NIO 的非阻塞式网络通信
1.阻塞与非阻塞
① 传统的 IO 流都是阻塞式的。也就是说,当一个线程调用 read() 或 write()时,
该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在此期间不能执行其他任务。
因此,在完成网络通信进行 IO 操作时,由于线程会阻塞,
所以服务器端必须为每个客户端都提供一个独立的线程进行处理,
当服务器端需要处理大量客户端时,性能急剧下降。
② Java NIO 是非阻塞模式的。当线程从某通道进行读写数据时,若没有数据可用时,
该线程可以进行其他任务。线程通常将非阻塞 IO 的空闲时间用于在其他通道上执行 IO 操作,
所以单独的线程可以管理多个输入和输出通道。、
因此,NIO 可以让服务器端使用一个或有限几个线程来同
时处理连接到服务器端的所有客户端。
阻塞式:TestBlockingNIO
package com.aff.nio2; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption; import org.junit.Test; /*使用NIO完成网络通信的三个核心技术
1.通道(Channel):负责连接
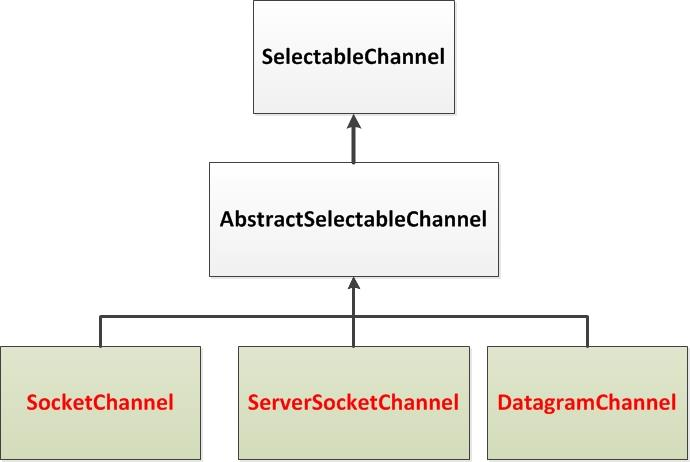
java.nio.channels.Channel 接口:
|----SockableChannel
|----SocketChannel
|----ServerSocketChannel
|----DatagramChannel
|
|----Pipe.SinkChannel
|----Pipe.SourceChannel 2.缓冲区(Buffer):负责数据的存储
3.选择器(Selector):是SelectorableChannel的多路复用器。
用于监控SelectableChannel的IO状况 */
//阻塞式IO
public class TestBlockingNIO {
// 客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
// 1.获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("192.168.3.10", 8989));
FileChannel inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
// 2.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
// 3.读取本地文件
while ((inChannel.read(buf)) != -1) {
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
// 关闭通道
inChannel.close();
sChannel.close();
} // 服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
// 1.获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
FileChannel outChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("8.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,
StandardOpenOption.CREATE); // 2.绑定端口号
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8989)); // 3.获取客户端连接的通道
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); // 4.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 5.接受客户端的数据,并保存到本地
while ((sChannel.read(buf)) != -1) {
buf.flip();
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
// 6.关闭通道
ssChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
ssChannel.close();
}
}
2.选择器(Selector) )
① 选择器(Selector)是 SelectableChannle 对象的多路复用器,
Selector 可以同时监控多个 SelectableChannel 的 IO 状况,
也就是说,利用 Selector可使一个单独的线程管理多个 Channel。
Selector 是非阻塞 IO 的核心。
② SelectableChannle 的结构如下图:
3.选择 器(Selector )的应用
①当调用 register(Selector sel, int ops) 将通道注册选择器时,选择器
对通道的监听事件,需要通过第二个参数 ops 指定。
②可以监听的事件类型(用 可使用 SelectionKey 的四个常量 表示):
读 : SelectionKey.OP_READ (1)
写 : SelectionKey.OP_WRITE (4)
连接 : SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT (8)
接收 : SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT (16)
③若注册时不止监听一个事件,则可以使用“位或”操作符连接
非阻塞式IO:TestBlockingNIO2
package com.aff.nio2; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner; import org.junit.Test; //非阻塞式IO
public class TestBlockingNIO2 {
// 客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException {
// 1.获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("192.168.3.10", 8989)); // 2.切换非阻塞式模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 3.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 4.发送数据给服务端
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scan.hasNext()) { // 相当于聊天室功能了
String str = scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString() + "\n" + str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
} // 关闭通道
sChannel.close();
} // 服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException {
// 1.获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open(); // 2.切换非阻塞模式
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 3..绑定端口号
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8989)); // 4..获取选择器
Selector selector = Selector.open(); // 5.将通道注册到选择器上,并且指定监听接受事件
ssChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT); // 6.轮巡式的获取选择器上已经 准备就绪 的事件
while (selector.select() > 0) {
// 7.获取当前选择器中所有注册的"选择键(已就绪的监听事件)"
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); // 8.迭代获取
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = it.next();
// 9.判断是什么事件准备就绪
if (sk.isAcceptable()) {
// 10.若"接收就绪",获取客户端连接
SocketChannel sChannel = ssChannel.accept(); // 11.切换非阻塞
sChannel.configureBlocking(false); // 将该通道注册到选择器上
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
} else if (sk.isReadable()) {
// 获取当前选择器上"读就绪"的通道
SocketChannel Schannel = (SocketChannel) sk.channel(); // 读取数据
int len = 0;
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while ((len = Schannel.read(buf)) > 0) {
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len));
buf.clear();
}
}
// 取消选择键
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
执行效果
Sun Apr 05 17:34:26 CST 2020
nihaoa
nisha
Sun Apr 05 17:34:44 CST 2020
nihenhao
DatagramChannel:Java NIO中的DatagramChannel是一个能收发UDP包的通道
DatagramChannel: TestBlockingUDP
package com.aff.nio2; import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Scanner; import org.junit.Test; public class TestBlockingUDP {
@Test
public void send() throws IOException {
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(); dc.configureBlocking(false); ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); while (scan.hasNext()) {
String str = scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString() + ":\n" + str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
dc.send(buf, new InetSocketAddress("192.168.3.10", 9898));
buf.clear();
} dc.close();
} @Test
public void receive() throws IOException {
DatagramChannel dc = DatagramChannel.open(); dc.configureBlocking(false); dc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898)); Selector selector = Selector.open(); dc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ); while (selector.select() > 0) {
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = it.next(); if (sk.isReadable()) {
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); dc.receive(buf);
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, buf.limit()));
buf.clear();
}
}
it.remove();
}
}
}
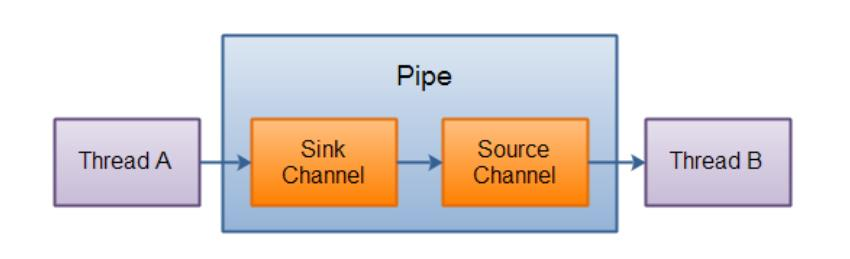
管道 (Pipe):
Java NIO 管道是2个线程之间的单向数据连接。
Pipe有一个source通道和一个sink通道。数据会
被写到sink通道,从source通道读取。
TestPipe
package com.aff.nio2;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.Pipe; import org.junit.Test; public class TestPipe { @Test
public void test1() throws IOException {
// 1. 获取管道
Pipe pipe = Pipe.open(); // 2. 将缓冲区中的数据写入管道
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel = pipe.sink();
buf.put("通过单向管道发送数据".getBytes());
buf.flip();
sinkChannel.write(buf); // 3. 读取缓冲区中的数据
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel = pipe.source();
buf.flip();
int len = sourceChannel.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(), 0, len)); sourceChannel.close();
sinkChannel.close();
}
}
NIO 的非阻塞式网络通信的更多相关文章
- JAVA NIO学习三:NIO 的非阻塞式网络通信
紧接着上一章,我们继续来研究NIO,上一章中我们讲了NIO 中最常见的操作即文件通道的操作,但实际上NIO的主要用途还是在于网络通信,那么这个时候就会涉及到选择器,这一章我们就会对其进行讲解操作. 一 ...
- 4.NIO的非阻塞式网络通信
/*阻塞 和 非阻塞 是对于 网络通信而言的*/ /*原先IO通信在进行一些读写操作 或者 等待 客户机连接 这种,是阻塞的,必须要等到有数据被处理,当前线程才被释放*/ /*NIO 通信 是将这个阻 ...
- Java基础——NIO(二)非阻塞式网络通信与NIO2新增类库
一.NIO非阻塞式网络通信 1.阻塞与非阻塞的概念 传统的 IO 流都是阻塞式的.也就是说,当一个线程调用 read() 或 write() 时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在 ...
- JAVA NIO学习记录2-非阻塞式网络通信
一.阻塞与非阻塞 传统的IO 流都是阻塞式的.也就是说,当一个线程调用read() 或write() 时,该线程被阻塞,直到有一些数据被读取或写入,该线程在此期间不能执行其他任务.因此,在完成网络通信 ...
- Java IO(3)非阻塞式输入输出(NIO)
在上篇<Java IO(2)阻塞式输入输出(BIO)>的末尾谈到了什么是阻塞式输入输出,通过Socket编程对其有了大致了解.现在再重新回顾梳理一下,对于只有一个“客户端”和一个“服务器端 ...
- Socket-IO 系列(三)基于 NIO 的同步非阻塞式编程
Socket-IO 系列(三)基于 NIO 的同步非阻塞式编程 缓冲区(Buffer) 用于存储数据 通道(Channel) 用于传输数据 多路复用器(Selector) 用于轮询 Channel 状 ...
- 基于NIO写的阻塞式和非阻塞式的客户端服务端
由于功能太过简单,就不过多阐述了,直接上阻塞式代码: package com.lql.nio; import org.junit.Test; import java.io.IOException; i ...
- Linux NIO 系列(03) 非阻塞式 IO
目录 一.非阻塞式 IO 附:非阻塞式 IO 编程 Linux NIO 系列(03) 非阻塞式 IO Netty 系列目录(https://www.cnblogs.com/binarylei/p/10 ...
- NIO非阻塞式编程
/** * NIO非阻塞式编程<p> * 服务端和客户端各自维护一个管理通道的对象,我们称之为selector,该对象能检测一个或多个通道 (channel) 上的事件. * 我们以服务端 ...
随机推荐
- jQuery中的查找节点、创建节点、插入节点、删除节点、替换节点、复制节点操作方法
jQuery操作节点我们可以分六点来讲,查找节点.创建节点.插入节点.删除节点.替换节点.复制节点. 一.查找节点 text() - 设置或返回所选元素的文本内容 ,html() - 设置或返回所 ...
- [hdu5225]逆序对统计
题目:给定一个1到n的排列,求字典序小于这个排列的所有排列的逆序对数之和. 思路:既然是求字典序小于这个排列的,不妨将排列根据和它前k位相同来分类,然后枚举第k+1位的数(小于原序列第k+1位的数), ...
- netty零基础入门
直接上代码,从最基本的接收消息规则开始 package cn.qdl; import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf; import io.netty.channel.ChannelH ...
- HDU 2005 (水)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2005题目大意:给定年份,计算是第几天 解题思路: 很水,判定下是否为闰年,方法:四年一闰,百年不闰,四 ...
- layui select下拉菜单联动
做的比较简单,先从后台直接把第一级菜单输出,然后点击二级菜单的时候再动态展示 <div class="layui-inline"> <label class=&q ...
- jbpm4 泳道
今天刚学习了jbpm4的泳道使用,方便以后查阅记录一下! 泳道定义: <swimlane name="myswim" assignee="userC"&g ...
- Codeforces Round #643 (Div.2)
前言:这套cf我感觉出的很不错,AB就不说了,唯一有点欠缺的就是C和D的位置应该换一下,C出的挺不错,反正我当时没有想出来(赛后补题的时候其实也不难..听朋友说还可以FFT优化,然而我是个图论手并不会 ...
- 全网最全Docker命令详解
由于最近在学习Docker,在这里把有关Docker的命令做一个集合,方便后面查看: # docker --help Usage: docker [OPTIONS] COMMAND [arg...] ...
- 「雕爷学编程」Arduino动手做(20)—水银开关模块
37款传感器与模块的提法,在网络上广泛流传,其实Arduino能够兼容的传感器模块肯定是不止37种的.鉴于本人手头积累了一些传感器和模块,依照实践出真知(一定要动手做)的理念,以学习和交流为目的,这里 ...
- 7.2 Go type assertion
7.2 Go type assertion 类型断言是使用在接口值上的操作. 语法x.(T)被称为类型断言,x代表接口的类型,T代表一个类型检查. 类型断言检查它操作对象的动态类型是否和断言类型匹配. ...
