CF1921F Sum of Progression 题解
题目链接:CF 或者 洛谷
一道经典的类型题,把这种类型的题拿出来单独说一下。
注意到问题中涉及到需要维护 \(a_{x+k\times step}\) 这样的信息,这样的信息很难用树型结构维护,比较容易用块级结构维护,我们注意到其实是每次这种步长 \(+step\) 的信息很难维护,我们考虑一类特殊的分块:如果 \(step\) 恰好为块长。
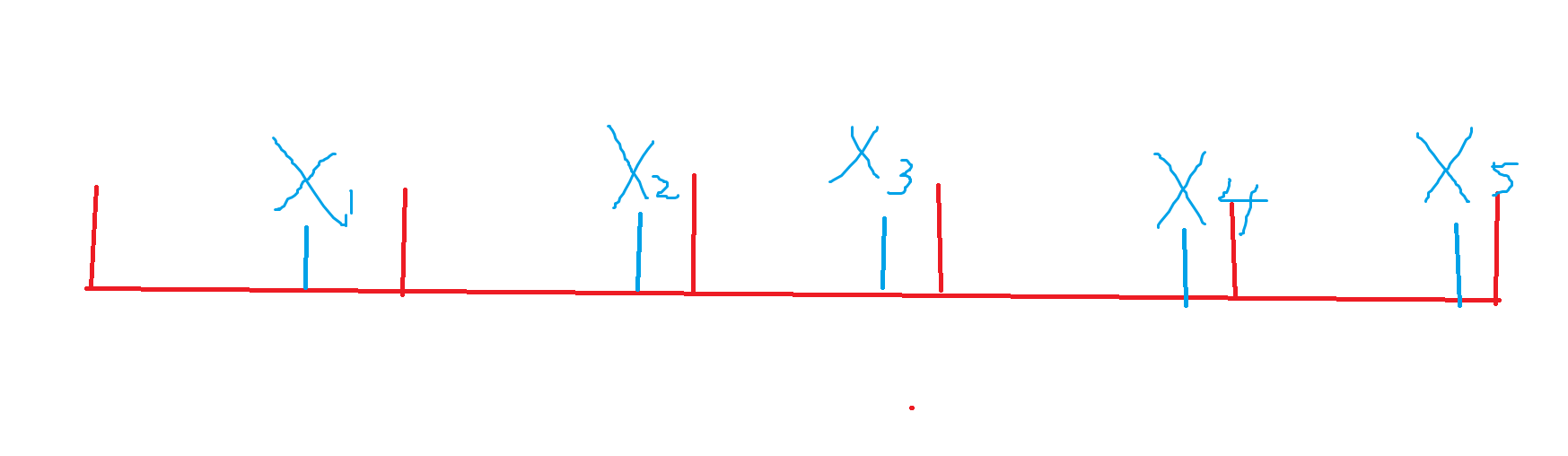
我们会惊讶地发现,从某个位置往后不断地走 \(step\) 就是说不断地恰好跨过一个块长,它的路径上的每个点的信息在块里都是同一个位置,这样一来其实我们可以为每一种块长分块的结果维护它特有的一些信息。
注意到一点,在预处理时,每一种块长如果我们都暴力的情况下,从小块长开始,比如从块长为 \(1\) 开始,显然处理的复杂度是 \(O(n)\),这样一来,其实我们能处理最多 \(\sqrt{n}\) 种块长,预处理的复杂度最多为 \(n\sqrt{n}\),如果更长的块长我们注意到,如果暴力地从 \(1\) 位置开始跳,那么最多也就跳 \(\sqrt{n}\) 次,此时每个 \(\ge \sqrt{n}\) 的块长其实是都是能直接暴力处理,这启发我们使用根号分治解决这类问题:
\(块长 < \sqrt{n}\),考虑为这类所有块长分块维护统一的信息。
\(块长 \ge \sqrt{n}\),考虑直接暴力。
这就是这类问题的模版框架。如果出现修改,我们对于查询的调整可能发生调整,比如有时候查询的是具体的值,那么可以考虑每种块长的贡献即可,最后会给出例题。
回到本题,我们需要对小块长维护怎样的信息,考虑到查询直接维护 \(a_i \times 当前查询中的下标\) 是困难的,注意到阿贝尔求和的方式,我们可以把它拆成若干个前缀和做差的方式:
a_{s}\times 1+a_{s+d}\times 2+a_{s+2d}\times 3+a_{s+3d} \times 4....a_{s+(k-1)\times d}\times k
\]
先考虑简单情形:
如果 \(d==1\):
\]
类似于阿贝尔求和假如知道:
\]
那么很显然有原式子拆成如下图求和:
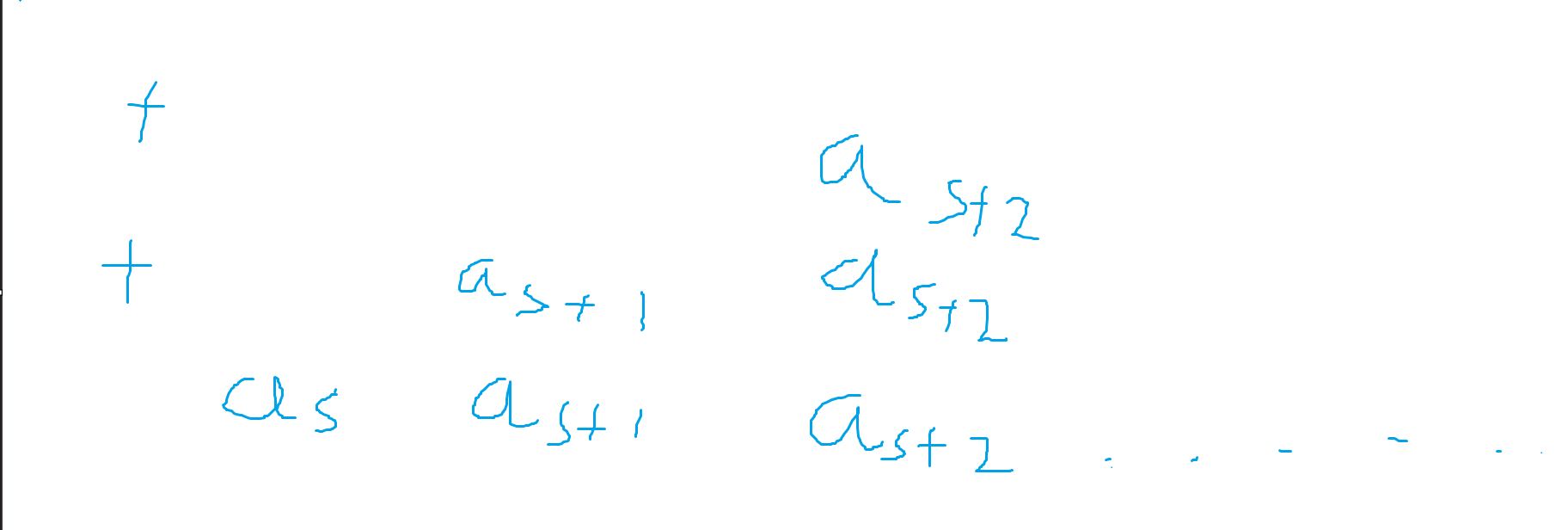
可以看出每一行都是一个区间和,借助前缀和,不妨设当前查询的最后一个数为 \(end\):
\]
\]
很容易看出,前面其实就为一个前缀和,后面则是“前缀和数组”的区间和形式,显然维护前缀和数组的前缀和就能办到了。
现在抽象一下,如果 \(d \neq 1\),怎么解决:
事实上,我们把上式改写一下:
\]
其中 \(start\) 为从 \(idx\) 往前不断走 \(d\) 长度能达到的最早起点,换句话来说,就是最开始我们提到的那张图:

\(idx\) 此时可能不位于第一个块处,比如 \(idx=x_2\),那么 \(x_1\) 就是它在第一个块的相对位置,也即是 \(start\),我们维护的就是这一步所有 \(x\) 之和。
那么上面的式子显然可以改写为:
\]
这里的 \(pre\) 第一维取 \(d\),省略第一维为上述形式。那么我们可以维护两个数组:
\(pre[d][idx]\) 表示 \(d\) 长度的块的这些 \(x\) 的前缀和信息。
\(Prepre[d][idx]\) 表示 \(d\) 长度的这些 \(pre[d][idx]\) 的前缀和信息。
其中易知道 \(Prepre[d][idx]=pre[d][start]+pre[d][start+d].....pre[d][idx]\)。
那么上述式子就可以轻易改写了:
\]
其实只需要注意到,前缀和作差中后一项不再是 \(-1\),改为 \(-d\) 即可。
最后的细节
注意到有类似 \(s-2\times d\) 这类下标,我们最好和 \(0\) 取个 \(max\),防止出现负数,究其原因可能这个块就是第一项了。然后注意到块比较小的时候,如果 \(k\) 比较小也可以暴力,那么我们可以对这两类情况同时走暴力分支也行。当然改写成后缀和也是可以的,不用怎么需要考虑越界问题,因为超过的部分你数组开大点直接能取值为 \(0\) 的后缀和了。记得多测情空。
带注释参考代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
// #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops")
// #pragma GCC optimize(2)
// #define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 i128;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return;
if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9)write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow)return three < other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3() { one = tow = three = 0; }
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y)x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y)x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 1e5 + 10;
constexpr int Size = ceil(sqrt(N));
constexpr int CNT = (N + Size - 1) / Size + 1;
int n, q;
ll a[N];
ll pre[CNT + 1][N];
ll Prepre[CNT + 1][N];
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n >> q;
forn(i, 1, n)cin >> a[i];
int siz = sqrt(n);
forn(i, 1, siz)
{
forn(j, 1, n)
{
pre[i][j] = a[j];
if (j > i)pre[i][j] += pre[i][j - i];
Prepre[i][j] = pre[i][j];
if (j > i)Prepre[i][j] += Prepre[i][j - i];
}
}
forn(i, 1, q)
{
ll s, d, k;
cin >> s >> d >> k;
ll ans = 0;
if (k <= siz or d >= siz)forn(i, 1, k)ans += a[s + (i - 1) * d] * i;
else
{
int end = s + (k - 1) * d;
int endpre = end - d;
ans = k * pre[d][end] - (Prepre[d][endpre] - Prepre[d][max(s - 2 * d, 0ll)]);
}
cout << ans << " ";
}
forn(i, 1, siz)forn(j, 1, n)pre[i][j] = Prepre[i][j] = 0;
cout << endl;
}
signed int main()
{
// MyFile
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
// clock_t start = clock();
int test = 1;
// read(test);
cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test)solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
// clock_t end = clock();
// cerr << "time = " << double(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "s" << endl;
}
\]
推荐经典题:P5309 [Ynoi2011] 初始化 题解
CF1921F Sum of Progression 题解的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] Range Sum Query - Mutable 题解
题目 题目 思路 一看就是单点更新和区间求和,故用线段树做. 一开始没搞清楚,题目给定的i是从0开始还是从1开始,还以为是从1开始,导致后面把下标都改掉了,还有用区间更新的代码去实现单点更新,虽然两者 ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 37-F.SUM and REPLACE题解
一.题目 二.题目链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/920/problem/F 三.题意 给定$N$个范围在$[1, 1e6)$的数字和$M$个操作.操作有两种类型: ...
- CF102B Sum of Digits 题解
Content 给定一个数 \(n\),每次操作可以将 \(n\) 变成 \(n\) 各位数之和.问你几次操作之后可以将 \(n\) 变为一位数. 数据范围:\(1\leqslant n\leqsla ...
- Codeforces 396B On Sum of Fractions 数论
题目链接:Codeforces 396B On Sum of Fractions 题解来自:http://blog.csdn.net/keshuai19940722/article/details/2 ...
- Path Sum leetcode java
题目: Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up ...
- 【CF914G】Sum the Fibonacci 快速??变换模板
[CF914G]Sum the Fibonacci 题解:给你一个长度为n的数组s.定义五元组(a,b,c,d,e)是合法的当且仅当: 1. $1\le a,b,c,d,e\le n$2. $(s_a ...
- [Leetcode Week16]Range Sum Query - Mutable
Range Sum Query - Mutable 题解 原创文章,拒绝转载 题目来源:https://leetcode.com/problems/range-sum-query-mutable/de ...
- 【leetcode刷题笔记】Path Sum
Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all ...
- CodeForces 85D Sum of Medians Splay | 线段树
Sum of Medians 题解: 对于这个题目,先想到是建立5棵Splay,然后每次更新把后面一段区间的树切下来,然后再转圈圈把切下来的树和别的树合并. 但是感觉写起来太麻烦就放弃了. 建立5棵线 ...
- Bestcoder Round #84
A题 Aaronson http://bestcoder.hdu.edu.cn/contests/contest_chineseproblem.php?cid=718&pid=1001 感觉一 ...
随机推荐
- AtCoder Beginner Contest 176 (ABC水题,D题01BFS,E数组处理)
补题链接:Here A - Takoyaki 很容易看出 \(\frac{N + X - 1}{X} \times T\) B - Multiple of 9 给定一个很大的整数,问其是否是 \(9\ ...
- 类加载机制-深入理解jvm
一.什么是类的加载: 如上图,java文件通过编译器变成了.class文件,接下来类加载器又将这些.class文件加载到JVM中.其中类装载器的作用其实就是类的加载. 二.原理 (类的加载过程及其最终 ...
- java两个list取交集
直接上代码 List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>(); list1.add(1); list1.add(2); list1.add(3); ...
- python常见面试题讲解(四)字符串分隔
题目描述 •连续输入字符串,请按长度为8拆分每个字符串后输出到新的字符串数组:•长度不是8整数倍的字符串请在后面补数字0,空字符串不处理. 输入描述: 连续输入字符串(输入2次,每个字符串长度小于10 ...
- 机器学习-决策树系列-决策树-剪枝-CART算法-27
目录 1. 剪枝 2. CCP-代价复杂度剪枝(CART) 4. α值的确定 1. 剪枝 将子树还原成一个叶子节点: 是解决过拟合的一个有效方法.当树训练得过于茂盛的时候会出现在测试集上的效果比训练集 ...
- 阿里云龙蜥8.6部署SQLSERVER2022的过程
阿里云龙蜥8.6部署SQLSERVER2022的过程 背景 之前总结过, 但是发现当时是preview版本. 这里想升级一下, 并且顺便抄一下他的部分说明 下载 wget https://packag ...
- [转帖]Navicat连接openGauss数据库报错
news/2023/10/19 21:23:19 错误信息:fe_sendauth:invalid authentication request from server:AUTH_REQ_SASL_C ...
- [转帖]《Linux性能优化实战》笔记(四)—— CPU 使用率
一. 节拍率与CPU时间 前一篇说到,Linux 作为一个多任务操作系统,将每个 CPU 的时间划分为很短的时间片,再通过调度器轮流分配给各个任务使用,因此造成多任务同时运行的错觉. 为了维护 CPU ...
- [转帖]OS Watcher (OSW)系统性能监控软件
https://www.anbob.com/archives/1143.html OS Watcher简称OSW(oswbb),用于收集并归档操作系统cpu,memery,disk io,networ ...
- [转帖]jvm学习三-MAT内存分析工具的使用
目录 1 模拟内存溢出程序 1.1 jvm配置 1.2 测试代码 2 MAT工具进行内存分析 2.1 大纲介绍 2.2 Histogram视图介绍 2.3 Leak Suspects视图介绍 2.4 ...
