spring上 -基于注解配置bean,动态代理,AOP笔记
用的是jdk8,spring框架里jar包的下载可以自己搜到
注解用到的jar包。
60,注解配置Bean快速入门
基本介绍


代码结构:
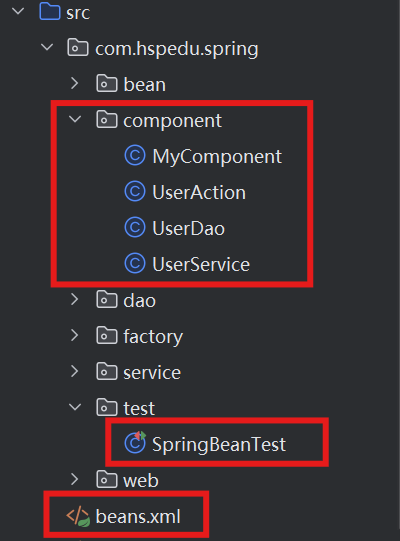
UserDao.java
package com.hspedu.spring.component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; /*
* 使用 @Repository 标识该类是一个Repository,是一个持久层的类/对象
*/
@Repository
public class UserDao {
}
UserService.java
package com.hspedu.spring.component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /*
* 使用 @Service 标识该类是一个Service类/对象
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
}
UserAction.java
package com.hspedu.spring.component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; /*
* 使用 @Controller 标识该类是一个控制器Controller,通常这个类是一个Servlet
*/
@Controller
public class UserAction {
}
MyComponent.java
package com.hspedu.spring.component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /*
* 使用 @Component 标识该类是一个组件,是一个通用的注解
*/
@Component
public class MyComponent {
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置容器要扫描的包
老师解读
1. component-scan 要对指定包下的类进行扫描, 并创建对象到容器
2. base-package 指定要扫描的包
3. 含义是当spring容器创建/初始化时,就会扫描com.hspedu.spring.component包
下的所有的 有注解 @Controller / @Service / @Respository / @Component类
将其实例化,生成对象,放入到ioc容器
4. resource-pattern="User*.class" 表示只扫描com.hspedu.spring.component 和它的子包下的User打头的类 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hspedu.spring.component" />
</beans>
SpringBeanTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.test; import com.hspedu.spring.bean.*;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.MyComponent;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserAction;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserDao;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService;
import com.hspedu.spring.factory.MyStaticFactory;
import com.hspedu.spring.service.MemberServiceImpl;
import com.hspedu.spring.web.OrderAction;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import java.awt.print.Book; public class SpringBeanTest { //通过注解来配置Bean
@Test
public void setBeanByAnnotation() {
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserDao userDao = ioc.getBean(UserDao.class);
UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserService.class);
UserAction userAction = ioc.getBean(UserAction.class);
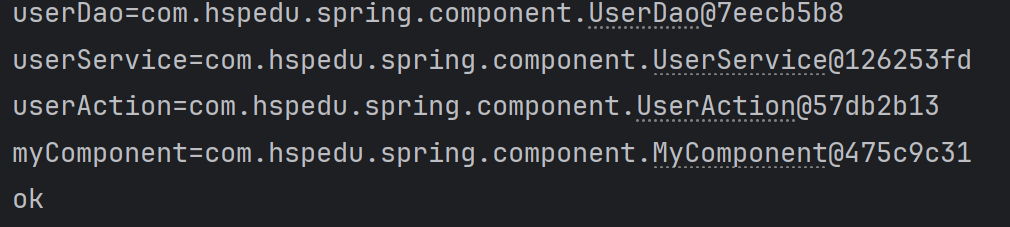
MyComponent myComponent = ioc.getBean(MyComponent.class); System.out.println("userDao=" + userDao);
System.out.println("userService=" + userService);
System.out.println("userAction=" + userAction);
System.out.println("myComponent=" + myComponent); System.out.println("ok"); }
}
运行结果:
63,注意事项和细节
4,resource-pattern="User*.class" 表示只扫描com.hspedu.spring.component 和它的子包下的User打头的类,,这个和第3点自己记住就行。

还有其他3个注意事项都放在代码里了,就是 排除哪些注解 ,指定扫描哪些注解,标记注解后,可以使用什么来指定id值。
代码结构不变,beans.xml,UserDao.java,SpringBeanTest.java
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:contect="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置容器要扫描的包
老师解读
1. component-scan 要对指定包下的类进行扫描, 并创建对象到容器
2. base-package 指定要扫描的包
3. 含义是当spring容器创建/初始化时,就会扫描com.hspedu.spring.component包
下的所有的 有注解 @Controller / @Service / @Respository / @Component类
将其实例化,生成对象,放入到ioc容器
4. resource-pattern="User*.class" 表示只扫描com.hspedu.spring.component 和它的子包下的User打头的类
-->
<!-- <context:component-scan base-package="com.hspedu.spring.component"/>--> <!--
需求:如果我们希望排除某个包/子包下的某种类型的注解,可以通过exclude-filter来指定
1. context:exclude-filter 指定要排除哪些类
2. type 指定排除方式 annotation表示按照注解来排除
3. expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service" 指定要排除的注解的全路径
-->
<!-- <context:component-scan base-package="com.hspedu.spring.component">-->
<!-- <context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/>-->
<!-- </context:component-scan>--> <!--
需求:如果我们希望按照自己的规则,来扫描包/子包下的某些注解, 可以通过 include-filter
1. use-default-filters="false" 表示不使用默认的过滤机制/扫描机制
2. context:include-filter 表示要去扫描哪些类
3. type="annotation" 按照注解方式来扫描/过滤
4. expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service" 指定要扫描的注解的全路径
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.hspedu.spring.component" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/>
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
</context:component-scan>
</beans>
UserDao.java
package com.hspedu.spring.component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; /*
* 使用 @Repository 标识该类是一个Repository,是一个持久层的类/对象
* 1,标记注解后,类名首字母小写作为id的值(默认)
* 2,value = "hspUserDao" 使用指定的 hspUserDao 作为 UserDao对象的 id
*/
@Repository(value = "hspUserDao")
public class UserDao {
}
SpringBeanTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.test; import com.hspedu.spring.bean.*;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.MyComponent;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserAction;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserDao;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.t.Pig;
import com.hspedu.spring.factory.MyStaticFactory;
import com.hspedu.spring.service.MemberServiceImpl;
import com.hspedu.spring.web.OrderAction;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import java.awt.print.Book; public class SpringBeanTest { //通过注解来配置Bean
@Test
public void setBeanByAnnotation() {
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserDao userDao = ioc.getBean(UserDao.class);
//默认情况:标记注解后,类名首字母小写作为 id 的值。也可以使用注解的 value 属性指定 id 值,并且 value 可以省略。
System.out.println("userDao=" + userDao); UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserService.class);
UserAction userAction = ioc.getBean(UserAction.class);
MyComponent myComponent = ioc.getBean(MyComponent.class); System.out.println("userService=" + userService);
System.out.println("userAction=" + userAction);
System.out.println("myComponent=" + myComponent); System.out.println("ok"); }
}
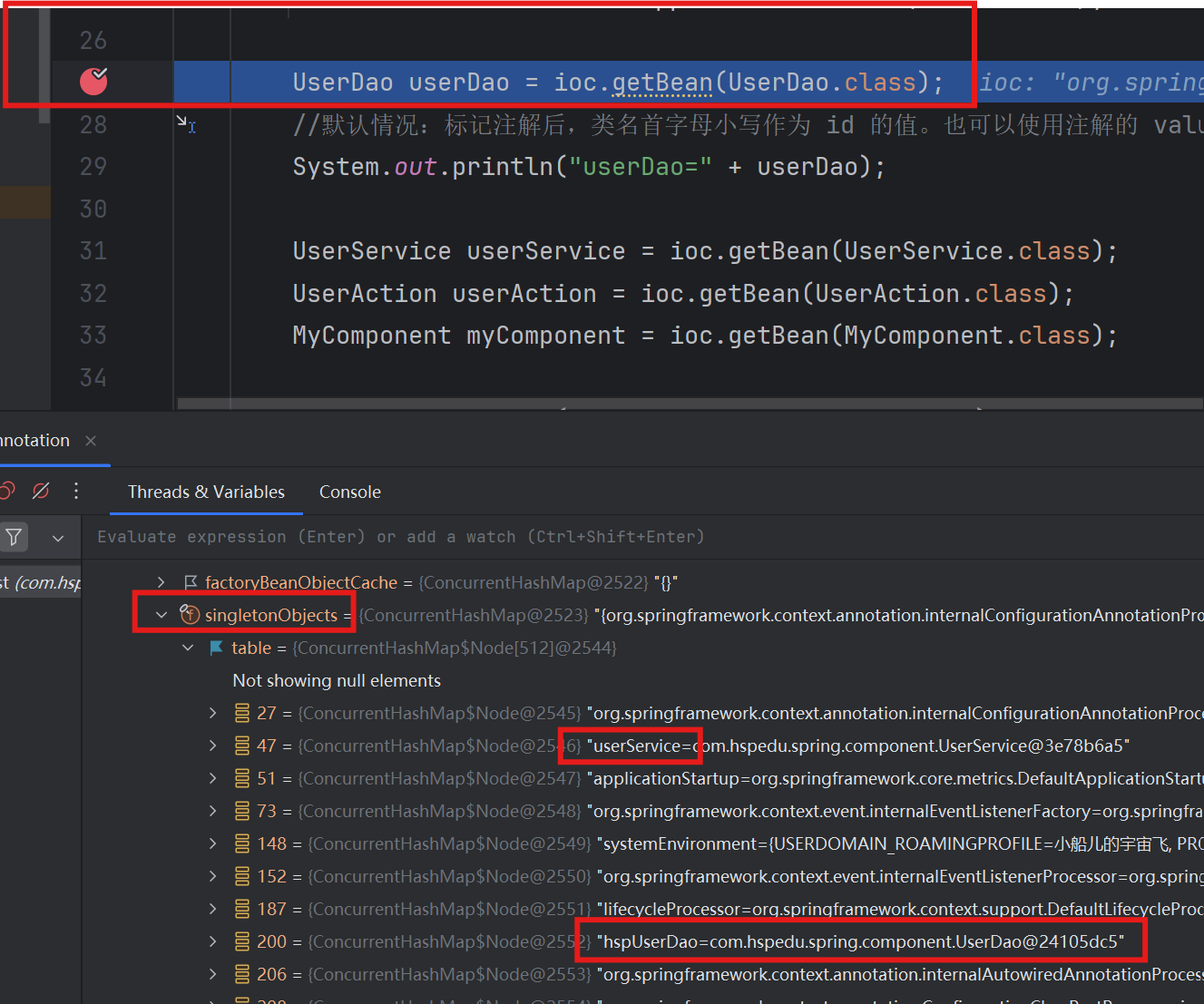
Debug结果:
通过下断点,然后Debug来测试最后一个注意事项。 点 ioc -- beanFactory -- singletonObjects 就能看到
68,自己实现Spring注解配置Bean机制


思路分析:

代码结构:
其中 component 包里的4个java文件都是 上一篇笔记的代码,没有改变。
ComponentScan.java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; /**
* @Target 用于修饰 Annotation定义,用于指定被修饰的 Annotation 能用于修饰哪些程序元素
* @Retention 只能用于修饰一个 Annotation定义,用于指定该 Annotation可以保留多长时间
* 1. @Target(ElementType.TYPE)指定我们的ComponentScan注解可以修饰 Type程序元素
* 2. @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 指定ComponentScan注解 保留范围:
表示:编译器将把注解记录在class文件中,当运行Java程序时,通过反射获取该注解
* 3. String value() default ""; 表示ComponentScan 可以传入 value
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface ComponentScan {
String value() default "";
}
HspSpringConfig.java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation; /**
* 这是一个配置类, 作用类似我们原生spring的 beans.xml 容器配置文件
*/
@ComponentScan(value = "com.hspedu.spring.component")
public class HspSpringConfig {
}
HspSpringApplicationContext.java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.io.File;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap; /**
* HspSpringApplicationContext 类的作用类似Spring原生ioc容器
*/ public class HspSpringApplicationContext {
private Class configClass;
//ioc我存放的就是通过反射创建的对象(基于注解方式)
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> ioc =
new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); //构造器
public HspSpringApplicationContext(Class configClass) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
this.configClass = configClass;
//System.out.println("this.configClass=" + this.configClass);
//获取要扫描的包
//1. 先得到HspSpringConfig配置的@ComponentScan(value = "com.hspedu.spring.component")
ComponentScan componentScan =
(ComponentScan)this.configClass.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class);
//2. 通过componentScan的value=> 即要扫描的包
String path = componentScan.value();
System.out.println("要扫描的包= " + path); //得到要扫描的包下的所有资源(类 .class)
//1.得到类的加载器
ClassLoader classLoader =
HspSpringApplicationContext.class.getClassLoader();
//2. 通过类的加载器获取到要扫描的包的资源 url=》类似一个路径
//一定要把. 替换成 /
path = path.replace(".","/");
URL resource =
classLoader.getResource("com/hspedu/spring/component");
System.out.println("resource=" + resource); //3. 将要加载的资源(.class) 路径下的文件进行遍历=>io
File file = new File(resource.getFile());
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
System.out.println("=============");
System.out.println("=" + f.getAbsolutePath());
//D:\javaProjects\Spring\spring5\out\production\spring5\com\hspedu\spring\component\UserService.class
//获取到 com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService
String fileAbsolutePath = f.getAbsolutePath();
//这里我们只处理.class文件
if (fileAbsolutePath.endsWith(".class")) {
//1. 获取到类名
String className =
fileAbsolutePath.substring(fileAbsolutePath.lastIndexOf("\\") + 1, fileAbsolutePath.indexOf(".class"));
//System.out.println("className=" + className);
//2. 获取类的完整的路径(全类名)
//老师解读 path.replace("/",".") => com.hspedu.spring.component.
String classFullName = path.replace("/", ".") + "." + className;
System.out.println("classFullName=" + classFullName); //3. 判断该类是不是需要注入容器, 就看该类是不是有注解 @Component @Service..
//这时,我们就得到老该类的Class对象
//Class clazz = Class.forName(classFullName)
//老师说一下
//1. Class clazz = Class.forName(classFullName) 可以反射加载类
//2. classLoader.loadClass(classFullName); 可以反射类的Class
//3. 区别是 : 上面方式后调用来类的静态方法, 下面方法不会
Class<?> aClass = classLoader.loadClass(classFullName);
//4. aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class) 判断该类是否有 @Component
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class) ||
aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Controller.class) ||
aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class) ||
aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Repository.class)) { //这里老师演示一个Component注解指定value,分配id
//老师就是演示了一下机制. //这时就可以反射对象,并放入到容器中
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classFullName);
Object instance = clazz.newInstance();
//放入到容器中, 将类名的首字母小写作为id
//StringUtils
ioc.put(StringUtils.uncapitalize(className) , instance);
}
}
}
}
} //编写方法返回对容器中对象
public Object getBean(String name) {
return ioc.get(name);
}
}
HspSpringApplicationContextTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.annotation; import com.hspedu.spring.component.MyComponent;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserAction;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserDao;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService; public class HspSpringApplicationContextTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
HspSpringApplicationContext ioc =
new HspSpringApplicationContext(HspSpringConfig.class); UserAction userAction = (UserAction) ioc.getBean("userAction");
System.out.println("userAction" + userAction); MyComponent myComponent = (MyComponent) ioc.getBean("myComponent");
System.out.println("myComponent" + myComponent); UserService userService = (UserService) ioc.getBean("userService");
System.out.println("userService=" + userService); UserDao userDao = (UserDao) ioc.getBean("userDao");
System.out.println("userDao=" + userDao); System.out.println("ok");
}
}
Debug结果:
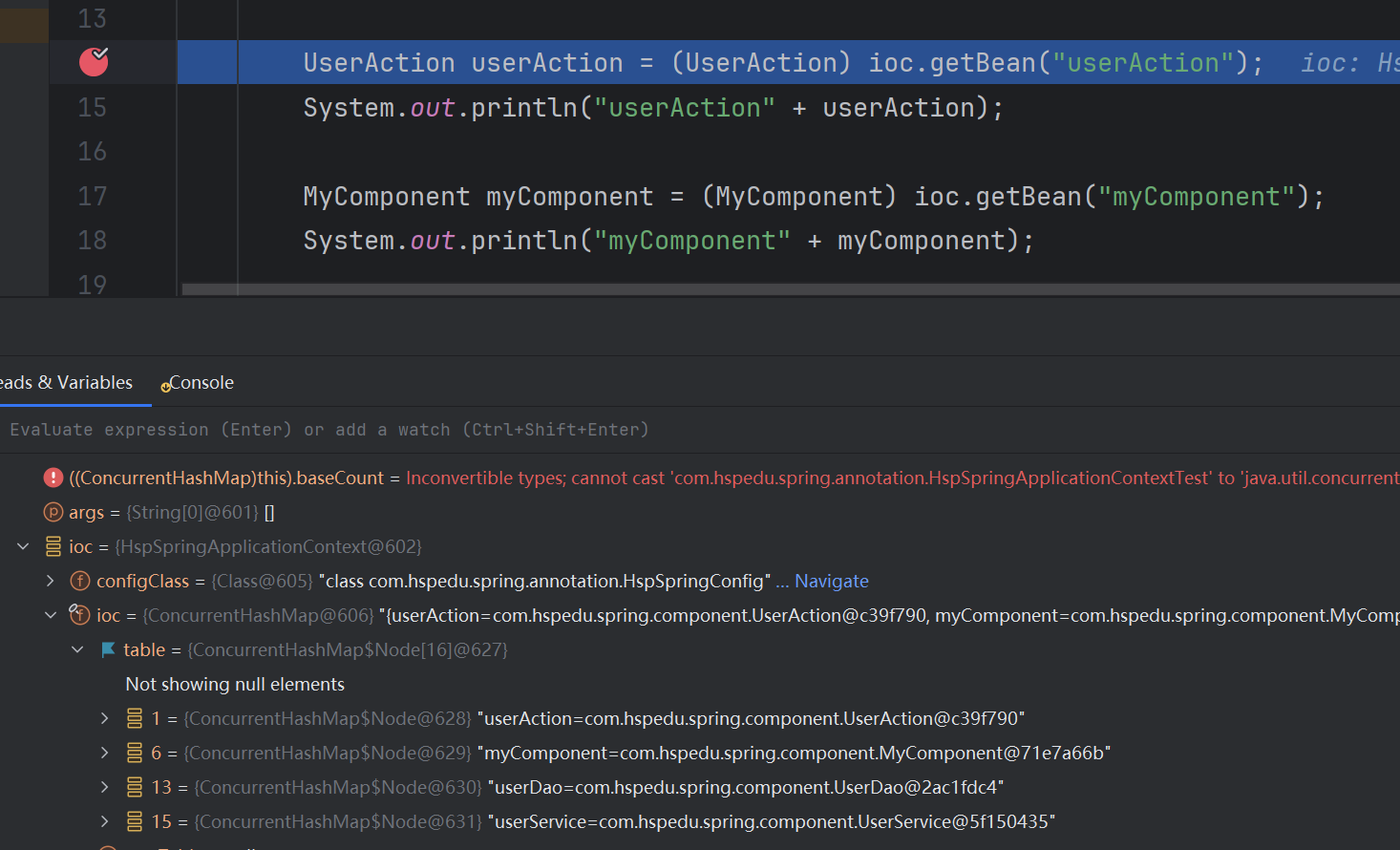
运行结果:
76,自动装配@Autowired
代码结构:

UserService.java
package com.hspedu.spring.component; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; /*
* 使用 @Service 标识该类是一个Service类/对象
*/
@Service
public class UserService {
public void hi() {
System.out.println("UserService hi()~");
}
}
UserAction.java
package com.hspedu.spring.component; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import sun.java2d.pipe.SpanIterator; /*
* 使用 @Controller 标识该类是一个控制器Controller,通常这个类是一个Servlet
*/
@Controller()
public class UserAction {
//xml配置 ref
//老师说明 @Autowired
//1)在IOC容器中查找待装配的组件的类型,如果有唯一的bean匹配(按照类型),则使用该bean装配
//2)如待装配的类型对应的bean在IOC容器中有多个,则使用待装配的属性的属性名作为id值再进行查找,
// 找到就装配,找不到就抛异常
@Autowired
//private UserService userService;
private UserService userService200; public void sayOk() {
// System.out.println("UserAction.userService=" + userService);
// System.out.println("userAction 装配的 userService属性=" + userService);
System.out.println("userAction 装配的 userService200属性=" + userService200);
//userService.hi();
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:contect="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan
base-package="com.hspedu.spring.component"/> <!--配置两个UserService对象-->
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService" id="userService200"/>
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService" id="userService300"/>
</beans>
SpringBeanTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.test; import com.hspedu.spring.bean.*;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.MyComponent;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserAction;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserDao;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService;
import com.hspedu.spring.factory.MyStaticFactory;
import com.hspedu.spring.service.MemberServiceImpl;
import com.hspedu.spring.web.OrderAction;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import java.awt.print.Book; public class SpringBeanTest { //通过注解来配置Bean
@Test
public void setProByAutowired() {
ApplicationContext ioc =
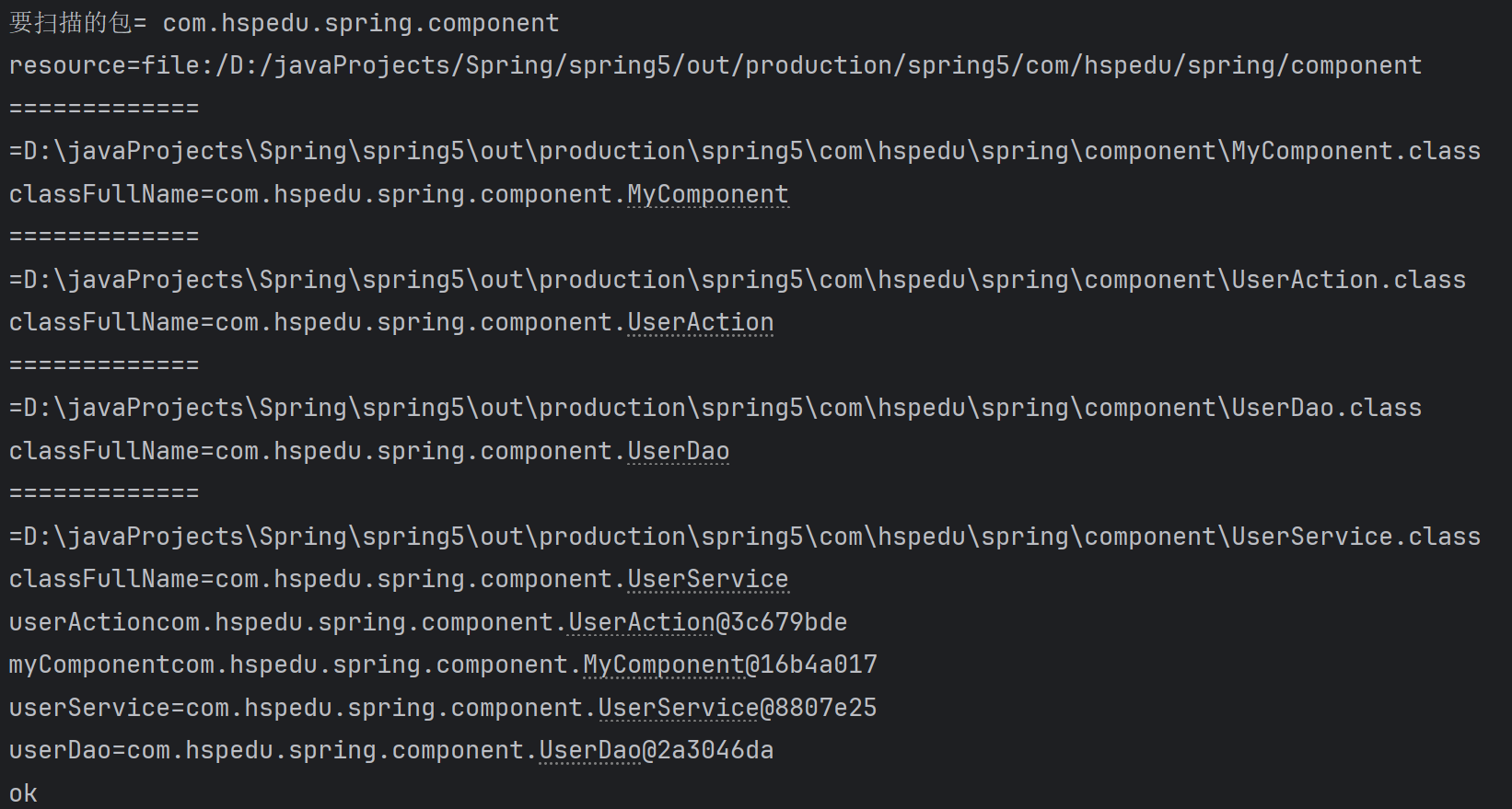
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService userService = ioc.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
System.out.println("ioc容器中的userService=" + userService); UserService userService200 = ioc.getBean("userService200", UserService.class);
System.out.println("ioc容器中的userService200=" + userService200); UserAction userAction = ioc.getBean("userAction", UserAction.class);
//System.out.println("ioc容器中的userAction=" + userAction);
userAction.sayOk(); }
}
运行结果:
80,自动装配@Resource
代码结构和上一节一样,UserAction.java, SpringBeanTest.java 改变了
UserAction.java
package com.hspedu.spring.component; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import sun.java2d.pipe.SpanIterator; import javax.annotation.Resource; /*
* 使用 @Controller 标识该类是一个控制器Controller,通常这个类是一个Servlet
*/
@Controller()
public class UserAction {
///老师说明 @Resource
//1) @Resource有两个属性是比较重要的,分是name和type,Spring将@Resource注解的name属性解析为bean的名字,
// 而type属性则解析为bean的类型.所以如果使用name属性,则使用byName的自动注入策略,
// 而使用type属性时则使用byType自动注入策略
// 比如@Resource(name = "userService") 表示装配 id=userService对象
// 比如@Resource(type = UserService.class) 表示按照UserService.class类型进行装配, 这时要求容器中,只能有一个这样类型的对象
//2) 如果@Resource 没有指定 name 和 type ,则先使用byName注入策略,
// 如果匹配不上, 再使用byType策略, 如果都不成功,就会报错 //=================================
//老师说明: @Autowired + @Qualifier(value = "userService02") 组合也可以完成指定 name/id 来进行自动装配
//指定id进行组装, 也可以使用@Autowired 和 @Qualifier(value = "userService02")
// 这时,是装配的 id=userService02 , 需要两个注解都需要写上,用@Resource(name="userSerice200") 更简单
//@Resource(name="userService200") @Resource(type = UserService.class) private UserService userService400; public void sayOk() { // System.out.println("UserAction.userService=" + userService); // System.out.println("userAction 装配的 userService属性=" + userService); System.out.println("userAction 装配的 userService属性=" + userService400); userService400.hi(); } }
SpringBeanTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.test; import com.hspedu.spring.bean.*;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.MyComponent;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserAction;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserDao;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService;
import com.hspedu.spring.factory.MyStaticFactory;
import com.hspedu.spring.service.MemberServiceImpl;
import com.hspedu.spring.web.OrderAction;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import java.awt.print.Book; public class SpringBeanTest { //通过注解来配置Bean
@Test
public void setProByAutowired() {
ApplicationContext ioc =
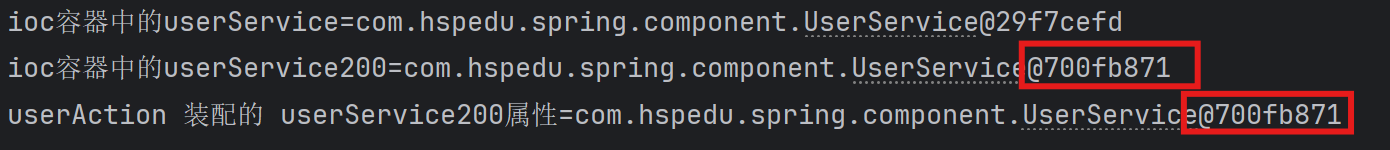
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); UserService userService = ioc.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
System.out.println("ioc容器中的userService=" + userService); // UserService userService200 = ioc.getBean("userService200", UserService.class);
// System.out.println("ioc容器中的userService200=" + userService200); UserAction userAction = ioc.getBean("userAction", UserAction.class);
//System.out.println("ioc容器中的userAction=" + userAction);
userAction.sayOk(); }
}
运行结果:
82,泛型依赖注入

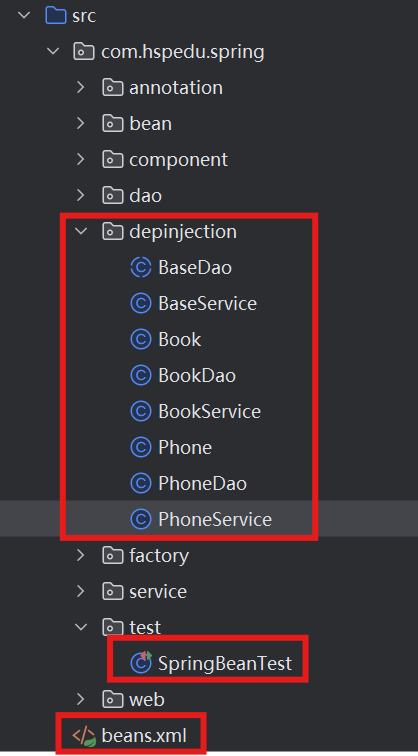
各个类的关系图:
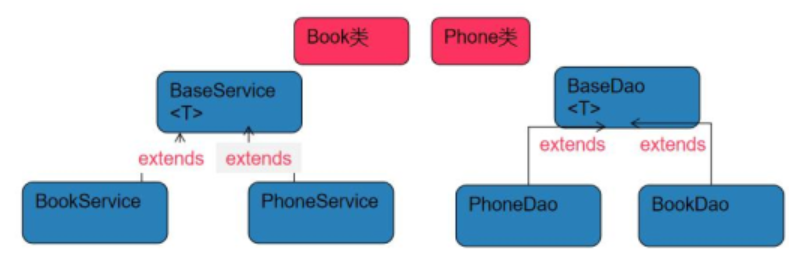
类关系图解释:
如果 BookService 想用到 BookDao,可以把BookDao属性装配到BookService上去,但问题是 BaseService 和 BaseDao 下有很多子类,写起来就很麻烦,所以spring提供了泛型依赖注入,就是把 BaseDao装配到BaseService上去,只是形式上的装配,不会实例化他们的对象,真正实现的是子类对象,在得到BookService的时候,传入泛型<Book>,根据泛型依赖装配,会自动把BookDao对象装配到 BookService上去
底层机制 是 : 反射+注解+IO+String+泛型.
代码结构:
Book.java
package com.hspedu.spring.depinjection;
public class Book {
}
Phone.java
package com.hspedu.spring.depinjection;
public class Phone {
}
BaseDao.java
package com.hspedu.spring.depinjection; //自定义泛型类
public abstract class BaseDao<T> {
public abstract void save();
}
BookDao.java
package com.hspedu.spring.depinjection; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository
public class BookDao extends BaseDao<Book>{
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("BookDao 的 save()..");
}
}
PhoneDao.java
package com.hspedu.spring.depinjection; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository
public class PhoneDao extends BaseDao<Phone>{
@Override
public void save() {
System.out.println("PhoneDao save()");
}
}
BaseService.java
package com.hspedu.spring.depinjection;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class BaseService<T> {
@Autowired
private BaseDao<T> baseDao;
public void save(){
baseDao.save();
}
}
BookService.java
package com.hspedu.spring.depinjection; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service
public class BookService extends BaseService<Book>{
//并没有写属性
}
PhoneService.java
package com.hspedu.spring.depinjection; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service
public class PhoneService extends BaseService<Phone>{
//是把PhoneDao对象装配到PhoneService,spring底层支持的
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:contect="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <context:component-scan
base-package="com.hspedu.spring.depinjection"/>
</beans>
SpringBeanTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.test; import com.hspedu.spring.bean.*;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.MyComponent;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserAction;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserDao;
import com.hspedu.spring.component.UserService;
import com.hspedu.spring.depinjection.PhoneService;
import com.hspedu.spring.factory.MyStaticFactory;
import com.hspedu.spring.service.MemberServiceImpl;
import com.hspedu.spring.web.OrderAction;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; import java.awt.print.Book; public class SpringBeanTest { //通过泛型依赖来配置Bean
@Test
public void setProByDependencyInjection() throws BeansException {
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
PhoneService phoneService = ioc.getBean("phoneService", PhoneService.class);
phoneService.save(); }
}
运行结果:
86,传统方法解决动态代理需求

代码结构:
接口Vehicle.java
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2; //该接口有run方法
public interface Vehicle {
public void run();
}
Car.java
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2;
public class Car implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了...");
System.out.println("小汽车在公路 running..");
System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了...");
}
}
Ship.java
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2;
public class Ship implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了...");
System.out.println("大轮船在水上 running...");
System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了...");
}
}
TestVehicle.java
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestVehicle {
@Test
public void run(){
//OOP基础
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
vehicle.run();
System.out.println("----------------");
Vehicle vehicle1 = new Ship();
vehicle1.run();
}
}
运行结果:


如果想改某几个对象,只能一个一个的改 ,得不到统一的管理
87,动态代理解决需求
动态代理解决思路,在调用方法时,使用反射机制,根据方法去决定调用哪个对象方法
代码结构:
Vehicle.java不变,动态代理机制是 debug得出的
Car.java
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2;
public class Car implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
//System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了...");
System.out.println("小汽车在公路 running..");
//System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了...");
}
}
Ship.java
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2;
public class Ship implements Vehicle{
@Override
public void run() {
//System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了...");
System.out.println("大轮船在水上 running...");
//System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了...");
}
}
VehicleProxyProvider.java
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; /**
* VehicleProxyProvider 该类可以返回一个代理对象.
*/
public class VehicleProxyProvider {
//定义一个属性
//target_vehicle 表示真正要执行的对象
//该对象实现了Vehicle接口
private Vehicle target_vehicle; //构造器
public VehicleProxyProvider(Vehicle target_vehicle) {
this.target_vehicle = target_vehicle;
} //编写一个方法,可以返回一个代理对象, 该代理对象可以通过反射机制调用到被代理对象的方法
//老师解读
//1. 这个方法非常重要, 理解有一定难度
public Vehicle getProxy() { //得到类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader =
target_vehicle.getClass().getClassLoader(); //得到要代理的对象/被执行对象 的接口信息,底层是通过接口来完成调用
Class<?>[] interfaces = target_vehicle.getClass().getInterfaces(); //创建InvocationHandler 对象
//因为 InvocationHandler 是接口,所以我们可以通过匿名对象的方式来创建该对象 InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {
/**
* invoke 方法是将来执行我们的target_vehicle的方法时,会调用到
* o: 表示代理对象
* method: 就是通过代理对象调用方法时,的哪个方法 代理对象.run()
* args: 表示调用 代理对象.run(xx) 传入的参数
* return: 表示 代理对象.run(xx) 执行后的结果
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] args)
throws Throwable {
System.out.println("交通工具开始运行了....");
//这里是我们的反射基础 => OOP
//method 是?: public abstract void com.hspedu.spring.proxy2.Vehicle.run()
//target_vehicle 是? Ship对象
//args 是null
//这里通过反射+动态绑定机制,就会执行到被代理对象的方法
//执行完毕就返回
Object result = method.invoke(target_vehicle, args);
System.out.println("交通工具停止运行了....");
return result;
}
};
/** public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
老师解读
1. Proxy.newProxyInstance() 可以返回一个代理对象
2. ClassLoader loader: 类的加载器.
3. Class<?>[] interfaces 就是将来要代理的对象的接口信息
4. InvocationHandler h 调用处理器/对象 有一个非常重要的方法invoke
*/
Vehicle proxy =
(Vehicle) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler);
return proxy;
}
}
TestVehicle.java
package com.hspedu.spring.proxy2;
import org.junit.Test;
public class TestVehicle {
@Test
public void run(){
//OOP基础
Vehicle vehicle = new Car();
//创建VehicleProxyProvider对象, 并且我们传入的要代理的对象
VehicleProxyProvider vehicleProxyProvider =
new VehicleProxyProvider(vehicle);
//获取代理对象, 该对象可以代理执行方法
//老师解读
//1. porxy 编译类型 Vehicle
//2. 运行类型 是代理类型 class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy9
Vehicle proxy = vehicleProxyProvider.getProxy();
System.out.println("proxy的编译类型是 Vehicle");
System.out.println("proxy的运行类型是 " + proxy.getClass());
//下面老韩就要给大家解读/debug怎么 执行到 代理对象的 public Object invoke(Object o, Method method, Object[] args)
//梳理完毕. proxy的编译类型是 Vehicle, 运行类型是 class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy9
//所以当执行run方法时,会执行到 代理对象的invoke
//如何体现动态 [1. 被代理的对象 2. 方法]
//1. proxy 运行类型是 com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0 该类型被转型成 Vehicle
// 因此可以调用 Vehicle 的接口方法
//2. 当执行 run() 的时候会调用, 根据 Java 的动态绑定机制, 这时直接调用 Car的 run(),
// 而是 proxy 对象的 invocationHandler 的 invoke 方法(!!!!!!)
//3. invoke 方法使用反射机制来调用 run()方法注意这个 run 方法也可以是Vehicle 的其它方法)
// 这时就可以在调用 run()方法前,进行前置处理和后置处理
//4. 也就是说 proxy 的 target_vehicle 运行类型只要是实现了 Vehicle 接口
// ,就可以去调用不同的方法, 是动态的,变化的,底层就是 使用反射完成的.
proxy.run();
}
}
运行结果:

91,动态代理深入(传统方法解决)


传统的解决思路,在各个方法的[前,执行过程, 后]输出日志。
代码结构:
SmartAnimalable.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.proxy; //接口
public interface SmartAnimalable { //求和
float getSum(float i, float j); //求差
float getSub(float i, float j);
}
SmartDog.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.proxy;
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimalable{
@Override
public float getSum(float i, float j) {
System.out.println("日志-方法名-getSum-参数 " + i + " " + j);
float result = i + j;
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
System.out.println("日志-方法名-getSum-结果result= " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public float getSub(float i, float j) {
System.out.println("日志-方法名-getSub-参数 " + i + " " + j);
float result = i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
System.out.println("日志-方法名-getSub-结果result= " + result);
return result;
}
}
AopTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.proxy;
import org.junit.Test;
public class AopTest {
@Test
public void smartDogTest() {
SmartAnimalable smartAnimalable = new SmartDog();
smartAnimalable.getSum(10, 2);
System.out.println("===========================");
smartAnimalable.getSub(10, 2);
}
}
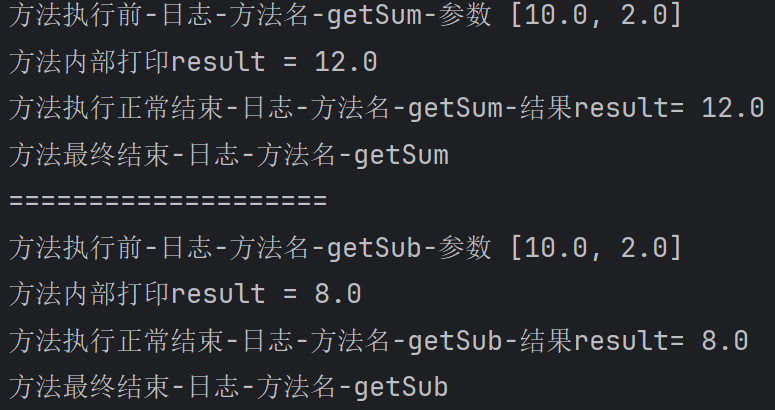
运行结果:


93,动态代理深入(动态代理方式解决)
代码结构:
SmartAnimalable.java不变

SmartDog.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.proxy;
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimalable{
@Override
public float getSum(float i, float j) {
//System.out.println("日志-方法名-getSum-参数 " + i + " " + j);
float result = i + j;
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
//System.out.println("日志-方法名-getSum-结果result= " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public float getSub(float i, float j) {
//System.out.println("日志-方法名-getSub-参数 " + i + " " + j);
float result = i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
//System.out.println("日志-方法名-getSub-结果result= " + result);
return result;
}
}
MyProxyProvider.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.proxy; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays; /**
* 可以返回一个动态代理对象, 可以执行SmartDog对象的方法
*/
public class MyProxyProvider {
//定义我们要执行的目标对象, 该对象需要实现SmartAnimalable
private SmartAnimalable target_obj; //构造器
public MyProxyProvider(SmartAnimalable target_obj) {
this.target_obj = target_obj;
} //方法, 可以返回代理对象,该代理对象可以执行目标对象
public SmartAnimalable getProxy() { //1. 先到的类加载器/对象
ClassLoader classLoader = target_obj.getClass().getClassLoader(); //2. 得到要执行的目标对象的接口信息
Class<?>[] interfaces = target_obj.getClass().getInterfaces(); //3. 创建InvocationHandler
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
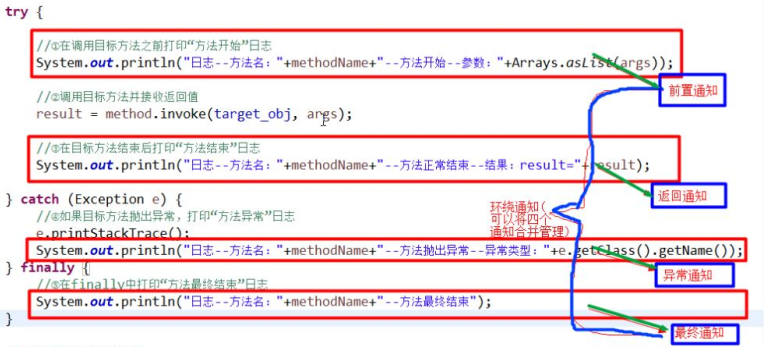
try {
System.out.println("方法执行前-日志-方法名-" + method.getName() + "-参数 "
+ Arrays.asList(args)); //这里从AOP看,就是一个横切关注点-前置通知
//使用反射调用方法
result = method.invoke(target_obj, args);
System.out.println("方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + method.getName() + "-结果result= "
+ result);//从AOP看, 也是一个横切关注点-返回通知 } catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//如果反射执行方法时,出现异常,就会进入到catch{}
System.out.println("方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + method.getName()
+ "-异常类型=" + e.getClass().getName());//从AOP看, 也是一个横切关注点-异常通知
} finally {//不管你是否出现异常,最终都会执行到finally{}
//从AOP的角度看, 也是一个横切关注点-最终通知
System.out.println("方法最终结束-日志-方法名-" + method.getName());
} return result;
}
};
//创建代理对象
SmartAnimalable proxy =
(SmartAnimalable) Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler);
return proxy;
}
}
AopTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.proxy;
import org.junit.Test;
public class AopTest {
@Test
public void smartDogTestByProxy() {
SmartAnimalable smartAnimalable = new SmartDog();
//创建MyProxyProvider对象, 并且我们传入的要代理的对象
MyProxyProvider myProxyProvider =
new MyProxyProvider(smartAnimalable);
//获取代理对象, 该对象可以代理执行方法
SmartAnimalable proxy =
myProxyProvider.getProxy();
proxy.getSum(10, 2);
System.out.println("====================");
proxy.getSub(10, 2);
}
}
运行结果:
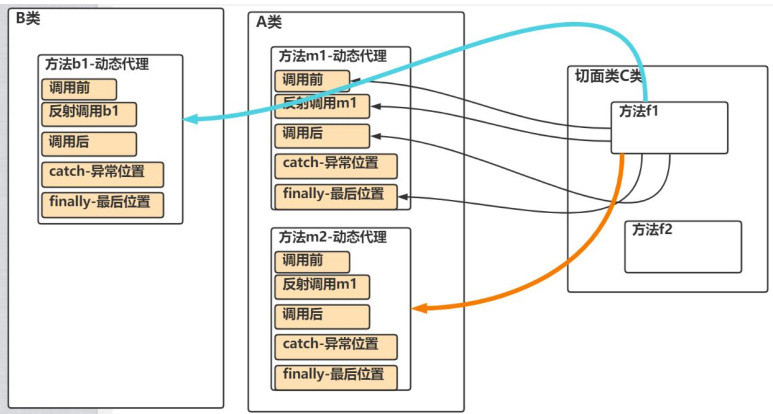
95,AOP快速入门
基本介绍
可以把切面类里的方法(想象成一把刀)切入到A类,B类任意一个位置

案例:


代码结构:
SmartAnimalable.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; //接口
public interface SmartAnimalable {
//求和
float getSum(float i, float j);
//求差
float getSub(float i, float j);
}
SmartDog.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component //使用@Component 当spring容器启动时,将 SmartDog注入到容器
public class SmartDog implements SmartAnimalable {
@Override
public float getSum(float i, float j) {
float result = i + j;
//int res = 9 / 0; //模拟一个算术异常
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
return result;
} @Override
public float getSub(float i, float j) {
float result = i - j;
System.out.println("方法内部打印result = " + result);
return result;
}
}
SmartAnimalAspect.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays; /**
* 切面类 , 类似于我们以前自己写的MyProxyProvider,但是功能强大很多
*/
//@Order(value = 2)//表示该切面类执行的顺序, value的值越小, 优先级越高
@Aspect //表示是一个切面类[底层切面编程的支撑(动态代理+反射+动态绑定...)]
@Component //会注入SmartAnimalAspect到容器
public class SmartAnimalAspect { //定义一个切入点, 在后面使用时可以直接引用, 提高了复用性
@Pointcut(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float)))")
public void myPointCut() {
} /**
* 老师解读
* 1. @Before 表示前置通知:即在我们的目标对象执行方法前执行
* 2. value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float)
* 指定切入到哪个类的哪个方法 形式是: 访问修饰符 返回类型 全类名.方法名(形参列表)
* 3. showBeginLog方法可以理解成就是一个切入方法, 这个方法名是可以程序员指定 比如:showBeginLog
* 4. JoinPoint joinPoint 在底层执行时,由AspectJ切面框架, 会给该切入方法传入 joinPoint对象
* , 通过该方法,程序员可以获取到 相关信息
*
* @param joinPoint
*/ //希望将f1方法切入到SmartDog-getSum前执行-前置通知
//@Before(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
//这里我们使用定义好的切入点
@Before(value = "myPointCut()")
public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//通过连接点对象joinPoint 可以获取方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-切面类showBeginLog()[使用的myPointCut()]-方法执行前-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + "-参数 "
+ Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
} //返回通知:即把showSuccessEndLog方法切入到目标对象方法正常执行完毕后的地方
//老韩解读
//1. 如果我们希望把目标方法执行的结果,返回给切入方法
//2. 可以再 @AfterReturning 增加属性 , 比如 returning = "res"
//3. 同时在切入方法增加 Object res
//4. 注意: returning = "res" 和 Object res 的 res名字一致
//@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))", returning = "res")
//使用切入点
@AfterReturning(value = "myPointCut()", returning = "res")
public void showSuccessEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-切面类showSuccessEndLog()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 返回的结果是=" + res);
} //异常通知:即把showExceptionLog方法切入到目标对象方法执行发生异常的的catch{}
//@AfterThrowing(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))", throwing = "throwable")
//直接使用切入点表达式
@AfterThrowing(value = "myPointCut()", throwing = "throwable")
public void showExceptionLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-切面类showExceptionLog()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 异常信息=" + throwable);
} //最终通知:即把showFinallyEndLog方法切入到目标方法执行后(不管是否发生异常,都要执行 finally{})
//@After(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
//直接使用切入点
@After(value = "myPointCut()")
public void showFinallyEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-切面类showFinallyEndLog()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <context:component-scan
base-package="com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj"/> <!-- 开启基于注解的AOP功能 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
AopAspectjTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AopAspectjTest {
@Test
public void smartDogTestByProxy(){
//得到spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); //这里我们需要通过接口类型来获取到注入的SmartDog对象-就是代理对象
SmartAnimalable smartAnimalable =
ioc.getBean(SmartAnimalable.class); smartAnimalable.getSum(10, 2);
// System.out.println("smartAnimalable运行类型="
// + smartAnimalable.getClass());//class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy17
}
}
运行结果:

代码里的getBean() 也相当于 动态代理里的 getProxy() ,返回的是代理对象。
108,课后作业

这个题用到了细节5 和 下节的 切入表达式。
细节:


代码结构:
beans.xml 不变,和上节一样。
接口UsbInterface.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj;
public interface UsbInterface {
public void work();
}
Phone.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component//将Phone对象当做一个组件注入容器
public class Phone implements UsbInterface{
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("手机开始工作了...");
} }
Camera.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component//将Camera对象当做一个组件注入容器
public class Camera implements UsbInterface{
@Override
public void work() {
System.out.println("相机开始工作了...");
}
}
SmartAnimalAspect.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays; /**
* 切面类 , 类似于我们以前自己写的MyProxyProvider,但是功能强大很多
*/
//@Order(value = 2)//表示该切面类执行的顺序, value的值越小, 优先级越高
@Aspect //表示是一个切面类[底层切面编程的支撑(动态代理+反射+动态绑定...)]
@Component //会注入SmartAnimalAspect到容器
public class SmartAnimalAspect { @Before(value = "execution(public void com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.Phone.work()) || execution(public void com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.Camera.work())")
public void hi(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类的hi()-执行的目标方法-" + signature.getName());
}
}
AopAspectjTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AopAspectjTest {
@Test
public void smartDogTestByProxy(){
//得到spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); //这里我们不能通过接口类型来获取到注入的Phone对象-就是代理对象,因为Phone对象和Camera对象都实现了UsbInterface接口
// UsbInterface bean = ioc.getBean(UsbInterface.class);
// bean.work(); UsbInterface phone = (UsbInterface) ioc.getBean("phone");
UsbInterface camera = (UsbInterface) ioc.getBean("camera"); phone.work();
System.out.println("---------------------");
camera.work();
}
}
运行结果:

109,切入表达式
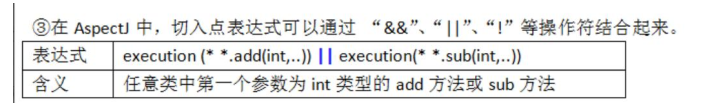
具体使用:

细节:

细节3代码结构:
beans.xml和上上一节一样。

Car.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component//将Phone对象当做一个组件注入容器
public class Car {
public void run(){
System.out.println("小汽车在running...");
}
}
SmartAnimalAspect.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays; /**
* 切面类 , 类似于我们以前自己写的MyProxyProvider,但是功能强大很多
*/
//@Order(value = 2)//表示该切面类执行的顺序, value的值越小, 优先级越高
@Aspect //表示是一个切面类[底层切面编程的支撑(动态代理+反射+动态绑定...)]
@Component //会注入SmartAnimalAspect到容器
public class SmartAnimalAspect { //给Car配置一个前置通知
@Before(value = "execution(public void com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.Car.run())")
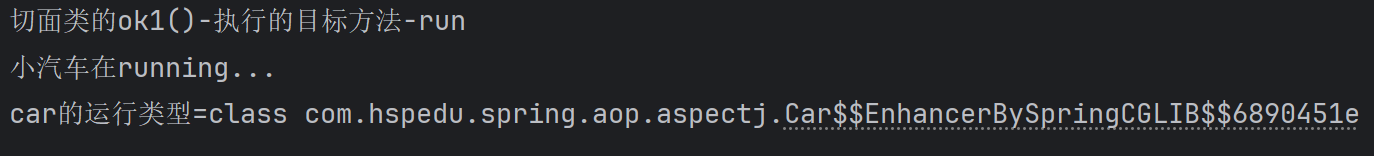
public void ok1(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("切面类的ok1()-执行的目标方法-" + signature.getName());
}
}
AopAspectjTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AopAspectjTest {
@Test
public void smartDogTestByProxy(){
//得到spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); //Car对象仍然是代理对象
Car car = ioc.getBean(Car.class);
car.run();
System.out.println("car的运行类型=" + car.getClass());
}
}
运行结果:
115,环绕通知

在第 95节代码的基础上修改 ,可以把 SmartAnimalAspect.java删了,重新复制成 SmartAnimalAspect2.java,还要修改 AopAspectjTest.java
SmartAnimalAspect2.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List; /**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
* 切面类 , 类似于我们以前自己写的MyProxyProvider,但是功能强大很多
*/
@Aspect //表示是一个切面类[底层切面编程的支撑(动态代理+反射+动态绑定...)]
@Component //会注入SmartAnimalAspect2到容器
public class SmartAnimalAspect2 { //演示环绕通知的使用-了解
//老师解读
//1. @Around: 表示这是一个环绕通知[完成其它四个通知的功能]
//2. value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float)) 切入点表达式
//3. doAround 表示要切入的方法 - 调用结构 try-catch-finally
@Around(value = "execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj.SmartDog.getSum(float, float))")
public Object doAround(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
Object result = null;
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
try {
//1.相当于前置通知完成的事情
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
List<Object> argList = Arrays.asList(args);
System.out.println("AOP环绕通知[-前置通知]" + methodName + "方法开始了--参数有:" + argList);
//在环绕通知中一定要调用joinPoint.proceed()来执行目标方法
result = joinPoint.proceed();
//2.相当于返回通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP环绕通知[-返回通知]" + methodName + "方法结束了--结果是:" + result);
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
//3.相当于异常通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP环绕通知[-异常通知]" + methodName + "方法抛异常了--异常对象:" + throwable);
} finally {
//4.相当于最终通知完成的事情
System.out.println("AOP环绕通知[-后置通知]" + methodName + "方法最终结束了...");
}
return result;
}
}
AopAspectjTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.aspectj; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AopAspectjTest {
@Test
public void testDoAround() {
//得到spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); SmartAnimalable smartAnimalable =
ioc.getBean(SmartAnimalable.class); smartAnimalable.getSum(10, 2);
}
}
运行结果:

119,基于XML配置的AOP

代码结构:
SmartAnimalable.java 和第95节的一样,就是要注意 import 那引入的包名。
SmartDog.java 把@Component 注解注释了。
SmartAnimalAspect.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.xml; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import java.util.Arrays; /**
* @author 韩顺平
* @version 1.0
*
* 这是我们开发一个切面类, 但是不用注解,而是使用XML配置
*/
public class SmartAnimalAspect {
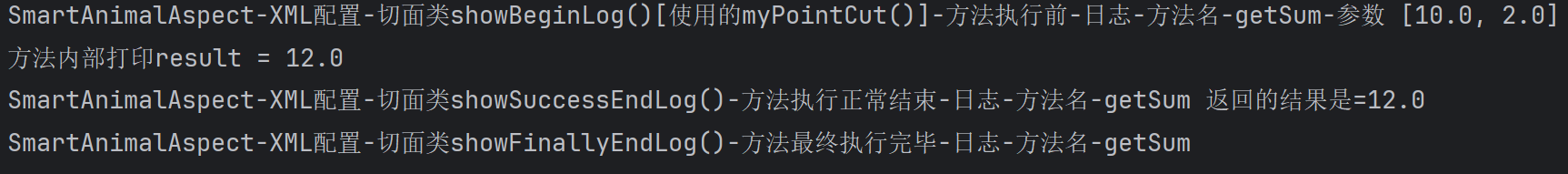
public void showBeginLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
//通过连接点对象joinPoint 可以获取方法签名
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-XML配置-切面类showBeginLog()[使用的myPointCut()]-方法执行前-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + "-参数 "
+ Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()));
} public void showSuccessEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object res) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-XML配置-切面类showSuccessEndLog()-方法执行正常结束-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 返回的结果是=" + res);
} public void showExceptionLog(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable throwable) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-XML配置-切面类showExceptionLog()-方法执行异常-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName() + " 异常信息=" + throwable);
} public void showFinallyEndLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("SmartAnimalAspect-XML配置-切面类showFinallyEndLog()-方法最终执行完毕-日志-方法名-" + signature.getName());
}
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--使用XML配置,完成AOP编程-->
<!--配置一个切面类对象-bean-->
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.aop.xml.SmartAnimalAspect" id="smartAnimalAspect"/> <!--配置一个SmartDog对象-bean-->
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.aop.xml.SmartDog" id="smartDog"/> <!--配置切面类, 细节一定要引入 xmlns:aop-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="myPointCut" expression="execution(public float com.hspedu.spring.aop.xml.SmartDog.getSum(float, float)))"/> <!--这里指定切面对象,切面的前置,返回, 异常, 最终通知-->
<aop:aspect ref="smartAnimalAspect" order="10">
<!--配置前置通知-->
<aop:before method="showBeginLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
<!--返回通知-->
<aop:after-returning method="showSuccessEndLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" returning="res"/>
<!--异常通知-->
<aop:after-throwing method="showExceptionLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut" throwing="throwable"/>
<!--最终通知-->
<aop:after method="showFinallyEndLog" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
<!--配置环绕通知-->
<!--<aop:around method=""/>-->
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
AopAspectjXMLTest.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.xml; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class AopAspectjXMLTest {
@Test
public void testDoAround() {
//得到spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
SmartAnimalable smartAnimalable =
ioc.getBean(SmartAnimalable.class);
smartAnimalable.getSum(10, 2);
}
}
运行结果:
123,作业(注解方式)


代码结构:
Cal.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework;
public interface Cal {
public int cal1(int n);
public int cal2(int n);
}
MyCal.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component//将MyCal对象当做一个组件注入容器
public class MyCal implements Cal{
@Override
public int cal1(int n) {
int res = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
res += i;
}
System.out.println("cal1 执行结果=" + res);
return res;
} @Override
public int cal2(int n) {
int res = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
res *= i;
}
System.out.println("cal2 执行结果=" + res);
return res;
}
}
MyCalAop.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect //MyCalAOP 是一个切面类
@Component //MyCalAOP/对象 作为组件注入到spring容器
public class MyCalAop { //前置通知
//这里注意,如果目标类和切面类,在同一个包,可以省略包名
//因为cal1和cal2方法,都要去输出开始执行时间,因此使用MyCal.*
@Before(value = "execution(public int MyCal.*(int))")
public void calStart(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println(signature.getName() + " 执行, 开始执行时间=" + System.currentTimeMillis());
} //返回通知
//这里注意,如果目标类和切面类,在同一个包,可以省略包名
//因为cal1和cal2方法,都要去输出开始执行时间,因此使用MyCal.*
@AfterReturning(value = "execution(public int MyCal.*(int))")
public void calEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println(signature.getName() + " 执行, 结束时间=" + System.currentTimeMillis()); }
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--扫描指定包-->
<context:component-scan
base-package="com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework"/> <!--启用基于注解的AOP功能-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
TestMyCalAOP.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework; import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class TestMyCalAOP {
@Test
public void testMyCalByAnnotation() { //得到spring容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); Cal cal = ioc.getBean(Cal.class); cal.cal1(10);
System.out.println("-------------------------");
cal.cal2(5);
}
}
运行结果:
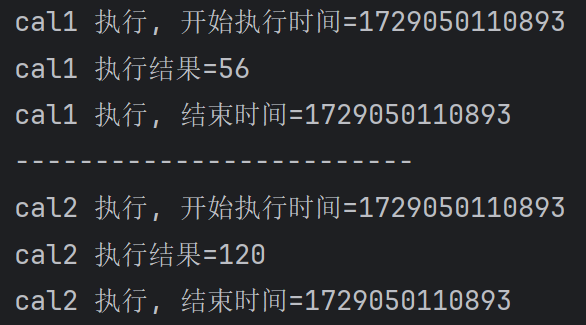
124,作业(基于XML)
代码结构:
Cal.java,MyCal.java , TestMyCalAOP.java和上节一样,要注意引入的包名。
MyCalAOP.java
package com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework.xml; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature; public class MyCalAOP { //前置通知
public void calStart(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
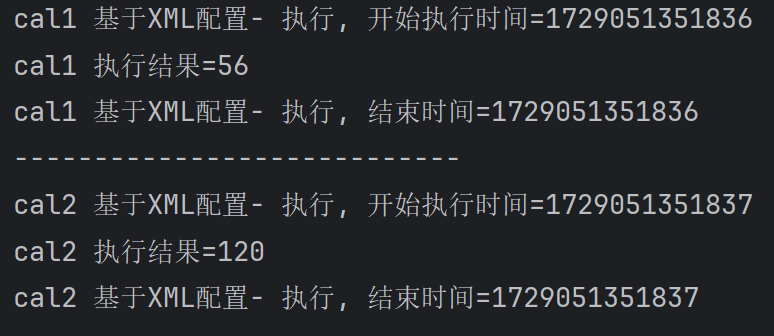
System.out.println(signature.getName() + " 基于XML配置- 执行, 开始执行时间=" + System.currentTimeMillis()); } //返回通知
public void calEnd(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println(signature.getName() + " 基于XML配置- 执行, 结束时间=" + System.currentTimeMillis()); }
}
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!--配置MyCalAOP-bean-->
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework.xml.MyCalAOP" id="myCalAOP" /> <!--配置MyCal-bean-->
<bean class="com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework.xml.MyCal" id="myCal"/> <!--配置切面类-->
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="myPointCut" expression="execution(public int com.hspedu.spring.aop.homework.xml.MyCal.*(int))"/> <!--配置前置,返回通知-->
<aop:aspect ref="myCalAOP" order="10">
<aop:before method="calStart" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/> <aop:after-returning method="calEnd" pointcut-ref="myPointCut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
运行结果:
spring上 -基于注解配置bean,动态代理,AOP笔记的更多相关文章
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记103:Spring学习---Spring Bean配置:基于注解的方式(基于注解配置bean,基于注解来装配bean的属性)
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- spring mvc 基于注解 配置默认 handlermapping
spring mvc 是类似于 Struts 的框架.他们都有一个最主要的功能就是URL路由.URL路由能将请求与响应请求处理逻辑的类(在Struts中即是action,在spring mvc 中即是 ...
- Spring学习--通过注解配置 Bean (三)
组件装配: <context:component-sacan> 元素还会自动注册 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcesser 实例 , 该实例可以自动装配具有 ...
- Spring学习--通过注解配置 Bean (二)
在 classpath 中扫描组件: 当在组件类上使用了特定的注解之后 , 还需要在 Spring 的配置文件中声明 <context:component-scan>: base-pack ...
- Spring学习--通过注解配置 Bean (一)
在 classpath 中扫描组件: 组件扫描(component scanning): Spring 能够从 classpath 下自动扫描 , 侦测和实例化具有特定注解的组件. 特定组件包括: @ ...
- Spring_自动组件扫描和 基于注解配置bean
自动组件扫描 启用Spring组件扫描功能. 使用@Component注释来表示这是类是一个自动扫描组件. package com.tanlei.dao; import org.springfram ...
- 基于注解配置spring
1 对 bean 的标注基于注解方式有3个注解 @Component @Repository 对DAO类进行标注 @Service 对Service类进行标注 @Controller 对Contro ...
- 13Spring通过注解配置Bean(1)
配置Bean的形式:基于XML文件的方式:基于注解的方式(基于注解配置Bean:基于注解来装配Bean的属性) 下面介绍基于注解的方式来配置Bean. ——组件扫描(component scannin ...
- spring(读取外部数据库配置信息、基于注解管理bean、DI)
###解析外部配置文件在resources文件夹下,新建db.properties(和数据库连接相关的信息) driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driverurl=jdbc ...
- Spring框架入门之基于Java注解配置bean
Spring框架入门之基于Java注解配置bean 一.Spring bean配置常用的注解 常用的有四个注解 Controller: 用于控制器的注解 Service : 用于service的注解 ...
随机推荐
- JavaWeb入门到实战学习笔记
了解,讲得并不是很好,很展开. 概念 动态web Web服务器 web服务器这节也是蜻蜓点水,引出tomcat而已 ASP(C#语言,微软) JSP PHP Java bootstrapclasslo ...
- 深度学习框架theano下的batch_norm实现代码——强化学习框架rllab
深度学习框架theano下的batch_norm实现代码--强化学习框架rllab # encoding: utf-8 import lasagne.layers as L import lasagn ...
- 2024年世界体育界的第一大丑闻:利昂内尔·梅西 (The biggest scandal in the world of sports in 2024: Unethical player - Lionel Messi.)
无德球员,梅西亲日辱华,不顾球迷感受,拒绝在中国的比赛中上场,并以所谓的伤病为借口,却在3天后的日本比赛中完全恢复如初,并进行了30分钟的高强度的对抗比赛并射门,可以说梅西的这一行径就是对中国亿万百姓 ...
- MindSpore 框架的官方预训练模型的加载 —— MindSpore / hub 的安装
MindSpore计算框架提供了一个官方版本的预训练模型存储库,或者叫做官方版本的预训练模型中心库,那就是 MindSpore / hub . 首先我们需要明确概念: 第一个就是 mindspore_ ...
- MAML —— Model-Agnostic Meta-Learning for Fast Adaptation of Deep Networks
论文地址: https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.03400 官方代码: 有监督学习: https://github.com/cbfinn/maml 强化学习: https://git ...
- P2P下载为什么不流行了——在线视频与P2P下载的一些比较
平时习惯性发呆,这两天发呆想到了这么一个问题,那就是"P2P下载为什么不流行了--在线视频与P2P下载的比较".想到这个问题其实还是与自己的一些个人经历有关,在14年前读大学的时候 ...
- RabbitMq高级特性之延迟队列 通俗易懂 超详细 【内含案例】
RabbitMq高级特性之延迟队列 介绍 消息进入队列后不能立即被消费,到达指定时间后才可被消费 实现 结合以下两种即可达到延迟队列 RabbitMq高级特性之TTL过期时间 RabbitMq高级特性 ...
- RabbitMq消息可靠性之确认模式 通俗易懂 超详细 【内含案例】
RabbitMq保证消息可靠性之确认模式 介绍 消息的确认,是指生产者投递消息后,如果 Broker 收到消息,则会给我们生产者一个应答.生产者进行接收应答,用来确定这条消息是否正常的发送到 Brok ...
- 使用 prerenderRoutes 进行预渲染路由
title: 使用 prerenderRoutes 进行预渲染路由 date: 2024/8/20 updated: 2024/8/20 author: cmdragon excerpt: prere ...
- JavaScript设计模式样例十五 —— 状态模式
状态模式(State Pattern) 定义:创建表示各种状态的对象和一个行为随着状态对象改变而改变的 context 对象.目的:允许对象在内部状态发生改变时改变它的行为,对象看起来好像修改了它的类 ...
