls,
InputFormat.class);
}
这里有一个很重要的类InputFormat,它位于“package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce”中,一共包含两种方法getSplits和createRecorecordReader
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public abstract class InputFormat<K, V> { //对输入的数据进行分片
public abstract List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException; //获取分片中的数据
public abstract RecordReader<K,V> createRecordReader(InputSplit split,TaskAttemptContext context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
}
getSplits对输入数据进行切片,最终获取一个InputSplit的返回列表。
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public abstract class InputSplit {
//获取分片split的大小,以便分片按其排序,并返回分片的字节数据
public abstract long getLength() throws IOException, InterruptedException;
//获取分片所在本地的命名列表(本地不需要序列化),并返回一个新的节点数组
public abstract String[] getLocations() throws IOException, InterruptedException;
//返回分片数据存储每一个位置的拆分信息列表,如果是空值表示所有的位置都有数组存储在磁盘上
@Evolving
public SplitLocationInfo[] getLocationInfo() throws IOException {
return null;
}
}
createRecorder方法获得一个RecordReader的返回值源码信息如下
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public abstract class RecordReader<KEYIN, VALUEIN> implements Closeable {
//初始化调用一次.
public abstract void initialize(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
//判断下一个key/value是否存在,如果存在则返回true
public abstract boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException;
//获取当前的key。如果存在,则返回true
public abstract KEYIN getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException;
//获取当前的值,返回读取的对象
public abstract VALUEIN getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException;
//记录 record reader通过数据的当前处理进度,返回0.0~1.0之间的数字。用于标记当前的进度。
public abstract float getProgress() throws IOException, InterruptedException;
//关闭recorde reader
public abstract void close() throws IOException;
}
Recorder主要的功能是将数据拆分成KV对,然后传递给Map任务。
TextInputFormat
输入采用的默认格式,如果Job对象不指定,系统默认会运行它,如果指定的话:
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
TextInputFormat包含RecordReader和isSplitable两种方法位于package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input;
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public class TextInputFormat extends FileInputFormat<LongWritable, Text> {
//定义文本的读取方式,是通过RecordReader返回的RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> 类实现的
@Override
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> createRecordReader(InputSplit split,TaskAttemptContext context) {
String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get(
"textinputformat.record.delimiter");
byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null;
if (null != delimiter)
recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);//采用UTF_8编码
return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes); //返回LineRecordReader实例
}
//判断是否分片吗,如果分片返回true
@Override
protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context, Path file) {
//根据文件后缀名来查找文件file的相关压缩编码器
final CompressionCodec codec =
new CompressionCodecFactory(context.getConfiguration()).getCodec(file);
if (null == codec) {
return true;// 没有压缩,返回true
}
//返回SplittableCompressionCodec的编码器实例。
return codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec;
}
}
TextInputFormat以(longWrite,Text)形式继承了FileinputFormat类的逻辑,重写了isSplittable方法():
protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context, Path filename) {
return true;
}
代码设定了默认分片的格式,在TextInputFormat类的isSplittable()方法,代码加入了压缩的判定,如果没有压缩,则设定为可分片,如果有压缩,返回的是分片压缩的解码器的实例。
createRecorderReader()是定义文本文件读取方式,实际文件读取时通过它返回的RecordReader(LongWritable,Text)的字类LineRecordReader的实例位于(package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input;)在源码的207行-215行
@Override
public LongWritable getCurrentKey() { //指定获取key类型 Mapper获取输入key的类型
return key;
} @Override
public Text getCurrentValue() { //指定获取value的类型也就是Mapper要获取输入value的类型
return value;
}
如果该条数据存在两个Block中
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit;
Configuration job = context.getConfiguration();
this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
start = split.getStart();
end = start + split.getLength();
final Path file = split.getPath();
final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job);
fileIn = fs.open(file);
CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(job).getCodec(file);
if (null!=codec) {
isCompressedInput = true;
decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec);
if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) {
final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn =
((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream(
fileIn, decompressor, start, end,
SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK);
in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job,
this.recordDelimiterBytes);
start = cIn.getAdjustedStart();
end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd();
filePosition = cIn;
} else {
in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn,
decompressor), job, this.recordDelimiterBytes);
filePosition = fileIn;
}
} else {
fileIn.seek(start);
in = new UncompressedSplitLineReader(
fileIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes, split.getLength());
filePosition = fileIn;
}
//if的判断条件是start != 0,即从第二行开始读取数据,那么第一行数据去哪里么呢
if (start != 0) {
start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
}
this.pos = start;
}
为了保证数据的第一行被切断的时候正确读取,并没有判断数据是否被切断,而是一视同仁地除了第一个split,其他所有split都经过if的判定,全部从第二行开始读数据,当然到达split结尾时总是再多读一行,这样就避开了数据被切断的烦恼。如果最后一个split的结尾没有下一行了呢:
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException {
if (key == null) {
key = new LongWritable();
}
key.set(pos);
if (value == null) {
value = new Text();
}
int newSize = 0;
// 使用的判定条件计算当前位置小于或等于split的结尾位置,即当前已处于split的结尾位置时,while依然会再执行一次,那么结束,这样就解决了InputSplit读取的跨界问题。
// split limit i.e. (end - 1)
while (getFilePosition() <= end || in.needAdditionalRecordAfterSplit()) {
if (pos == 0) {
newSize = skipUtfByteOrderMark();
} else {
newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume(pos));
pos += newSize;
}
if ((newSize == 0) || (newSize < maxLineLength)) {
break;
}
// line too long. try again
LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " +
(pos - newSize));
}
if (newSize == 0) {
key = null;
value = null;
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
优化策略
作为Mapper输入,分片是一个很重要的环节,它主要将HDFS上的Block再进行Map计算之前进行逻辑划分,通常情况下分片大小和HDFS的Block块大小一样,也可以自定义。
/**
*isSplitable方法确定文件是否分片
*如果文件可以拆分,此处设定分片为真
*否则如压缩文件不持支拆分的,则不进行拆分
*/
protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context, Path filename) {
return true;
} public static void setInputPathFilter(Job job, Class<? extends PathFilter> filter) {
job.getConfiguration().setClass(PATHFILTER_CLASS, filter, PathFilter.class);
} public static void setMinInputSplitSize(Job job,long size) {
job.getConfiguration().setLong(SPLIT_MINSIZE, size);
}
/**
*获取由格式强加的分片大小的下限,默认值是1。
*/
public static long getMinSplitSize(JobContext job) {
return job.getConfiguration().getLong(SPLIT_MINSIZE, 1L);
} public static void setMaxInputSplitSize(Job job, long size) {
job.getConfiguration().setLong(SPLIT_MAXSIZE, size);
}
//返回一个分片中最大的有效字符数
public static long getMaxSplitSize(JobContext context) {
return context.getConfiguration().getLong(SPLIT_MAXSIZE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
} public static PathFilter getInputPathFilter(JobContext context) {
Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();
Class<?> filterClass = conf.getClass(PATHFILTER_CLASS, null,
PathFilter.class);
return (filterClass != null) ?
(PathFilter) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(filterClass, conf) : null;
} protected List<FileStatus> listStatus(JobContext job
) throws IOException {
Path[] dirs = getInputPaths(job);
if (dirs.length == 0) {
throw new IOException("No input paths specified in job");
}
//用getSplits方法生成文件列表并将其制作成FileSplits
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException {
//返回getFormatMinSplitSize,getMinSplitSize的较大值。
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch().start();
long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
_ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
for (FileStatus file: files) {
//文件分片为真的话进行分片大小的计算
Path path = file.getPath();
long length = file.getLen();
if (length != 0) {
BlockLocation[] blkLocations;
if (file instanceof LocatedFileStatus) {
blkLocations = ((LocatedFileStatus) file).getBlockLocations();
} else {
FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration());
blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
}
//文件分片为真的话,进行分片大小的计算。
if (isSplitable(job, path)) {
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize); long bytesRemaining = length;
while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
} _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ //分片大小的计算
protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize,long maxSize) {
return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
}
最小分片大小通常是1个字节,最大分片大小默认是由Java的long类型表示的最大值(Long.MAX_VALUE),只有把它的值设置成小于HDFS Block才有效果。computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize)计算分片的的大小。再默认情况下minSize<blockSize<maxSize。因此分片通常情况下就是HDFS的Block块的大小。
这些值可以通过mapred.min.split.size、mapred.min.split.size、mapred.max.split.size和dfs.block.size,进行设定。
默认情况下 TextInputformat 对任务的切片机制是按文件规划切片,不管文件多小,都会是一个单独的切片,都会交给一个 maptask,这样如果有大量小文件,就会产生大量的maptask,处理效率极其低下。
(1)最好的办法,在数据处理系统的最前端(预处理/采集),将小文件先合并成大文件,再上传到 HDFS 做后续分析。
(2)补救措施:如果已经是大量小文件在 HDFS 中了,可以使用另一种
InputFormat来做切片。(CombineTextInputFormat),它的切片逻辑跟 TextFileInputFormat
不同:它可以将多个小文件从逻辑上规划到一个切片中,这样,多个小文件就可以交给一个 maptask。
(3)优先满足最小切片大小,不超过最大切片大小 。
CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 4194304);// 4m CombineTextInputFormat.setMinInputSplitSize(job, 2097152);// 2m
// 举例:0.5m+1m+0.3m+5m=2m + 4.8m=2m + 4m + 0.8m
// 如果不设置 InputFormat,它默认用的是 TextInputFormat.class
job.setInputFormatClass(CombineTextInputFormat.class) CombineTextInputFormat.setMaxInputSplitSize(job, 4194304);// 4m
CombineTextInputFormat.setMinInputSplitSize(job, 2097152);// 2m
分区
分区是划分键值空间,Partitioner负责控制Map输出结果key的分隔,key(或者key子集)被用于产生分区,通常使用Hash函数。分区的数目与一个作业的Reduce任务的数目时一样的,因此,Partitioner控制将中间过程key(也就是这条记录)发送给m个Reduce任务中的哪一个来进行Reduce操作,它位于“org.apche.hadoop.mapreduce”中:
public abstract class Partitioner<KEY, VALUE> {
public abstract int getPartition(KEY key, VALUE value, int numPartitions);
}

HashPartitioner
它位于“org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition”中式是默认的Partition。
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
其中key和value式Map的输出的(K,V)numReduceTasks式Reduce的任务数。Job的Reduce任务数可以指定:
job.setNumberTask(3);//设定Reduce任务数量
此时getPartition的numReduceTasks值为3.
用key.hashCode() 和 Integer.MAX_VALUE) 进行与操作,保证了数据的整数表达,再和numReduceTasks进行取余操作,保证了key值被大致分配给相应的Reduce任务,保证任务分配的均衡性。
job.setPartitionerClass(HashPartitioner.class);
此代码不写,默认是HashPartitioner。
TotalOrderPartitioner
分区过程通过从外部生成的源文件中读取分割点来影响总体顺序。这个类可以实现输出的全排序。这个类不是基于Hash的。他的getPartitione方法如下:
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) {
return partitions.findPartition(key);
}
KeyFieldBasedPartitioner
KeyFieldBasedPartitioner是基于Hash的Partitioner,它提供了多个区间计算Hash,当区间数为0时,KeyFieldBasedPartitioner退化成HashPartitioner:
public int getPartition(K2 key, V2 value, int numReduceTasks) {
byte[] keyBytes;
List <KeyDescription> allKeySpecs = keyFieldHelper.keySpecs();
if (allKeySpecs.size() == 0) {
return getPartition(key.toString().hashCode(), numReduceTasks);
}
try {
keyBytes = key.toString().getBytes("UTF-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("The current system does not " +
"support UTF-8 encoding!", e);
}
// return 0 if the key is empty
if (keyBytes.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int []lengthIndicesFirst = keyFieldHelper.getWordLengths(keyBytes, 0,
keyBytes.length);
int currentHash = 0;
for (KeyDescription keySpec : allKeySpecs) {
int startChar = keyFieldHelper.getStartOffset(keyBytes, 0,
keyBytes.length, lengthIndicesFirst, keySpec);
// no key found! continue
if (startChar < 0) {
continue;
}
int endChar = keyFieldHelper.getEndOffset(keyBytes, 0, keyBytes.length,
lengthIndicesFirst, keySpec);
currentHash = hashCode(keyBytes, startChar, endChar,
currentHash);
}
return getPartition(currentHash, numReduceTasks);
}
BinaryPartitioner
BinaryPartitioner继承Partitioner 是Partitioner的偏特化子类该类提供两个偏移量:
mapreduce.partition.binarypartitioner.left.offset //数组左偏移量(默认为0)
mapreduce.partition.binarypartitioner.right.offset //数组右偏移量(默认为0)
leftOffset = conf.getInt(LEFT_OFFSET_PROPERTY_NAME, 0);
rightOffset = conf.getInt(RIGHT_OFFSET_PROPERTY_NAME, -1);
在计算任何一个Reduce任务是仅仅对键值K的[rightOffset,leftOffset]这个区间区Hash。分区BinaryComparable键使用BinaryComparable键使用BinaryComparable.getBytes()返回的bytes数组的可配置部分。它的部分源码如下:
public int getPartition(BinaryComparable key, V value, int numPartitions) {
int length = key.getLength();
int leftIndex = (leftOffset + length) % length;
int rightIndex = (rightOffset + length) % length;
int hash = WritableComparator.hashBytes(key.getBytes(),
leftIndex, rightIndex - leftIndex + 1);
return (hash & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numPartitions;
}
}
自定义Partition
public class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, Text> { //定义分区名
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, Text value, int numReduceTasks) {//重写分区防火阀
return (Integer.parseInt(key.toString()) & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
job中引用自定义分区
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
排序
排序Sort式MapReduce计算中的核心部分,默认按照字典排序,优势按照业务需求,就需要自定义排序,自定义排序编写排序时候要继承WritableComparator类,重写compare计算方法,对于接收key类型可以通过当前的构造方法super来指定。
public class MySort extends WritableComparator { //自定义排序名称
public MySort() {
super(IntWritable.class, true); //因为Shuffle过程是以key进行排序,这里指定keytWritablel类型
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) { //重写compare方法
IntWritable v1 = (IntWritable) a;
IntWritable v2 = (IntWritable) b;
return v2.compareTo(v1);
}
}
job中引用自定义排序
job.setSortComparatorClass(MySort.class);
分组
默认情况下,reduce方法每次接收的是一组相同key的value值,所以每个reduce方法每次只能通过相同key所对应的值进行计算。但有时用户会期望不同的key所对应的value值能再一次reduce方法调用时进行操作。这样的期望与默认的行为不符合,此时需要用户进行自定义分组的操作。
public class MyGroupSort extends WritableComparator { //定义分组名称
public MyGroupSort() {
super(IntWritable.class, true); //指定key的writable类型
}
@Override //重写compare方法
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
IntWritable v1 = (IntWritable) a;
IntWritable v2 = (IntWritable) b;
if (v1.get() > 10) {
return 0; //表示同一数组
} else {
return -1; //代表不是同一数组
}
}
}
job中引用自定义分组
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyGroupSort.class);
Combiner
Shuffle运行原理可以知道,启用Combiner可以减少磁盘和网络的IO,Combiner时相当于本地的Reduce进行计算,把相同 的key累加在一起,如果再RPC传输之前把相同的key进行规约。即不应先给最终的结果,又可以减轻网络传输压力。
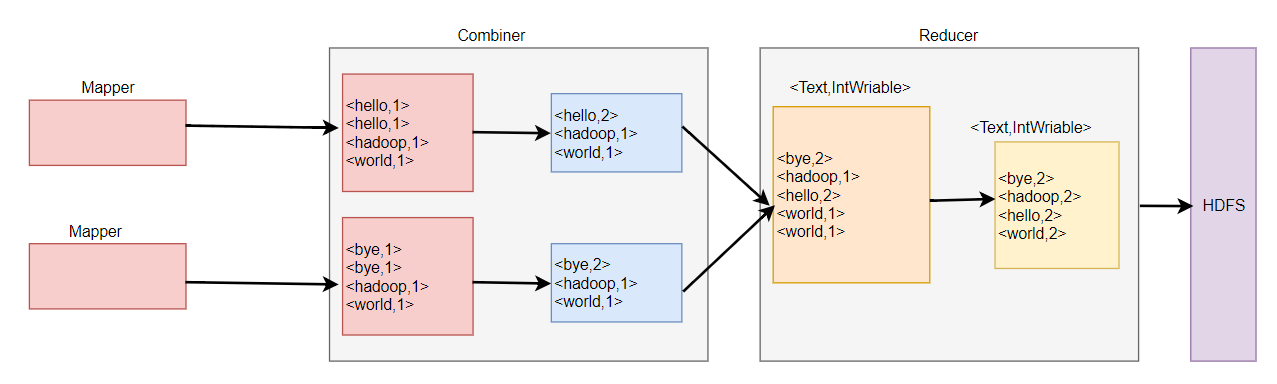
Combiner实现了在RPC传输之前对相同key的值进行了一次类似Reduce的计算操作,累加了值。然后把key和累加后的值作为k v通过RPC传输给Reduce。
public class WordCount_combiner_job {
public static class WordCountMap extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("split:<" + key + ": " + value + ">");
String[] words = value.toString().split(" ");
for (String word : words) {
System.out.println("split:<" + key + ": " + word + ">");
context.write(new Text(word), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}
public static class WordCountReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int total = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
total += value.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(total));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); //获取环境变量
job.setJarByClass(WordCount_combiner_job.class); //设置jar包
job.setJobName("WordCount");
job.setMapperClass(WordCountMap.class); //map作业
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
job.setCombinerClass(WordCountReducer.class);//在此处设置ombinerClass
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReducer.class); //reduce作业
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); // k
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //v
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
SVG业务
有些业务在应用Combiner时必须仔细考虑一些问题,否则就会出错:
avg1.txt avg2.txt
20 25
10 17
3
错误代码
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; public class TxSVG_Erro_job {
public static class TxSVGMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, IntWritable> { @Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(new IntWritable(1), new IntWritable(Integer.parseInt(value.toString())));
}
} public static class TxSVGReducer extends Reducer<IntWritable, IntWritable, IntWritable, IntWritable> { @Override
protected void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int totoal = 0;
int count = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
totoal += value.get();
count++;
}
context.write(new IntWritable(1), new IntWritable(totoal / count));
}
} public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //获取环境变量
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); //实例化任务 job.setJobName("AVG_ERRO"); //设置任务名
job.setJarByClass(TxSVG_Erro_job.class); //设置指定jar job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); //设置输出k
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //设置输出v job.setMapperClass(TxSVGMapper.class); //设置map类 job.setCombinerClass(TxSVGReducer.class);
job.setReducerClass(TxSVGReducer.class); FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
计算如图:

正确的结果应该是(20+10+3+25+17)/5=15,
但是WordCOunt应用Combiner的求法求SVG会出现错误,如果代码不变的情况下去掉 job.setCombinerClass(TxSVGReducer.class);可以提获得正确的结果,但是如果去掉COmbiner,整个数据都会全给一个Reduce计算,如果数据量大会导致Reduce任务所在的节点资源会出现宕机。
思路
- 定义一个Writable用于存储数据量的值的平均值
- 计算总和,用Writable中的数据乘以品滚之来反推回总值。
- 计算平均值,平均值=综合/总共数据量。
TxtSVG_Writable
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException; public class TxtSVG_Writable implements Writable {
private int count = 0;
private int average = 0; public int getCount() {
return count;
} public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
} public int getAverage() {
return average;
} public void setAverage(int average) {
this.average = average;
} @Override
public String toString() {
return count + "\t" + average;
} public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
count = in.readInt();
average = in.readInt();
} public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(count);
out.writeInt(average);
}
}
TxtSVG_TRUE_job
public class TxtSVG_TRUE_job {
public static class SVGMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, IntWritable, TxtSVG_Writable> {
private TxtSVG_Writable w = new TxtSVG_Writable();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
w.setCount(1);
w.setAverage(Integer.parseInt(value.toString()));
context.write(new IntWritable(1), w);
}
}
public static class SVGReduce extends Reducer<IntWritable, TxtSVG_Writable, IntWritable, TxtSVG_Writable> {
private TxtSVG_Writable result = new TxtSVG_Writable();
@Override
protected void reduce(IntWritable key, Iterable<TxtSVG_Writable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
for (TxtSVG_Writable value : values) {
sum += value.getCount() * value.getAverage();
count += value.getCount();
}
result.setCount(count);
result.setAverage(sum / count);
context.write(key, result);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(); //获取环境变量
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration); //实例化任务
job.setJobName("TRUE_AVG");//设置任务名称
job.setJarByClass(TxtSVG_TRUE_job.class); //设置运行Jar类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class); //输出Key格式
job.setOutputValueClass(TxtSVG_Writable.class);//设置Value格式
job.setMapperClass(SVGMapper.class);//设置mapper
job.setCombinerClass(SVGReduce.class);//Combiner在本地运行
job.setReducerClass(SVGReduce.class);//设置Reducer
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); //设置输入路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));//设置输出路径
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
平均值最麻烦的情况就是分子和计算的时候,一定用总和除以数据总量,因为错误的代码Combiner运行在本地,总体把 分子和分母的关系处理错了,导致结果出错,总之就是无论什么时候都要保证总和和总数量不能错。

OutPutFormat
源码包位于包“package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce;”中,是一个抽象类,能够设置文件的输出格式,完成输出规范检查,并未文件输出格式提供作业结果数据输出的功能。

NullOutputFormat
继承OutputFormat的类的一个抽象类,位于org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output;
/**
* Consume all outputs and put them in /dev/null.
*/
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public class NullOutputFormat<K, V> extends OutputFormat<K, V>
消耗所有的输出,并把键值对写入/dev/null。相当于舍弃他们。
FileOutputFormat
位于org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output;是一个从FileSystem读取数据的基类。有子类MapFileOutputFormat,SequenceFileOutputFormat、TextOutputFormat。
FileOutputFormat
提供了若干静态方法,用户可以用他们进行设置输入路径设置、分块大小设置等全局设置。
MapFileOutputFormat
把MapFile作为输出。需要确保Reducer输出的key已经排好序。
SequenceFileOutputFormat
SequenceFileOutputFormat将他的输出写进一个二进制顺序文件。容易压缩,如果为后续MapReduce任务的输出,是很好的输出格式。
TextOutputFormat
在FileOutputFormat所有的子类中,TextOutputFormat类是默认的输出格式,将每条记录记录写成文本行。由于TextOutputFormat调用toString()方法把键和值转换成任意类型。
FilterOutputFormat
对OutputFormat的再一次封装,类似于Java的流的Filter方式
对OutputFormat的输出可以自定义编写他的格式,自定义InputFormat类似首先要继承FileOutputFormat然后重写getRecordWrite方法,返回值类型是RecordeWriter。OutputFormat输出可以指定多路径。和Reduce任务数联系密切,当Reduce任务书为1时,分区数多于1也能运行,也就是说Reduce任务数大于1时,它于分区数必须时保持一致的。
DBOutputFormat
继承OutputFormat接收 K V 对,其中key的继承类DBWritable接口,OutputFormat将Reduce输出发送到SQL表。DBOutPutFormat返回的RecordWriter值使用批量SQL查询写入数据库。
实例分区
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner; public class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, IntWritable> {
public int getPartition(Text key, IntWritable value, int numPartitions) {
if (key.toString().equals("bye")) { //key 为bye 进度第0分区
return 0;
} else if (key.toString().equals("hello")) { //key为hello进度第1分区
return 1;
} else if (key.toString().equals("hadoop")) { //key为hadoop 进度第2分区
return 2;
} else {
return 3; //其他的进入第3分区
}
}
}
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; import java.io.IOException; public class TxtCounter_job {
public static class wordCountMap extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] words = value.toString().split(" "); for (String word : words) {
context.write(new Text(word), new IntWritable(1));
}
}
}
public static class WordCountReduce extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable value : values) {
System.out.println("<" + key + ": " + value + ">");
sum += value.get();
}
context.write(key, new IntWritable(sum));
}
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Configuration conf = new Configuration(); //获取环境变量
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf); //实例化任务 job.setJarByClass(TxtCounter_job.class); //设定jar类型 job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); //设置输出key格式
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class); //设置value格式 job.setMapperClass(wordCountMap.class); //设置Mapper类
job.setReducerClass(WordCountReduce.class); //设置reduce类 job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class); //自定义分区 job.setNumReduceTasks(4); //设置reduce任务数量
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0])); //添加输入路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1])); // 添加输出路径 job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
MapReduce源码刨析的更多相关文章
- 30s源码刨析系列之函数篇
前言 由浅入深.逐个击破 30SecondsOfCode 中函数系列所有源码片段,带你领略源码之美. 本系列是对名库 30SecondsOfCode 的深入刨析. 本篇是其中的函数篇,可以在极短的时间 ...
- Flask上下文管理及源码刨析
基本流程概述 - 与django相比是两种不同的实现方式. - django/tornado是通过传参数形式实现 - 而flask是通过上下文管理, 两种都可以实现,只不实现的方式不一样罢了. - 上 ...
- ConcurrentHashMap源码刨析(基于jdk1.7)
看源码前我们必须先知道一下ConcurrentHashMap的基本结构.ConcurrentHashMap是采用分段锁来进行并发控制的. 其中有一个内部类为Segment类用来表示锁.而Segment ...
- HashMap源码刨析(面试必看)
目录 1.Hash的计算规则? 2.HashMap是怎么形成环形链表的(即为什么不是线程安全)?(1.7中的问题) 3.JDK1.7和1.8的HashMap不同点? 4.HashMap和HashTab ...
- Java 源码刨析 - String
[String 是如何实现的?它有哪些重要的方法?] String 内部实际存储结构为 char 数组,源码如下: public final class String implements java. ...
- Java 源码刨析 - HashMap 底层实现原理是什么?JDK8 做了哪些优化?
[基本结构] 在 JDK 1.7 中 HashMap 是以数组加链表的形式组成的: JDK 1.8 之后新增了红黑树的组成结构,当链表大于 8 并且容量大于 64 时,链表结构会转换成红黑树结构,它的 ...
- Java 源码刨析 - 线程的状态有哪些?它是如何工作的?
线程(Thread)是并发编程的基础,也是程序执行的最小单元,它依托进程而存在. 一个进程中可以包含多个线程,多线程可以共享一块内存空间和一组系统资源,因此线程之间的切换更加节省资源.更加轻量化,也因 ...
- SSM-SpringMVC-04:SpringMVC深入浅出理解HandleMapping(源码刨析)
------------吾亦无他,唯手熟尔,谦卑若愚,好学若饥------------- 先从概念理解,从中央调度器,携带参数request,调度到HandleMapping处理器映射器,处理器映射器 ...
- form 源码刨析
def clean_name(self) value = self.cleaned_data.get('name') if "金-瓶-梅" not in value: raise ...
随机推荐
- 用Hi3518EV200板当spi烧录器
1. setenv bootargs setenv bootcmd 2.ddr烧录uboot 3.uboot下tftp下载文件 mw.b ff ;tftp ;sf erase ;sf write ; ...
- 【HI3520DV200】sample
1.vdec不支持1280x720,支持640x480及以下
- RTP RTCP RTSP
1.RTP over UDP和RTP over RTSP有什么区别?2.RTP over RTSP是不是就是RTP over TCP?3.RTP over TCP 打包视频是不是要加4个字节的头,是 ...
- Java基础语法 第4节 常见软件安装-Mysql和SQLyog
§ mysql数据库安装 一.下载安装包并安装 Windows 上安装 MySQL 相对来说会较为简单,地那就链接 https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/下载 ...
- HttpServletResponse和HttpServletRequest
1.相关的接口 HttpServletRequest HttpServletRequest接口最常用的方法就是获得请求中的参数,这些参数一般是客户端表单中的数据.同时,HttpServletReq ...
- CentOS6.5_64位系统下安装配置postfix邮件系统 启用并配置SMTP虚拟账户
http://blog.jjonline.cn/linux/185.html http://www.cnblogs.com/apexchu/p/4271264.html 用户新增和删除 http:// ...
- openwrt挂载摄像头及视频保存
一.编译选项的选择: -> Utilities ->usbutils (这个里面包含lsusb的命令,是查看你的摄像头型号的) -> Kernel modules -> I2C ...
- 2017.11.7 ant design - upload 组件的使用, react 条件渲染以及 axios.all() 的使用
一.主要任务:悉尼小程序管理后台,添加景点页面的开发 二.所遇问题及解决 1. 上传多个不同分类音频信息时,如中文音频和英文音频,要求音频不是放在一个数组中的,每个音频是一个独立的字段,此时: < ...
- MySQL GTID 错误处理汇总
MySQL GTID是在传统的mysql主从复制的基础之上演化而来的产物,即通过UUID加上事务ID的方式来确保每一个事物的唯一性.这样的操作方式使得我们不再需要关心所谓的log_file和log_P ...
- Hiero的spreadsheet中添加tag属性列
Hiero在对剪辑线上的item进行管理的时候,往往会添加能多tag,而在管 理面板spreadsheet中却无法对tag进行查询,这是一件很麻烦的事,Hiero Development Guide中 ...
