Seaborn分布数据可视化---箱型分布图
箱型分布图
boxplot()
sns.boxplot(
x=None,
y=None,
hue=None,
data=None,
order=None,
hue_order=None,
orient=None,
color=None,
palette=None,
saturation=0.75,
width=0.8,
dodge=True,
fliersize=5,
linewidth=None,
whis=1.5,
notch=False,
ax=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Draw a box plot to show distributions with respect to categories.
A box plot (or box-and-whisker plot) shows the distribution of quantitative
data in a way that facilitates comparisons between variables or across
levels of a categorical variable. The box shows the quartiles of the
dataset while the whiskers extend to show the rest of the distribution,
except for points that are determined to be "outliers" using a method
that is a function of the inter-quartile range.
Input data can be passed in a variety of formats, including:
- Vectors of data represented as lists, numpy arrays, or pandas Series
objects passed directly to the ``x``, ``y``, and/or ``hue`` parameters.
- A "long-form" DataFrame, in which case the ``x``, ``y``, and ``hue``
variables will determine how the data are plotted.
- A "wide-form" DataFrame, such that each numeric column will be plotted.
- An array or list of vectors.
In most cases, it is possible to use numpy or Python objects, but pandas
objects are preferable because the associated names will be used to
annotate the axes. Additionally, you can use Categorical types for the
grouping variables to control the order of plot elements.
This function always treats one of the variables as categorical and
draws data at ordinal positions (0, 1, ... n) on the relevant axis, even
when the data has a numeric or date type.
See the :ref:`tutorial <categorical_tutorial>` for more information.
Parameters
----------
x, y, hue : names of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Inputs for plotting long-form data. See examples for interpretation.
data : DataFrame, array, or list of arrays, optional
Dataset for plotting. If ``x`` and ``y`` are absent, this is
interpreted as wide-form. Otherwise it is expected to be long-form.
order, hue_order : lists of strings, optional
Order to plot the categorical levels in, otherwise the levels are
inferred from the data objects.
orient : "v" | "h", optional
Orientation of the plot (vertical or horizontal). This is usually
inferred from the dtype of the input variables, but can be used to
specify when the "categorical" variable is a numeric or when plotting
wide-form data.
color : matplotlib color, optional
Color for all of the elements, or seed for a gradient palette.
palette : palette name, list, or dict, optional
Colors to use for the different levels of the ``hue`` variable. Should
be something that can be interpreted by :func:`color_palette`, or a
dictionary mapping hue levels to matplotlib colors.
saturation : float, optional
Proportion of the original saturation to draw colors at. Large patches
often look better with slightly desaturated colors, but set this to
``1`` if you want the plot colors to perfectly match the input color
spec.
width : float, optional
Width of a full element when not using hue nesting, or width of all the
elements for one level of the major grouping variable.
dodge : bool, optional
When hue nesting is used, whether elements should be shifted along the
categorical axis.
fliersize : float, optional
Size of the markers used to indicate outlier observations.
linewidth : float, optional
Width of the gray lines that frame the plot elements.
whis : float, optional
Proportion of the IQR past the low and high quartiles to extend the
plot whiskers. Points outside this range will be identified as
outliers.
notch : boolean, optional
Whether to "notch" the box to indicate a confidence interval for the
median. There are several other parameters that can control how the
notches are drawn; see the ``plt.boxplot`` help for more information
on them.
ax : matplotlib Axes, optional
Axes object to draw the plot onto, otherwise uses the current Axes.
kwargs : key, value mappings
Other keyword arguments are passed through to ``plt.boxplot`` at draw
time.
Returns
-------
ax : matplotlib Axes
Returns the Axes object with the plot drawn onto it.
See Also
--------
violinplot : A combination of boxplot and kernel density estimation.
stripplot : A scatterplot where one variable is categorical. Can be used
in conjunction with other plots to show each observation.
swarmplot : A categorical scatterplot where the points do not overlap. Can
be used with other plots to show each observation.
#设置风格
sns.set_style('white')
#导入数据
tip_datas = sns.load_dataset('tips', data_home='seaborn-data')
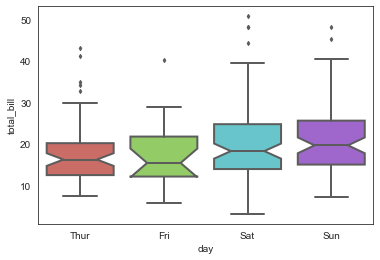
# 绘制传统的箱型图
sns.boxplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
linewidth=2, #线宽
width=0.8, #箱之间的间隔比例
fliersize=3, #异常点大小
palette='hls', #设置调色板
whis=1.5, #设置IQR
notch=True, #设置中位值凹陷
order=['Thur','Fri','Sat','Sun'], #选择类型并排序
)
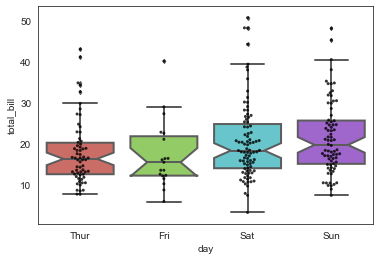
# 绘制箱型图
sns.boxplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
linewidth=2,
width=0.8,
fliersize=3,
palette='hls',
whis=1.5,
notch=True,
order=['Thur','Fri','Sat','Sun'],
)
#添加散点图
sns.swarmplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas, color='k', size=3, alpha=0.8)
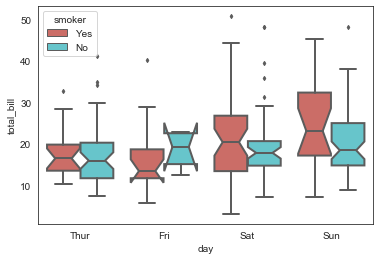
# 绘制箱型图,hue参数设置再分类
sns.boxplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
linewidth=2,
width=0.8,
fliersize=3,
palette='hls',
whis=1.5,
notch=True,
order=['Thur','Fri','Sat','Sun'],
hue='smoker',
)
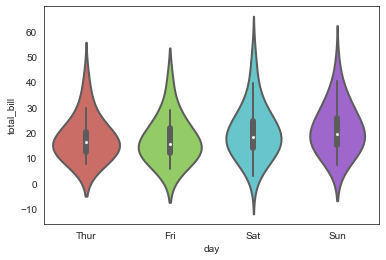
violinplot()
sns.violinplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
linewidth=2,
width=0.8,
palette='hls',
order=['Thur','Fri','Sat','Sun'],
scale='area', #设置提琴宽度:area-面积相同,count-按照样本数量决定宽度,width-宽度一样
gridsize=50, #设置提琴图的边线平滑度,越高越平滑
inner='box', #设置内部显示类型--"box","quartile","point","stick",None
bw=0.8 #控制拟合程度,一般可以不设置
)
sns.violinplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
linewidth=2,
width=0.8,
palette='hls',
order=['Thur','Fri','Sat','Sun'],
scale='width',
gridsize=50,
inner='quartile', #内部标记分位线
bw=0.8
)
sns.violinplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
linewidth=2,
width=0.8,
palette='hls',
order=['Thur','Fri','Sat','Sun'],
scale='width',
gridsize=50,
inner='point', #内部添加散点
bw=0.8
)
sns.violinplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
linewidth=2,
width=0.8,
palette='hls',
order=['Thur','Fri','Sat','Sun'],
scale='width',
gridsize=50,
inner='stick', #内部添加细横线
bw=0.8
)
boxenplot()
sns.boxenplot(
x=None,
y=None,
hue=None,
data=None,
order=None,
hue_order=None,
orient=None,
color=None,
palette=None,
saturation=0.75,
width=0.8,
dodge=True,
k_depth='proportion',
linewidth=None,
scale='exponential',
outlier_prop=None,
ax=None,
**kwargs,
)
Docstring:
Draw an enhanced box plot for larger datasets.
This style of plot was originally named a "letter value" plot because it
shows a large number of quantiles that are defined as "letter values". It
is similar to a box plot in plotting a nonparametric representation of a
distribution in which all features correspond to actual observations. By
plotting more quantiles, it provides more information about the shape of
the distribution, particularly in the tails. For a more extensive
explanation, you can read the paper that introduced the plot:
https://vita.had.co.nz/papers/letter-value-plot.html
Input data can be passed in a variety of formats, including:
- Vectors of data represented as lists, numpy arrays, or pandas Series
objects passed directly to the ``x``, ``y``, and/or ``hue`` parameters.
- A "long-form" DataFrame, in which case the ``x``, ``y``, and ``hue``
variables will determine how the data are plotted.
- A "wide-form" DataFrame, such that each numeric column will be plotted.
- An array or list of vectors.
In most cases, it is possible to use numpy or Python objects, but pandas
objects are preferable because the associated names will be used to
annotate the axes. Additionally, you can use Categorical types for the
grouping variables to control the order of plot elements.
This function always treats one of the variables as categorical and
draws data at ordinal positions (0, 1, ... n) on the relevant axis, even
when the data has a numeric or date type.
See the :ref:`tutorial <categorical_tutorial>` for more information.
Parameters
----------
x, y, hue : names of variables in ``data`` or vector data, optional
Inputs for plotting long-form data. See examples for interpretation.
data : DataFrame, array, or list of arrays, optional
Dataset for plotting. If ``x`` and ``y`` are absent, this is
interpreted as wide-form. Otherwise it is expected to be long-form.
order, hue_order : lists of strings, optional
Order to plot the categorical levels in, otherwise the levels are
inferred from the data objects.
orient : "v" | "h", optional
Orientation of the plot (vertical or horizontal). This is usually
inferred from the dtype of the input variables, but can be used to
specify when the "categorical" variable is a numeric or when plotting
wide-form data.
color : matplotlib color, optional
Color for all of the elements, or seed for a gradient palette.
palette : palette name, list, or dict, optional
Colors to use for the different levels of the ``hue`` variable. Should
be something that can be interpreted by :func:`color_palette`, or a
dictionary mapping hue levels to matplotlib colors.
saturation : float, optional
Proportion of the original saturation to draw colors at. Large patches
often look better with slightly desaturated colors, but set this to
``1`` if you want the plot colors to perfectly match the input color
spec.
width : float, optional
Width of a full element when not using hue nesting, or width of all the
elements for one level of the major grouping variable.
dodge : bool, optional
When hue nesting is used, whether elements should be shifted along the
categorical axis.
k_depth : "proportion" | "tukey" | "trustworthy", optional
The number of boxes, and by extension number of percentiles, to draw.
All methods are detailed in Wickham's paper. Each makes different
assumptions about the number of outliers and leverages different
statistical properties.
linewidth : float, optional
Width of the gray lines that frame the plot elements.
scale : "linear" | "exponential" | "area"
Method to use for the width of the letter value boxes. All give similar
results visually. "linear" reduces the width by a constant linear
factor, "exponential" uses the proportion of data not covered, "area"
is proportional to the percentage of data covered.
outlier_prop : float, optional
Proportion of data believed to be outliers. Used in conjunction with
k_depth to determine the number of percentiles to draw. Defaults to
0.007 as a proportion of outliers. Should be in range [0, 1].
ax : matplotlib Axes, optional
Axes object to draw the plot onto, otherwise uses the current Axes.
kwargs : key, value mappings
Other keyword arguments are passed through to ``plt.plot`` and
``plt.scatter`` at draw time.
Returns
-------
ax : matplotlib Axes
Returns the Axes object with the plot drawn onto it.
See Also
--------
violinplot : A combination of boxplot and kernel density estimation.
boxplot : A traditional box-and-whisker plot with a similar API.
#单变量简易图
ax = sns.boxenplot(x=tip_datas['total_bill'])
#多变量箱型图
ax = sns.boxenplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas)

#多变量分类箱型图,hue
ax = sns.boxenplot(x='day', y='total_bill',
data=tip_datas,hue='smoker'
)
#多变量分类箱型图,hue
ax = sns.boxenplot(x='day', y='total_bill',
data=tip_datas,hue='time',
linewidth=2.5)
#多变量排序箱型图,order
ax = sns.boxenplot(x='time', y='tip',
data=tip_datas,order=['Dinner','Lunch']
)
ax = sns.boxenplot(x='day', y='total_bill',
data=tip_datas)
#添加散点图
ax = sns.stripplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
size=4,jitter=True, color="gray"
)
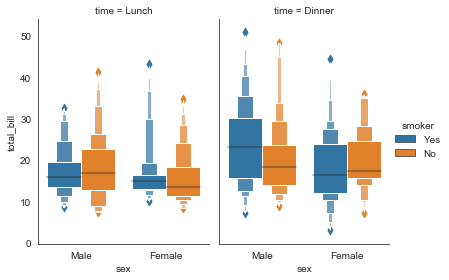
#分栏箱型图
g = sns.catplot(x="sex", y="total_bill",
hue="smoker", col="time",
data=tip_datas, kind="boxen",
height=4, aspect=.7)
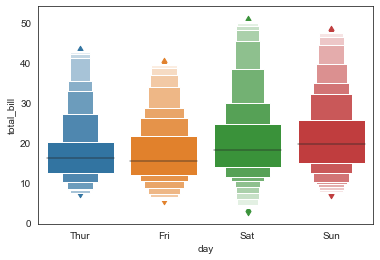
#其他参数,scale\k_depth
sns.boxenplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
width=0.8,
linewidth=12,
scale='area', #设置框大小:"linear"、"exponential"、"area"
k_depth='proportion', #设置框的数量: "proportion"、"tukey"、"trustworthy"
)
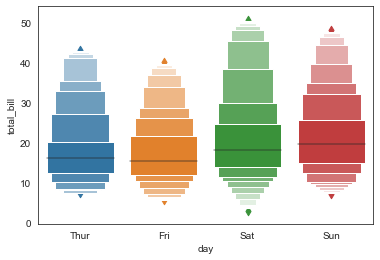
sns.boxenplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
width=0.8,
linewidth=12,
scale='linear', #设置框大小:"linear"、"exponential"、"area"
k_depth='proportion', #设置框的数量: "proportion"、"tukey"、"trustworthy"
)
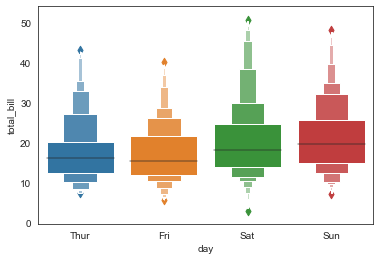
sns.boxenplot(x='day', y='total_bill', data=tip_datas,
width=0.8,
linewidth=12,
scale='exponential', #设置框大小:"linear"、"exponential"、"area"
k_depth='proportion', #设置框的数量: "proportion"、"tukey"、"trustworthy"
)
#多变量横向箱型图,orient
iris_datas = sns.load_dataset('iris', data_home='seaborn-data')
ax = sns.boxenplot(data=iris_datas, orient='h')
Seaborn分布数据可视化---箱型分布图的更多相关文章
- seaborn分布数据可视化:直方图|密度图|散点图
系统自带的数据表格(存放在github上https://github.com/mwaskom/seaborn-data),使用时通过sns.load_dataset('表名称')即可,结果为一个Dat ...
- Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:1. 风格| 分布数据可视化-直方图| 密度图| 散点图
conda install seaborn 是安装到jupyter那个环境的 1. 整体风格设置 对图表整体颜色.比例等进行风格设置,包括颜色色板等调用系统风格进行数据可视化 set() / se ...
- Python图表数据可视化Seaborn:2. 分类数据可视化-分类散点图|分布图(箱型图|小提琴图|LV图表)|统计图(柱状图|折线图)
1. 分类数据可视化 - 分类散点图 stripplot( ) / swarmplot( ) sns.stripplot(x="day",y="total_bill&qu ...
- seaborn分类数据可视化:散点图|箱型图|小提琴图|lv图|柱状图|折线图
一.散点图stripplot( ) 与swarmplot() 1.分类散点图stripplot( ) 用法stripplot(x=None, y=None, hue=None, data=None, ...
- seaborn分类数据可视化
转载:https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1178368 seaborn针对分类型的数据有专门的可视化函数,这些函数可大致分为三种: 分类数据散点图 ...
- seaborn线性关系数据可视化:时间线图|热图|结构化图表可视化
一.线性关系数据可视化lmplot( ) 表示对所统计的数据做散点图,并拟合一个一元线性回归关系. lmplot(x, y, data, hue=None, col=None, row=None, p ...
- 用seaborn对数据可视化
以下用sns作为seaborn的别名 1.seaborn整体布局设置 sns.set_syle()函数设置图的风格,传入的参数可以是"darkgrid", "whiteg ...
- Python Seaborn综合指南,成为数据可视化专家
概述 Seaborn是Python流行的数据可视化库 Seaborn结合了美学和技术,这是数据科学项目中的两个关键要素 了解其Seaborn作原理以及使用它生成的不同的图表 介绍 一个精心设计的可视化 ...
- Seaborn数据可视化入门
在本节学习中,我们使用Seaborn作为数据可视化的入门工具 Seaborn的官方网址如下:http://seaborn.pydata.org 一:definition Seaborn is a Py ...
- 第六篇:R语言数据可视化之数据分布图(直方图、密度曲线、箱线图、等高线、2D密度图)
数据分布图简介 中医上讲看病四诊法为:望闻问切.而数据分析师分析数据的过程也有点相似,我们需要望:看看数据长什么样:闻:仔细分析数据是否合理:问:针对前两步工作搜集到的问题与业务方交流:切:结合业务方 ...
随机推荐
- sql注入简单初
import requests,sys,time from PyQt5.QtWidgets import * from PyQt5.QtGui import QIcon from threading ...
- DataGear 自定义数据可视化看板的图表主题
DataGear 看板的 dg-chart-theme 属性,提供了简单且强大的自定义图表主题功能. 通常,只需要设置其color.backgroundColor.actualBackgroundCo ...
- 可视化探索开源项目的 contributor 关系
引语:作为国内外最大的代码托管平台,根据最新的 GitHub 数据,它拥有超 372,000,000 个仓库,其中有 28,000,000 是公开仓.分布式图数据库 NebulaGraph 便是其中之 ...
- dart特殊符号语法(一)
许久没有写博客.浏览以往的博客,是那么稚嫩.就让它们当成成长的照片吧.重新开始操起这个记录的爱好,一方面把它当成可以查阅的资料,方便自己:另一方面希望有帮助于人.由于个人能力,认知有限,如读者发现有纰 ...
- CentOS8安装与配置jdk1.8 与远程分发复制jdk到另一个虚拟机
安装配置JDK 一.卸载系统自带的OpenJDK及相关的java文件 1.查看系统自带OpenJDK版本 命令介绍: 2.卸载java 命令介绍: 二.下载安装jdk 1.命令式安装 查看JDK软件包 ...
- 日常办公——Excel中重复打印标题的设置
打印预览时,所在数据行或列不能显示在同一页,在打印区域之外还有内容,为了方便阅读,可使用顶端标题行重复或左端标题行重复,具体方法如下: 按顺序操作,完成后点击确定即完成操作.
- uniapp使用uview报错Cannot find module ‘@/uni_modules/uview-ui/components
参考:https://github.com/umicro/uView 记录使用uniapp报的错 注意uview目前只支持vue2 按照教程引入uview,然后执行的时候还是会报Cannot find ...
- Java基础知识篇01——Java基本介绍
一.什么是 Java Java 是 Sun Microsystems 于 1995 年首次发布的一种编程语言和计算平台.编程语言还是比较好理解的,什么是计算平台呢? 计算平台是电脑中运行应用程序(软件 ...
- 投屏项目中Sink端CPU占用过高问题
一.背景 今天来总结一下,自己在项目中遇到的一个CPU占用过高的问题,详细的结束从发现到定位在到解决问题的过程. 原因是性能测试那边提出了一个bug,就是在投屏过程中,平板端也就是Sink端功耗非常高 ...
- Ubuntu 14.04 Intel 处理器 硬编解码配置(Intel® Media Server Studio)
PS:要转载请注明出处,本人版权所有. PS: 这个只是基于<我自己>的理解, 如果和你的原则及想法相冲突,请谅解,勿喷. 前置说明 本文作为本人csdn blog的主站的备份.(Bl ...
