Guava Cache 缓存实现与源码分析
一、概述
1、内存缓存
可看作一个jdk7的concurrentHashMap,核心功能get,put
但是比一般的map多了一些功能,如:
- ⭐️过限失效(根据不同的维度失效,读后N秒,写后N秒,最大size,最大weight)
- 自动刷新
- 支持软引用和弱引用
- 监听删除
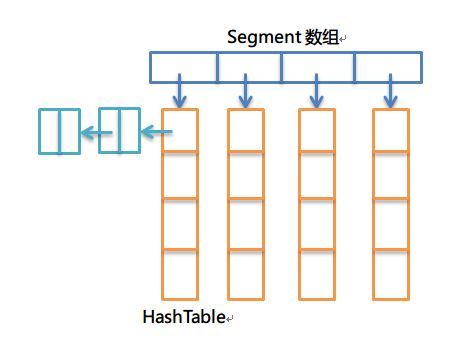
2、核心数据结构
和jdk7的HashMap相似
有N个Segment,每个Segment下是一个HashTable,每个HashTable里是一个链表
Guava的锁是一个比较重的操作,锁住的是整个Segment(Segment继承的是ReetrentLock,惊)
二、具体实现
0、一览众山小
主要的类:
CacheBuilder 设置参数,构建Cache
LocalCache 是核心实现,虽然builder构建的是LocalLoadingCache(带refresh功能)和LocalManualCache(不带refresh功能),但其实那两个只是个壳子
1、CacheBuilder 构建器
提要:
记录所需参数
public final class CacheBuilder<K, V> {
public <K1 extends K, V1 extends V> LoadingCache<K1, V1> build(
CacheLoader<? super K1, V1> loader) { // loader是用来自动刷新的
checkWeightWithWeigher();
return new LocalCache.LocalLoadingCache<>(this, loader);
}
public <K1 extends K, V1 extends V> Cache<K1, V1> build() { // 这个没有loader,就不会自动刷新
checkWeightWithWeigher();
checkNonLoadingCache();
return new LocalCache.LocalManualCache<>(this);
}
int initialCapacity = UNSET_INT; // 初始map大小
int concurrencyLevel = UNSET_INT; // 并发度
long maximumSize = UNSET_INT;
long maximumWeight = UNSET_INT;
Weigher<? super K, ? super V> weigher;
Strength keyStrength; // key强、弱、软引,默认为强
Strength valueStrength; // value强、弱、软引,默认为强
long expireAfterWriteNanos = UNSET_INT; // 写过期
long expireAfterAccessNanos = UNSET_INT; //
long refreshNanos = UNSET_INT; //
Equivalence<Object> keyEquivalence; // 强引时为equals,否则为==
Equivalence<Object> valueEquivalence; // 强引时为equals,否则为==
RemovalListener<? super K, ? super V> removalListener; // 删除时的监听
Ticker ticker; // 时间钟,用来获得当前时间的
Supplier<? extends StatsCounter> statsCounterSupplier = NULL_STATS_COUNTER; // 计数器,用来记录get或者miss之类的数据
}
2、LocalCache
1)初始化
提要:
a)赋值
b)初始化Segment[]数组
LocalCache(
CacheBuilder<? super K, ? super V> builder, @Nullable CacheLoader<? super K, V> loader) {
// a)把builder的参数赋值过来,略
// b)构建Segment[]数组,原理可参照jdk7点concurrentHashMap
int segmentShift = 0;
int segmentCount = 1; // 设置为刚刚好比concurrencyLevel大的2的幂次方的值
while (segmentCount < concurrencyLevel && (!evictsBySize() || segmentCount * 20 <= maxWeight)) {
++segmentShift;
segmentCount <<= 1;
}
this.segmentShift = 32 - segmentShift;
segmentMask = segmentCount - 1;
this.segments = newSegmentArray(segmentCount);
int segmentCapacity = initialCapacity / segmentCount; //每个Segment的容量
int segmentSize = 1; // 刚刚好比容量大的2等幂次方的值
while (segmentSize < segmentCapacity) {
segmentSize <<= 1;
}
if (evictsBySize()) {
// Ensure sum of segment max weights = overall max weights
long maxSegmentWeight = maxWeight / segmentCount + 1;
long remainder = maxWeight % segmentCount;
for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) {
if (i == remainder) {
maxSegmentWeight--;
}
this.segments[i] =
createSegment(segmentSize, maxSegmentWeight, builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get());
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < this.segments.length; ++i) {
this.segments[i] =
createSegment(segmentSize, UNSET_INT, builder.getStatsCounterSupplier().get()); // 往Segment数组里塞
}
}
}
Segment(
LocalCache<K, V> map,
int initialCapacity,
long maxSegmentWeight,
StatsCounter statsCounter) {
this.map = map;
this.maxSegmentWeight = maxSegmentWeight;
this.statsCounter = checkNotNull(statsCounter);
initTable(newEntryArray(initialCapacity));
// 当key是弱、软引用时,初始化keyReferenceQueue;其父类特性决定其gc时,会将被GC的元素放入该队列中
keyReferenceQueue = map.usesKeyReferences() ? new ReferenceQueue<K>() : null;
valueReferenceQueue = map.usesValueReferences() ? new ReferenceQueue<V>() : null;
recencyQueue =
map.usesAccessQueue()
? new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>()
: LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue();
writeQueue =
map.usesWriteQueue()
? new WriteQueue<K, V>()
: LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue();
accessQueue =
map.usesAccessQueue()
? new AccessQueue<K, V>()
: LocalCache.<ReferenceEntry<K, V>>discardingQueue();
}
2)put
提要
a)找到key所在的segment,调用segment.put方法
b)锁住segment,清理
i)如果key存在
ii)如果key不存在
c)清理
class LocalCache {
public V put(K key, V value) {
checkNotNull(key);
checkNotNull(value);
int hash = hash(key); // 计算hash
return segmentFor(hash).put(key, hash, value, false); // 找到hash所分配到的的Segment,put进去
}
}
// 转而来看Segment的put方法
class Segment<K,V> implements ReentrantLock {
V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
lock(); // 锁住一个segment
try {
long now = map.ticker.read(); //获得当前时间
preWriteCleanup(now); //清除软/弱引用 详见 2.4
int newCount = this.count + 1;
if (newCount > this.threshold) { // 如有需要则扩容
expand();
newCount = this.count + 1;
}
AtomicReferenceArray<ReferenceEntry<K, V>> table = this.table;
int index = hash & (table.length() - 1);
ReferenceEntry<K, V> first = table.get(index);
// Look for an existing entry.
// 根据不同情况决定是否要执行操作,1)count++ 更新数量 2)enqueueNotification 入队通知 3)setValue 更新值 4)evictEntries 淘汰缓存
for (ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = first; e != null; e = e.getNext()) {
K entryKey = e.getKey();
// 如果该key已经存在
if (e.getHash() == hash
&& entryKey != null
&& map.keyEquivalence.equivalent(key, entryKey)) {
// We found an existing entry.
ValueReference<K, V> valueReference = e.getValueReference();
V entryValue = valueReference.get();
if (entryValue == null) {
++modCount;
if (valueReference.isActive()) {
enqueueNotification(
key, hash, entryValue, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.COLLECTED);
setValue(e, key, value, now);
newCount = this.count; // count remains unchanged
} else {
setValue(e, key, value, now);
newCount = this.count + 1;
}
this.count = newCount; // write-volatile
evictEntries(e);
return null;
} else if (onlyIfAbsent) {
recordLockedRead(e, now);
return entryValue;
} else {
// clobber existing entry, count remains unchanged
++modCount;
enqueueNotification(
key, hash, entryValue, valueReference.getWeight(), RemovalCause.REPLACED);
setValue(e, key, value, now);
evictEntries(e);
return entryValue;
}
}
}
// 如果该key不存在,则新建一个entry.
++modCount;
ReferenceEntry<K, V> newEntry = newEntry(key, hash, first);
setValue(newEntry, key, value, now);
table.set(index, newEntry);
newCount = this.count + 1;
this.count = newCount; // write-volatile
evictEntries(newEntry);
return null;
} finally {
unlock();
postWriteCleanup();
}
}
@GuardedBy("this")
ReferenceEntry<K, V> newEntry(K key, int hash, @Nullable ReferenceEntry<K, V> next) {
return map.entryFactory.newEntry(this, checkNotNull(key), hash, next);
}
}
利用map.entryFactory创建Entry。其中entryFactory的初始化是下述得到的
EntryFactory entryFactory = EntryFactory.getFactory(keyStrength, usesAccessEntries(), usesWriteEntries());
EntryFactory是个枚举类,枚举类还可以这么用,涨知识了!
enum EntryFactory {
STRONG {
@Override
<K, V> ReferenceEntry<K, V> newEntry(
Segment<K, V> segment, K key, int hash, @Nullable ReferenceEntry<K, V> next) {
return new StrongEntry<>(key, hash, next);
}
},...,// 省略部分
WEAK { // 软/弱引用的精髓!!!
@Override
<K, V> ReferenceEntry<K, V> newEntry(
Segment<K, V> segment, K key, int hash, @Nullable ReferenceEntry<K, V> next) { // 所以!!!就是在这里!!!把这个queue放进去了,终于找到了
return new WeakEntry<>(segment.keyReferenceQueue, key, hash, next);
}
}};
// Masks used to compute indices in the following table.
static final int ACCESS_MASK = 1;
static final int WRITE_MASK = 2;
static final int WEAK_MASK = 4;
/** Look-up table for factories. */
static final EntryFactory[] factories = {
STRONG,
STRONG_ACCESS,
STRONG_WRITE,
STRONG_ACCESS_WRITE,
WEAK,
WEAK_ACCESS,
WEAK_WRITE,
WEAK_ACCESS_WRITE,
};
static EntryFactory getFactory(
Strength keyStrength, boolean usesAccessQueue, boolean usesWriteQueue) {
int flags =
((keyStrength == Strength.WEAK) ? WEAK_MASK : 0)
| (usesAccessQueue ? ACCESS_MASK : 0)
| (usesWriteQueue ? WRITE_MASK : 0);
return factories[flags];
}
// 抽象方法:创建一个entry
abstract <K, V> ReferenceEntry<K, V> newEntry(
Segment<K, V> segment, K key, int hash, @Nullable ReferenceEntry<K, V> next);
}
static class WeakEntry<K, V> extends WeakReference<K> implements ReferenceEntry<K, V> {
WeakEntry(ReferenceQueue<K> queue, K key, int hash, @Nullable ReferenceEntry<K, V> next) {
super(key, queue); // 抽丝剥茧,这个是Reference的方法,所以放到这个queue里面去,是Java WeakReference类自带的功能
this.hash = hash;
this.next = next;
}
}
3)get
提要
a)找到key所在的segment,调用segment.get方法
b)得到ReferenceEntry,若存在,检查value是否过期,返回结果
c)清理
class LocalCache{
public @Nullable V get(@Nullable Object key) {
if (key == null) {
return null;
}
int hash = hash(key);
return segmentFor(hash).get(key, hash);
}
}
class Segment{
V get(Object key, int hash) {
try {
if (count != 0) { // read-volatile
long now = map.ticker.read();
ReferenceEntry<K, V> e = getLiveEntry(key, hash, now); //如果发现没有找到或者过期了,则返回为null
if (e == null) {
return null;
}
V value = e.getValueReference().get();
if (value != null) {
recordRead(e, now);
return scheduleRefresh(e, e.getKey(), hash, value, now, map.defaultLoader);// 如果有loader且在刷新时间段中则刷新,否则跳过
}
tryDrainReferenceQueues(); // 这个幽灵一般的操作,难受
}
return null;
} finally {
postReadCleanup();
}
}
}
4)清理软/弱引用
每次put、get前后都会进行清理检查
@GuardedBy("this")
void preWriteCleanup(long now) { // 写前调用,其他方法类似,只是起了个不同的名字
runLockedCleanup(now);
}
void runLockedCleanup(long now) { // 加锁+执行方法
if (tryLock()) {
try {
drainReferenceQueues();
expireEntries(now); // calls drainRecencyQueue
readCount.set(0);
} finally {
unlock();
}
}
}
@GuardedBy("this")
void drainReferenceQueues() { // 清空软/弱引用key和value
if (map.usesKeyReferences()) {
drainKeyReferenceQueue();
}
if (map.usesValueReferences()) {
drainValueReferenceQueue();
}
}
@GuardedBy("this")
void drainKeyReferenceQueue() { // 清空软/弱引用key
Reference<? extends K> ref;
int i = 0;
while ((ref = keyReferenceQueue.poll()) != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
ReferenceEntry<K, V> entry = (ReferenceEntry<K, V>) ref;
map.reclaimKey(entry);
if (++i == DRAIN_MAX) {
break;
}
}
}
}
// 之前一直没想明白的地方就是,这个keyReferenceQueue到底是什么时候被塞进去元素的???
// 需要看下创建entry的时候的操作!!!抽丝剥茧就能知道了
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
private Sync sync;
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);
}
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;
abstract void lock();
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); // 获取当前线程
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) { // 无线程持有,即无锁状态
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { // 设置持有线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { // 如果持有者就是当前线程,perfect
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
}
Guava Cache 缓存实现与源码分析的更多相关文章
- Volley源码解析(三) 有缓存机制的情况走缓存请求的源码分析
Volley源码解析(三) 有缓存机制的情况走缓存请求的源码分析 Volley之所以高效好用,一个在于请求重试策略,一个就在于请求结果缓存. 通过上一篇文章http://www.cnblogs.com ...
- guava限流器RateLimiter原理及源码分析
前言 RateLimiter是基于令牌桶算法实现的一个多线程限流器,它可以将请求均匀的进行处理,当然他并不是一个分布式限流器,只是对单机进行限流.它可以应用在定时拉取接口数据, 预防单机过大流量使用. ...
- Java 自动拆箱 装箱 包装类的缓存问题--结合源码分析
都0202 了 java 1.8 已经是主流 自动装箱 .拆箱已经很普遍使用了,那么有时候是不是会遇到坑呢? 我们先来看一段代码: public class TestWraperClass { pub ...
- Guava cacha 机制及源码分析
1.ehcahce 什么时候用比较好:2.问题:当有个消息的key不在guava里面的话,如果大量的消息过来,会同时请求数据库吗?还是只有一个请求数据库,其他的等待第一个把数据从DB加载到Guava中 ...
- 开源分布式数据库中间件MyCat源码分析系列
MyCat是当下很火的开源分布式数据库中间件,特意花费了一些精力研究其实现方式与内部机制,在此针对某些较为重要的源码进行粗浅的分析,希望与感兴趣的朋友交流探讨. 本源码分析系列主要针对代码实现,配置. ...
- Kubernetes client-go DeltaFIFO 源码分析
概述Queue 接口DeltaFIFO元素增删改 - queueActionLocked()Pop()Replace() 概述 源码版本信息 Project: kubernetes Branch: m ...
- Guava 源码分析(Cache 原理 对象引用、事件回调)
前言 在上文「Guava 源码分析(Cache 原理)」中分析了 Guava Cache 的相关原理. 文末提到了回收机制.移除时间通知等内容,许多朋友也挺感兴趣,这次就这两个内容再来分析分析. 在开 ...
- Guava 源码分析之Cache的实现原理
Guava 源码分析之Cache的实现原理 前言 Google 出的 Guava 是 Java 核心增强的库,应用非常广泛. 我平时用的也挺频繁,这次就借助日常使用的 Cache 组件来看看 Goog ...
- ABP源码分析十三:缓存Cache实现
ABP中有两种cache的实现方式:MemroyCache 和 RedisCache. 如下图,两者都继承至ICache接口(准确说是CacheBase抽象类).ABP核心模块封装了MemroyCac ...
随机推荐
- Python常用代码2
用matplotlib画图时,若设置全部行输出,会得到包括图标在内的所有输出结果. plt.show() 输出全部行,参数为“all”:输出最后一行,参数为“last_expr”
- react,react-router,redux+react-redux 构建一个React Demo
创建初始化应用 加速我们的npm. npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org 利用create-react-app ...
- 浅谈Object.prototype.toString.call()方法
在JavaScript里使用typeof判断数据类型,只能区分基本类型,即:number.string.undefined.boolean.object.对于null.array.function.o ...
- 排序算法的c++实现——归并排序
归并排序是典型分治思想的代表——首先把原问题分解为两个或多个子问题,然后求解子问题的解,最后使用子问题的解来构造出原问题的解. 对于归并排序,给定一个待排序的数组,首先把该数组划分为两个子数组,然后对 ...
- Golang: 解析JSON数据之一
JSON 作为目前最流行的数据传输格式, 相信每个程序员都跟它打过交道吧.使用 Go 语言时,也不可避免的要操作 JSON 数据,令人惊喜的是,Go 内置了序列化和反序列化 JSON 的功能,今天就来 ...
- win10系统下安装Ubuntu18.04双系统
1.http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04/ubuntu-18.04.2-desktop-amd64.iso下载Ubuntu 18.04镜像,准备好一个空的U盘 2.下载ru ...
- go build -tags 的使用
go build 使用tag来实现编译不同的文件 go-tooling-workshop 中关于go build的讲解可以了解到go bulid的一些用法,这篇文章最后要求实现一个根据go bulid ...
- go mod开发模式设置
文章要解决的仅仅是一个问题 当你使用go get 无论如何get不到所需的包的问题 第一步就是下载goland 新手极其推荐goland,因为直接使用gland几乎没有挫败感,使用其他工具可能要折腾好 ...
- pandas的pivot_table
参考文献: [1]pivot_table
- spring Boot + MyBatis + Maven 项目,日志开启打印 sql
在 spring Boot + MyBatis + Maven 项目中,日志开启打印 sql 的最简单方法,就是在文件 application.properties 中新增: logging.leve ...
