TCP-IP Architecture and IP Packet
Why Internet working?
- To build a “network of networks” or internet.
- operating over multiple, coexisting(共存的), different networks
- providing ubiquitous(无处不在的) connectivity through IP packet transfer .
- achieving huge economies of scale.
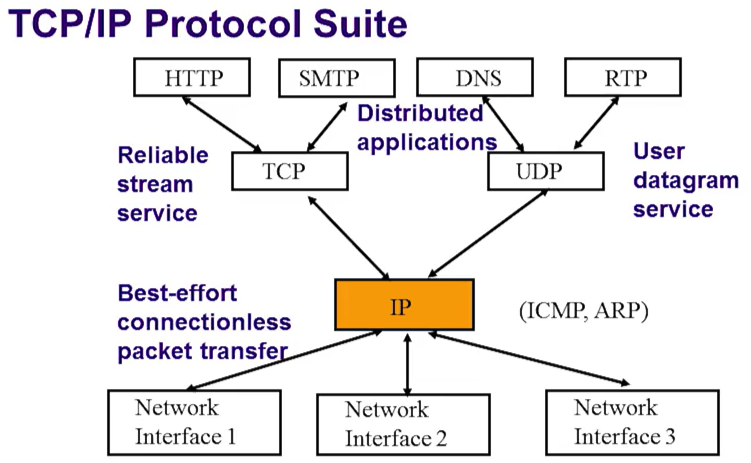
TCP/IP Protocol Suite
Encapsulation(封装)
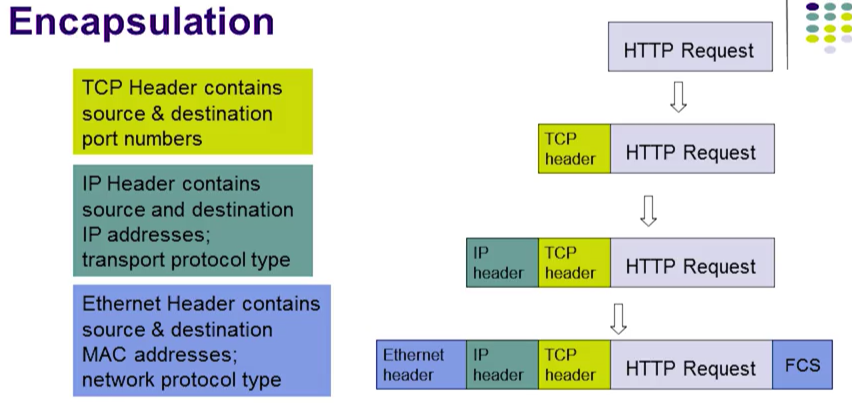
- Base:HTTP Request ->TCP header->IP header->Ethernet header
Internet Addresses
- Each host has globally unique logical IP address
- Separate address for each physical connection to a network
- Routing decision is done based on destination IP address
- IP address has two parts:
- netid(网络标识符) and hostid
- netid unique, facilitates routing
- Dotted Decimal(十进制) Notation(记号):
int1.int2.int3.int4
(intj = jth octet)
128.100.10.13
Internet Protocol
- Provides best effort, connectionless packet delivery
- motivated by need to keep routers simple and by adaptibility to failure of network elements
- packets may be lost, out of order, or even duplicated(复制)
- higher layer protocols must deal with these, if necessary
- IP also includes:
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
IP Packet Header
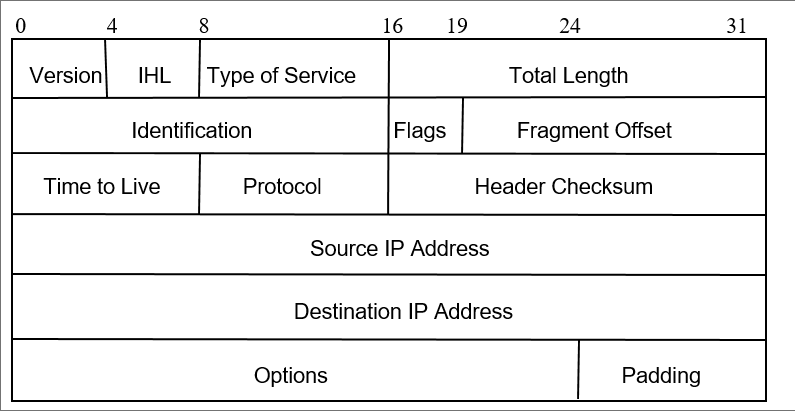
- Minimum 20 bytes
- Up to 40 bytes in options fields
- Version: current IP version is 4.
- Internet header length (IHL): length of the header in 32-bit words.
- Type of service (TOS): traditionally priority of packet at each router. Recent Differentiated Services redefines TOS field to include other services besides best effort.
- Total length: number of bytes of the IP packet including header and data
- Identification, Flags, and Fragment Offset: for fragmentation and reassembly.
- Time to live (TTL): number of hops packet is allowed to traverse(穿过) in network.
- Each router along the path to the destination decrements this value by one.
- If the value reaches zero before the packet reaches the destination, the router discards the packet and sends an error message back to the source.
- Protocol: specifies upper-layer protocol that is to receive IP data at the destination. Examples include TCP (protocol = 6), UDP (protocol = 17), and ICMP (protocol = 1).
- Header checksum(校验和): verifies the integrity of the IP header.
- Source IP address and destination IP address: contain the addresses of the source and destination hosts.
- Options: Variable length field, allows packet to request special features such as security level, route to be taken by the packet, and timestamp at each router. Detailed descriptions of these options can be found in [RFC 791].
- Padding: This field is used to make the header a multiple of 32-bit words.
IP Header Processing
- Compute header checksum(校验和) for correctness and check that fields in header (e.g. version and total length) contain valid values
- Consult routing table to determine next hop
- Change fields that require updating (TTL, header checksum)
TCP-IP Architecture and IP Packet的更多相关文章
- TCP/IP——内外网IP+子网掩码作用+PING(网络总结)
目录: 1.如何区分内网IP和外网IP? 保留字段 2.子网掩码是起什么作用的? 将DNS和IP异或,表示哪段起作用 3.ping到底起什么作用? ping本地.ping远程 下面针对上面三个问题分别 ...
- TCP/IP 协议:IP 协议
首先来看一下IP协议在实际中的位置: 我们只关系流程,不关系当前具体的服务类型 1.IP协议概述 作用: 从上图或从应用层->运输层->网络层->链路层来看,IP协议属于网络层,也就 ...
- TCP/IP笔记(四)IP协议
前言 IP相当于OSI参考模型的第3层--网络层:主要作用是"实现终端节点之间的通信"又称"点对点通信". IP作为整个TCP/IP中至关重要的协议,主要负责将 ...
- TCP/IP笔记(五)IP协议相关技术
IP旨在让最终目标主机收到数据包,但是在这一过程中仅仅有IP时无法实现通信的.必须还要又能够解析主机名称和MACdivide功能,以技术包在发送过程中异常情况处理的功能. 这篇主要介绍下DNS.ARP ...
- TCP/IP协议栈 --- 网络层(IP 首部 和分片)
IP 是TCP/IP协议栈中重要的层次, TCP UDP ICMP IGMP都是依赖IP层进行传输的.首先它是一种不可靠,无连接的协议.不可靠:它不保证IP包能正确到达目的地,无连接:表示IP并不会维 ...
- tcp、udp、ip、icmp报文格式分析
TCP .UDP .IP. ICMP协议报文格式分析 Tcp报文格式: Wireshark抓包如图: 源端口/目的端口(16bit): 在TCP报文中包涵了源端口/目的端口,源端口标识了发送进程,目的 ...
- TCP/IP协议族——IP工作原理及实例具体解释(上)
IP协议具体解释 本文主要介绍了IP服务特点,头部结构,IP分片知识,并用tcpdump抓取数据包.来观察IP数据报传送过程中IP的格式,以及分片的过程. IP头部信息:IP头部信息出如今每一个 ...
- 常见协议TCP、UDP、IP图
ip tcp udp icmp help ip tcp http icmp
- tcp/iP协议族——IP工作原理及实例具体解释(下)
IP协议具体解释 上一篇文章文章主要介绍了IP服务的特点,IPv4头部结构IP分片.并用tcpdump抓取数据包,来观察IP数据报传送过程中IP的格式,以及分片的过程.本文主要介绍IP路由,IP ...
随机推荐
- IDEA集成 SpringBoot+Mybaties 之 @Autowired注入报错
原因分析: 因为@Mapper注解是由ibates提供的,需要在application.yml里加上下图配置 以及在启动类入口加上 扫描你mapper接口所在的包 ,所以Spring容器是不认识这个注 ...
- canal —— 阿里巴巴mysql数据库binlog的增量订阅&消费组件
阿里巴巴mysql数据库binlog的增量订阅&消费组件canal ,转载自 https://github.com/alibaba/canal 最新更新 canal QQ讨论群已经建立,群号 ...
- TCP基础知识(二)三次握手与四次挥手
TCP详解(2):三次握手与四次挥手 TCP(Transmission Control Protocol,传输控制协议)是基于连接的协议,也就是说,在正式收发数据前,必须和对方建立可靠的连接,就好像你 ...
- img图片加载失败默认图片
<img :src="item.goods_pic" onerror="javascript:this.src='../static/images/default. ...
- SQL COUNT DISTINCT
Create table trade ( sell_id int, --卖家 buy_id int, -- 卖家 time date --交易时间 ) sell_id, buy_id, time s ...
- 如何让div覆盖canvas元素
第一步 请让该div和canvas同样处于同一画布,都用position:absolute; 然后设置canvas的z-index="-1",是的,你没看错 然后把要覆盖canva ...
- css flexbox 弹性布局
flexbox 即css flexible box layout. ie9及以下不支持flexbox. flex详细规范(https://www.w3.org/TR/css-flexbox/) 为什么 ...
- MySQL性能优化的20+条经验
1. 为查询缓存优化你的查询 大多数的MySQL服务器都开启了查询缓存.这是提高性最有效的方法之一,而且这是被MySQL的数据库引擎处理的.当有很多相同的查询被执行了多次的时候,这些查询结果会被放到一 ...
- 【Python】多重赋值之值互换
右边的值先确定,然后再开始向左赋值 s = 1 t = 2 s,t = t,s print s print t >>> 2 >>> 1 区分 s = t t = s ...
- imooc课程:Java高并发秒杀API 记录
Java高并发秒杀API之业务分析与DAO层 Java高并发秒杀API之Service层 Java高并发秒杀API之web层 Java高并发秒杀API之高并发优化 除了并发部分外的这个web开发的总结 ...
