[Ngbatis源码学习][Spring] Spring 的资源管理 ResourceLoader
在学习Ngbatis的源码时,看到了有关xml文件的加载,涉及到了资源的加载,对相关知识进行总结与整理。
1. 相关类
ResourceAbstractResourceResourceLoaderDefaultResourceLoaderResourcePatternResolverPathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
以下逐一说明。
2. Resource
Resource 是 Spring 框架资源的抽象接口。用于表示应用程序中的各种资源,比如文件、类路径资源、URL等。
Resource 提供了同意的方式来访问这些资源,无论资源处于何处都可以通过 Resource 接口进行操作。
定义的接口如下:
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {// 某个资源是否以物理形式存在boolean exists();// 资源的目录读取是否可通过getInputStream()进行读取default boolean isReadable() {return this.exists();}// 判断资源是否具有开放流的句柄default boolean isOpen() {return false;}// 是否是一个文件default boolean isFile() {return false;}// 返回一个URL句柄,如果资源不能够被解析为URL,将抛出IOExceptionURL getURL() throws IOException;// 返回一个URI句柄,如果资源不能够被解析为URL,将抛出IOExceptionURI getURI() throws IOException;// 返回文件File getFile() throws IOException;// 获取可读取的字节通道。在任何时间可读通道上只能有一个读操作正在进行default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException {return Channels.newChannel(this.getInputStream());}// 获取content长度long contentLength() throws IOException;// 资源最后一次修改的时间戳long lastModified() throws IOException;// 创建此资源的相关资源Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;// 获取资源的文件名@NullableString getFilename();// 获取资源描述String getDescription();}
Resource 接口的实现类有很多,比如 UrlResource、ClassPathResource、InputStreamResource、FileSystemResource等等,看名称可知道作用,不多赘述。
3. AbstractResource
AbstractResource 是 Resource 的默认实现类,实现了 Resource 大部分方法。
如果需要实现自定义的 Resource 接口,直接去继承 AbstractResource 抽象类,并根据需求重写相关方法就好。
4. ResourceLoader
ResourceLoader 接口提供了一个资源加载策略,是 Spring 资源加载的同一抽象,具体的资源加载由相应的实现类完成。默认实现类是 DafultResourceLoader.。
public interface ResourceLoader {String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = "classpath:";// 根据所提供的路径 location 获取 Resource 实例,但是不确保 Resource 一定存在。// 支持 URL、ClassPath、相对路径资源Resource getResource(String location);// 返回 ClassLoader 实例@NullableClassLoader getClassLoader();}
可以看到 ResourceLoader 提供了两个接口:getResource、getClassLoader。
5. DefaultResourceLoader
DefaultResourceLoader 是 ResourceLoader 的默认实现。代码如下:
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {@Nullableprivate ClassLoader classLoader;private final Set<ProtocolResolver> protocolResolvers = new LinkedHashSet(4);private final Map<Class<?>, Map<Resource, ?>> resourceCaches = new ConcurrentHashMap(4);public DefaultResourceLoader() {}public DefaultResourceLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {this.classLoader = classLoader;}public void setClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {this.classLoader = classLoader;}@Nullablepublic ClassLoader getClassLoader() {return this.classLoader != null ? this.classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();}// 添加 ProtocolResolverpublic void addProtocolResolver(ProtocolResolver resolver) {Assert.notNull(resolver, "ProtocolResolver must not be null");this.protocolResolvers.add(resolver);}// 获取 ProtocolResolver 集合public Collection<ProtocolResolver> getProtocolResolvers() {return this.protocolResolvers;}public <T> Map<Resource, T> getResourceCache(Class<T> valueType) {return (Map)this.resourceCaches.computeIfAbsent(valueType, (key) -> {return new ConcurrentHashMap();});}public void clearResourceCaches() {this.resourceCaches.clear();}// 根据 location 获取 Resourcepublic Resource getResource(String location) {Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");Iterator var2 = this.getProtocolResolvers().iterator();Resource resource;do {if (!var2.hasNext()) {if (location.startsWith("/")) {return this.getResourceByPath(location);}if (location.startsWith("classpath:")) {return new ClassPathResource(location.substring("classpath:".length()), this.getClassLoader());}try {URL url = new URL(location);return (Resource)(ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));} catch (MalformedURLException var5) {return this.getResourceByPath(location);}}ProtocolResolver protocolResolver = (ProtocolResolver)var2.next();resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);} while(resource == null);return resource;}protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {return new ClassPathContextResource(path, this.getClassLoader());}protected static class ClassPathContextResource extends ClassPathResource implements ContextResource {public ClassPathContextResource(String path, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {super(path, classLoader);}public String getPathWithinContext() {return this.getPath();}public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(this.getPath(), relativePath);return new ClassPathContextResource(pathToUse, this.getClassLoader());}}}
可以看到代码中涉及到了 ProtocolResolver。重点关注一下 ProtocolResolver 这个类。ProtocolResolver 与 DefaultResourceLoader 密不可分。
ProtocolResolver 翻译一下叫协议解析器,它允许用户自定义协议资源解析策略,作为 DefaultResourceLoader 的SPI,而不需要继承 ResourceLoader 的子类。
浅看一下 ProtocolResolver 的源码:
@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface ProtocolResolver {@NullableResource resolve(String location, ResourceLoader resourceLoader);}
可以看到是个函数式接口,根据传入的 location 和自定义的 ResourceLoader 加载器解析出对应的 Resource 资源。
一般来说如果要实现自定义的 Resource,只需要继承 AbstractResource 就好。但有了 ProtocolResolver 就不需要直接继承 DefaultResourceLoader,实现了 ProtocolResolver 接口也可以实现自定义的 ResourceLoader。
回头看 DefaultResourceLoader 里的 getResource 方法,我们单独拿出来:
// 根据 location 获取 Resourcepublic Resource getResource(String location) {Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");// 获取 ProtocolResolver 集合迭代器Iterator var2 = this.getProtocolResolvers().iterator();Resource resource;do {// 如果获取不到 ProtocolResolver 元素if (!var2.hasNext()) {// 如果是以 / 开头if (location.startsWith("/")) {return this.getResourceByPath(location);}// 如果是以 classpath: 开头if (location.startsWith("classpath:")) {return new ClassPathResource(location.substring("classpath:".length()), this.getClassLoader());}try {// 构造 URL 进行资源定位URL url = new URL(location);return (Resource)(ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource(url) : new UrlResource(url));} catch (MalformedURLException var5) {return this.getResourceByPath(location);}}// 获取 ProtocolResolver 并调用 resolve 接口获取 ResourceProtocolResolver protocolResolver = (ProtocolResolver)var2.next();resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);} while(resource == null);return resource;}
6. ResourcePatternResolver
ResourcePatternResolver 是 ResourceLoader 的扩展。
代码如下:
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;}
对比一下 ResourceLoader 的 getResource 方法就会发现,ResourceLoader 的 getResource 通过传入 location 来返回一个 Resource,当需要加载多个资源的时候就必须多次调用 getResourece。
而 ResourcePatternResolver 作为 ResourceLoader 的扩展定义了可以根据指定的资源路径匹配模式每次返回多个 Resource 实例。
可以看到新增了新的协议前缀 classpath*: 。
7. PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 是 ResourcePatternResolver 很常用的子类,它新增了 Ant 风格的路径匹配模式。
扩展:Ant 风格匹配模式
Ant 风格的路径匹配规则是一种常用的路径模式匹配规则
包括以下几种模式:
?: 匹配任意单个字符*: 匹配任意数量,包括零个的字符**: 匹配任意数量,包括零个的目录路径
举例说明:
**/*.xml/user/**/user/*/profile
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 有三种构造方法:
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();}public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;}public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader(classLoader);}
可以看到,如果不指定 ResourceLoader 资源加载器的话,默认都是使用 DefaultResourceLoader。
关于获取 Resource 提供了两种方法:
// 委托给相应的 ResourceLoader 获取public Resource getResource(String location) {return this.getResourceLoader().getResource(location);}public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");// 是否以 classpath*: 开头if (locationPattern.startsWith("classpath*:")) {return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length())) ? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) : this.findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length()));} else {int prefixEnd = locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 : locationPattern.indexOf(58) + 1;return this.getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd)) ? this.findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern) : new Resource[]{this.getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};}}
getResource 方法很好理解,不多做赘述。
getResources 方法,逻辑的流程图如下:
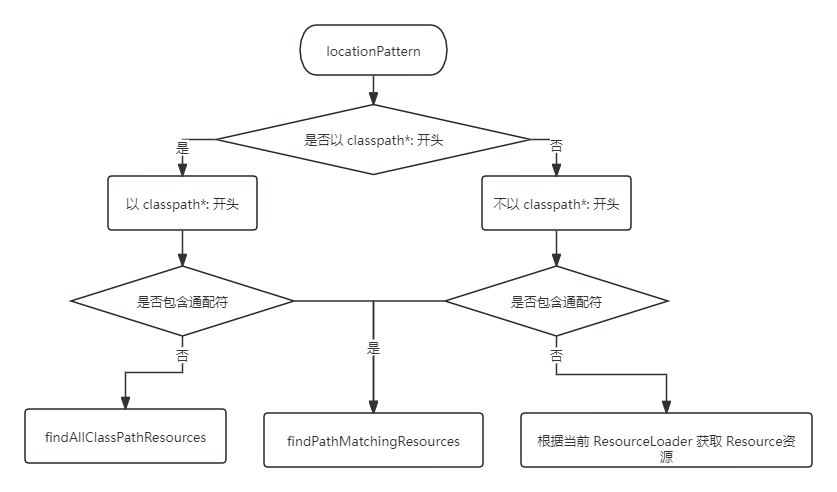
getResources 中调用了 findAllClassPathResources 方法,该方法返回 classes 路径下和所有 jar 包中相匹配的资源。
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {String path = location;if (location.startsWith("/")) {path = location.substring(1);}Set<Resource> result = this.doFindAllClassPathResources(path);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Resolved classpath location [" + location + "] to resources " + result);}return (Resource[])result.toArray(new Resource[0]);}// 获取当前路径下的所有资源protected Set<Resource> doFindAllClassPathResources(String path) throws IOException {Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet(16);ClassLoader cl = this.getClassLoader();Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path);while(resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {URL url = (URL)resourceUrls.nextElement();result.add(this.convertClassLoaderURL(url));}if (!StringUtils.hasLength(path)) {this.addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(cl, result);}return result;}
getResources 中还调用了另一个方法 findPathMatchingResources,主要分两步:
- 确定目录并获取目录下所有资源
- 在所有获取的资源中进行迭代匹配获取所需资源
代码有点长,就不贴了,有兴趣的小伙伴可以自行查看,位置是:
org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver#findPathMatchingResources
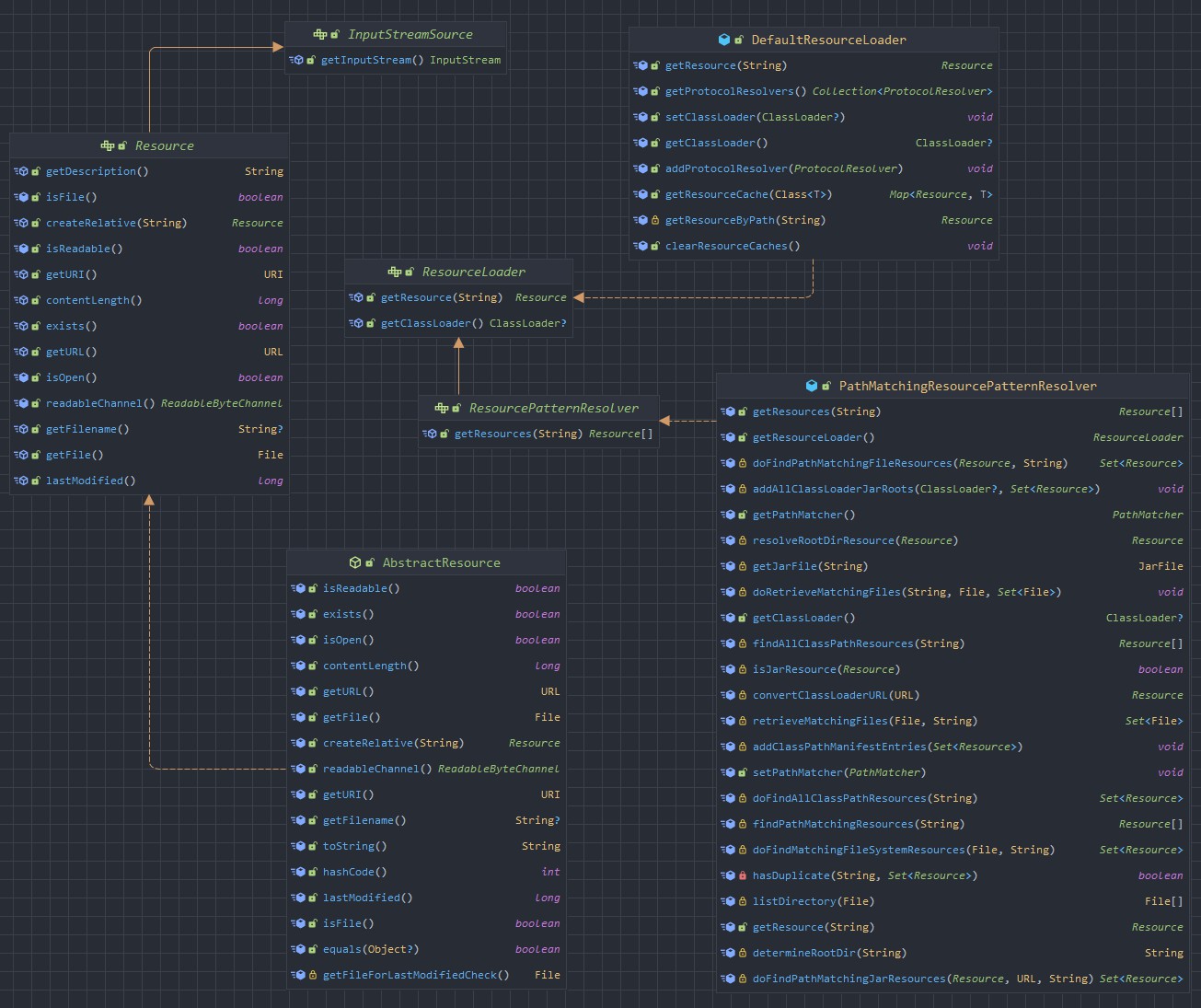
最后放一张 UML 图:
[Ngbatis源码学习][Spring] Spring 的资源管理 ResourceLoader的更多相关文章
- 框架源码系列六:Spring源码学习之Spring IOC源码学习
Spring 源码学习过程: 一.搞明白IOC能做什么,是怎么做的 1. 搞明白IOC能做什么? IOC是用为用户创建.管理实例对象的.用户需要实例对象时只需要向IOC容器获取就行了,不用自己去创建 ...
- spring源码学习(三)--spring循环引用源码学习
在spring中,是支持单实例bean的循环引用(循环依赖)的,循环依赖,简单而言,就是A类中注入了B类,B类中注入了A类,首先贴出我的代码示例 @Component public class Add ...
- 【spring源码学习】spring的远程调用实现源码分析
[一]spring的远程调用提供的基础类 (1)org.springframework.remoting.support.RemotingSupport ===>spring提供实现的远程调用客 ...
- 框架源码系列八:Spring源码学习之Spring核心工作原理(很重要)
目录:一.搞清楚ApplicationContext实例化Bean的过程二.搞清楚这个过程中涉及的核心类三.搞清楚IOC容器提供的扩展点有哪些,学会扩展四.学会IOC容器这里使用的设计模式五.搞清楚不 ...
- 【spring源码学习】Spring @PostConstruct和@PreDestroy实例
在Spring中,既可以实现InitializingBean和DisposableBean接口或在bean配置文件中指定 init-method 和 destroy-method 在初始化和销毁回调函 ...
- 【spring源码学习】spring的task配置
=================spring线程池的配置策略含义========================== id:当配置多个executor时,被@Async("id" ...
- 【spring源码学习】spring的aop目标对象中进行自我调用,且需要实施相应的事务定义的解决方案
转载:http://www.iteye.com/topic/1122740 1.预备知识 aop概念请参考[http://www.iteye.com/topic/1122401]和[http://ji ...
- 【spring源码学习】spring配置的事务方式是REQUIRED,但业务层抛出TransactionRequiredException异常问题
(1)spring抛出异常的点:org.springframework.orm.jpa.EntityManagerFactoryUtils public static DataAccessExcept ...
- 【spring源码学习】spring集成orm数据框架
[一]简易的数据源配置 (1)配置文件 <!--springJdbcTemplemate数据操作配置信息 --> <bean id="driver" class= ...
- 【spring源码学习】spring的事务管理的源码解析
[一]spring事务管理(1)spring的事务管理,是基于aop动态代理实现的.对目标对象生成代理对象,加入事务管理的核心拦截器==>org.springframework.transact ...
随机推荐
- opensips简介
概述 在众多的sip服务器中,主要有俩大类,一类侧重于媒体/业务服务器,比如freeswitch/asterisk,另一类侧重于代理/负载服务器,比如opensips/kamailio. 今天我们对o ...
- idea安装并使用maven依赖分析插件:Maven Helper
本文为博主原创,转载请注明出处: 在maven工程中,经常会查看maven的依赖树,在没使用该插件时,需要maven dependency:tree命令进行查看依赖树, 通过maven helper ...
- 使用vs插件进行远程调试linux服务器
魔改Raspberry Debugger插件实现linux远程开发 本插件是在树莓派的远程调试下修改实现并未全部本人实现 插件基本使用: 插件目前只能在.net core 3.1到.net 6的框架下 ...
- 【ThreadX-FileX】Azure RTOS FileX概述
Azure RTOS FileX嵌入式文件系统是Azure RTOS的高级工业级解决方案,适用于Microsoft FAT文件格式,专门针对深度嵌入式,实时和IoT应用程序而设计.Azure RTOS ...
- -- spi flash 擦除接口调用HAL库不同函数的区别
[描述] 在使用STM32F429操作W25Q128时,为验证flash工作正常,做简单的读写数据校验,在擦除接口中使用 HAL_SPI_Transmit 方法一直工作异常,使用 HAL_SPI_Tr ...
- 2023浙江省大学生信息安全竞赛技能赛初赛 部分wp
CRYPTO 小小数学家 1.题目信息 查看代码 19+49=? 96-31=? 86-3=? 20+47=? 29+55=? 35+35=? 81+42=? 73-16=? 52+48=? 0+56 ...
- Java - 输出空心菱形
1. 思路:发现菱形的规律 ,定义三个变量,左边距和右边距,中间的边距 . 具体规律观察上图 . 2.上代码: //输出空心菱形 public class ForToLingXing { pub ...
- .NET技术面试题系列(2) -sql server数据库优化规范
1.数据库优化规范 a.索引 每个表格都要求建立主键,主键上不一定需要强制建立聚集索引. 聚集索引,表中存储的数据按照索引的顺序存储,即逻辑顺序决定了表中相应行的物理顺序,因此聚集索引的字段值应是不会 ...
- C++开发PHP扩展
前端时间用C开发PHP扩展,用C实现字符串和简单的cache不友好,因而有了用C++开发的想法. 相关环境初始化配置准备 1.用php源码提供的脚手架生成扩展名 php ext/ext_skel.ph ...
- SpringBoot开启动态定时任务并手动、自动关闭
场景需求:在执行某个方法的两小时之后进行某个操作 涉及:定时任务.哈希表 需要注意:业务逻辑层是单一实例的,所以在定时任务类内操作业务逻辑层的某个属性和在业务逻辑层内操作的都是同一个. 疑问:Thre ...
