Python第一课
一、模块的常用方法
- __name__ #主模块name值main
- __file__ #文件所在的路径+文件名
- __doc__ #文件级别的注释
二、函数
- 参数
- 参数默认值
- 可变参数
- 返回值
''' def Foo():
print 'Foo'
def Foo(arg)
print arg
def Foo(arg='alex'):
print arg
#必须放在最后
def Foo(arg1,arg2):
print arg1,arg2
Foo(arg2='alex',arg1='kelly')
def Foo(arg,*args):
print arg,args
Foo('alex','kelly','tom')
def Foo(**kargs):
print kargs.keys()
print kargs.values()
Foo(k1='sb',k2='alex')
'''
三、yield
def AlexReadlines():
seek = 0
while True:
with open('D:/temp.txt','r') as f:
f.seek(seek)
data = f.readline()
if data:
seek = f.tell()
yield data
else:
returnfor i in AlexReadlines():
print i
yield
四、三元运算和lambda表达式
result = 'gt' if 1>3 else 'lt'
print result
a = lambda x,y:x+y
print a(4,10)
五、内置函数
#print help()
print dir()
print vars()
#print type()
import temp
import temp
reload(temp)
id([12])
#is ------------------
cmp(2,3)
cmp(2,2)
cmp(2,1)
cmp(10,1)
abs()
bool()
divmod()
max()
min()
sum()
pow(2, 11)
------------------
len()
all()
any()
------------------
chr()
ord()
hex()
oct()
bin()
------------------
print range(10)
print xrange(10)
for i in xrange(10):
print i
for k,v in enumerate([1,2,3,4]):
print k,v
------------------
s= 'i am {0}'
print s.format('alex')
str(1)
------------------
def Function(arg):
print arg
print apply(Function,('aaaa')) #执行函数
print map(lambda x:x+1,[1,2,3]) #all
print filter(lambda x: x==1,[1,23,4]) #True序列
print reduce(lambda x,y:x+y,[1,2,3]) #累加
x = [1, 2, 3]
y = [4, 5, 6]
z = [4, 5, 6]
print zip(x, y,z)
------------------
#__import__()
#hasattr()
#delattr()
#getattr()
module = __import__('temp')
print dir(module)
val = hasattr(module, 'version')
print val
------------------
#callable()
#函数、类必须要有 __call__ 方法
#compile
#eval
com = compile('1+1','','eval')
print eval(com)
#exec语句
code = "for i in range(0, 10): print i"
cmpcode = compile(code, '', 'exec')
exec cmpcode
code = "print 1"
cmpcode = compile(code, '', 'single')
exec cmpcode
------------------
#isinstance()
#issubclass()
#super()
#staticmethod()
更多,猛击这里
六、常用模块
1、random 用于生成随机数
import random
print random.random()
print random.randint(1,2)
print random.randrange(1,10)
应用场景:生成随机验证码
import random
checkcode = ''
for i in range(4):
current = random.randrange(0,4)
if current != i:
temp = chr(random.randint(65,90))
else:
temp = random.randint(0,9)
checkcode += str(temp)
print checkcode
2、md5 加密
import md5
hash = md5.new()
hash.update('admin')
print hash.hexdigest()
import hashlib
hash = hashlib.md5()
hash.update('admin')
print hash.hexdigest()
3、序列化和json

4、re
- compile
- match search findall
- group groups
正则表达式常用格式:
字符:\d \w \t .
次数:* + ? {m} {m,n}
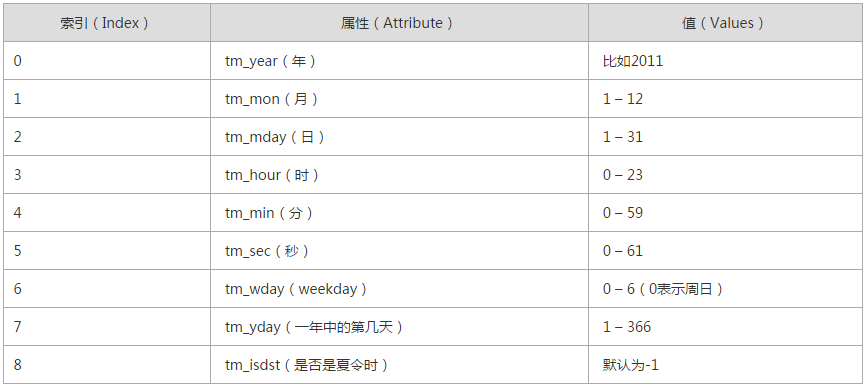
5、time
import time
#1、时间戳 1970年1月1日之后的秒
#3、元组 包含了:年、日、星期等... time.struct_time
#4、格式化的字符串 2014-11-11 11:11
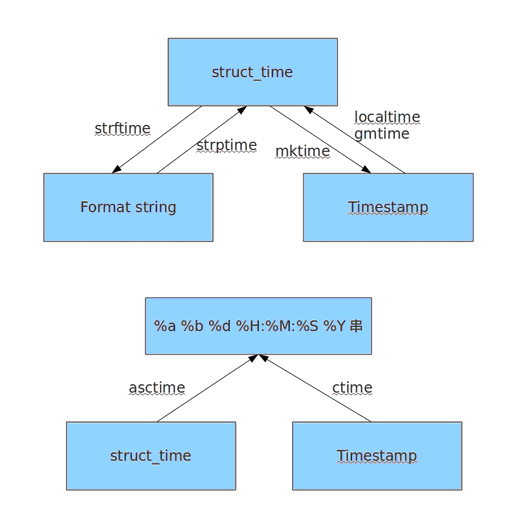
print time.time()
print time.mktime(time.localtime())
print time.gmtime() #可加时间戳参数
print time.localtime() #可加时间戳参数
print time.strptime('2014-11-11', '%Y-%m-%d')
print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') #默认当前时间
print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d',time.localtime()) #默认当前时间
print time.asctime()
print time.asctime(time.localtime())
print time.ctime(time.time())
import datetime
'''
datetime.date:表示日期的类。常用的属性有year, month, day
datetime.time:表示时间的类。常用的属性有hour, minute, second, microsecond
datetime.datetime:表示日期时间
datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点之间的长度
timedelta([days[, seconds[, microseconds[, milliseconds[, minutes[, hours[, weeks]]]]]]])
strftime("%Y-%m-%d")
'''
import datetime
print datetime.datetime.now()
print datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=5)
6、sys
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径 sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0) sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息 sys.maxint 最大的Int值 sys.maxunicode 最大的Unicode值 sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值 sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称 sys.stdout.write('please:')
val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1]
print val
7、os
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd
os.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.')
os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..')
os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录
os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推
os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname
os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname
os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印
os.remove() 删除一个文件
os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录
os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息
os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/"
os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n"
os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串
os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix'
os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示
os.environ 获取系统环境变量
os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径
os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回
os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素
os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素
os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False
os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True
os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False
os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False
os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间
os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
8、装饰器
'''
def foo():
print 'foo'
def foo():
print 'before do something'
print 'foo'
print 'after'
def foo():
print 'foo'
def wrapper(func):
print 'before'
func()
print 'after'
wrapper(foo)
def foo():
print 'foo'
def wrapper(func):
def result():
print 'before'
func()
print 'after'
return result
Do = wrapper(foo)
Do()
'''
def wrapper(func):
def result():
print 'before'
func()
print 'after'
return result
@wrapper
def foo():
print 'foo'
foo()
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding:utf-8
def Before(request,kargs):
print 'before'
def After(request,kargs):
print 'after'
def Filter(before_func,after_func):
def outer(main_func):
def wrapper(request,kargs):
before_result = before_func(request,kargs)
if(before_result != None):
return before_result;
main_result = main_func(request,kargs)
if(main_result != None):
return main_result;
after_result = after_func(request,kargs)
if(after_result != None):
return after_result;
return wrapper
return outer
@Filter(Before, After)
def Index(request,kargs):
print 'index'
if __name__ == '__main__':
Index(1,2)
Python第一课的更多相关文章
- <-0基础学python.第一课->
初衷:我电脑里面的歌曲很久没换了,我想听一下新的歌曲,把他们下载下来听,比如某个榜单的,但是一首一首的点击下载另存为真的很恶心 所以我想有没有办法通过程序的方式来实现,结果还真的有,而且网上已经有有人 ...
- Python 第一课笔记
1.Hello World程序的两种方法 在windows下执行 1.编辑器里输入,不用编译 print("Hello World!") 直接就可以运行 2.可以 ...
- python 第一课 helloworld
#!/usr/bin/env python #-*-coding:utf-8-*- #以上是配置编写环境的开始 #第一行env表示运行当前环境变量内的python版本(2.x or 3.x) #第二行 ...
- python第一课——关于python的一些概念
day01(上午): 1.学习方法(建议): 1).不要依赖于我的视频,绝对不要晚上将视频全部在过一遍 2).上课不要记笔记,而且不要用纸质的笔记本去整理笔记 3).不要只看不敲,代码方面我们需要做到 ...
- python第一课--基础知识
python简介 Python是一种计算机程序设计语言.是一种面向对象的动态类型语言,最初被设计用于编写自动化脚本(shell),随着版本的不断更新和语言新功能的添加,越来越多被用于独立的.大型项目的 ...
- Python 第一课
Python语言特点: 优雅,明确,简单 适合开发: Web网络和各种网络服务 系统工具和脚本 作为胶水语言把其他语言开发的模块包装起来方便使用 Python2.7.10的安装(path环境变量) ...
- python 第一课作用
1.使用while循环输入 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 x=0while x<10: x=x+1 if x==7: print(' ') continue print(x)#学 ...
- Python第一课-Python的下载与安装
官网 https://www.python.org/ 我们安装的是windows 系统 Python3和Python2版本不兼容,我们下载最新的Python3.7.4 下载executatable版本 ...
- 小甲鱼 python——第一课作业!
0: python是脚本语言把?虽然不是很清楚什么是脚本语言就是了.复制一下: 脚本语言(英语:Scripting language)是为了缩短传统的"编写.编译.链接.运行"( ...
随机推荐
- 【USACO 2.2.1】序言页码
[题目描述] 一类书的序言是以罗马数字标页码的.传统罗马数字用单个字母表示特定的数值,以下是标准数字表: I 1 L 50 M 1000 V 5 C 100 X 10 D 500 最多3个同样的可以表 ...
- 使用wireshark抓本机之间的包(转)
所转地址:http://www.chinadmd.com/file/oc6evrwtzieitexvoupppisr_1.html 在进行通信开发的过程中,我们往往会把本机既作为客户端又作为服务器端来 ...
- jQuery1.6以上版本prop和attr的区别
- [Python笔记]第四篇:内置函数
本篇主要内容:内置函数 函数 参考:https://docs.python.org/3.5/library/functions.html 内置函数列表 一.数学运算类 abs(x)求绝对值 >& ...
- [Python笔记]第三篇:深浅拷贝、函数
本篇主要内容:深浅拷贝,自定义函数,三目运算,lambda表达式, 深浅拷贝 一.数字和字符串 对于 数字 和 字符串 而言,赋值.浅拷贝和深拷贝无意义,因为其永远指向同一个内存地址. import ...
- UVA 11722 几何概型
第六周A题 - 几何概型 Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:0KB 64bit IO Format:%lld & %llu Descriptio ...
- Sqlserver 正则替换函数的一种实现
--函数 IF OBJECT_ID(N'dbo.RegexReplace') IS NOT NULL DROP FUNCTION dbo.RegexReplace GO CREATE FUNCTION ...
- 构建高可用web站点(四)
首先我们来了解负载均衡的概念:英文名称为Load Balance,其意思就是将负载(工作任务)进行平衡.分摊到多个操作单元上进行执行,例如Web服务器.FTP服务器.企业关键应用服务器和其它关键任务服 ...
- chrome代理服务器设置
在百度的内网很难访问chrome的相关站点,如果安装一些chrome的插件很不方便,所以呢,研究了一下chrome浏览器的代理模式,FQ安装插件. Chrome设置代理服务器的方法大体有几种: 1. ...
- 【中国剩余定理】【容斥原理】【快速乘法】【数论】HDU 5768 Lucky7
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5768 题目大意: T组数据,求L~R中满足:1.是7的倍数,2.对n个素数有 %pi!=ai 的数 ...
