朴素贝叶斯(Naive Bayesian)
- 简介
Naive Bayesian算法 也叫朴素贝叶斯算法(或者称为傻瓜式贝叶斯分类)
朴素(傻瓜):特征条件独立假设
贝叶斯:基于贝叶斯定理
这个算法确实十分朴素(傻瓜),属于监督学习,它是一个常用于寻找决策面的算法。
- 基本思想
(1)病人分类举例
有六个病人 他们的情况如下:
| 症状 | 职业 | 病名 |
| 打喷嚏 | 护士 | 感冒 |
| 打喷嚏 | 农夫 | 过敏 |
| 头痛 | 建筑工人 | 脑震荡 |
| 头痛 | 建筑工人 | 感冒 |
| 打喷嚏 | 教师 | 感冒 |
| 头痛 | 教师 | 脑震荡 |
根据这张表 如果来了第七个病人 他是一个 打喷嚏 的 建筑工人
那么他患上感冒的概率是多少
根据贝叶斯定理:
- P(A|B) = P(B|A) P(A) / P(B)
可以得到:
- P(感冒|打喷嚏x建筑工人) = P(打喷嚏x建筑工人|感冒) x P(感冒) / P(打喷嚏x建筑工人)
假定 感冒 与 打喷嚏 相互独立 那么上面的等式变为:
- P(感冒|打喷嚏x建筑工人) = P(打喷嚏|感冒) x P(建筑工人|感冒) x P(感冒) / ( P(打喷嚏) x P(建筑工人) )
P(感冒|打喷嚏x建筑工人) = 2/3 x 1/3 x 1/2 /( 1/2 x 1/3 )= 2/3
因此 这位打喷嚏的建筑工人 患上感冒的概率大约是66%
(2)朴素贝叶斯分类器公式
假设某个体有n项特征,分别为F1、F2、…、Fn。现有m个类别,分别为C1、C2、…、Cm。贝叶斯分类器就是计算出概率最大的那个分类,也就是求下面这个算式的最大值:
- P(C|F1 x F2 ...Fn) = P(F1 x F2 ... Fn|C) x P(C) / P(F1 x F2 ... Fn)
由于 P(F1xF2 … Fn) 对于所有的类别都是相同的,可以省略,问题就变成了求
- P(F1 x F2 ... Fn|C)P(C)
的最大值
根据朴素贝叶斯的朴素特点(特征条件独立假设),因此:
- P(F1 x F2 ... Fn|C)P(C) = P(F1|C) x P(F2|C) ... P(Fn|C)P(C)
上式等号右边的每一项,都可以从统计资料中得到,由此就可以计算出每个类别对应的概率,从而找出最大概率的那个类。
- 代码实现
环境:MacOS mojave 10.14.3
Python 3.7.0
使用库:scikit-learn 0.19.2
在终端输入下面的代码安装sklearn
- pip install sklearn
sklearn库官方文档http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.naive_bayes.GaussianNB.html
- >>> import numpy as np
- >>> X = np.array([[-1, -1], [-2, -1], [-3, -2], [1, 1], [2, 1], [3, 2]])
- >>> Y = np.array([1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2])
- #生成六个训练点,其中前三个属于标签(分类)1 后三个属于标签(分类)2
- >>> from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
- #导入外部模块
- >>> clf = GaussianNB()#创建高斯分类器,把GaussianNB赋值给clf(分类器)
- >>> clf.fit(X, Y)#开始训练
- #它会学习各种模式,然后就形成了我们刚刚创建的分类器(clf)
- #我们在分类器上调用fit函数,接下来将两个参数传递给fit函数,一个是特征x 一个是标签y#最后我们让已经完成了训练的分类器进行一些预测,我们为它提供一个新点[-0.8,-1]
- >>> print(clf.predict([[-0.8, -1]]))
- [1]
上面的流程为:创建训练点->创建分类器->进行训练->对新的数据进行分类
上面的新的数据属于标签(分类)2
- 绘制决策面
对于给定的一副散点图,其中蓝色是慢速区 红色是快速区,如何画出一条线 将点分开
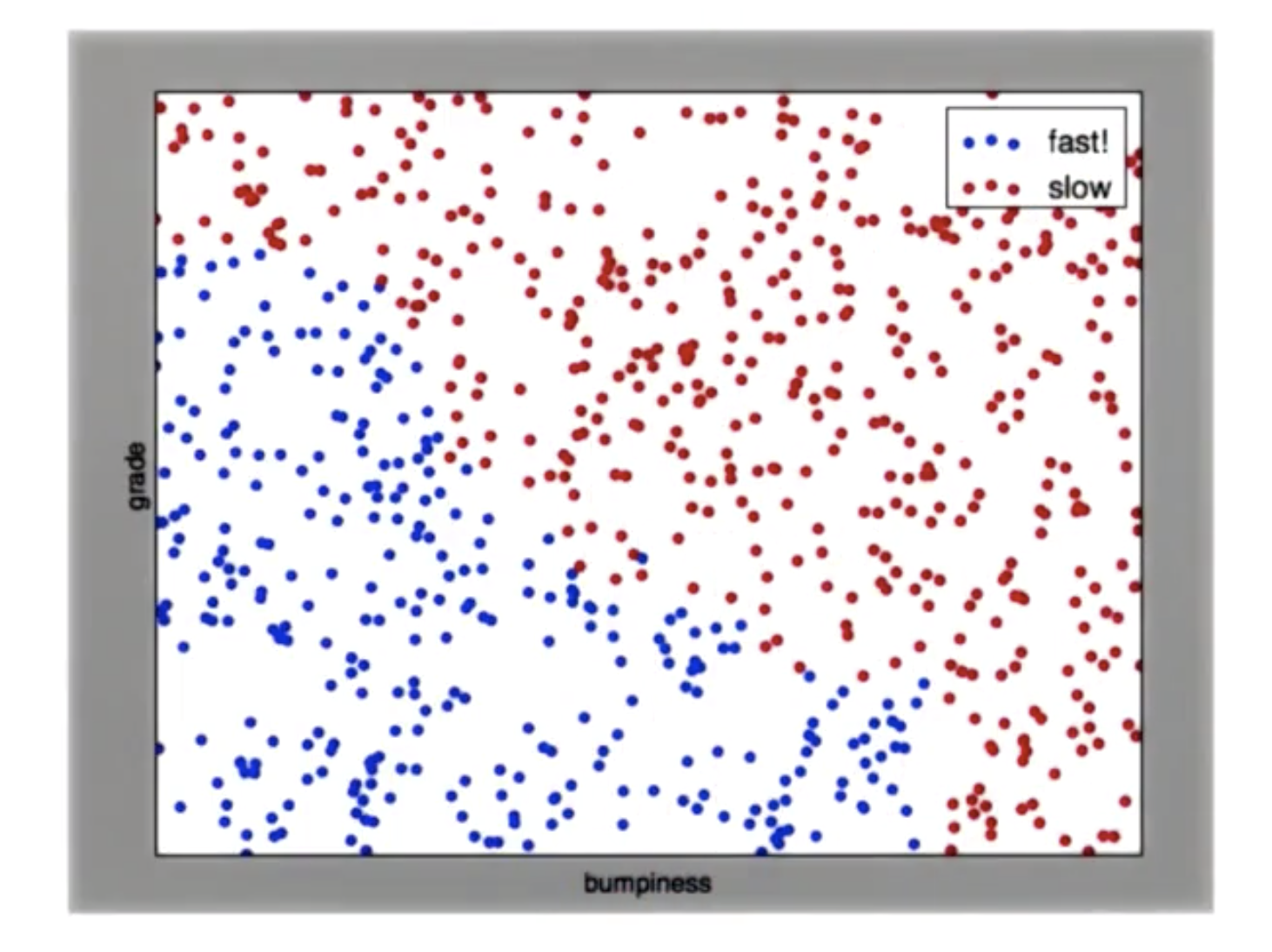
perp_terrain_data.py
生成训练点
- import random
- def makeTerrainData(n_points=1000):
- ###############################################################################
- ### make the toy dataset
- random.seed(42)
- grade = [random.random() for ii in range(0,n_points)]
- bumpy = [random.random() for ii in range(0,n_points)]
- error = [random.random() for ii in range(0,n_points)]
- y = [round(grade[ii]*bumpy[ii]+0.3+0.1*error[ii]) for ii in range(0,n_points)]
- for ii in range(0, len(y)):
- if grade[ii]>0.8 or bumpy[ii]>0.8:
- y[ii] = 1.0
- ### split into train/test sets
- X = [[gg, ss] for gg, ss in zip(grade, bumpy)]
- split = int(0.75*n_points)
- X_train = X[0:split]
- X_test = X[split:]
- y_train = y[0:split]
- y_test = y[split:]
- grade_sig = [X_train[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_train)) if y_train[ii]==0]
- bumpy_sig = [X_train[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_train)) if y_train[ii]==0]
- grade_bkg = [X_train[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_train)) if y_train[ii]==1]
- bumpy_bkg = [X_train[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_train)) if y_train[ii]==1]
- # training_data = {"fast":{"grade":grade_sig, "bumpiness":bumpy_sig}
- # , "slow":{"grade":grade_bkg, "bumpiness":bumpy_bkg}}
- grade_sig = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
- bumpy_sig = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
- grade_bkg = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1]
- bumpy_bkg = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1]
- test_data = {"fast":{"grade":grade_sig, "bumpiness":bumpy_sig}
- , "slow":{"grade":grade_bkg, "bumpiness":bumpy_bkg}}
- return X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test
- # return training_data, test_data
ClassifyNB.py
高斯分类
- def classify(features_train, labels_train):
- ### import the sklearn module for GaussianNB
- ### create classifier
- ### fit the classifier on the training features and labels
- ### return the fit classifier
- from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
- clf = GaussianNB()
- clf.fit(features_train, labels_train)
- return clf
- pred = clf.predict(features_test)
class_vis.py
绘图与保存图像
- import warnings
- warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
- import matplotlib
- matplotlib.use('agg')
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import pylab as pl
- import numpy as np
- #import numpy as np
- #import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- #plt.ioff()
- def prettyPicture(clf, X_test, y_test):
- x_min = 0.0; x_max = 1.0
- y_min = 0.0; y_max = 1.0
- # Plot the decision boundary. For that, we will assign a color to each
- # point in the mesh [x_min, m_max]x[y_min, y_max].
- h = .01 # step size in the mesh
- xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))
- Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])
- # Put the result into a color plot
- Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
- plt.xlim(xx.min(), xx.max())
- plt.ylim(yy.min(), yy.max())
- plt.pcolormesh(xx, yy, Z, cmap=pl.cm.seismic)
- # Plot also the test points
- grade_sig = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
- bumpy_sig = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==0]
- grade_bkg = [X_test[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1]
- bumpy_bkg = [X_test[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(X_test)) if y_test[ii]==1]
- plt.scatter(grade_sig, bumpy_sig, color = "b", label="fast")
- plt.scatter(grade_bkg, bumpy_bkg, color = "r", label="slow")
- plt.legend()
- plt.xlabel("bumpiness")
- plt.ylabel("grade")
- plt.savefig("test.png")
Main.py
主程序
- from prep_terrain_data import makeTerrainData
- from class_vis import prettyPicture
- from ClassifyNB import classify
- import numpy as np
- import pylab as pl
- features_train, labels_train, features_test, labels_test = makeTerrainData()
- ### the training data (features_train, labels_train) have both "fast" and "slow" points mixed
- ### in together--separate them so we can give them different colors in the scatterplot,
- ### and visually identify them
- grade_fast = [features_train[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(features_train)) if labels_train[ii]==0]
- bumpy_fast = [features_train[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(features_train)) if labels_train[ii]==0]
- grade_slow = [features_train[ii][0] for ii in range(0, len(features_train)) if labels_train[ii]==1]
- bumpy_slow = [features_train[ii][1] for ii in range(0, len(features_train)) if labels_train[ii]==1]
- clf = classify(features_train, labels_train)
- ### draw the decision boundary with the text points overlaid
- prettyPicture(clf, features_test, labels_test)
运行得到分类完成图像:
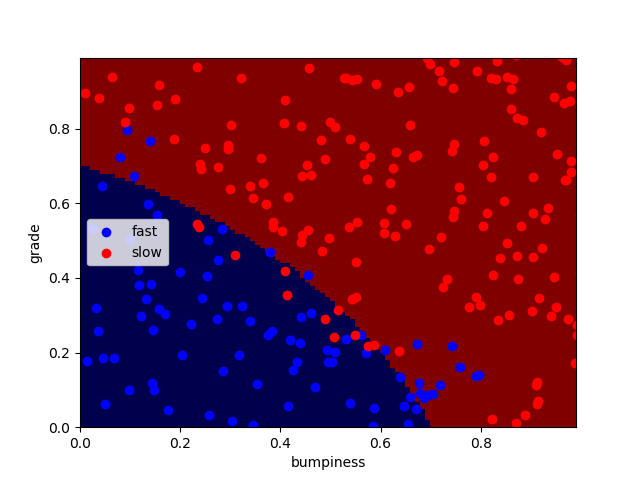
可以看到并不是所有的点都正确分类了,还有一小部分点被错误分类了
计算分类正确率:
accuracy.py
- from class_vis import prettyPicture
- from prep_terrain_data import makeTerrainData
- from classify import NBAccuracy
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import numpy as np
- import pylab as pl
- features_train, labels_train, features_test, labels_test = makeTerrainData()
- def submitAccuracy():
- accuracy = NBAccuracy(features_train, labels_train, features_test, labels_test)
- return accuracy
在主程序Main结尾加入一段:
- from studentCode import submitAccuracy
- print(submitAccuracy())
得到正确率:0.884
- 朴素贝叶斯的优势与劣势
优点:1、非常易于执行 2、它的特征空间非常大 3、运行非常容易、非常有效
缺点:它会与间断、由多个单词组成且意义明显不同的词语不太适合(eg:芝加哥公牛)
朴素贝叶斯(Naive Bayesian)的更多相关文章
- 朴素贝叶斯 Naive Bayes
2017-12-15 19:08:50 朴素贝叶斯分类器是一种典型的监督学习的算法,其英文是Naive Bayes.所谓Naive,就是天真的意思,当然这里翻译为朴素显得更学术化. 其核心思想就是利用 ...
- 机器学习算法实践:朴素贝叶斯 (Naive Bayes)(转载)
前言 上一篇<机器学习算法实践:决策树 (Decision Tree)>总结了决策树的实现,本文中我将一步步实现一个朴素贝叶斯分类器,并采用SMS垃圾短信语料库中的数据进行模型训练,对垃圾 ...
- 【机器学习速成宝典】模型篇05朴素贝叶斯【Naive Bayes】(Python版)
目录 先验概率与后验概率 条件概率公式.全概率公式.贝叶斯公式 什么是朴素贝叶斯(Naive Bayes) 拉普拉斯平滑(Laplace Smoothing) 应用:遇到连续变量怎么办?(多项式分布, ...
- NLP系列(2)_用朴素贝叶斯进行文本分类(上)
作者:龙心尘 && 寒小阳 时间:2016年1月. 出处: http://blog.csdn.net/longxinchen_ml/article/details/50597149 h ...
- 【Udacity】朴素贝叶斯
机器学习就像酿制葡萄酒--好的葡萄(数据)+好的酿酒方法(机器学习算法) 监督分类 supervised classification Features -->Labels 保留10%的数据作为 ...
- [ML学习笔记] 朴素贝叶斯算法(Naive Bayesian)
[ML学习笔记] 朴素贝叶斯算法(Naive Bayesian) 贝叶斯公式 \[P(A\mid B) = \frac{P(B\mid A)P(A)}{P(B)}\] 我们把P(A)称为"先 ...
- 后端程序员之路 18、朴素贝叶斯模型(Naive Bayesian Model,NBM)
贝叶斯推断及其互联网应用(一):定理简介 - 阮一峰的网络日志http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2011/08/bayesian_inference_part_one.ht ...
- [机器学习] 分类 --- Naive Bayes(朴素贝叶斯)
Naive Bayes-朴素贝叶斯 Bayes' theorem(贝叶斯法则) 在概率论和统计学中,Bayes' theorem(贝叶斯法则)根据事件的先验知识描述事件的概率.贝叶斯法则表达式如下所示 ...
- Python机器学习算法 — 朴素贝叶斯算法(Naive Bayes)
朴素贝叶斯算法 -- 简介 朴素贝叶斯法是基于贝叶斯定理与特征条件独立假设的分类方法.最为广泛的两种分类模型是决策树模型(Decision Tree Model)和朴素贝叶斯模型(Naive Baye ...
随机推荐
- MEAN框架学习笔记
MEAN框架学习笔记 MEAN开发框架的资料非常少.基本的资料还是来自于learn.mean.io站点上的介绍. 于是抱着一种零基础学习的心态,在了解的过程中,通过翻译加上理解将MEAN框架一点点消化 ...
- csu 1030: 素数槽
素数槽 Description 处于相邻的两个素数p和p + n之间的n - 1个连续的合数所组成的序列我们将其称为长度为n的素数槽.比如,‹24, 25, 26, 27, 28›是处于素数23 ...
- ZOJ2588 Burning Bridges 无向图的割边
题目大意:求无向图的割边编号. 割边定义:在一个连通图中,如果删去一个边e,图便变成不连通的两个部分,则e为该图的割边. 求法:边(u,v) 不是割边,当且仅当边(u,v)在一个环内.因此所有不在环内 ...
- 理解和配置 Linux 下的 OOM Killer【转】
本文转载自:http://www.vpsee.com/2013/10/how-to-configure-the-linux-oom-killer/ 最近有位 VPS 客户抱怨 MySQL 无缘无故挂掉 ...
- 用虚拟机创建win7 32位系统来测试win 7 64位系统无法安装cad 2004 缺少acdb16.dll的问题
- Python环境设置-zlib not available
今天在Linux中安Python3的时候,出现了一个错误:zipimport.ZipImportError: can‘t decompress data; zlib not available 网上找 ...
- PLSQL简介
目录 什么是PLSQL PLSQL起源 PLSQL早期版本 改善可移植性 改进执行权限于事务的完整性 原书:steven feuerstei-oracle PLSQL grogramming 2014 ...
- IO流读取文件内容时,出现空格的问题(未找到原因)
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOExceptio ...
- C++程序开发的基本过程
前两天说去一家小公司实习,被他们的一个技术员工的一个问题问到了,问的我当时都没有反应过来,回来后突然发现这个问题我会啊 ,只是当时没想到这么浅显.现在总结下: C++程序开发的基本过程: 1)编辑 开 ...
- 使用Micrisoft.net设计方案 第三章Web表示模式
第三章Web表示模式 体系结构设计者在设计第一个作品时比较精简和干练.在第一次设计时,并清除自己做什么,因此比较小心谨慎.第二个作品是最危险的一个作品,此时他会对第一个作品做修饰和润色,以及把第一次设 ...
