Python模块:time、datetime、random、os、sys、optparse
time模块的方法:
时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量。
struct_time时间元组,共有九个元素组。如下图:
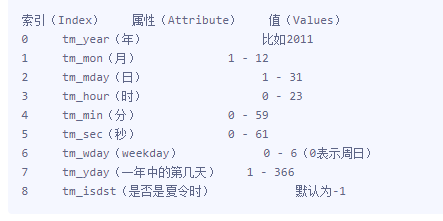
time.localtime([secs]): 将一个时间戳转换为当前时区的struct_time。 secs参数如果没有提供,则以当前时间为准,如:
print(time.localtime()) # 根据操作系统的时间。 操作系统时间改了,它也改 # 输出结果:
# time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=2, tm_mday=6, tm_hour=11, tm_min=42, tm_sec=23, tm_wday=1, tm_yday=37, tm_isdst=0)
time.localtime()还可以做如下操作:
a = time.localtime() print(a.tm_year)
print(a.tm_mon)
print(a.tm_mday) # 输出结果:
#
#
# # 通过这种方式就可以对年月日拼接 # 如: '%s-%s-%s'%(a.tm_year,a.tm_mon,a.tm_mday)
加上时间戳:
print(time.localtime(1500067890)) # 输出结果:
# time.struct_time(tm_year=2017, tm_mon=7, tm_mday=15, tm_hour=5, tm_min=31, tm_sec=30, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=196, tm_isdst=0)
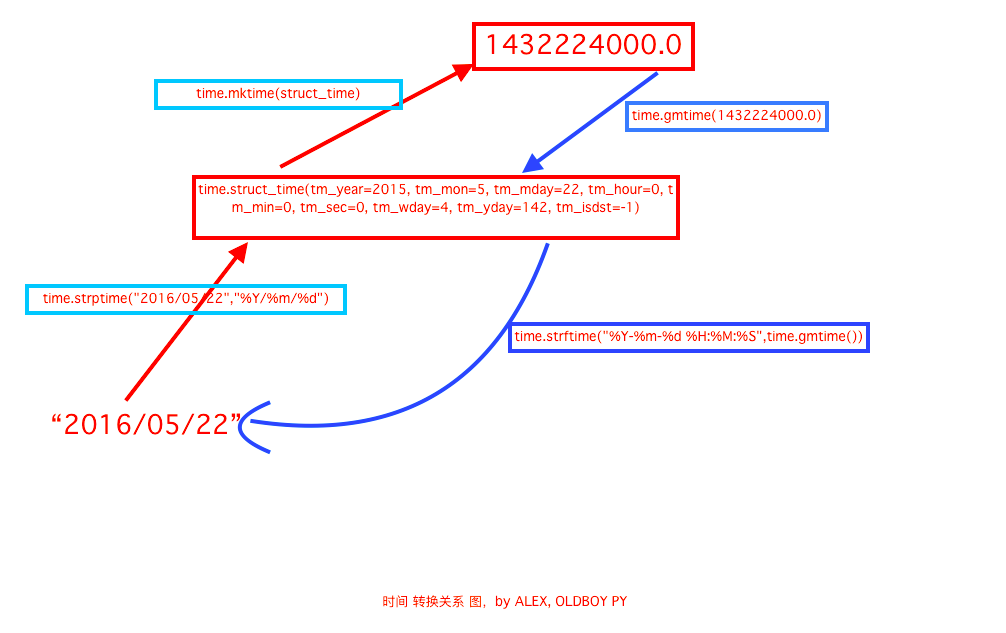
time.gmtime([secs]): 和localtime()方法类似,gmtime()是将一个时间戳转换为UTC时区(0时区)的struct_time(英国时间)。
time.time(): 返回当前时间戳,如:
print(time.time()) # 输出结果:
# 1517890126.8476076
time.mktime(t):将一个struct_time转化成为时间戳。
time.sleep(secs):线程推迟指定的时间再运行,单位为秒。就是说,让你的运行程序在time.sleep(secs) 这一步停留多少秒再继续运行。
import time
print(time.time())
for i in range(3):
print(i)
time.sleep(2)
print(time.time()) # 输出结果:
# 1517893315.1095674
#
#
#
# 1517893321.115609
time.asctime([t]): 把一个表示时间的元祖或者struct_time表示为这种形式: 'Sun Oct 1 12:04:38 2017'。如果没有参数,会将time.localtime()作为参数传入。
time.ctime([secs]):把一个时间戳(按秒计算的浮点数)转化为time.asctime()的形式。如果参数未给或者为None, 将会默认time.time()为参数。它的作用相当于time.asctime(time.localtime(secs))
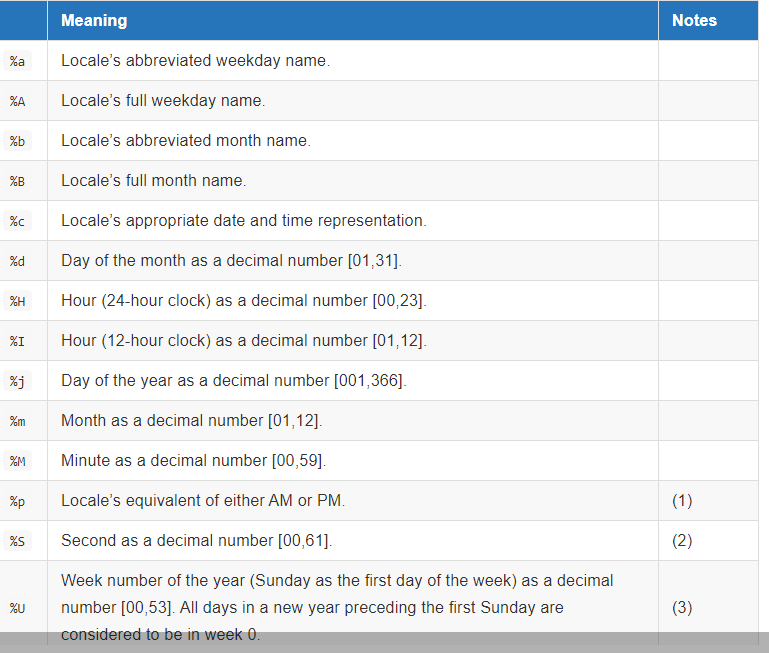
time.strftime(format , p_tuple) : 把一个代表时间的元祖或者struct_time(如由time.localtime()和time.gmtime()返回)转化为格式化的时间字符串。如果t 未指定,将传入time.localtime()。如:
import time
print(time.strftime('%y %m-%d %H:%M:%S %p %a %A %U',time.localtime())) # 输出结果:
# 18 02-06 13:50:04 PM Tue Tuesday 05
time.strptime(string,format): 把一个格式化时间字符串转化成struct_time。实际上它是strftime()的逆操作。如:
import time
print(time.strptime('2018-02-06 14:00:08','%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
# 输出结果:
# time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=2, tm_mday=6, tm_hour=14, tm_min=0, tm_sec=8, tm_wday=1, tm_yday=37, tm_isdst=-1)
转换关系图:
附: 字符串转时间格式对应表:

datetime模块:
相较于time模块,datetime模块的接口更直接、更容易调用
datetime模块定义了下面这几个类:
- datetime.date:表示日期的类。 常用的属性有:year,month,day;
- datetime.time:表示时间的类。常用的属性有hour,minute,second, microsecond;
- datetime.datetime:表示日期时间
- datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点之间的长度
- datetime.tzinfo: 与时区相关的信息 (这里不详细讨论该类)
需要掌握的方法有:
1. d = datetime.datetime.now() # 返回当前的datetime日期类型
import datetime
print(datetime.datetime.now()) # 输出结果:
# datetime.datetime(2018, 2, 6, 14, 50, 24, 65493) # 年月日时分秒
另外, d = datetime.datetime.now()
d.timestamp() , d.today() , d.year, d.timetuple() 等方法可以调用
2. datetime.date.fromtimestamp(时间戳) # 把一个时间戳转换成datetime 日期类型
import datetime
import date print(datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time())) # 输出结果:
# datetime.date(2018, 2, 6) # 快速得到了年月日
3. 时间运算:
import datetime t = datetime.timedelta(days=1,hours=12) # datetime.timedelta() 括号里面默认的是天数(days), 可以输入weeks,hours,minutes,seconds,... 但不能输入months和years print(datetime.datetime.now() - t) # 也可以和datetime.timedelta(时间间隔) 相加 # 输出结果:
# datetime.datetime(2018, 2, 5, 3, 21, 2, 587762)
4. 时间替换:
import datetime
d = datetime.datetime.now()
print(d)
print(d.replace(year=2016,month=1)) # replace() 在括号里可以修改任何变量(年月日时分秒等等) # 输出结果:
# datetime.datetime(2018, 2, 6, 15, 41, 48, 571626)
# datetime.datetime(2016, 1, 6, 15, 41, 48, 571626)
注: datetime主要用于时间运算和时间替换,time主要用于时间戳字符串之间的来回转换
random模块:
random.randint(整数1,整数2) : 取整数1到整数2之间随机的一个整数(包括整数2)
random.randrange(整数1,整数2): 随机取整数1到整数2之间的一个整数(不包括整数2)
random.random() # 返回一个随机浮点数
random.choice(sequence) # Choose a random element from a non-empty sequence. ---> 返回的值是字符串格式
import random a = ['a','b','c','da','eaga','bartfwe',1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] print(random.choice(a)) # a是一个sequence, 列表、字符串等都可以
random.sample(population,k) # Chooses k unique random elements from a population sequence or set. 从一个序列群中随机返回k个唯一的元素,随机返回的元素在一个列表中。
import random
print(random.sample('abasernvawuoerh16576135',4))
print(random.sample('abasernvawuoerh16576135',4))
# 输出结果:
# ['n', 'w', 'o', 'e']
# ['1', 's', 'b', '6']
生成随机字符串:import random
import string # 字符串模块
s = string.ascii_letters + string.digits + string.punctuation # 这个相当于随机的数据源
print(random.sample(s,4))
print(''.join(random.sample(s,4)))
# 输出结果:
# ['S', 'Y', 'Q', '%'] # 随机了两次,所以结果不一样
# f!Ws # 得到了随机字符串,可做验证码 # 另外, string模块的用法:
print(string.ascii_letters) # 大小写所有的字母
print(string.ascii_uppercase) # 所有的大写字母
print(string.ascii_lowercase) # 所有的小写字母
print(string.digits) # 0到9的数字
print(string.punctuation) # 特殊符号; punctuation就是标点符号的意思 # 输出结果:
# 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
# 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ'
# 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
# '0123456789'
# '!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~'
洗牌:
random.shuffle() # 注意: 这个函数没有返回值 ,另外, 一个字符串不能shuffle
import random a = list(range(20))
print(a) random.shuffle(a)
print(a) # random.shuffle()没有返回值,所以应该打印a # 输出结果:
# [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19]
# [11, 14, 5, 16, 1, 15, 0, 17, 12, 2, 13, 4, 6, 3, 10, 8, 19, 7, 18, 9]
os模块:
os模块提供了很多允许你的程序与操作系统直接交互的功能。
得到当前工作目录,即当前Python脚本工作的目录路径: os.getcwd() # Return a unicode string representing the current working directory. (cwd应该是current working directory的缩写) (Python解释器从哪里启动的就是哪个路径,不一定是所执行Python文件所在的目录;即Python解释器启动所在的位置,不是执行脚本所在的位置)
os.listdir() # 返回指定目录下的所有文件和目录名 # Return a list containing the names of the files in the directory.
os.remove( '目录路径\文件名.后缀' ) # 用来删除一个文件 # 目录路径可以是绝对路径,也可以是 ..\的相对路径
os.rmdir(path) # 删除一个空目录
os.removedirs('路径\目录名') # 递归删除空目录,从最底层的目录开始,如果最底层的目录是空文件则删除它,然后一层一层往上删除空文件,直到遇到非空文件,如果最底层的目录不是空文件则报错。
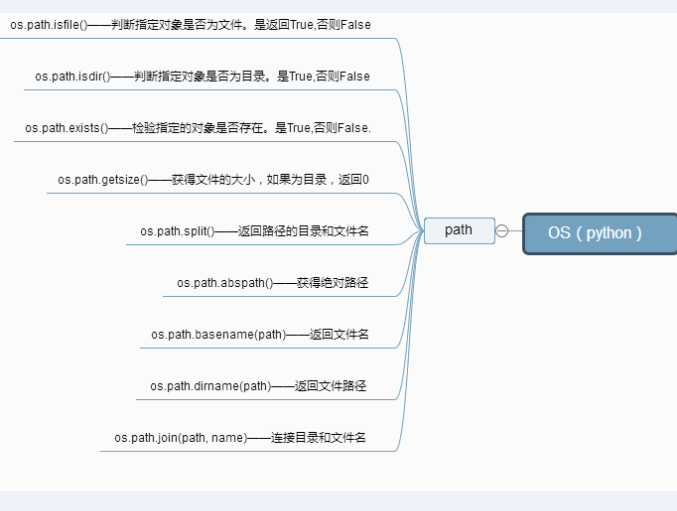
os.path.isfile('path) # 检验一个路径是不是一个文件
os.path.isdir('path') # 检验一个路径是不是一个目录
os.path.isabs('path') # 检验一个路径是不是绝对路径
os.path.exists('path') # 检验一个路径是否真实存在 # 文件、目录都可以
os.path.split('path') # 返回一个路径的目录名和文件名 , 如:
import os
print(os.path.split('F:\learning\pycharm_pro\检测\视频课件\第二模块\module练习\import练习.py')) # 输出结果:
# ('F:\\learning\\pycharm_pro\\检测\\视频课件\\第二模块\\module练习', 'import练习.py')
os.path.splitext('path') # 分离扩展名
os.path.dirname( ) # 获取路径名
os.path.abspath( ) # 获取绝对路径
os.path.basename( ) # 获取文件名
os.system() # 运行shell命令 # 执行一条系统命令
os.getenv('HOME') # 读取操作系统环境变量HOME的值
os.environ # 返回操作系统所有的环境变量 # 返回值是一个列表
os.environ.setdefault( xx, xxx)
os.linesep # 返回当前平台使用的行终止符。 # Windows使用\r \n, Linux和Mac使用 \n
os.name # 指示你正在使用的平台 # Windows是 nt , Linux/Unix是 posix
os.replace( xx, xxx) # 重命名
os.makedirs( ' c: x\xx\xxx') # 创建多级目录
os.mkdir( 'xx') # 创建单个目录
os.stat(文件名) # 获取文件属性 # 主要用于获取文件大小
os.path.getsize(filename) # 获取文件大小
os.path.join(dir,dir,...,filename) # 结合目录名和文件名
os.chdir(dirname) # 改变工作目录到dirname # 只在程序运行过程中有效
os.get_terminal_size() # 获取当前终端的大小

sys模块:
sys.argv # 命令行参数list ,第一个元素是程序本身的路径
sys.exit(n) # 退出程序,n代表退出时打印的内容,正常退出时exit(0)
sys.version # 获取Python解释器的版本信息
sys.maxint # 最大的int值 (Python2中)
sys.maxsize # 最大的int值 (Python3)
sys.path # 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值 # 可以利用 sys.path.append(...) 把某个路径添加到环境变量中
sys.platform # 返回操作系统平台的名称
sys.stdout.write('please:') # 标准输出,引入进度条的例子。注:Python3上不行,可以用print代替
val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1] # 标准输入
sys.getrecursionlimit() # 获取最大递归层数
sys.setrecursionlimit(数字) # 设置最大递归层数
sys.getdefaultencoding() # 获取解释器默认编码
sys.getfilesystemencoding() # 获取内存数据存到文件里的默认编码
optparse模块:
import optparse
class Client:
def __init__(self):
parser = optparse.OptionParser()
parser.add_option("-s","--server",dest="server",help="ftp server ip_addr")
parser.add_option("-P","--port",type="int",dest="port",help="ftp server port")
self.options,self.args = parser.parse_args()
print(self.options,type(self.options))
print(self.options.server)
# {'server': None, 'port': None} <class 'optparse.Values'>
# None
"""
self.options 不是字典,而是一个类; 可利用类的方法调用,如: self.options.server
"""
print(self.options.server)
print(self.args,type(self.args))
client = Client()
"""
optparse模块与 sys.argv 类似,都用于接收程序外的参数(在命令行输入参数),但功能比sys.argv强大
"""
terminal如下:

Python模块:time、datetime、random、os、sys、optparse的更多相关文章
- Python常用模块(time, datetime, random, os, sys, hashlib)
time模块 在Python中,通常有这几种方式来表示时间: 时间戳(timestamp) : 通常来说,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量.我们运 ...
- python笔记-1(import导入、time/datetime/random/os/sys模块)
python笔记-6(import导入.time/datetime/random/os/sys模块) 一.了解模块导入的基本知识 此部分此处不展开细说import导入,仅写几个点目前的认知即可.其 ...
- day19:常用模块(collections,time,random,os,sys)
1,正则复习,re.S,这个在用的最多,re.M多行模式,这个主要改变^和$的行为,每一行都是新串开头,每个回车都是结尾.re.L 在Windows和linux里面对一些特殊字符有不一样的识别,re. ...
- python笔记-6(import导入、time/datetime/random/os/sys模块)
一.了解模块导入的基本知识 此部分此处不展开细说import导入,仅写几个点目前的认知即可.其它内容待日后有深入理解了再来细说 1.import可以导入的两种不同的内容 1.1 *.py文件结尾的文件 ...
- 常用模块之 time,datetime,random,os,sys
time与datetime模块 先认识几个python中关于时间的名词: 时间戳(timestamp):通常来说,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量.我们运行“ty ...
- time,datetime,random,os,sys,hashlib,logging,configparser,re模块
#-----time模块----- print(help(time)) #打印time帮助文档 print(time.time()) #打印时间戳 1569824501.6265268 time.sl ...
- CSIC_716_20191116【常用模块的用法 time ,datetime, random, os, sys, hashlib】
import time import datetime import os import sys import random import hashlib time模块 时间戳(Timestamp) ...
- 模块、包及常用模块(time/random/os/sys/shutil)
一.模块 模块的本质就是一个.py 文件. 导入和调用模块: import module from module import xx from module.xx.xx import xx as re ...
- 模块:time,random,os,sys
时间模块 import time # print(time.time()) #时间戳 # print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X')) #格式化字符 # print(time ...
- python模块详解 random os
random模块 常用方法 random.random() 随机产生一个小于1的浮点数 import random print(random.random()) #0.4153761818276826 ...
随机推荐
- Proactive Patching Overview
1.Proactive Patching Overview Between Patch Set releases, Oracle's proactive patching program provid ...
- 436 Find Right Interval 寻找右区间
给定一组区间,对于每一个区间 i,检查是否存在一个区间 j,它的起始点大于或等于区间 i 的终点,这可以称为 j 在 i 的“右侧”.对于任何区间,你需要存储的满足条件的区间 j 的最小索引,这意味着 ...
- 222 Count Complete Tree Nodes 完全二叉树的节点个数
给出一个完全二叉树,求出该树的节点个数.完全二叉树的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置.若最底层为第 h ...
- python的des和3des加解密
1.加密: pyDes.des(key, [mode], [IV], [pad], [padmode]) pyDes.triple_des(key, [mode], [IV], [pad], [pad ...
- 移动端UI自动化Appium测试——Appium server两种启动方式
执行自动化测试之前,需要先运行appium server,这样才能形成server与java client的通信,启动server有两种方式,一种是命令,一种是按钮图标,具体使用如下: 1.用命令启动 ...
- Webform 内置对象 Session对象、Application全局对象,ViewState
Session 每台电脑访问服务器,都有独立的session,key值都一样,内容不一样. 1.session保存在服务器上. 2.session没有持久性,保存周期就是20分钟. 重点: sessi ...
- jdk线程池,使用手记
Executors----------------------------------------------Executors------------------------------------ ...
- C/C++ 函数模板、全局变量、register、存储周期
1.函数声明时可以简写,如: int max(int,int): 2.函数模板: 格式: template <typename haha>或template <class haha& ...
- win7电脑桌面壁纸曝光过高影响图标怎么办?亲测实用解决方法
现在用win7系统的人应该还是挺多的吧,虽然说windows家族已经升级到现在的win11了,相信大多数人家用的电脑系统还是win7吧,今天要讲的是一个壁纸曝光度过高的解决办法,虽然还不清楚为什么,但 ...
- Beta测试团队
---恢复内容开始--- Beta版本测试 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xnsy/SoftwareEngineeringClass1/?page ...
