CS231n 2016 通关 第二章-KNN 作业分析
KNN作业要求:
1、掌握KNN算法原理
2、实现具体K值的KNN算法
3、实现对K值的交叉验证
1、KNN原理见上一小节
2、实现KNN
过程分两步:
1、计算测试集与训练集的距离
2、通过比较label出现比例的方式,确定选取的最终label
代码分析:
cell1 - cell5 对数据的预处理
cell6创建KNN类,初始化类的变量,此处是传递测试数据和训练数据
cell7实现包含两个循环的KNN算法:
通过计算单一的向量与矩阵之间的距离(在之前的cell中,已经将图像转换成列:32*32 的图像转换为 1*3072,,
测试集是500张:500*3072,训练集是5000张:5000*3072)
代码基础:使用python 2.7.9 + numpy 1.11.0
技巧:使用help 查看相关函数的用法,或者google
举例:np.square
q 键退出help
可知,np.square() 为了加快运算速度,是用c写的,在这里查不到具体用法。google查看:

例子为计算数组[-1j,1]里边各元素的平方,得到的结果为[-1,1]
代码:实现compute_distances_two_loops(self, X)
1 def compute_distances_two_loops(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using a nested loop over both the training data and the
test data. Inputs:
- X: A numpy array of shape (num_test, D) containing test data. Returns:
- dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j]
is the Euclidean distance between the ith test point and the jth training
point.
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
for i in xrange(num_test):
for j in xrange(num_train):
#####################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and the jth #
# training point, and store the result in dists[i, j]. You should #
# not use a loop over dimension. #
#####################################################################
dists[i,j] = np.sqrt(np.sum(np.square(X[i,:]-self.X_train[j,:])))
#####################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#####################################################################
return dists
实现对一张测试图像对应的矩阵与一张训练集图像的矩阵做L2距离。
也可以用numpy.linalg.norm函数实现:
此函数执行的公式: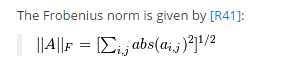
所以核心代码可以写作:
dists[i,j] = np.linalg.norm(self.X_train[j,:]-X[i,:])
cell8 得到的距离可视化,白色表示较大的距离值,黑色是较小距离值
cell9 实现K=1的label预测
代码:实现 classifier.predict_labels()
def predict_labels(self, dists, k=1):
"""
Given a matrix of distances between test points and training points,
predict a label for each test point. Inputs:
- dists: A numpy array of shape (num_test, num_train) where dists[i, j]
gives the distance betwen the ith test point and the jth training point. Returns:
- y: A numpy array of shape (num_test,) containing predicted labels for the
test data, where y[i] is the predicted label for the test point X[i].
"""
num_test = dists.shape[0]
y_pred = np.zeros(num_test)
for i in xrange(num_test):
# A list of length k storing the labels of the k nearest neighbors to
# the ith test point.
closest_y = []
count = []
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Use the distance matrix to find the k nearest neighbors of the ith #
# testing point, and use self.y_train to find the labels of these #
# neighbors. Store these labels in closest_y. #
# Hint: Look up the function numpy.argsort. #
#########################################################################
buf_labels = self.y_train[np.argsort(dists[i,:])]
closest_y = buf_labels[0:k]
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Now that you have found the labels of the k nearest neighbors, you #
# need to find the most common label in the list closest_y of labels. #
# Store this label in y_pred[i]. Break ties by choosing the smaller #
# label. #
#########################################################################
#for j in closest_y :
# count.append(closest_y.count(j))
#m = max(count)
#n = count.index(m)
#y_pred[i] = closest_y[n]
c = Counter(closest_y)
y_pred[i] = c.most_common(1)[0][0]
#########################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
######################################################################### return y_pred
步骤:
1.使用numpy.argsort对所以距离进行排序,得到排序后的索引。
2.通过索引找到对应的label
3.通过collection包的Counter,对label进行统计表示
4.通过counter的Most common方法得到出现最多的label
cell9 在计算完成后,同时实现了准确率的计算

cell10 实现K =5的KNN
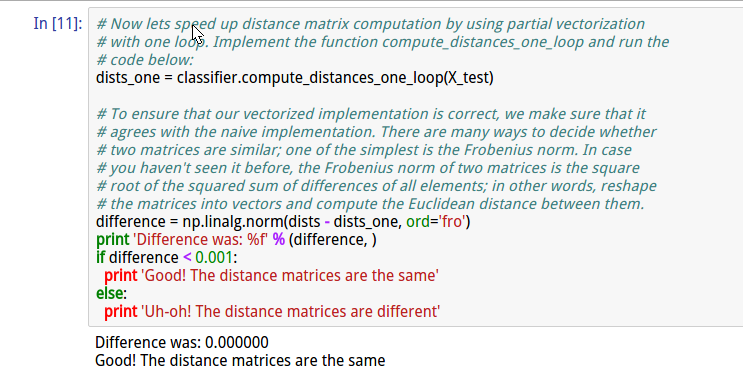
cell11 实现compute_distances_one_loop(X_test)
代码:
def compute_distances_one_loop(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using a single loop over the test data. Input / Output: Same as compute_distances_two_loops
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
for i in xrange(num_test):
#######################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between the ith test point and all training #
# points, and store the result in dists[i, :]. #
#######################################################################
buf = np.square(self.X_train-X[i,:])
dists[i,:] = np.sqrt(np.sum(buf,axis=1))
#######################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#######################################################################
return dists
并通过计算一个循环与两个循环分别得到的结果的差值平方,来衡量准确性。
cell12 实现完全的数组操作,不使用循环。
def compute_distances_no_loops(self, X):
"""
Compute the distance between each test point in X and each training point
in self.X_train using no explicit loops. Input / Output: Same as compute_distances_two_loops
"""
num_test = X.shape[0]
num_train = self.X_train.shape[0]
dists = np.zeros((num_test, num_train))
#########################################################################
# TODO: #
# Compute the l2 distance between all test points and all training #
# points without using any explicit loops, and store the result in #
# dists. #
# #
# You should implement this function using only basic array operations; #
# in particular you should not use functions from scipy. #
# #
# HINT: Try to formulate the l2 distance using matrix multiplication #
# and two broadcast sums. #
#########################################################################
#buf = np.tile(X,(1,num_train))
buf = np.dot(X, self.X_train.T)
buf_test = np.square(X).sum(axis = 1)
buf_train = np.square(self.X_train).sum(axis = 1)
dists = np.sqrt(-2*buf+buf_train+np.matrix(buf_test).T)
#########################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
#########################################################################
return dists
使用(a-b)2=a2+b2-2ab 的公式
27行: 此时buf_test 为500*1数组 buf_train为5000*1的数组 需要得到500*5000的数组 此处通过构造矩阵的方式进行broadcast
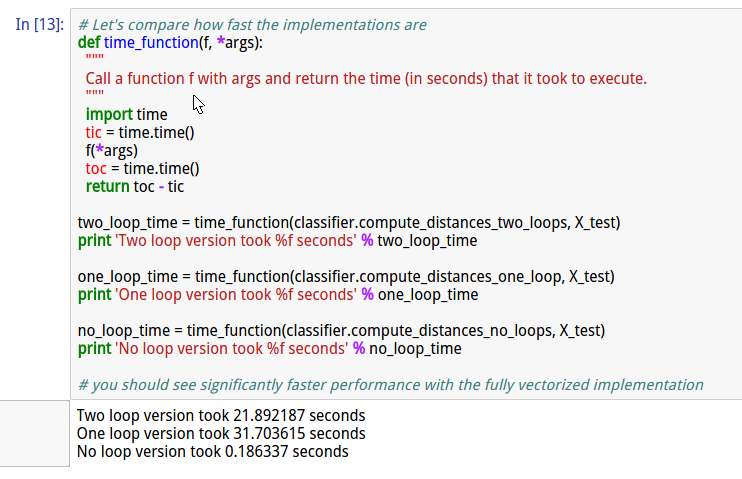
cell13 比较3种方案的执行效率
cell14 交叉验证
交叉验证的思想在上一节有解释过了
代码:(其中带有注释)
num_folds = 5
k_choices = [1, 3, 5, 8, 10, 12, 15, 20, 50, 100] X_train_folds = []
y_train_folds = []
################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Split up the training data into folds. After splitting, X_train_folds and #
# y_train_folds should each be lists of length num_folds, where #
# y_train_folds[i] is the label vector for the points in X_train_folds[i]. #
# Hint: Look up the numpy array_split function. #
################################################################################
X_train_folds = np.array_split(X_train, num_folds)
y_train_folds = np.array_split(y_train, num_folds)
################################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
################################################################################ # A dictionary holding the accuracies for different values of k that we find
# when running cross-validation. After running cross-validation,
# k_to_accuracies[k] should be a list of length num_folds giving the different
# accuracy values that we found when using that value of k.
k_to_accuracies = {} ################################################################################
# TODO: #
# Perform k-fold cross validation to find the best value of k. For each #
# possible value of k, run the k-nearest-neighbor algorithm num_folds times, #
# where in each case you use all but one of the folds as training data and the #
# last fold as a validation set. Store the accuracies for all fold and all #
# values of k in the k_to_accuracies dictionary. #
################################################################################
for k in k_choices:
k_to_accuracies[k] = [] for k in k_choices:
print 'evaluating k=%d' % k
for j in range(num_folds):
#get validation
X_train_cv = np.vstack(X_train_folds[0:j]+X_train_folds[j+1:])
X_test_cv = X_train_folds[j]
y_train_cv = np.hstack(y_train_folds[0:j]+y_train_folds[j+1:])
y_test_cv = y_train_folds[j]
#train
classifier.train(X_train_cv, y_train_cv)
dists_cv = classifier.compute_distances_no_loops(X_test_cv)
#get accuracy
y_test_pred = classifier.predict_labels(dists_cv, k)
num_correct = np.sum(y_test_pred == y_test_cv)
accuracy = float(num_correct) / num_test
#add j th accuracy of k to array
k_to_accuracies[k].append(accuracy)
################################################################################
# END OF YOUR CODE #
################################################################################ # Print out the computed accuracies
for k in sorted(k_to_accuracies):
for accuracy in k_to_accuracies[k]:
print 'k = %d, accuracy = %f' % (k, accuracy)
cell15 显示k值对应的准确率

上述包含了均值和标准差
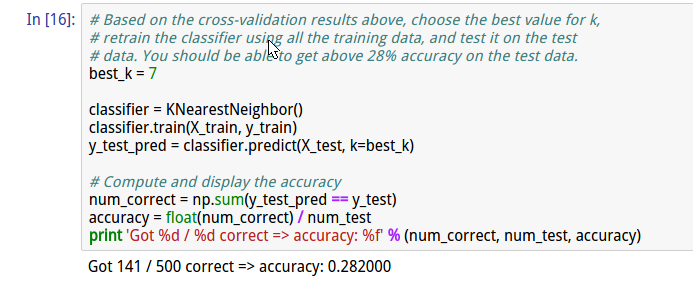
cell16 使用最优值,得到较好的准确率
总结:
整体来说,第一个作业难度较大,主要难度不是在算法部分,而是在熟悉python相关函数与相应的用法方面。对于python大神而言,难度低。
但是经过扎实的第一次作业后,后边的作业相对简单了。之后的作业细节方面讲解的少些。
附:通关CS231n企鹅群:578975100 validation:DL-CS231n
CS231n 2016 通关 第二章-KNN 作业分析的更多相关文章
- CS231n 2016 通关 第二章-KNN
课程内容全纪录: 1.讲解图像分类的难点 1.光照强度 2.主体变形 3.主体与背景咬合 4.主体与背景相接近 5.同类别间存在区别 2.KNN 1.最近邻算法 2.Knn 3.hyperpara ...
- CS231n 2016 通关 第一章-内容介绍
第一节视频的主要内容: Fei-Fei Li 女神对Computer Vision的整体介绍.包括了发展历史中的重要事件,其中最为重要的是1959年测试猫视觉神经的实验. In 1959 Harvar ...
- CS231n 2016 通关 第三章-SVM与Softmax
1===本节课对应视频内容的第三讲,对应PPT是Lecture3 2===本节课的收获 ===熟悉SVM及其多分类问题 ===熟悉softmax分类问题 ===了解优化思想 由上节课即KNN的分析步骤 ...
- CS231n 2016 通关 第三章-SVM 作业分析
作业内容,完成作业便可熟悉如下内容: cell 1 设置绘图默认参数 # Run some setup code for this notebook. import random import nu ...
- CS231n 2016 通关 第三章-Softmax 作业
在完成SVM作业的基础上,Softmax的作业相对比较轻松. 完成本作业需要熟悉与掌握的知识: cell 1 设置绘图默认参数 mport random import numpy as np from ...
- CS231n 2016 通关 第五、六章 Dropout 作业
Dropout的作用: cell 1 - cell 2 依旧 cell 3 Dropout层的前向传播 核心代码: train 时: if mode == 'train': ############ ...
- CS231n 2016 通关 第五、六章 Batch Normalization 作业
BN层在实际中应用广泛. 上一次总结了使得训练变得简单的方法,比如SGD+momentum RMSProp Adam,BN是另外的方法. cell 1 依旧是初始化设置 cell 2 读取cifar- ...
- CS231n 2016 通关 第五、六章 Fully-Connected Neural Nets 作业
要求:实现任意层数的NN. 每一层结构包含: 1.前向传播和反向传播函数:2.每一层计算的相关数值 cell 1 依旧是显示的初始设置 # As usual, a bit of setup impor ...
- CS231n 2016 通关 第四章-NN 作业
cell 1 显示设置初始化 # A bit of setup import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from cs231n.class ...
随机推荐
- python把日期转换为秒数;日期转为字符串;datetime、date
1.秒数是相对于1970.1.1号的秒数 2.日期的模块有time.datetime 3. import datetime t = datetime.datetime(2009, 10, 21, 0, ...
- antd 如何让 Row 中的 Col 自动换行?
1.解决方案 在需要换行处,设置一个空的 Col // 空白(特殊情况处理) const empty = ( <Col md={6} sm={24}></Col> ); .
- HDU 2955 Robberies(01背包变形)
Robberies Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total S ...
- MFC 的 Picture Control 加载 BMP/PNG 图片的方法
1. 加载 BMP CStatic* pWnd = (CStatic*)GetDlgItem(IDC_PIC); // 得到 Picture Control 句柄 pWnd->ModifySty ...
- 设计模式学习笔记——Chain of Responsibility职责链模式
重点在链.一条链,如果本节点处理不了,则传递给下一个节点处理. 关键是如何传给下一个节点? 主要是由本节点决定传给哪一个节点. public class Client { public static ...
- inheritance super overrides printMethod in Superclass override重写父方法
Core Java Web Page http://horstmann.com/corejava.html [ inheritance ] package v1ch05.inheritance; im ...
- 关于 SWT 的UI线程和非UI线程
要理解UI线程,先要了解一下“消息循环”这个概念.链接是百度百科上的条目,简单地说,操作系统把用户界面上的每个操作都转化成为对应的消息,加入消息队列.然后把消息转发给对应的应用程序(一般来说,就是活动 ...
- oracle case where 复杂sql语句
update hr_user u set u.is_approve=(case when u.curr_org_id in (select t.org_id from hr_organization ...
- UVAlive 6611 Alice's Print Service 二分
Alice is providing print service, while the pricing doesn't seem to be reasonable, so people using h ...
- webpack 构建多页面应用
如何使用webpack构建多页面应用,这是一个我一直在想和解决的问题.网上也给出了很多的例子,很多想法.猛一看,觉得有那么点儿意思,但仔细看也就那样. 使用webpack这个构建工具,可以使我们少考虑 ...
