C. Queen Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) dfs
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given a rooted tree with vertices numerated from 11 to nn. A tree is a connected graph without cycles. A rooted tree has a special vertex named root.
Ancestors of the vertex ii are all vertices on the path from the root to the vertex ii, except the vertex ii itself. The parent of the vertex ii is the nearest to the vertex ii ancestor of ii. Each vertex is a child of its parent. In the given tree the parent of the vertex ii is the vertex pipi. For the root, the value pipi is −1−1.
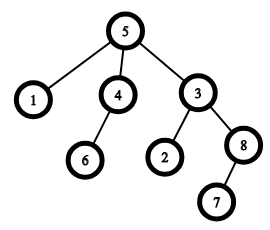 An example of a tree with n=8n=8, the root is vertex 55. The parent of the vertex 22 is vertex 33, the parent of the vertex 11 is vertex 55. The ancestors of the vertex 66 are vertices 44 and 55, the ancestors of the vertex 77 are vertices 88, 33 and 55
An example of a tree with n=8n=8, the root is vertex 55. The parent of the vertex 22 is vertex 33, the parent of the vertex 11 is vertex 55. The ancestors of the vertex 66 are vertices 44 and 55, the ancestors of the vertex 77 are vertices 88, 33 and 55
You noticed that some vertices do not respect others. In particular, if ci=1ci=1, then the vertex ii does not respect any of its ancestors, and if ci=0ci=0, it respects all of them.
You decided to delete vertices from the tree one by one. On each step you select such a non-root vertex that it does not respect its parent and none of its children respects it. If there are several such vertices, you select the one with the smallest number. When you delete this vertex vv, all children of vv become connected with the parent of vv.
 An example of deletion of the vertex 77.
An example of deletion of the vertex 77.
Once there are no vertices matching the criteria for deletion, you stop the process. Print the order in which you will delete the vertices. Note that this order is unique.
The first line contains a single integer nn (1≤n≤1051≤n≤105) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The next nn lines describe the tree: the ii-th line contains two integers pipi and cici (1≤pi≤n1≤pi≤n, 0≤ci≤10≤ci≤1), where pipi is the parent of the vertex ii, and ci=0ci=0, if the vertex ii respects its parents, and ci=1ci=1, if the vertex ii does not respect any of its parents. The root of the tree has −1−1 instead of the parent index, also, ci=0ci=0 for the root. It is guaranteed that the values pipi define a rooted tree with nn vertices.
In case there is at least one vertex to delete, print the only line containing the indices of the vertices you will delete in the order you delete them. Otherwise print a single integer −1−1.
5
3 1
1 1
-1 0
2 1
3 0
1 2 4
5
-1 0
1 1
1 1
2 0
3 0
-1
8
2 1
-1 0
1 0
1 1
1 1
4 0
5 1
7 0
5
The deletion process in the first example is as follows (see the picture below, the vertices with ci=1ci=1 are in yellow):
- first you will delete the vertex 11, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (the vertex 22) do not respect it, and 11 is the smallest index among such vertices;
- the vertex 22 will be connected with the vertex 33 after deletion;
- then you will delete the vertex 22, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (the only vertex 44) do not respect it;
- the vertex 44 will be connected with the vertex 33;
- then you will delete the vertex 44, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (there are none) do not respect it (vacuous truth);
- you will just delete the vertex 44;
- there are no more vertices to delete.
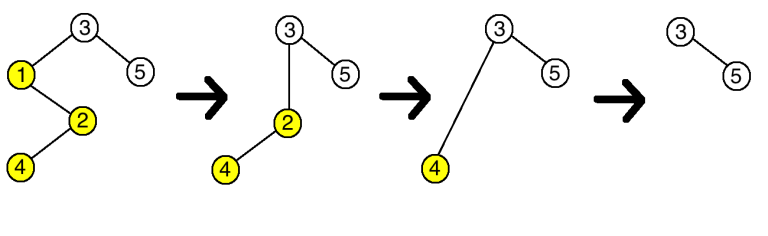
In the second example you don't need to delete any vertex:
- vertices 22 and 33 have children that respect them;
- vertices 44 and 55 respect ancestors.

In the third example the tree will change this way:
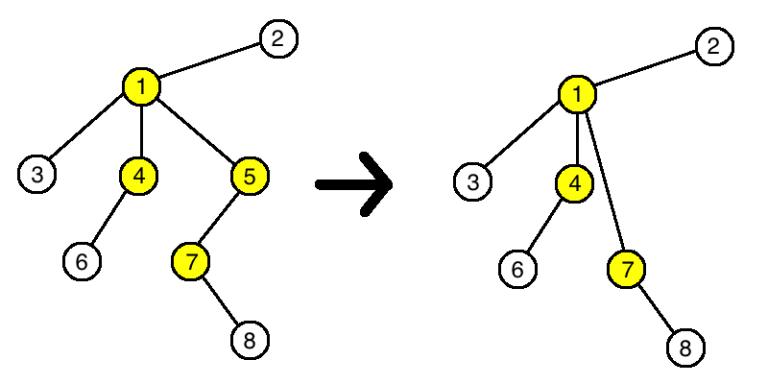 这个题目也比较简单,就是一个dfs,我发现一般的图都可以用dfs解决,这个题目看起来还比较可怕,实际很简单啦。看代码吧。
这个题目也比较简单,就是一个dfs,我发现一般的图都可以用dfs解决,这个题目看起来还比较可怕,实际很简单啦。看代码吧。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 100;
struct node
{
int to, dist;
node(int to=0,int dist=0):to(to),dist(dist){}
};
vector<node>vec[maxn];
int cnt=0,a[maxn]; int dfs(int s,int d)
{
int flag = 1;
int len = vec[s].size();
// if (len == 0 && d) return 1;
// if (len == 0 && !d) return 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if (dfs(vec[s][i].to, vec[s][i].dist) == 0) flag = 0;
}
if (d)
{
//printf("%d %d %d\n",cnt, s, d);
if(flag) a[cnt++] = s;
return 1;
}
return 0;
} int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int root = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int b, x;
cin >> b >> x;
if (b == -1) root = i;
else
{
vec[b].push_back(node(i, x));
}
}
cnt = 0;
int ans=dfs(root,0);
// printf("cnt=%d\n", cnt);
sort(a, a+cnt);
if(cnt==0)
{
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<cnt-1;i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", a[cnt - 1]);
return 0;
}
C. Queen Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) dfs的更多相关文章
- C. Queen Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) (搜索)
---恢复内容开始--- You are given a rooted tree with vertices numerated from 11 to nn . A tree is a connect ...
- [题解] Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) B. Nirvana
Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) B. Nirvana [题目描述] B. Nirvana time limit per test1 second memory limit ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 1)
今天试图用typora写题解 真开心 参考 你会发现有很多都是参考的..zblzbl Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 1) 最近脑子不行啦 需要cf来缓解一下 A. The B ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2)C. Queen
C. Queen time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input outpu ...
- B. Nirvana Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) (递归dfs)
---恢复内容开始--- Kurt reaches nirvana when he finds the product of all the digits of some positive integ ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) 训练实录 (5/6)
The Doors +0 找出输入的01数列里,0或者1先出完的的下标. Nirvana +3 输入n,求1到n的数字,哪个数逐位相乘的积最大,输出最大积. 思路是按位比较,从低到高,依次把小位换成全 ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) Solution
传送门 A.The Doors 看懂题目就会写的题 给一个 $01$ 序列,找到最早的位置使得 $0$ 或 $1$ 已经全部出现 #include<iostream> #include&l ...
- CodeForces Round #549 Div.2
A. The Doors 代码: #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ; int N; , One = ; int a[maxn], ...
- [ Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2)][D. The Beatles][exgcd]
https://codeforces.com/contest/1143/problem/D D. The Beatles time limit per test 1 second memory lim ...
随机推荐
- 结构型---组合模式(Composite Pattern)
组合模式的定义 组合模式允许你将对象组合成树形结构来表现”部分-整体“的层次结构,使得客户以一致的方式处理单个对象以及对象的组合. 组合模式实现的最关键的地方是——简单对象和复合对象必须实现相同的接口 ...
- 从零开始学安全(十)●TCP/IP协议栈
局域网靠mac 地址通信
- laravel的时间日期处理包Carbon用法
时间日期处理包--Carbon Carbon – 是继承自 PHP DateTime 类的 API 扩展,它使得处理日期和时间更加简单.Laravel 中默认使用的时间处理类就是 Carbon. La ...
- Centos6.5安装MySQL5.6备忘记录
Centos6.5安装MySQL5.6 1. 查看系统状态 [root@itzhouq32 tools]# cat /etc/issue CentOS release 6.5 (Final) Kern ...
- Java 注解原理
下面来看看Java中注解是如何实现的 创建注解类Inter: 创建测试类Test: 在程序第二句设置断点,可以看到: 可以看到,注解的实例是一个动态代理类的对象. 要想查看这个动态代理类,可以在代码中 ...
- xml方式封装数据方法
1.xml方式封装数据方法 2.demo <?php xml方式封装数据方法 /** * [xmlEncode description] * @param [type] $code [descr ...
- thinkphp3.2模块名如何不区分大小写?
thinkphp3.2中已配置:'URL_CASE_INSENSITIVE' => true,对于控制器及操作名大小写都可以,但仍对于模块名的大小写就运行机制出错,比如:http://www.x ...
- Javascript 跨域知识详细介绍
JS跨域知识总结: 在“跨域”一词经常性地出现以前,我们其实已经频繁地使用它了.如在A网站的img,src指向B网站的某一图片地址,毫无疑问,这在通常情况下都是能正常显示的(且不论防盗链技术):同样, ...
- H5新增特性、方法
1.FileReader和progress实现实时监控文件上传进度 2.HTML5新增的客户端校验 1.调用checkValidity方法进行校验 2.setCustomValidity自定义错误
- SpringMVC 异步与定时使用示例
1.Spring 的xml配置: <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <task:annotation-driven executor="annotation ...
