tensorflow 数据集对象(tf.data)的使用( tf.data.Dataset 、tf.data.TextLineDataset 、 tf.data.TFRecordDataset ) 示例
tensorflow 使用数据集(tf.data)的方法对数据集进行操纵。
1. 对 数组(内存向量) 进行操纵 :
import tensorflow as tf input_data = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] #从数组生成数据集
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(input_data) #dataset = dataset.shuffle(3)
#dataset = dataset.repeat(10)
#dataset = dataset.batch(2)
dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(10).batch(2) # 定义迭代器。
iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator() # get_next() 返回代表一个输入数据的张量(batch)。
x = iterator.get_next()
y = x * x coord=tf.train.Coordinator()
with tf.Session() as sess:
for i in range(25):
print(sess.run(y))
2. 读取文本文件里的数据 ( tf.data.TextLineDataset )
import tensorflow as tf # 创建文本文件作为本例的输入。
with open("./test1.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("File1, line1.\n")
file.write("File1, line2.\n")
file.write("File1, line3.\n")
file.write("File1, line4.\n")
file.write("File1, line5.\n") with open("./test2.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("File2, line1.\n")
file.write("File2, line2.\n")
file.write("File2, line3.\n")
file.write("File2, line4.\n")
file.write("File2, line5.\n") # 从文本文件创建数据集。这里可以提供多个文件。
input_files = ["./test1.txt", "./test2.txt"]
dataset = tf.data.TextLineDataset(input_files)
#dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(2).batch(2) # 定义迭代器。
iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator() # 这里get_next()返回一个字符串类型的张量,代表文件中的一行。
x = iterator.get_next()
with tf.Session() as sess:
for i in range(10):
print(sess.run(x))
3. 解析TFRecord文件里的数据
准备工作:(mnist数据集的tfrecord格式的保存)
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import numpy as np def _float32_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=[value])) def _int64_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[value])) def _bytes_feature(value):
return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[value])) mnist=input_data.read_data_sets('./data', dtype=tf.uint8, one_hot=True)
"""
print(mnist.train.images)
print(mnist.train.labels)
print(mnist.test.images)
print(mnist.test.labels)
"""
train_images=mnist.train.images
train_labels=mnist.train.labels
#test_images=mnist.test.images
#test_labels=mnist.test.labels train_num=mnist.train.num_examples
#test_num=mnist.test.num_examples pixels=train_images.shape[1] # 784 = 28*28 file_out='./data/output.tfrecords'
writer=tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(file_out) for index in range(train_num):
image_raw=train_images[index].tostring() #转换为bytes序列 example=tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'pixels': _int64_feature(pixels),
'label':_int64_feature(np.argmax(train_labels[index])),
'x':_float32_feature(0.1),
'y':_bytes_feature(bytes('abcde', 'utf-8')),
'image_raw':_bytes_feature(image_raw)})) writer.write(example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
准备工作:(mnist数据集的tfrecord格式的读取)
import tensorflow as tf
reader=tf.TFRecordReader()
files=tf.train.match_filenames_once('./data/output.*')
#filename_queue=tf.train.string_input_producer(['./data/output.tfrecords'])
filename_queue=tf.train.string_input_producer(files)
_, serialized_example=reader.read(filename_queue)
features=tf.parse_single_example(serialized_example,
features={
'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'x':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
'y':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
})
#print(features['image_raw']) # tensor string (bytes tensor string tensor)
# necessary operation
# bytes_list to uint8_list
image=tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)
#print(image) # tensor uint8
x=features['x']
#y=tf.cast(features['y'], tf.string)
y=features['y']
label=tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
pixels=tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32)
#image.set_shape([pixels**0.5, pixels**0.5])
image.set_shape([784])
batch_size=2
image_batch, label_batch, pixels_batch, x_batch, y_batch=tf.train.batch([image, label, pixels,x,y], batch_size=batch_size, capacity=1000+3*batch_size)
coord=tf.train.Coordinator()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer())
threads=tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
for i in range(1):
print(sess.run([image_batch, label_batch, pixels_batch, x_batch, y_batch]))
coord.request_stop()
coord.join(threads)
正式工作:(mnist数据集的tfrecord格式 使用 TFRecordDataset 数据集读取)
import tensorflow as tf
files=tf.gfile.Glob('./data/output.*')
dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(files)
def parser(record):
features=tf.parse_single_example(record,
features={
'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'x':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
'y':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
})
#print(features['image_raw']) # tensor string (bytes tensor string tensor)
# necessary operation
# bytes_list to uint8_list
image=tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)
#print(image) # tensor uint8
x=features['x']
#y=tf.cast(features['y'], tf.string)
y=features['y']
label=tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
pixels=tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32)
#image.set_shape([pixels**0.5, pixels**0.5])
image.set_shape([784])
return image, label, pixels, x, y
# map()函数表示对数据集中的每一条数据进行调用解析方法。
dataset = dataset.map(parser)
# dataset 数据集操纵
dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(2).batch(2)
# 定义遍历数据集的迭代器。
iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
# 读取数据,可用于进一步计算
image, label, pixels, x, y = iterator.get_next()
with tf.Session() as sess:
for i in range(1):
print(sess.run([image, label, pixels, x, y]))

4. 使用 initializable_iterator 来动态初始化数据集
# 从TFRecord文件创建数据集,具体文件路径是一个placeholder,稍后再提供具体路径。
input_files = tf.placeholder(tf.string)
dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(input_files)
dataset = dataset.map(parser) # 定义遍历dataset的initializable_iterator。
iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator()
image, label = iterator.get_next() with tf.Session() as sess:
# 首先初始化iterator,并给出input_files的值。
sess.run(iterator.initializer,
feed_dict={input_files: ["output.tfrecords"]})
# 遍历所有数据一个epoch。当遍历结束时,程序会抛出OutOfRangeError。
while True:
try:
x, y = sess.run([image, label])
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
break
详细例子:
import tensorflow as tf files=tf.placeholder(tf.string) dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(files) def parser(record):
features=tf.parse_single_example(record,
features={
'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'x':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
'y':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
}) #print(features['image_raw']) # tensor string (bytes tensor string tensor) # necessary operation
# bytes_list to uint8_list
image=tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)
#print(image) # tensor uint8 x=features['x'] #y=tf.cast(features['y'], tf.string)
y=features['y'] label=tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
pixels=tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32) #image.set_shape([pixels**0.5, pixels**0.5])
image.set_shape([784])
return image, label, pixels, x, y # map()函数表示对数据集中的每一条数据进行调用解析方法。
dataset = dataset.map(parser) # dataset 数据集操纵
dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(2).batch(2) # 定义遍历数据集的迭代器。
#iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
# 定义遍历dataset的initializable_iterator。
iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator() # 读取数据,可用于进一步计算
image, label, pixels, x, y = iterator.get_next() with tf.Session() as sess:
# 首先初始化iterator,并给出input_files的值。
sess.run(iterator.initializer,
feed_dict={files: ["data/output.tfrecords"]})
for i in range(1):
print(sess.run([image, label, pixels, x, y]))
或(修改版):
import tensorflow as tf
files=tf.train.match_filenames_once('./data/output.*')
dataset = tf.data.TFRecordDataset(files)
def parser(record):
features=tf.parse_single_example(record,
features={
'image_raw':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'pixels':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64),
'x':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.float32),
'y':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string)
})
#print(features['image_raw']) # tensor string (bytes tensor string tensor)
# necessary operation
# bytes_list to uint8_list
image=tf.decode_raw(features['image_raw'], tf.uint8)
#print(image) # tensor uint8
x=features['x']
#y=tf.cast(features['y'], tf.string)
y=features['y']
label=tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int32)
pixels=tf.cast(features['pixels'], tf.int32)
#image.set_shape([pixels**0.5, pixels**0.5])
image.set_shape([784])
return image, label, pixels, x, y
# map()函数表示对数据集中的每一条数据进行调用解析方法。
dataset = dataset.map(parser)
# dataset 数据集操纵
dataset = dataset.shuffle(3).repeat(2).batch(2)
# 定义遍历数据集的迭代器。
#iterator = dataset.make_one_shot_iterator()
# 定义遍历dataset的initializable_iterator。
iterator = dataset.make_initializable_iterator()
# 读取数据,可用于进一步计算
image, label, pixels, x, y = iterator.get_next()
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 初始化变量。
sess.run((tf.global_variables_initializer(),
tf.local_variables_initializer()))
# 首先初始化iterator,并给出input_files的值。
sess.run(iterator.initializer)
while True:
try:
print(sess.run([image, label, pixels, x, y]))
except tf.errors.OutOfRangeError:
break
==========================================================
注:
迭代器:
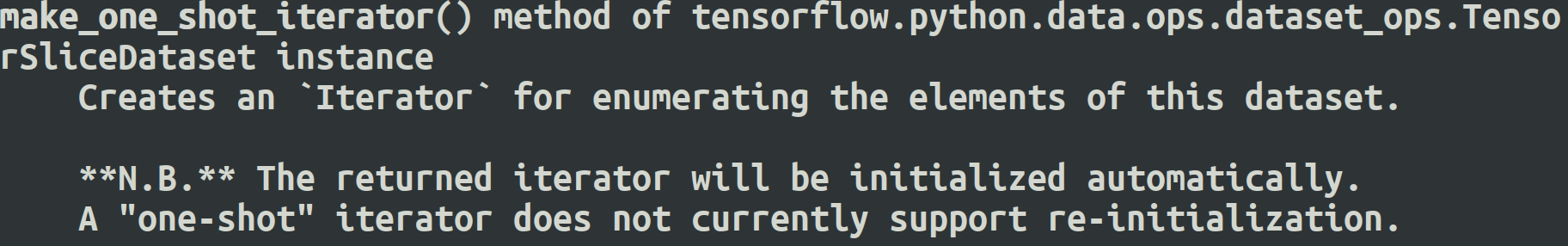
make_one_shot_iterator 方法不能重复初始化,即one-shot(一次性),但是可以自动初始化。
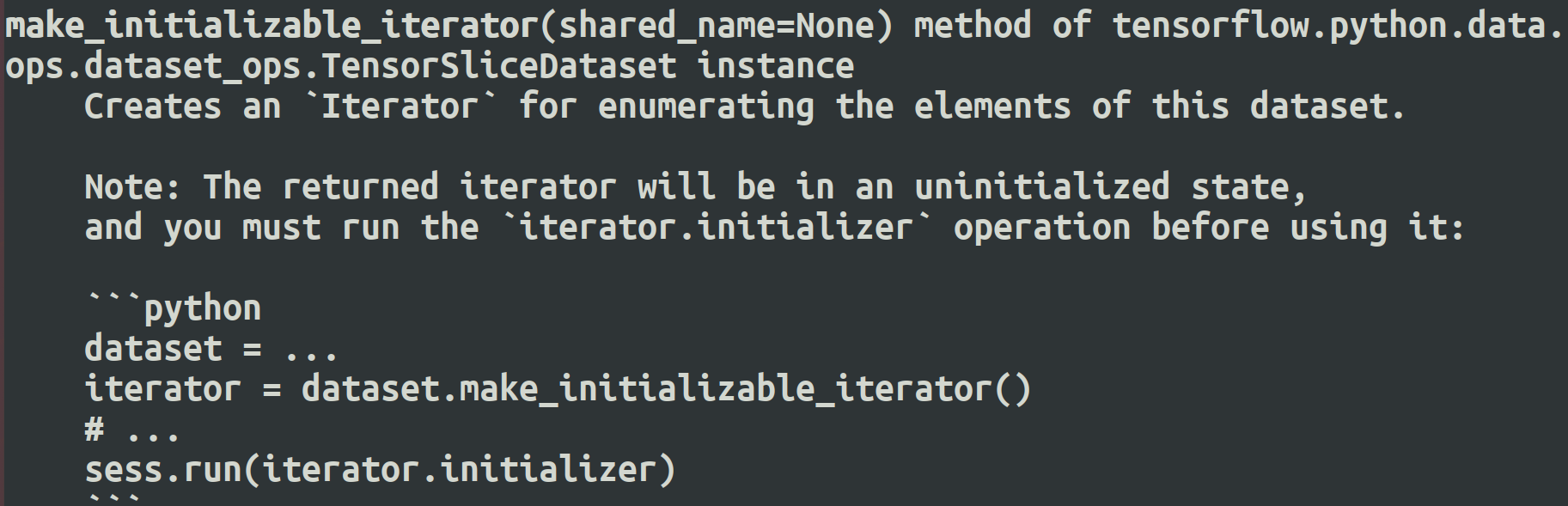
make_initializable_iterator 必须手动初始化,但是可以重复初始化。
tensorflow 数据集对象(tf.data)的使用( tf.data.Dataset 、tf.data.TextLineDataset 、 tf.data.TFRecordDataset ) 示例的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow数据集(二)——数据集的高层操作
参考书 <TensorFlow:实战Google深度学习框架>(第2版) 一个使用数据集进行训练和测试的完整例子. #!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: ...
- TensorFlow数据集(一)——数据集的基本使用方法
参考书 <TensorFlow:实战Google深度学习框架>(第2版) 例子:从一个张量创建一个数据集,遍历这个数据集,并对每个输入输出y = x^2 的值. #!/usr/bin/en ...
- DataSnap数据库连接池,数据集对象池的应用
传统的应用服务器的开发往往是在ServerMethods单元中拖放一堆TDataSet, TDaTaSetProvider控件,这是一个最简单粗暴的开发方向,往往会造成服务端程序文件的臃肿.服务运行期 ...
- SSAS系列——【03】多维数据(多维数据集对象)
原文:SSAS系列--[03]多维数据(多维数据集对象) 1.什么是Cube? 简单 Cube 对象由基本信息.维度和度量值组组成. 基本信息包括多维数据集的名称.多维数据集的默认度量值.数据源和存储 ...
- Tensorflow学习教程------读取数据、建立网络、训练模型,小巧而完整的代码示例
紧接上篇Tensorflow学习教程------tfrecords数据格式生成与读取,本篇将数据读取.建立网络以及模型训练整理成一个小样例,完整代码如下. #coding:utf-8 import t ...
- Failed to collect certificates from /data/app/vmdl201020547.tmp/base.apk: META-INF/CERT.SF indicates /data/app/vmdl201020547.tmp/base.apk is signed using APK Signature Scheme v2, but no such signature
错误信息: 12-26 11:08:44.809 1501-1535/system_process E/PackageInstaller: Commit of session 201020547 fa ...
- devmapper: Thin Pool has 162394 free data blocks which is less than minimum required 163840 free data blocks. Create more free space in thin pool or use dm.min_free_space option to change behavior
问题: 制作镜像的时候报错 devmapper: Thin Pool has 162394 free data blocks which is less than minimum required 1 ...
- devmapper: Thin Pool has 162394 free data blocks which is less than minimum required 163840 free data blocks
问题: 制作镜像的时候报错 devmapper: Thin Pool has 162394 free data blocks which is less than minimum required 1 ...
- Parameter 0 of method redisTemplate in org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration required a bean of type 'org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactor
Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with 'de ...
- 现代英特尔® 架构上的 TensorFlow* 优化——正如去年参加Intel AI会议一样,Intel自己提供了对接自己AI CPU优化版本的Tensorflow,下载链接见后,同时可以基于谷歌官方的tf版本直接编译生成安装包
现代英特尔® 架构上的 TensorFlow* 优化 转自:https://software.intel.com/zh-cn/articles/tensorflow-optimizations-on- ...
随机推荐
- Linux下,安装单机版Flink
安装前准备 jdk环境 开始安装 下载安装包 地址1:https://archive.apache.org/dist/flink/flink-1.18.0/flink-1.18.0-bin-scala ...
- “Newtonsoft.Json”已拥有为“Microsoft.CSharp”定义的依赖项。
安装较低版本的Newtonsoft.Json: Newtonsoft.Json官网:https://www.nuget.org/packages/Newtonsoft.Json/ Install-Pa ...
- 夜莺监控发布 v6.7 版本,推送部分商业版功能
熟悉夜莺的小伙伴都知道夜莺分为开源版.专业版.企业版,三个版本良性发展.近期夜莺团队发布了 v6.7 版本,把机器Metadata管理功能推送到了开源版,下面是该功能的简单介绍. 如上图,机器列表页面 ...
- 开源的Datadog?可观测性平台SigNoz是否名副其实?
SigNoz号称自己是开源领域的Datadog,基于OpenTelemetry做了一套可观测性方案.夜莺从V6版本开始,也希望做全栈可观测性方案,巧了,大家目标一致,今天我们一起来对SigNoz做个初 ...
- python正则表达式替换所有内容并同时保留找到的内容
除了一些专业的工具,例如ue,大部分编程语言的函数包都挺让人迷惑的,例如Java,js. 因为的确有许多功能是很常用的,但是他们又不提供,非得要程序员自己去实现,或者是利用三方的包. 到底是什么理由了 ...
- C# Linq.FirstOrDefault、Linq.Where、Linq.AsParallel、List.Exists、List.Find、Dictionar.TryGetValue、HashSet.Contains 性能的比较
今天我们来比较一下集合检索方法性能更优问题,测试代码 public class Entity { public int Id { get; set; } public int No { get; se ...
- 【主流技术】聊一聊消息队列 RocketMQ 的基本结构与概念
目录 前言 一.初识 RocketMQ 1.1基本模型 二.基本概念 2.1Producer 2.2Consumer 2.3Topic 2.4Tag 2.5Message 2.6Broker 2.7P ...
- Libgdx游戏开发(6)——游戏暂停
原文: Libgdx游戏开发(6)--游戏暂停-Stars-One的杂货小窝 暂停也是一个游戏的必要功能了,本文研究了Libgdx实现游戏暂停 例子以桌面端游戏实现讲解为主,至于移动端,可能之后会进行 ...
- selenium无头浏览器
from selenium.webdriver import Edge # 在这里导入浏览器设置相关的类 from selenium.webdriver.edge.options import Opt ...
- windows server + iis 部署若伊前端vue项目
一.背景说明 工作原因,一直使用若伊前后端分离版框架进行二次开发.客户的服务器多数为windows server系统,少部分为linux系统.过去一直是使用nginx进行前端的部署,nginx的代理功 ...
