iOS - Block 代码块
1、Block
Block 是一段预先准备好的代码,可以在需要的时候执行,可以当作参数传递。Block 可以作为函数参数或者函数的返回值,而其本身又可以带输入参数或返回值。Block 是 C 语言的,类似于一个匿名函数,它和传统的函数指针很类似,但是 Block 是 inline(内联函数)的,并且默认情况下它对局部变量是只读的。
苹果官方建议尽量多用 Block。在多线程、异步任务、集合遍历、集合排序、动画转场用的很多。
Block 语法
// Block as a local variable
returnType (^blockName)(parameterTypes) = ^returnType(parameters) {...}; // Block as a property
@property (nonatomic, copy) returnType (^blockName)(parameterTypes); // Block as a method parameter
- (void)someMethodThatTakesABlock:(returnType (^)(parameterTypes))blockName; // Block as an argument to a method call
[someObject someMethodThatTakesABlock: ^returnType (parameters) {...}]; // Block as typedef
typedef returnType (^TypeName)(parameterTypes);
TypeName blockName = ^returnType(parameters) {...};
2、Block 的使用
2.1 Block 的定义
Block 的简单定义
// 定义 Block
/*
定义了一个名叫 MySum 的 Block 对象,它带有两个 int 型参数,返回 int 型。等式右边就是 Block 的具体实现,大括号后需加分号
*/
int (^MySum)(int, int) = ^(int a, int b){ return a + b;
}; // 调用 Block
int sum = MySum(10, 12);
Block 数据类型的定义
// 定义 block 数据类型 MyBlock
typedef int (^MyBlock)(int, int); // 定义 MyBlock 的变量
MyBlock myblock; // 实现 MyBlock 的变量 1
myblock = ^(int a, int b){ return a + b;
}; // 调用 MyBlock 的变量 1
int sum = myblock(10, 12); // 实现 MyBlock 的变量 2
myblock = ^(int a, int b){ return a - b;
}; // 调用 MyBlock 的变量 2
int minus = myblock(13, 2);
2.2 Block 访问局部变量
Block 可以访问局部变量,但是不能修改,如果要修改需加关键字 __block(双下划线)。
// 这样定义时,局部变量 sum 只能读取值不能修改,编译时会报错
// int sum = 10; // 这样定义时,局部变量 sum 既可以读取值又能修改
__block int sum = 10; int (^MyBlock)(int) = ^(int a){ // 对局部变量值修改
sum ++; // 读取局部变量的值
return a * sum;
}; int result = MyBlock(5);
3、Block 的回调
3.1 Block 回调使用
// Block1.h
// block 属性变量定义
/*
要使用 copy 类型,格式:@property (nonatomic, copy) 返回值类型 (^变量名) (参数类型列表);
*/
@property (nonatomic, copy) void (^completion) (NSString *);
// 调用 block 代码段声明
- (void)useBlock;
// Block1.m
// 调用 block 代码段
- (void)useBlock {
// 设置 block 的回调值
// 判断是否设置了 block
if (self.completion != nil) {
// 设置回调值
self.completion(@"hello world");
}
}
// Block.m
#import "Block1.h"
Block1 *block = [[Block1 alloc] init];
// 设置 block 代码段
block.completion = ^(NSString *str) {
// 结果:string = @"hello world"
NSString *string = str;
};
// 调用 block 代码段
[block useBlock];
3.2 Block 回调封装
// Block2.h
// block 方法参数定义
// 类方法定义
+ (Block2 *)blockWithCompletion:(void (^) (NSString *)) completion;
// 调用 block 代码段声明
- (void)useBlock;
// Block2.m
// block 属性变量定义
// 要使用 copy 类型,格式:@property (nonatomic, copy) 返回值类型 (^变量名) (参数类型列表);
@property (nonatomic, copy) void (^completion) (NSString *);
// 调用 block 代码段
- (void)useBlock {
// 设置 block 的回调值
// 判断是否设置了 block
if (self.completion != nil) {
// 设置回调值
self.completion(@"hello world");
}
}
// 类方法实现
+ (Block2 *)blockWithCompletion:(void (^)(NSString *))completion {
Block2 *bl = [[Block2 alloc] init];
// 设置属性的值
bl.completion = completion;
return bl;
}
// Block.m
#import "Block2.h”
// 设置 block 代码段
Block2 *block = [Block2 blockWithCompletion:^(NSString *str) {
// 结果:string = @"hello world"
NSString *string = str;
}];
// 调用 block 代码段
[block useBlock];
4、Block 属性定义中为什么使用 copy 修饰
ARC 开发的时候,编译器底层对 block 做过一些优化,使用 copy 修饰可以防止出现内存泄漏。
从内存管理的角度而言,程序员需要管理的内存只有堆区的。如果用 strong 修饰,相当于强引用了一个栈区的变量。
而使用 copy 修饰,在设置数值的时候,可以把局部变量从栈区复制到堆区。
// 用 copy 修饰定义属性
@property (nonatomic, copy) void (^myTask)(); // 定义,myBlock 是保存在栈区的,出了作用域,就应该被销毁
void (^myBlock)() = ^ { NSLog(@"hello");
}; // 用属性记录
self.myTask = myBlock; // 执行
self.myTask();
5、循环引用
1、在 Block 中调用 self 容易产生循环引用,一旦出现循环引用的话内存就得不到释放,因此一定要小心内存管理问题。
@implementation ViewController // 在 Block 中调用 self 容易产生循环引用
[[QWebImageManager sharedManager] downloadImage:self.urlStr completion:^(UIImage *image) {
self.image = image;
}]; @end
- 查询内存管理问题解决办法:
1> 打印法
最好在基类 controller 下重写 dealloc,加一句打印日志,表示类可以得到释放。如果出现无打印信息,说明这个类一直得不到释放,表明很有可能是使用 block 的地方出现循环引用了。对于 block 中需要引用外部 controller 的属性或者成员变量时,一定要使用弱引用,特别是成员变量像
_testId这样的,很多人都没有使用弱引用,导致内存得不到释放。// 判断是否存在循环引用,无法释放时即存在循环引用
- (void)dealloc {
NSLog(@"成功退出");
}
2> 利用 instrument 检测内存泄露
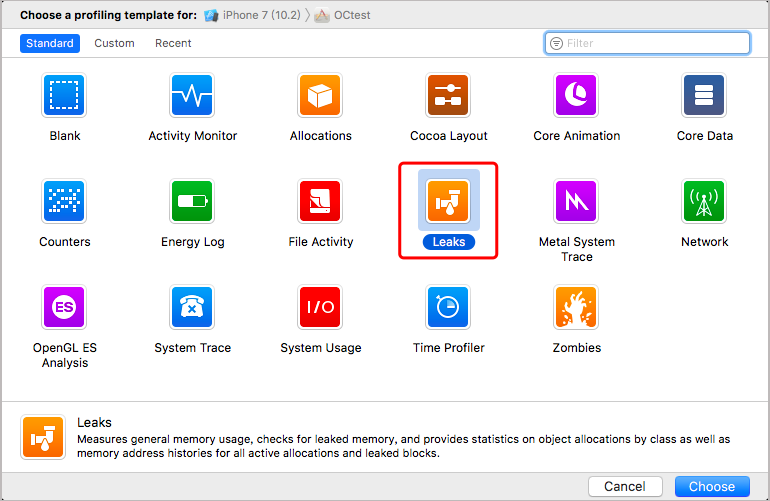
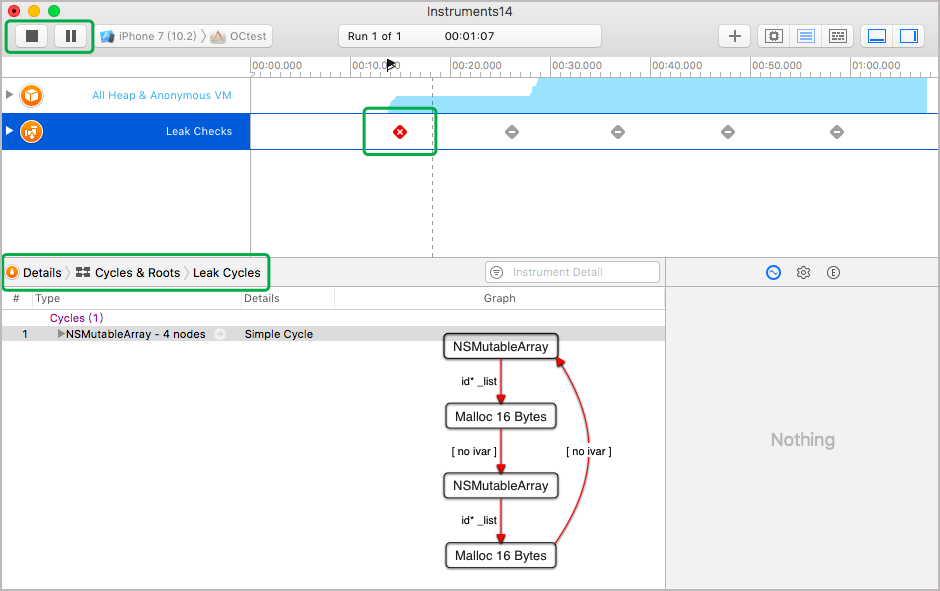
在 Xcode 的 instrument 工具集可以很方便的检测循环引用。Product => profile => 选择 Leaks,之后点击运行,如果出现红色,点击 Details => Cycles&Roots
- 解决循环引用方法
可以使用关键字 __weak 声明一个弱变量,或者为属性指定 weak 特性。如:
@implementation ViewController // 弱引用 self,typeof(self) 等价于 ViewController
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self; [[QWebImageManager sharedManager] downloadImage:self.urlStr completion:^(UIImage *image) {
weakSelf.image = image;
}]; @end
2、当 block 本身不被 self 持有,而被别的对象持有,同时不产生循环引用的时候,就不需要使用 weak self 了。最常见的代码就是 UIView 的动画代码,我们在使用 UIView 的 animateWithDuration:animations 方法 做动画的时候,并不需要使用 weak self,因为引用持有关系是:
UIView 的某个负责动画的对象持有了 block
block 持有了 self
因为 self 并不持有 block,所以就没有循环引用产生,所以就不需要使用 weak self 了。
[UIView animateWithDuration:0.2 animations:^{
self.alpha = 1;
}];
当动画结束时,UIView 会结束持有这个 block,如果没有别的对象持有 block 的话,block 对象就会释放掉,从而 block 会释放掉对于 self 的持有。整个内存引用关系被解除。
3、为什么 weakSelf 需要配合 strong self 使用
我们知道,在使用 block 的时候,为了避免产生循环引用,通常需要使用 weakSelf 与 strongSelf,写下面这样的代码。那么请问:为什么 block 里面还需要写一个 strong self。
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
[self doSomeBackgroundJob:^{ __strong typeof(weakSelf) strongSelf = weakSelf;
if (strongSelf) {
...
}
}];
在 block 中先写一个 strong self,其实是为了避免在 block 的执行过程中,突然出现 self 被释放的尴尬情况。通常情况下,如果不这么做的话,还是很容易出现一些奇怪的逻辑,甚至闪退。我们以 AFNetworking 中 AFNetworkReachabilityManager.m 的一段代码举例:
__weak __typeof(self)weakSelf = self;
AFNetworkReachabilityStatusBlock callback = ^(AFNetworkReachabilityStatus status) { __strong __typeof(weakSelf)strongSelf = weakSelf; strongSelf.networkReachabilityStatus = status;
if (strongSelf.networkReachabilityStatusBlock) {
strongSelf.networkReachabilityStatusBlock(status);
}
};
如果没有 strongSelf 的那行代码,那么后面的每一行代码执行时,self 都可能被释放掉了,这样很可能造成逻辑异常。特别是当我们正在执行 strongSelf.networkReachabilityStatusBlock(status); 这个 block 闭包时,如果这个 block 执行到一半时 self 释放,那么多半情况下会 Crash。
这里有一篇文章详细解释了这个问题:https://dhoerl.wordpress.com/2013/04/23/i-finally-figured-out-weakself-and-strongself/
6、多个异步 Block 按照顺序执行
异步 Block 的执行顺序一般为先执行 Block 前的代码,再执行 Block 之后的代码,最后执行 Block 中的代码,如下代码。
创建
@property (nonatomic, copy) void (^completion) (NSString *); - (void)dlownloadCompletion:(void (^)(NSString *str))completion { self.completion = completion; if (self.completion) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{ [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:2]; self.completion(@"Hello World");
});
}
}
使用
NSLog(@"Hello World 1"); [self dlownloadCompletion:^(NSString *str) { NSLog(@"%@ 2, %@", str, [NSThread currentThread]);
}]; NSLog(@"Hello World 3");
执行效果
22:07:12.520 OCTest[79089:3232021] Hello World 1
22:07:12.521 OCTest[79089:3232021] Hello World 3
22:07:14.521 OCTest[79089:3232160] Hello World 2, <NSThread: 0x60000006a500>{number = 3, name = (null)}
那么如何实现先执行 Block 中的代码,再执行 Block 之后的代码呢?使用线程阻塞的方式。
6.1 单个异步 Block
使用
NSLog(@"Hello World 1"); // 需要在子线程中执行,否则会阻塞主线程
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{ NSLog(@"Hello World 2"); // 创建 semaphore
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0); [self dlownloadCompletion:^(NSString *str) { NSLog(@"%@ 3, %@", str, [NSThread currentThread]); // 发出已完成的信号
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
}]; // 等待执行,阻塞线程
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); NSLog(@"Hello World 4");
}); NSLog(@"Hello World 5");
执行效果
22:13:40.457 OCTest[63696:2154201] Hello World 1
22:13:40.458 OCTest[63696:2154201] Hello World 5
22:13:40.458 OCTest[63696:2154254] Hello World 2
22:13:42.460 OCTest[63696:2154404] Hello World 3, <NSThread: 0x60000007b840>{number = 3, name = (null)}
22:13:42.461 OCTest[63696:2154254] Hello World 4
6.2 多个异步 Block
使用
NSLog(@"Hello World 1"); // 需要在子线程中执行,否则会阻塞主线程
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{ NSLog(@"Hello World 2"); // 创建 semaphore
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore1 = dispatch_semaphore_create(0); [self dlownloadCompletion:^(NSString *str) { NSLog(@"%@ 3, %@", str, [NSThread currentThread]); // 发出已完成的信号
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore1);
}]; // 等待执行,阻塞线程
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore1, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); // 创建 semaphore
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore2 = dispatch_semaphore_create(0); [self dlownloadCompletion:^(NSString *str) { NSLog(@"%@ 4, %@", str, [NSThread currentThread]); // 发出已完成的信号
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore2);
}]; // 等待执行,阻塞线程
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore2, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); NSLog(@"Hello World 5");
}); NSLog(@"Hello World 6");
执行效果
22:15:24.288 OCTest[63748:2156048] Hello World 1
22:15:24.289 OCTest[63748:2156048] Hello World 6
22:15:24.289 OCTest[63748:2156165] Hello World 2
22:15:26.361 OCTest[63748:2156450] Hello World 3, <NSThread: 0x608000266700>{number = 3, name = (null)}
22:15:28.429 OCTest[63748:2156450] Hello World 4, <NSThread: 0x608000266700>{number = 3, name = (null)}
22:15:28.429 OCTest[63748:2156165] Hello World 5
6.3 单 for 循环中异步 Block
使用
NSLog(@"Hello World 1"); // 需要在子线程中执行,否则会阻塞主线程
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{ NSLog(@"Hello World 2"); // 创建 semaphore
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0); // block 完成回调计数
__block NSInteger count = 0; __weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self; int loopCount = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < loopCount; i++) { [self dlownloadCompletion:^(NSString *str) { NSLog(@"%@ 3 - %li, %@", str, count, [NSThread currentThread]); @synchronized (weakSelf) { // 完成回调计数加 1
count++; if (count == loopCount) { [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:5]; // 发出已完成的信号
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
}
}
}];
} // 等待执行,阻塞线程
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); NSLog(@"Hello World 4");
}); NSLog(@"Hello World 6");
执行效果
22:54:27.550 OCTest[64721:2187151] Hello World 1
22:54:27.551 OCTest[64721:2187151] Hello World 6
22:54:27.551 OCTest[64721:2187249] Hello World 2
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187248] Hello World 3 - 2, <NSThread: 0x60000026e600>{number = 4, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187276] Hello World 3 - 4, <NSThread: 0x608000266980>{number = 6, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187280] Hello World 3 - 7, <NSThread: 0x608000265c80>{number = 8, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187278] Hello World 3 - 5, <NSThread: 0x608000266740>{number = 7, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187251] Hello World 3 - 1, <NSThread: 0x60000007e200>{number = 3, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187277] Hello World 3 - 3, <NSThread: 0x608000266800>{number = 5, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187281] Hello World 3 - 8, <NSThread: 0x60000026e540>{number = 9, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187279] Hello World 3 - 6, <NSThread: 0x608000266a40>{number = 10, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187282] Hello World 3 - 9, <NSThread: 0x608000266bc0>{number = 11, name = (null)}
22:54:29.615 OCTest[64721:2187283] Hello World 3 - 10, <NSThread: 0x60000026e800>{number = 12, name = (null)}
22:54:34.676 OCTest[64721:2187249] Hello World 4
6.4 嵌套 for 循环中异步 Block
使用
NSLog(@"Hello World 1"); // 需要在子线程中执行,否则会阻塞主线程
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(0, 0), ^{ NSLog(@"Hello World 2"); // 创建 semaphore
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0); // block 完成回调计数
__block NSInteger count = 0; __weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self; int loopCount1 = 4;
int loopCount2 = 5;
for (int i = 0; i < loopCount1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < loopCount2; j++) { [self dlownloadCompletion:^(NSString *str) { NSLog(@"%@ 3 - %li, %@", str, count, [NSThread currentThread]); @synchronized (weakSelf) { // 完成回调计数加 1
count++; if (count == loopCount1 * loopCount2) { [NSThread sleepForTimeInterval:5]; // 发出已完成的信号
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
}
}
}];
}
} // 等待执行,阻塞线程
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER); NSLog(@"Hello World 4");
}); NSLog(@"Hello World 6");
执行效果
23:01:09.926 OCTest[64907:2192862] Hello World 1
23:01:09.928 OCTest[64907:2192862] Hello World 6
23:01:09.928 OCTest[64907:2193485] Hello World 2
23:01:11.931 OCTest[64907:2192981] Hello World 3 - 1, <NSThread: 0x608000260680>{number = 3, name = (null)}
23:01:11.931 OCTest[64907:2193486] Hello World 3 - 2, <NSThread: 0x600000073080>{number = 23, name = (null)}
23:01:11.932 OCTest[64907:2193487] Hello World 3 - 3, <NSThread: 0x60000007c880>{number = 24, name = (null)}
23:01:11.932 OCTest[64907:2193488] Hello World 3 - 4, <NSThread: 0x60000007c8c0>{number = 25, name = (null)}
23:01:11.933 OCTest[64907:2193489] Hello World 3 - 5, <NSThread: 0x60000007c900>{number = 26, name = (null)}
23:01:11.933 OCTest[64907:2193490] Hello World 3 - 6, <NSThread: 0x60000007c940>{number = 27, name = (null)}
23:01:11.933 OCTest[64907:2193491] Hello World 3 - 7, <NSThread: 0x60000007c980>{number = 28, name = (null)}
23:01:11.933 OCTest[64907:2193492] Hello World 3 - 8, <NSThread: 0x60000007c9c0>{number = 29, name = (null)}
23:01:11.934 OCTest[64907:2193493] Hello World 3 - 9, <NSThread: 0x60000007ca00>{number = 30, name = (null)}
23:01:11.934 OCTest[64907:2193494] Hello World 3 - 10, <NSThread: 0x60000007ca40>{number = 31, name = (null)}
23:01:11.935 OCTest[64907:2193495] Hello World 3 - 11, <NSThread: 0x60000007ca80>{number = 32, name = (null)}
23:01:11.936 OCTest[64907:2193496] Hello World 3 - 12, <NSThread: 0x608000073f80>{number = 33, name = (null)}
23:01:11.937 OCTest[64907:2193497] Hello World 3 - 13, <NSThread: 0x60000007cac0>{number = 34, name = (null)}
23:01:11.938 OCTest[64907:2193498] Hello World 3 - 14, <NSThread: 0x60000007cb00>{number = 35, name = (null)}
23:01:11.938 OCTest[64907:2193499] Hello World 3 - 15, <NSThread: 0x60000007cb40>{number = 36, name = (null)}
23:01:11.938 OCTest[64907:2193500] Hello World 3 - 16, <NSThread: 0x60000007cb80>{number = 37, name = (null)}
23:01:11.939 OCTest[64907:2193501] Hello World 3 - 17, <NSThread: 0x60000007cbc0>{number = 38, name = (null)}
23:01:11.939 OCTest[64907:2193502] Hello World 3 - 18, <NSThread: 0x60000007cc00>{number = 39, name = (null)}
23:01:11.940 OCTest[64907:2193503] Hello World 3 - 19, <NSThread: 0x60000007cc40>{number = 40, name = (null)}
23:01:11.940 OCTest[64907:2193504] Hello World 3 - 20, <NSThread: 0x60000007cc80>{number = 41, name = (null)}
23:01:17.006 OCTest[64907:2193485] Hello World 4
iOS - Block 代码块的更多相关文章
- IOS Block代码块的定义与使用
代码块的本质是和其他的变量类似,不同的是,代码块存储的数据是一个函数体.使用代码块,你可以像调用其他标准函数一样的调用,可以传入参数,并得到返回值. 脱字符是代码块的语法标记.下图表示代码块的 ...
- block(代码块)的介绍以及使用方法和变量之间的关系
http://blog.csdn.net/menxu_work/article/details/8762848 block(代码块)的介绍以及使用方法和变量之间的关系 block(代码块)的介绍以及使 ...
- block代码块介绍
关于block的简单介绍 什么是block? Block是C语言的一个语法特性,同时也是C语言的运行时特性,它很像C中的函数指针,因为你可以像使用函数指针一样的去使用block对象:它也很像C++中的 ...
- Block代码块中使用局部变量注意点
第一次写代码遇到报这个错,实在是想不通为什么,按常理应该是不会有问题,报错的呀??纠结了一会之后只好仔细查看报错原因咯,原来是: 当我们在block代码块中使用局部变量时,就会很容易出现如图的错误. ...
- IOS学习4——block代码块
本文转载自:iOS开发-由浅至深学习block 一.关于block 在iOS 4.0之后,block横空出世,它本身封装了一段代码并将这段代码当做变量,通过block()的方式进行回调.这不免让我们想 ...
- iOS - OC Block 代码块
前言 Block 是一段预先准备好的代码,可以在需要的时候执行,可以当作参数传递.Block 可以作为函数参数或者函数的返回值,而其本身又可以带输入参数或返回值.Block 是 C 语言的,类似于一个 ...
- OC Block(代码块)
#import "ViewController.h" @interface ViewController () @end @implementation ViewControlle ...
- ios 显示代码块(show the code snippet library)
在项目的实际开发中,我们会重复的书写很多的代码,我经常是需要用到某一个功能,就从以前的项目中复制粘贴过来,很是麻烦 下面就为大家提供两种不错的方法, 一.宏定义,这个大家应该很熟悉,在这里就不做多的介 ...
- iOS:自定义代码块{ }
1.Xcode本身带有编码常用的代码块可供使用,如下图 调用方法: (1)直接拖到代码区域中: (2)使用快捷键,键入 “while”, Xcode就会出现自动完成的提示 也可以自定义自己常用的代码块 ...
随机推荐
- Jython安装步骤
1.下载安装包 2.执行安装 Java -jar [此处是下载的jython jar包名],或者双击jar包夜可以 3.配置环境变量 新增JYTHON_THOME的环境变量,并设置为安装路径. 配置c ...
- MEANIO
sudo npm install -g bower sudo npm install -g meanio sudo bower cache clean --allow-root sudo mean i ...
- 【PHP设计模式 06_GuanChaZhe.php】观察者模式
<?php /** * [观察者模式] * PHP5中提供了 观察者(observer) 和 被观察者(subject) 的接口 * 在手册搜索:SplSubject (PHP 5 >= ...
- 27、oracle(三)
1)掌握增.删.改数据和事务操作 2)掌握[视图]和同义词 3)掌握[序列]和索引 4)了解有关用户和权限的控制 ------------------------------------------- ...
- 霸气的jQ插件
http://codepen.io/ canvas的各种实例 1.The Responsive jQuery Content Slider http://bxslider.com/ 2.ThemePu ...
- IOCTL函数用法
http://blog.163.com/he_junwei/blog/static/19793764620152510533753/ http://blog.csdn.net/styyzxjq2009 ...
- Eclipse 中outline的小图标的含义(zend也一样)
颜色:绿色:public黄色:protected蓝色:no modifier红色:private形状:实心:method空心:variable实心中间有字母C:classClass右侧有向右的箭头:运 ...
- gcc/g++动态链接库和静态库的链接顺序
转自:http://withc8212.blog.163.com/blog/static/11656983820109263562854/ so文件:动态库a文件: 静态库exe文件:可执行程序(li ...
- 2014江西理工大学C语言程序竞赛高级组
Beautiful Palindrome Number 题意:求N里面有多少个符合要求的数字(数字要求:回文数,且前一半部分是不严格递增) 解法:打表 #include<bits/stdc++. ...
- [转]Windows8下设置VS默认启动方式为管理员启动
在Windows7下通常使用修改属性的方式:在任意快捷方式上右击,选择属性,选择高级,选择以管理员身份启动: 在Windows8下如上设置后,右击直接打开项目的话是不会以管理员身份启动的,这里用比较h ...
