Machine Learning 算法可视化实现1 - 线性回归
一、原理和概念
1.回归
回归最简单的定义是,给出一个点集D,用一个函数去拟合这个点集。而且使得点集与拟合函数间的误差最小,假设这个函数曲线是一条直线,那就被称为线性回归;假设曲线是一条二次曲线,就被称为二次回归。
以下仅介绍线性回归的基本实现。
2.假设函数、误差、代价函数
参考 Machine Learning 学习笔记2 - linear regression with one variable(单变量线性回归)
最小化误差一般有两个方法:最小二乘法和梯度下降法
最小二乘法可以一步到位,直接算出未知参数,但他是有前提的。梯度下降法和最小二乘法不一样,它通过一步一步的迭代,慢慢的去靠近到那条最优直线。
平方误差:

代价函数:
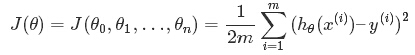 (系数是为了之后求梯度的时候方便)
(系数是为了之后求梯度的时候方便)
3.梯度下降算法
梯度下降算法是一种优化算法,它可以帮助我们找到一个函数的局部极小值,不仅用在线性回归模型中,非线性也可以。在求解损失函数的最小值时,可以通过梯度下降法来一步步的迭代求解,得到最小化的损失函数和模型参数值。反过来,如果我们需要求解损失函数的最大值,这时就需要用梯度上升法来迭代了。
下图是假设函数 h(x)、 代价函数J()和梯度下降算法:
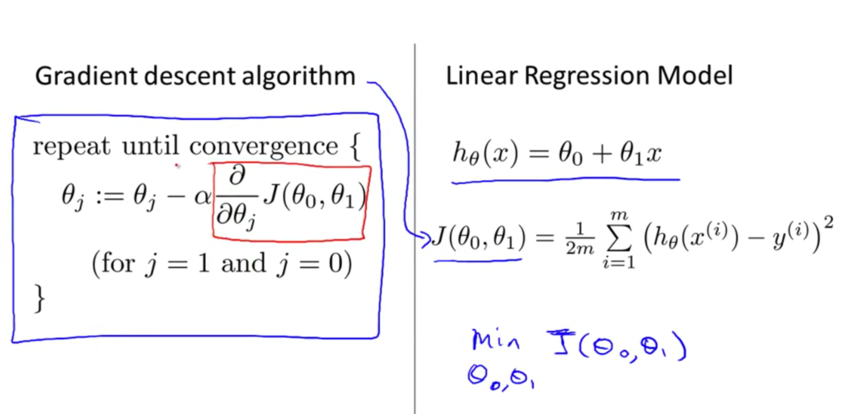
完整的梯度下降算法:
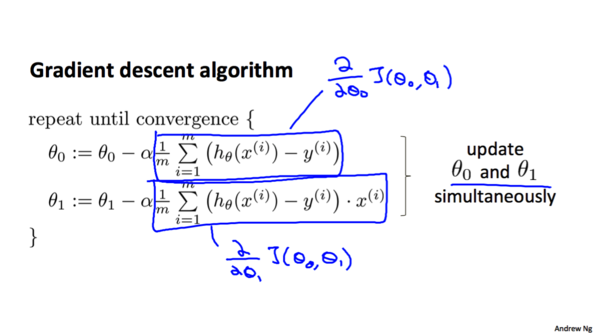
梯度下降算法的Python实现:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# @Time : 2018/3/6 18:32
# @Author : TanRong
# @Software: PyCharm
# @File : gradient descent.py import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot
import pylab # 参数含义:y=kx+b;learning_rate学习速率、步长幅度;num_iter迭代的次数 #计算梯度并更新k,b
def gradient(current_k, current_b, data, learning_rate):
k_gradient = 0
b_gradient = 0
m = float(len(data))
for i in range(0, len(data)):
x = data[i,0]
y = data[i,1]
k_gradient += (1/m)*(current_k*x + current_b - y) * x
b_gradient += (1/m)*(current_k*x + current_b - y)
update_k = current_k - learning_rate * k_gradient
update_b = current_b - learning_rate * b_gradient
return[update_k, update_b] #优化器
def optimizer(data, initial_k, initial_b, learning_rate, num_iter):
k = initial_k
b = initial_b #Gradient descent 梯度下降
for i in range(num_iter):
#更新 k、b
k,b = gradient(k, b, data, learning_rate)
return [k,b] #绘图
def plot_data(data, k, b):
x = data[:,0]
y = data[:,1]
y_predict = k * x + b
pylab.plot(x,y,'o')
pylab.plot(x,y_predict,'k-')
pylab.show() #计算平方差
def error(data, k, b):
totalError = 0;
for i in range(0, len(data)):
x = data[i,0]
y = data[i,1]
totalError += (k*x+b-y)**2
return totalError / float(len(data))
#梯度下降算法 实现线性回归
def Linear_regression():
data = np.loadtxt('train_data.csv', delimiter = ',') #训练数据
learning_rate = 0.01
initial_k = 0.0
initial_b = 0.0
num_iter = 1000 [k,b] = optimizer(data, initial_k, initial_b, learning_rate, num_iter)
print("k:", k,";b:", b)
print("平方差/代价函数:", error(data, k, b)) plot_data(data, k, b) Linear_regression()
代码和数据的下载:https://github.com/~~~
(数据用的别人的)
参考代码:
#http://blog.csdn.net/sxf1061926959/article/details/66976356?locationNum=9&fps=1 import numpy as np
import pylab def compute_error(b,m,data): totalError = 0
#Two ways to implement this
#first way
# for i in range(0,len(data)):
# x = data[i,0]
# y = data[i,1]
#
# totalError += (y-(m*x+b))**2 #second way
x = data[:,0]
y = data[:,1]
totalError = (y-m*x-b)**2
totalError = np.sum(totalError,axis=0) return totalError/float(len(data)) def optimizer(data,starting_b,starting_m,learning_rate,num_iter):
b = starting_b
m = starting_m #gradient descent
for i in range(num_iter):
#update b and m with the new more accurate b and m by performing
# thie gradient step
b,m =compute_gradient(b,m,data,learning_rate)
if i%100==0:
print 'iter {0}:error={1}'.format(i,compute_error(b,m,data))
return [b,m] def compute_gradient(b_current,m_current,data ,learning_rate): b_gradient = 0
m_gradient = 0 N = float(len(data))
#Two ways to implement this
#first way
# for i in range(0,len(data)):
# x = data[i,0]
# y = data[i,1]
#
# #computing partial derivations of our error function
# #b_gradient = -(2/N)*sum((y-(m*x+b))^2)
# #m_gradient = -(2/N)*sum(x*(y-(m*x+b))^2)
# b_gradient += -(2/N)*(y-((m_current*x)+b_current))
# m_gradient += -(2/N) * x * (y-((m_current*x)+b_current)) #Vectorization implementation
x = data[:,0]
y = data[:,1]
b_gradient = -(2/N)*(y-m_current*x-b_current)
b_gradient = np.sum(b_gradient,axis=0)
m_gradient = -(2/N)*x*(y-m_current*x-b_current)
m_gradient = np.sum(m_gradient,axis=0)
#update our b and m values using out partial derivations new_b = b_current - (learning_rate * b_gradient)
new_m = m_current - (learning_rate * m_gradient)
return [new_b,new_m] def plot_data(data,b,m): #plottting
x = data[:,0]
y = data[:,1]
y_predict = m*x+b
pylab.plot(x,y,'o')
pylab.plot(x,y_predict,'k-')
pylab.show() def Linear_regression():
# get train data
data =np.loadtxt('data.csv',delimiter=',') #define hyperparamters
#learning_rate is used for update gradient
#defint the number that will iteration
# define y =mx+b
learning_rate = 0.001
initial_b =0.0
initial_m = 0.0
num_iter = 1000 #train model
#print b m error
print 'initial variables:\n initial_b = {0}\n intial_m = {1}\n error of begin = {2} \n'\
.format(initial_b,initial_m,compute_error(initial_b,initial_m,data)) #optimizing b and m
[b ,m] = optimizer(data,initial_b,initial_m,learning_rate,num_iter) #print final b m error
print 'final formula parmaters:\n b = {1}\n m={2}\n error of end = {3} \n'.format(num_iter,b,m,compute_error(b,m,data)) #plot result
plot_data(data,b,m) if __name__ =='__main__': Linear_regression()
有一些其他方法实现某个功能,可以再看一遍
参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yangykaifa/p/7261316.html
http://blog.csdn.net/sxf1061926959/article/details/66976356?locationNum=9&fps=1
Machine Learning 算法可视化实现1 - 线性回归的更多相关文章
- Machine Learning 算法可视化实现2 - Apriori算法实现
目录 关联分析 Apriori原理 Apriori算法实现 - 频繁项集 Apriori算法实现 - 从频繁项集挖掘关联规则 一.关联分析 关联分析是一种在大规模数据集中寻找有趣关系的任务. 这些关系 ...
- 机器学习---用python实现最小二乘线性回归算法并用随机梯度下降法求解 (Machine Learning Least Squares Linear Regression Application SGD)
在<机器学习---线性回归(Machine Learning Linear Regression)>一文中,我们主要介绍了最小二乘线性回归算法以及简单地介绍了梯度下降法.现在,让我们来实践 ...
- 《Machine Learning in Action》—— 浅谈线性回归的那些事
<Machine Learning in Action>-- 浅谈线性回归的那些事 手撕机器学习算法系列文章已经肝了不少,自我感觉质量都挺不错的.目前已经更新了支持向量机SVM.决策树.K ...
- Machine Learning读书会,面试&算法讲座,算法公开课,创业活动,算法班集锦
Machine Learning读书会,面试&算法讲座,算法公开课,创业活动,算法班集锦 近期活动: 2014年9月3日,第8次西安面试&算法讲座视频 + PPT 的下载地址:http ...
- 【Machine Learning】KNN算法虹膜图片识别
K-近邻算法虹膜图片识别实战 作者:白宁超 2017年1月3日18:26:33 摘要:随着机器学习和深度学习的热潮,各种图书层出不穷.然而多数是基础理论知识介绍,缺乏实现的深入理解.本系列文章是作者结 ...
- Coursera《machine learning》--(2)单变量线性回归(Linear Regression with One Variable)
本笔记为Coursera在线课程<Machine Learning>中的单变量线性回归章节的笔记. 2.1 模型表示 参考视频: 2 - 1 - Model Representation ...
- 【Machine Learning】单参数线性回归 Linear Regression with one variable
最近开始看斯坦福的公开课<Machine Learning>,对其中单参数的Linear Regression(未涉及Gradient Descent)做个总结吧. [设想] ...
- [Machine Learning] 浅谈LR算法的Cost Function
了解LR的同学们都知道,LR采用了最小化交叉熵或者最大化似然估计函数来作为Cost Function,那有个很有意思的问题来了,为什么我们不用更加简单熟悉的最小化平方误差函数(MSE)呢? 我个人理解 ...
- machine learning 之 多元线性回归
整理自Andrew Ng的machine learning课程 week2. 目录: 多元线性回归 Multivariates linear regression /MLR Gradient desc ...
随机推荐
- ant自动编译打包android项目
源代码及可执行文件下载地址:http://files.cnblogs.com/rainboy2010/antdemo.zip Android打包APK的流程如下: 下面我们开始尝试使用ant进行ap ...
- python与用户交互、数据类型
一.与用户交互 1.什么是用户交互: 程序等待用户输入一些数据,程序执行完毕反馈信息. 2.如何使用 在python3中使用input,input会将用户输入的如何内容存为字符串:在python中分为 ...
- (*(volatile unsigned long *)详解
(*(volatile unsigned long *) 对于不同的计算机体系结构,设备可能是端口映射,也可能是内存映射的.如果系统结构支持独立的IO地址空间,并且是端口映射,就必须使用汇编语言完成实 ...
- 使用 mod_rewrite 来修改 Confluence 6 的 URLs
备注:这个页面的文档是 Apache 的配置,而不是 Confluence 自己的配置.Atlassian 将会对 Confluence 的配置提供支持,但是我们不能保证能够对你所有在配置 Apach ...
- elementui上传图片到七牛云服务器
注册七牛云 首先,注册七牛云,并且完成实名认证,完成后会在个人中心->秘钥管理中看到两个秘钥AccessKey/SecretKey 创建存储空间(必须要实名认证) 生成上传凭证 为了实现上传,我 ...
- SSM框架整合篇
目录 SSM整合 框架搭建步骤 SSM整合 Author:SimpleWu github(已上传SSMrest风格简单增删该查实例):https://gitlab.com/450255266/code ...
- laravel 配置设置
public function updateRegisterSetting(Request $request, Configuration $config) { $conf = $request-&g ...
- fastJson常用方法总结
1.了解json json就是一串字符串 只不过元素会使用特定的符号标注. {} 双括号表示对象 [] 中括号表示数组 "" 双引号内是属性或值 : 冒号表示后者是前者的值(这个值 ...
- 饮冰三年-人工智能-linux-08 软件包管理(Python的安装)
1:软件包存放的位置 media/CentOS_6.9_Final/Packages文件夹下 2.RPM就是Red Hat Package Manger(红帽软件包管理工具)的缩写. 2.1 常用的命 ...
- HDU5950 Recursive sequence (矩阵快速幂)
Recursive sequence Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Other ...
