ssm+reids缓存整合
在说正文之前我们先介绍一下redis:
redis是当今比较热门的非关系型数据库之一,他使用的是key-value的键值对来进行存储,是一个存在于内存之中的数据库,我们一般用于做数据缓存。当我们需要大量的数据查询时,如果我们都直接访问数据库时,会严重影响数据库性能。所以我们一般的操作就是在db层之上的各级使用多级的no-sql来为db提供缓冲。
因为redis是存在于内存之中,那么问题来了当我们断电时或者宕机时就会产生数据丢失,所以redis为我们提供了rdb和aof的两种持久化保存的方式,这也是为什么同样是缓存数据库我们选择redis而不选择memcache的原因。而且为了在大流量下提供稳定业务,redis还提供了redis-cluster,twemproxy,codis等集群化方案,为我们搭建分布式系统提供了可能。废话说了这么多下面开始正文。
一.添加redis对应的依赖
<!-- reids缓存-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework.data/spring-data-redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>${redis.data.version}</version>
</dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/redis.clients/jedis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>${redis.clients.version}</version>
</dependency>
依赖版本大家可以下用的最多的比较稳定。
二.添加相应的spring配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--开启aop代理-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy expose-proxy="true"/>
<!--spring添加注解扫描-->
<context:annotation-config></context:annotation-config>
<!--spring 注解扫描但是要排除spring mvc的控制器-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation"
expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"></context:exclude-filter>
</context:component-scan> <!--加载资源文件,该标签全文只能有一个-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties,classpath:redisconfig.properties"/> <!--配置数据源,阿里数据连接池-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="${jdbc.dataType}" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.usename}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/> <!-- 数据库连接池配置 -->
<property name="initialSize" value="20"/><!-- 初始化连接数量 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="5"/> <!-- 最小空闲连接数量 -->
<property name="maxActive" value="1500"/> <!-- 最大连接数量 -->
<property name="maxWait" value="60000"/> <!-- 最大建立连接等待时间(毫秒)。如果超过此时间将接到异常。设为-1表示无限制-->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="60000"/> <!-- 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="minEvictableIdleTimeMillis" value="300000"/> <!-- 配置一个连接在池中最小生存的时间,单位是毫秒 -->
<property name="validationQuery" value="SELECT 'x'"/>
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="true"/> <!--空闲时是否进行验证,检查对象是否有效 -->
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="false"/> <!--取得对象时是否进行验证,检查对象是否有效 -->
<property name="testOnReturn" value="false"/> <!--返回对象时是否进行验证 -->
<!-- 打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小 -->
<property name="poolPreparedStatements" value="true"/> <!-- 表明是否开启statement cache,默认为false,也就是不开启 -->
<property name="maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize"
value="20"/> <!-- statement cache的大小,默认为-1,也就是不限制 --> <!-- 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计 -->
<property name="filters" value="stat"/>
</bean> <bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<!-- 扫描entity包 使用别名 -->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.lwc.pojo"/>
<!-- 扫描sql配置文件:mapper需要的xml文件 -->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath*:com/lwc/dao/mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<!--根据接口名生成对应的代理类-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.lwc.dao"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName" value="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean> <!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- 注入数据库连接池 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean> <!--配置事务切面-->
<aop:config>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut="execution(* com.lwc.service.*.*(..))"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
<!-- 2 事务详情(事务通知) , 在aop筛选基础上,比如对ABC三个确定使用什么样的事务。例如:AC读写、B只读 等
<tx:attributes> 用于配置事务详情(属性属性)
<tx:method name=""/> 详情具体配置
propagation 传播行为 , REQUIRED:必须;REQUIRES_NEW:必须是新的
isolation 隔离级别
-->
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--配置redis缓存-->
<!--redis配置-->
<bean id="jedisPoolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig"> <!--控制一个pool最多有多少个状态为空闲的jedis实例-->
<property name="maxIdle" value="${redis.maxIdle}"></property>
<!--当borrow(引入)一个实例时,最大的等待时间,如果超过则抛出jedisConnectionException-->
<property name="maxWaitMillis" value="${redis.maxWaitMillis}"></property>
<property name="maxTotal" value="${redis.maxTotal}"></property>
<!-- 在在borrow一个jedis实例时,是否提前进行validate操作;如果为true,则得到的jedis实例均是可用的-->
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="${redis.testOnBorrow}"></property> </bean> <!--redis连接池-->
<bean id="jedisPool" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="jedisPoolConfig"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="1" value="${redis.host}"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="2" value="${redis.port}"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg index="3" value="${redis.timeout}"></constructor-arg> </bean>
<!-- redis连接工厂 -->
<bean id="JedisConnectionFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory">
<property name="hostName" value="${redis.host}" ></property>
<property name="port" value="${redis.port}"></property>
<property name="poolConfig" ref="jedisPoolConfig"></property>
</bean>
<!-- redis操作模板,这里采用尽量面向对象的模板 -->
<bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="JedisConnectionFactory"/>
<property name="keySerializer" ref="stringReadisSerializer"/>
<property name="valueSerializer" ref="stringReadisSerializer"/>
<property name="hashKeySerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<property name="hashValueSerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer"/>
</property>
<!--开启事务-->
<property name="enableTransactionSupport" value="true"/>
</bean> <!--使用字符串进行序列化-->
<bean id="stringReadisSerializer" class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer"/>
<!--使用JDK的序列化器进行转化-->
<bean id="jdkSerializationRedisSerializer" class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.JdkSerializationRedisSerializer"/> <bean id="getCache" class="com.lwc.redis.aspectj.GetCachAop">
<property name="redisTemplate" ref="redisTemplate"/>
</bean>
</beans>
这里是spring的基本配置,这里我没有分开来,反正都有注释
三.redis的一些基本资源文件
redis.host=localhost
redis.port=6379
redis.maxIdle=50
redis.maxTotal=100
redis.maxWaitMillis=3000
redis.testOnBorrow=true
redis.timeout=5000
这里我没有配置密码,所以就没有写pass,但是如果有需要的话可以找到redis的配置文件加上如下语句
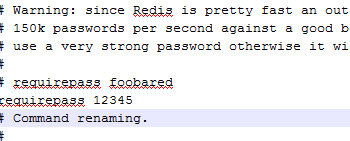
这样就可以了,如果没有配置密码而配置了<property name="password" value="${redis.password}" />将会报错
四.利用aop和自定义注解来进行实现环绕
下面是自定义注解,并且配上了一些注解的解释,还没有学过自定注解的小伙伴可以看看
package com.lwc.redis.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.*; /**自定义注解
* 2.1.1 Target:表示注解的作用目标
*
* @Target(ElementType.TYPE) //接口、类、枚举、注解
*
* @Target(ElementType.FIELD) //字段、枚举的常量
*
* @Target(ElementType.METHOD) //方法
*
* @Target(ElementType.PARAMETER) //方法参数
*
* @Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) //构造函数
*
* @Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)//局部变量
*
* @Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)//注解
*
* @Target(ElementType.PACKAGE) ///包
*
* 2.1.2 @Documented:说明该注解将被包含在javadoc中;
*
* 2.1.3 @Inherited:说明子类可以继承父类中的该注解 ;
*
* 2.1.4 @Retention:注解的保留位置;
*
* @Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE) //注解仅存在于源码中,在class字节码文件中不包含
*
* @Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) // 默认的保留策略,注解会在class字节码文件中存在,但运行时无法获得,
*
* @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) // 注解会在class字节码文件中存在,在运行时可以通过反射获取到
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//目标为方法
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//注解在类中存在,运行时通过反射获取
@Documented
@Inherited
public @interface GetCache {
String name() default "";
String value() default "";
}
定义这个注解是为了让aop可以直接根据注解来进行切面环绕,而不需要根据传统的方法来进行切点,这样会方便很多,否则的话就需要
定义接口然后对接口需要的方法进行定义切点,在实现该接口,这样也可以做到切面环绕,但是会更麻烦点,有兴趣的小伙伴可以自己试试
通知类:
package com.lwc.redis.aspectj; import com.lwc.redis.annotation.GetCache;
import com.lwc.util.RedisCache;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.io.Serializable;
import java.lang.reflect.Method; @Component
@Aspect
public class GetCachAop {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Serializable,Object> redisTemplate;
private RedisCache redisCache=new RedisCache();
//定义切点
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.lwc.redis.annotation.GetCache)")
public void getCache(){
System.out.println("获取内存数据切入点");
}
/*在所有标注了GetCache的地方切入*/
@Around("getCache()")
public Object beforeExec(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
//生成redis中的id,根据自己指定的格式
String redisKey=getCacheKey(joinPoint); //获取从redis中查询得到的对象
Object object=redisCache.getDataFromRedis(redisKey); //如果查询到了
if(null!=object){
System.out.println("从redis中获取到了数据");
return object;
}else{
System.out.println("从数据库中查询数据");
//如果没有查询到,则在数据库中进行查询
try {
object=joinPoint.proceed();
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
}
} //在目标方法执行完之后:将查到的数据放入到redis中
redisCache.setDataToRedis(redisKey,object);
return object;
} /**
* 根据方法名参数名类名获取唯一的一个键值
* 格式为yourpackage.classname.methodname(int).argsvalue123
* @param joinPoint
* @return
*/
//变量没有用到时不让警告
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private String getCacheKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint){
//获取切入方法的一些相关的信息
MethodSignature ms=(MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature(); Method method=ms.getMethod();
//获取注解中设置的对应参数
String ActionName=method.getAnnotation(GetCache.class).value();
String fieldList=method.getAnnotation(GetCache.class).name();
for(String field:fieldList.split("."))
ActionName+="."+field; //获取切点方法的参数
String id=null;
Object[] args=joinPoint.getArgs();
if(args!=null && args.length>0)
id=String.valueOf(args[0]);
ActionName+="="+id;
String redisKey=ms+"."+ActionName;
return redisKey;
} public void setRedisTemplate( RedisTemplate<Serializable, Object> redisTemplate){
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
}
上面代码都有详细注释这里就不重复了
下面是序列化的工具类:
package com.lwc.util;
import java.io.*;
public class SerializableUtil {
//将字节数组反序列化为对象
public static Object toObject(byte[] bytes){
Object obj=null;
try{
ByteArrayInputStream bis=new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(bis);
obj=ois.read();
ois.close();
bis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
//将对象序列化为字节数组
public static byte[] toByteArray(Object obj){
byte[] bytes =null;
ByteArrayOutputStream bos =new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try{
ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(bos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.flush();
bytes=bos.toByteArray();
oos.close();
bos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bytes;
}
}
下面是缓存工具类:
package com.lwc.util; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
/**
* redis缓存工具类
*/ public class RedisCache { private static JedisPool jedisPool;
//静态类进行参数的初始化
static {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext cxac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
jedisPool=(JedisPool) cxac.getBean("jedisPool");
}
//从缓存中读取数据,进行反序列化
public Object getDataFromRedis(String redisKey){
Jedis jedis=jedisPool.getResource();
byte[] result=jedis.get(redisKey.getBytes());
//如果没有查询到,就返回空
if(null==result)
return null;
return SerializableUtil.toObject(result);
} //将数据库中查到的数据放入redis中
public void setDataToRedis(String redisKey,Object obj){
byte[] bytes =SerializableUtil.toByteArray(obj);
Jedis jedis=jedisPool.getResource();
String sucess=jedis.set(redisKey.getBytes(),bytes);
if("OK".equals(sucess)){
System.out.println("数据保存成功");
}
}
}
当然我也看到有人继承cach类来使用redis缓存,下面贴出别人的代码并进行解释:
package com.ssm.redis; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock; import org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig; public class RedisCache implements Cache { private final ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
/**
* Jedis客户端
*/ @Autowired
private Jedis redisClient = createClient(); private String id; public RedisCache(final String id) {
if (id == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("必须传入ID");
}
System.out.println("MybatisRedisCache:id=" + id);
this.id = id;
} @Override
public void clear() {
redisClient.flushDB();
} @Override
public String getId() {
return this.id;
} @Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
byte[] ob = redisClient.get(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()));
if (ob == null) {
return null;
}
Object value = SerializeUtil.unSerialize(ob);
return value;
} @Override
public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() {
return readWriteLock;
} @Override
public int getSize() {
return Integer.valueOf(redisClient.dbSize().toString());
} @Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
redisClient.set(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()), SerializeUtil.serialize(value));
} @Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return redisClient.expire(SerializeUtil.serialize(key.toString()), 0);
} protected static Jedis createClient() { try {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
JedisPool pool = new JedisPool(new JedisPoolConfig(), "127.0.0.1", 6379);
return pool.getResource();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throw new RuntimeException("初始化连接池错误");
} }
这个其实是使用mybatis自带的二级缓存,从写mybatis中的缓存类来进行实现使用这种方法就不需要额外的添加aop之类的只需要在映射的dao文件中添加<cache type="packagename.RedisCache" />这样便可以直接使用redis而不需要aop配置
言归正传,我们接着使用aop来实现redis整合,下面是service使用注解来进行实现redis存取
package com.lwc.service; import com.lwc.dao.UserDao;
import com.lwc.pojo.User;
import com.lwc.redis.annotation.GetCache;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@GetCache(name = "user" ,value = "id")
public User getUser(Integer id){
return userDao.selectUser(id);
}
}
这样我们每次调用service的这个方法就可以实现从redis存取数据了。其他的UserDao和对应的映射文件我这里就不贴出来了
值得一说的是这里的实体类要继承Serializable 接口,不然会报错,因为他时间实例化对象进行序列化存入内存之中。
以上就完成了基本的redis的使用,下篇博文将会介绍redis的持久化
ssm+reids缓存整合的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC详解(四)------SSM三大框架整合之登录功能实现
为了后面讲解的需要,我们取数据都会从数据库中获取,所以这里先讲讲三大框架(Spring.SpringMVC.MyBatis)的整合.前面讲解 MyBatis 时,写了一篇 MyBatis 和 Spri ...
- SSM之框架整合
前言 SSM框架,即Spring + Spring MVC + MyBatis的整合框架集,是继SSH后比较主流的Java EE企业级框架,采用标准的MVC模式,项目结构与微软的ASP.NET MVC ...
- SSM框架的整合思路&功能实现
这是我第一篇博客,关于SSM框架的整合思路以及简单功能实现. 首先,最近刚刚学习Spring+SpringMVC+Mybatis,在开发时遇到形形色色的问题,周遭人也为我提供了一些思路,我会一点点整理 ...
- SSM框架——详细整合教程(Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis)【申明:来源于网络】
SSM框架--详细整合教程(Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis)[申明:来源于网络] 地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u014662268/article/details ...
- SSM 框架快速整合实例--学生查询
一.快速准备 SSM 框架即 Spring 框架.SpringMVC 框架.MyBatis 框架,关于这几个框架的基础和入门程序,我前面已经写过几篇文章作为基础和入门介绍了.对于这 3 个框架还不熟悉 ...
- SSM框架快速整合实例——学生查询
一.快速准备 SSM 框架即 Spring 框架.SpringMVC 框架.MyBatis 框架,关于这几个框架的基础和入门程序,我前面已经写过几篇文章作为基础和入门介绍了.这里再简单的介绍一下: 1 ...
- SSM框架——详细整合教程
SSM框架——详细整合教程(Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis) 1.基本概念 1.1.Spring Spring是一个开源框架,Spring是于2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的Jav ...
- ssm三大框架整合基本配置
ssm三大框架整合基本配置 maven目录结构 数据库脚本mysql create database maven; use maven ; -- --------------------------- ...
- SSM框架的整合与使用——实现简单的转账系统
一.整合思路 SSM框架即SpringMVC + Spring + MyBati框架集,是一种轻量级的Web开源框架.它们各自在JAVA三层架构中负责的模块如下图所示: 其中,SpringMVC与Sp ...
随机推荐
- [Luogu] 兽径管理
题面:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P1340 题解:https://www.zybuluo.com/wsndy-xx/note/1153773
- mac 安装oh-my-zsh的问题
安装完,如果想切换回mac原来的bash终端,可以: chsh -s /bin/bash 反之,切换回zsh: chsh -s /bin/zsh
- 沙雕题目 来自luogu
P5316 恋恋的数学题 题目描述 现在恋恋正在处理的题目十分简单:现在有k (2≤k≤4)k \space (2\leq k\leq 4)k (2≤k≤4)个数,恋恋不知道它们分别是几,只知道它们两 ...
- CF1197A
CF1197A 题意: 定义k阶梯子为两边各一块木板长度至少k+1,中间k块木板至少为1 .问 给你n块木板,最多能搭成几阶的梯子. 解法: 读题两小时,代码五分钟. 考虑贪心,构成梯子的两侧的木棍一 ...
- Python 自学笔记(二)
3-1.条件判断 3-1.条件判断 3-1-1.单项判断 if 3-1-2.双向判断 if...else... 3-1-3.多向判断 if...elif...else 3-2.if嵌套 4.输入 4- ...
- vue-cli项目模板的一些思考
之前有个想法,就是要利用vue写一套ui.然后当时也没有搞清楚到底怎么写. 几经周转吧,通过付费的方式在gitbook上面找到了答案. 找到答案之后再看我们正在开发的项目,看伙伴写的代码,突然发现完全 ...
- js for (i=0;i<a.length;a[i++]=0) 中等于0怎么理解?
js的问题for (i=0;i<a.length;a[i++]=0) 中等于0怎么理解? 很奇怪的一个for循环 竟然是将原来数组的数据全改为0
- react native Expo适配全面屏/Expo识别全面屏和正常屏
一.最新版本的expo已经默认支持了全面屏,即不会像react native cli一样出现底部黑边 二.但是全面屏通过Dimensions.get('window')获取的高度还是不准确,因为全面屏 ...
- c++ STL 最大值最小值
#include <iostream>#include <algorithm>#include <deque> using namespace std; //二元谓 ...
- MySQL连接错误:Can't connect to MySQL server on'localhost' (10055)
在Windows服务器上确认服务器和mysql都是正常运行,但就是连接不上.搜了一下别人的解决方案, 参考这篇https://blog.csdn.net/langren697/article/deta ...
