Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) A.B.C
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Ted has a pineapple. This pineapple is able to bark like a bulldog! At time t (in seconds) it barks for the first time. Then every s seconds after it, it barks twice with 1 second interval. Thus it barks at times t, t + s, t + s + 1, t + 2s, t + 2s + 1, etc.

Barney woke up in the morning and wants to eat the pineapple, but he can't eat it when it's barking. Barney plans to eat it at time x (in seconds), so he asked you to tell him if it's gonna bark at that time.
The first and only line of input contains three integers t, s and x (0 ≤ t, x ≤ 109, 2 ≤ s ≤ 109) — the time the pineapple barks for the first time, the pineapple barking interval, and the time Barney wants to eat the pineapple respectively.
Print a single "YES" (without quotes) if the pineapple will bark at time x or a single "NO" (without quotes) otherwise in the only line of output.
3 10 4
NO
3 10 3
YES
3 8 51
YES
3 8 52
YES
In the first and the second sample cases pineapple will bark at moments 3, 13, 14, ..., so it won't bark at the moment 4 and will bark at the moment 3.
In the third and fourth sample cases pineapple will bark at moments 3, 11, 12, 19, 20, 27, 28, 35, 36, 43, 44, 51, 52, 59, ..., so it will bark at both moments 51 and 52.
题意:一个序列 t, t + s, t + s + 1, t + 2s, t + 2s + 1,。。。。。;判断x是否在里面;
思路:x-t对s取模,判断是否为0或1;特判(x-t)/s>0;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define esp 0.00000000001
const int N=2e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9;
int main()
{
int x,y,z,i,t;
scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z);
if(x>z)
printf("NO\n");
else if(x==z)
printf("YES\n");
else if((z-x)%y==||(z-x)%y==)
{
if(z-x>=y)
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
else
printf("NO\n");
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Barney is standing in a bar and starring at a pretty girl. He wants to shoot her with his heart arrow but he needs to know the distance between him and the girl to make his shot accurate.

Barney asked the bar tender Carl about this distance value, but Carl was so busy talking to the customers so he wrote the distance value (it's a real number) on a napkin. The problem is that he wrote it in scientific notation. The scientific notation of some real number x is the notation of form AeB, where A is a real number and B is an integer and x = A × 10B is true. In our case A is between 0 and 9 and B is non-negative.
Barney doesn't know anything about scientific notation (as well as anything scientific at all). So he asked you to tell him the distance value in usual decimal representation with minimal number of digits after the decimal point (and no decimal point if it is an integer). See the output format for better understanding.
The first and only line of input contains a single string of form a.deb where a, d and b are integers and e is usual character 'e' (0 ≤ a ≤ 9, 0 ≤ d < 10100, 0 ≤ b ≤ 100) — the scientific notation of the desired distance value.
a and b contain no leading zeros and d contains no trailing zeros (but may be equal to 0). Also, b can not be non-zero if a is zero.
Print the only real number x (the desired distance value) in the only line in its decimal notation.
Thus if x is an integer, print it's integer value without decimal part and decimal point and without leading zeroes.
Otherwise print x in a form of p.q such that p is an integer that have no leading zeroes (but may be equal to zero), and q is an integer that have no trailing zeroes (and may not be equal to zero).
8.549e2
854.9
8.549e3
8549
0.33e0
0.33
题意:将这个数改成整数或小数,。不能有前后导0;
思路:0.0e0这种数据小心点;
我yong码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <stack>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#define PI acos(-1.0)
const int inf = (<<) - ;
using namespace std;
inline int get_int()
{
int r=;
char c;
while((c=getchar())!=' '&&c!='\n')
r=r*+c-'';
return r;
}
inline void out(int x)
{
if(x>)
{
out(x/);
}
putchar(x % + '');
putchar('\n');
}
/****************************************/ char a[],b[],c[],d[];
int xiao(int xx,int yy){return xx<yy?xx:yy;}
int main()
{
int aa,dd,bb,l,n,i,j,xx;
cin>>c;
n=strlen(c);
aa=c[]-'';
for(j=,i=;i<n;i++,j++){
if(c[i]=='e')
break;
d[j]=c[i];
}
bb=;
for(j=,i++;i<n;i++,j++)
bb=bb*+c[i]-'';
//aa=strlen(a);
//bb=strlen(b);
dd=strlen(d);
l=;
if(aa)
printf("%d",aa);
l=aa;
xx=xiao(bb,dd);
for(i=;i<xx;i++){
if(l==&&d[i]=='')
continue;
printf("%c",d[i]);
l=;
}
if(xx==dd){
for(i=dd;i<bb;i++)
printf("");
}
else{
if(l==)
printf("");
l=;
for(int i=xx;i<dd;i++){
if(d[i]>''){
l=;
break;
}
}
if(l){
printf(".");
for(i=xx;i<dd;i++)
printf("%c",d[i]);
} }
printf("\n");
}
代码
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Barney lives in NYC. NYC has infinite number of intersections numbered with positive integers starting from 1. There exists a bidirectional road between intersections i and 2i and another road between i and 2i + 1 for every positive integer i. You can clearly see that there exists a unique shortest path between any two intersections.

Initially anyone can pass any road for free. But since SlapsGiving is ahead of us, there will q consecutive events happen soon. There are two types of events:
1. Government makes a new rule. A rule can be denoted by integers v, u and w. As the result of this action, the passing fee of all roads on the shortest path from u to v increases by w dollars.
2. Barney starts moving from some intersection v and goes to intersection u where there's a girl he wants to cuddle (using his fake name Lorenzo Von Matterhorn). He always uses the shortest path (visiting minimum number of intersections or roads) between two intersections.
Government needs your calculations. For each time Barney goes to cuddle a girl, you need to tell the government how much money he should pay (sum of passing fee of all roads he passes).
The first line of input contains a single integer q (1 ≤ q ≤ 1 000).
The next q lines contain the information about the events in chronological order. Each event is described in form 1 v u w if it's an event when government makes a new rule about increasing the passing fee of all roads on the shortest path from u to v by w dollars, or in form 2 v u if it's an event when Barnie goes to cuddle from the intersection v to the intersection u.
1 ≤ v, u ≤ 1018, v ≠ u, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109 states for every description line.
For each event of second type print the sum of passing fee of all roads Barney passes in this event, in one line. Print the answers in chronological order of corresponding events.
7
1 3 4 30
1 4 1 2
1 3 6 8
2 4 3
1 6 1 40
2 3 7
2 2 4
94
0
32
In the example testcase:
Here are the intersections used:
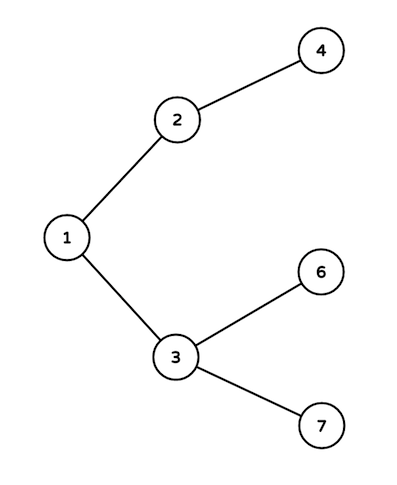
- Intersections on the path are 3, 1, 2 and 4.
- Intersections on the path are 4, 2 and 1.
- Intersections on the path are only 3 and 6.
- Intersections on the path are 4, 2, 1 and 3. Passing fee of roads on the path are 32, 32 and 30 in order. So answer equals to32 + 32 + 30 = 94.
- Intersections on the path are 6, 3 and 1.
- Intersections on the path are 3 and 7. Passing fee of the road between them is 0.
- Intersections on the path are 2 and 4. Passing fee of the road between them is 32 (increased by 30 in the first event and by 2 in the second).
题意:给你一颗二叉树;q个询问;
1:在u->v经过的线段+权值;
2:询问u->v的总权值;
思路:利用map标记;有点类似求lca的过程;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll __int64
#define mod 1000000007
#define esp 0.00000000001
const int N=2e5+,M=1e6+,inf=1e9;
map<ll,ll>m;
ll check(ll x)
{
ll sum=;
while(x)
{
sum++;
x>>=;
}
return sum;
}
void update(ll u,ll v,ll w)
{
while(check(u)>check(v))
{
m[u]+=w;
u/=;
}
while(check(u)<check(v))
{
m[v]+=w;
v/=;
}
while(check(u)!=&&u!=v)
{
m[v]+=w;
m[u]+=w;
v>>=;
u>>=;
}
}
ll query(ll u,ll v)
{
ll ans=;
while(check(u)>check(v))
{
ans+=m[u];
u/=;
}
while(check(u)<check(v))
{
ans+=m[v];
v/=;
}
while(check(u)!=&&u!=v)
{
ans+=m[v];
ans+=m[u];
v>>=;
u>>=;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ll x,y,z,i,t;
scanf("%I64d",&x);
for(i=;i<x;i++)
{
ll flag,u,v;
scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d",&flag,&u,&v);
if(flag==)
{
ll w;
scanf("%I64d",&w);
update(u,v,w);
}
else
{
printf("%I64d\n",query(u,v));
}
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) A.B.C的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) C. Lorenzo Von Matterhorn (类似LCA)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/697/D 给你一个有规则的二叉树,大概有1e18个点. 有两种操作:1操作是将u到v上的路径加上w,2操作 ...
- #map+LCA# Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)-C. Lorenzo Von Matterhorn
2018-03-16 http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/697/C C. Lorenzo Von Matterhorn time limit per t ...
- 【转载】【树形DP】【数学期望】Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) D.Puzzles
期望计算的套路: 1.定义:算出所有测试值的和,除以测试次数. 2.定义:算出所有值出现的概率与其乘积之和. 3.用前一步的期望,加上两者的期望距离,递推出来. 题意: 一个树,dfs遍历子树的顺序是 ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)->B. Barnicle
B. Barnicle time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ou ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)->A. Pineapple Incident
A. Pineapple Incident time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) B 模拟
B. Barnicle time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ou ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) A 水也挂
A. Pineapple Incident time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2)
闲来无事一套CF啊,我觉得这几个题还是有套路的,但是很明显,这个题并不难 A. Pineapple Incident time limit per test 1 second memory limit ...
- Codeforces Round #362 (Div. 2) D. Puzzles
D. Puzzles time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input out ...
随机推荐
- AngularJs学习笔记--Guide教程系列文章索引
在很久很久以前,一位前辈向我推荐AngularJs.但当时我没有好好学习,仅仅是讲文档浏览了一次.后来觉醒了……于是下定决心好好理解这系列的文档,并意译出来(英文水平不足……不能说是翻译,有些实在是看 ...
- [HTML/CSS]display:none和visibility:hidden的区别
写在前面 在群里有朋友问这样一个问题,display:none的标签,影响了布局.这就引出了本篇这样的问题,印象中display:none的块元素是不占位置的. 一个例子 <!DOCTYPE h ...
- svn 分支与合并的使用
在使用svn的时候我们往往有这样的需求.我们修改某些代码,因为对某项技术不是非常的熟悉,担心自己当前的修改(或者叫测试)会影响到服务器中版本库代码的崩溃等.传统做法我们会手动复制一份代码,然后修改 ...
- mysql 数据库优化
提到优化,先要确定出现的问题,是存储引擎选择问题,还是sql语句使用问题(如:索引)亦或者是单一存储服务器对于千万级别的数据力不从心. 解决方法:1.根据不同业务选用不同存储引擎,虽然一般情况下都优先 ...
- 云计算中iaas、paas、saas的区别和联系
概念: iass : Infrastructure(基础设施)-as-a-Service, paas : Platform(平台)-as-a-Service, saas : Software(软件)- ...
- 7 天玩转 ASP.NET MVC — 第 6 天
目录 第 1 天 第 2 天 第 3 天 第 4 天 第 5 天 第 6 天 第 7 天 0. 前言 欢迎来到第六天的 MVC 系列学习中.希望你在阅读此篇文章的时候,已经学习了前五天的内容,这也是第 ...
- MFC单文档程序结构
MFC单文档程序结构三方面: Doc MainFrame View
- POJ 2140
#include<iostream> #include<stdio.h> using namespace std; int main() { int num; int i; i ...
- Android图片缩放方法
安卓开发中应用到图片的处理时候,我们通常会怎么缩放操作呢,来看下面的两种做法: 方法1:按固定比例进行缩放 在开发一些软件,如新闻客户端,很多时候要显示图片的缩略图,由于手机屏幕限制,一般情况下,我们 ...
- http://blog.csdn.net/wxwzy738/article/details/16968767
http://blog.csdn.net/wxwzy738/article/details/16968767
