【python之路7】python基本数据类型(一)
一、运算符
1、算数运算符
+、-、*、/、%(求余数)、//(取整数部分)
python2.x中,如果计算浮点数其中一个数字必须是浮点数否则按整数计算:
如python2.7中:print 9/2 结果是4
python2.7中:print 9.0/2 结果是4.5
python3.0中:print 9/2 结果是4.5
那么怎么在python2.7中让9/2输出4.5呢?可以通过下面的代码实现:
- from __future__ import division
- print 9/2
2、 比较运算符
==、!=或<>、>、<、>=、<=
3、赋值运算符
=、+=、-=、*=、/=、%=、**=、//=
4、逻辑运算符
and、or、not
5、成员运算符
in、not in
二、基本数据类型
- #!/usr/bin/env python
- # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
- i = 1
- print(type(i)) #查看属于哪个类
- print(dir(i)) #查看有哪些方法
- help(i) #类及方法的详细介绍
1、int(数字)
在32位机器上,整数的位数为32位,取值范围为-2**31~2**31-1,即-2147483648~2147483647
在64位系统上,整数的位数为64位,取值范围为-2**63~2**63-1,即-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807
- class int(object):
- """
- int(x=0) -> int or long
- int(x, base=10) -> int or long
- Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
- are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
- If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
- If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
- Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
- literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
- The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
- interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
- >>> int('0b100', base=0)
- """
- def bit_length(self):
- """ 返回表示该数字的时占用的最少位数 """
- """
- int.bit_length() -> int
- Number of bits necessary to represent self in binary.
"""用二进制必须的比特数来表示self参数"""- >>> bin(37)
- '0b100101'
- >>> (37).bit_length()
- """
- return 0
- def conjugate(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
- """ 返回该复数的共轭复数 """
- """ Returns self, the complex conjugate of any int. """
- pass
- def __abs__(self):
- """ 返回绝对值 """
- """ x.__abs__() <==> abs(x) """
- pass
- def __add__(self, y):
- """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
- pass
- def __and__(self, y):
- """ x.__and__(y) <==> x&y """
- pass
- def __cmp__(self, y):
- """ 比较两个数大小 """
- """ x.__cmp__(y) <==> cmp(x,y) """
- pass
- def __coerce__(self, y):
- """ 强制生成一个元组 """
- """ x.__coerce__(y) <==> coerce(x, y) """
- pass
- def __divmod__(self, y):
- """ 相除,得到商和余数组成的元组 """
- """ x.__divmod__(y) <==> divmod(x, y) """
- pass
- def __div__(self, y):
- """ x.__div__(y) <==> x/y """
- pass
- def __float__(self):
- """ 转换为浮点类型 """
- """ x.__float__() <==> float(x) """
- pass
- def __floordiv__(self, y):
- """ x.__floordiv__(y) <==> x//y """
- pass
- def __format__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
- pass
- def __getattribute__(self, name):
- """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
- pass
- def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
- """ 内部调用 __new__方法或创建对象时传入参数使用 """
- pass
- def __hash__(self):
- """如果对象object为哈希表类型,返回对象object的哈希值。哈希值为整数。在字典查找中,哈希值用于快速比较字典的键。两个数值如果相等,则哈希值也相等。"""
- """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
- pass
- def __hex__(self):
- """ 返回当前数的 十六进制 表示 """
- """ x.__hex__() <==> hex(x) """
- pass
- def __index__(self):
- """ 用于切片,数字无意义 """
- """ x[y:z] <==> x[y.__index__():z.__index__()] """
- pass
- def __init__(self, x, base=10): # known special case of int.__init__
- """ 构造方法,执行 x = 123 或 x = int(10) 时,自动调用,暂时忽略 """
- """
- int(x=0) -> int or long
- int(x, base=10) -> int or long
- Convert a number or string to an integer, or return 0 if no arguments
- are given. If x is floating point, the conversion truncates towards zero.
- If x is outside the integer range, the function returns a long instead.
- If x is not a number or if base is given, then x must be a string or
- Unicode object representing an integer literal in the given base. The
- literal can be preceded by '+' or '-' and be surrounded by whitespace.
- The base defaults to 10. Valid bases are 0 and 2-36. Base 0 means to
- interpret the base from the string as an integer literal.
- >>> int('0b100', base=0)
- # (copied from class doc)
- """
- pass
- def __int__(self):
- """ 转换为整数 """
- """ x.__int__() <==> int(x) """
- pass
- def __invert__(self):
- """ x.__invert__() <==> ~x """
- pass
- def __long__(self):
- """ 转换为长整数 """
- """ x.__long__() <==> long(x) """
- pass
- def __lshift__(self, y):
- """ x.__lshift__(y) <==> x<<y """
- pass
- def __mod__(self, y):
- """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
- pass
- def __mul__(self, y):
- """ x.__mul__(y) <==> x*y """
- pass
- def __neg__(self):
- """ x.__neg__() <==> -x """
- pass
- @staticmethod # known case of __new__
- def __new__(S, *more):
- """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
- pass
- def __nonzero__(self):
- """ x.__nonzero__() <==> x != 0 """
- pass
- def __oct__(self):
- """ 返回改值的 八进制 表示 """
- """ x.__oct__() <==> oct(x) """
- pass
- def __or__(self, y):
- """ x.__or__(y) <==> x|y """
- pass
- def __pos__(self):
- """ x.__pos__() <==> +x """
- pass
- def __pow__(self, y, z=None):
- """ 幂,次方 """
- """ x.__pow__(y[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
- pass
- def __radd__(self, y):
- """ x.__radd__(y) <==> y+x """
- pass
- def __rand__(self, y):
- """ x.__rand__(y) <==> y&x """
- pass
- def __rdivmod__(self, y):
- """ x.__rdivmod__(y) <==> divmod(y, x) """
- pass
- def __rdiv__(self, y):
- """ x.__rdiv__(y) <==> y/x """
- pass
- def __repr__(self):
- """转化为解释器可读取的形式 """
- """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
- pass
- def __str__(self):
- """转换为人阅读的形式,如果没有适于人阅读的解释形式的话,则返回解释器课阅读的形式"""
- """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
- pass
- def __rfloordiv__(self, y):
- """ x.__rfloordiv__(y) <==> y//x """
- pass
- def __rlshift__(self, y):
- """ x.__rlshift__(y) <==> y<<x """
- pass
- def __rmod__(self, y):
- """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
- pass
- def __rmul__(self, y):
- """ x.__rmul__(y) <==> y*x """
- pass
- def __ror__(self, y):
- """ x.__ror__(y) <==> y|x """
- pass
- def __rpow__(self, x, z=None):
- """ y.__rpow__(x[, z]) <==> pow(x, y[, z]) """
- pass
- def __rrshift__(self, y):
- """ x.__rrshift__(y) <==> y>>x """
- pass
- def __rshift__(self, y):
- """ x.__rshift__(y) <==> x>>y """
- pass
- def __rsub__(self, y):
- """ x.__rsub__(y) <==> y-x """
- pass
- def __rtruediv__(self, y):
- """ x.__rtruediv__(y) <==> y/x """
- pass
- def __rxor__(self, y):
- """ x.__rxor__(y) <==> y^x """
- pass
- def __sub__(self, y):
- """ x.__sub__(y) <==> x-y """
- pass
- def __truediv__(self, y):
- """ x.__truediv__(y) <==> x/y """
- pass
- def __trunc__(self, *args, **kwargs):
- """ 返回数值被截取为整形的值,在整形中无意义 """
- pass
- def __xor__(self, y):
- """ x.__xor__(y) <==> x^y """
- pass
- denominator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
- """ 分母 = 1 """
- """the denominator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
- imag = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
- """ 虚数,无意义 """
- """the imaginary part of a complex number"""
- numerator = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
- """ 分子 = 数字大小 """
- """the numerator of a rational number in lowest terms"""
- real = property(lambda self: object(), lambda self, v: None, lambda self: None) # default
- """ 实属,无意义 """
- """the real part of a complex number"""
- int
- num=4 #相当于 num = int(4),其实实际是调用的 __init__()方法
- print(int('0b100',0))#输出4,0b100的十进制是4
- len_a = a.bit_length()
- print(len_a) #结果返回3,因为4的2进制为100,最少用3位可以表示
- n = 123 #实际是调用了 n = int(123) ,而python内部实际调用了int.__init__方法
- print(int('0b100',0))#输出4,0b100的十进制是4
查询变量指向的地址:id(变量名)
在通常程序语言中,变量n1和n2是指向不同的内存地址:
- n1 = 123
- n2 = 123
而下面代码表示指向同一内存地址:
- n1 = 123
- n2 = n1
而在python中为了优化内存空间使用,把经常使用的int类型的变量范围-5~257这个范围的变量指向的值,只要值相等则都指向同一内存地址:
最新版本的python,只要值相同则都指向同一内存地址。
- n1 = 20
- n2 = 20
- print(id(n1),id(n2)) #结果返回1802282688 1802282688表示使用的是同一内存地址
2、布尔类型(bool)
True 除0以外的任何值都表示Ture
False 0值表示为False
3、字符串(str)
1)可以用索引和切片、字符串长度
- #!usr/bin/env python
- # -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
- st = 'congratulations'
- s1 = st[0] #返回c
- s2 = st[1] #返回o
- s3 = st[2] #返回n
- s4 = st[0:2] #返回co,不包含2
- s5 = st[-1] #返回字符串的最后一个字符s
- #循环输出,每一个字符
- for i in st:
- print(i)
- print(len(st)) #长度返回15
切片补充:
- st = "我们都有一个家名字叫中国"
- #普通切片
- #切出“一个家”
- s = st[4:7] #注意是顾头不顾腚,
- #切出“我们”
- s = st[:2] #从头开始切可以省略0
- #切出“都有一个家名字叫中国”
- s = st[2:] #切到最后冒号后面的数字可以省略
- #切出最后两个字
- s = st[-2:] #注意不能是-1,因为顾头不顾腚取不到-1
- #切出全部字符
- s = st[:] #数字省略表示从头切到尾
- #切片语法:
- #s[起始位置:结束位置:步长] 步长是指每几个取一个
- #切出“我都一家字中”
- s = st[::2] #每两个取一个
- #步长为负数可以反着取
- #切出“家一都”
- s = st[6:1:-2] #从6到1反着每两个取一个,注意此时一样顾头不顾腚取不到1
- #切出“国中叫字名家个一有都们我”
- s = st[::-1] #从尾到头反着每一个取一个
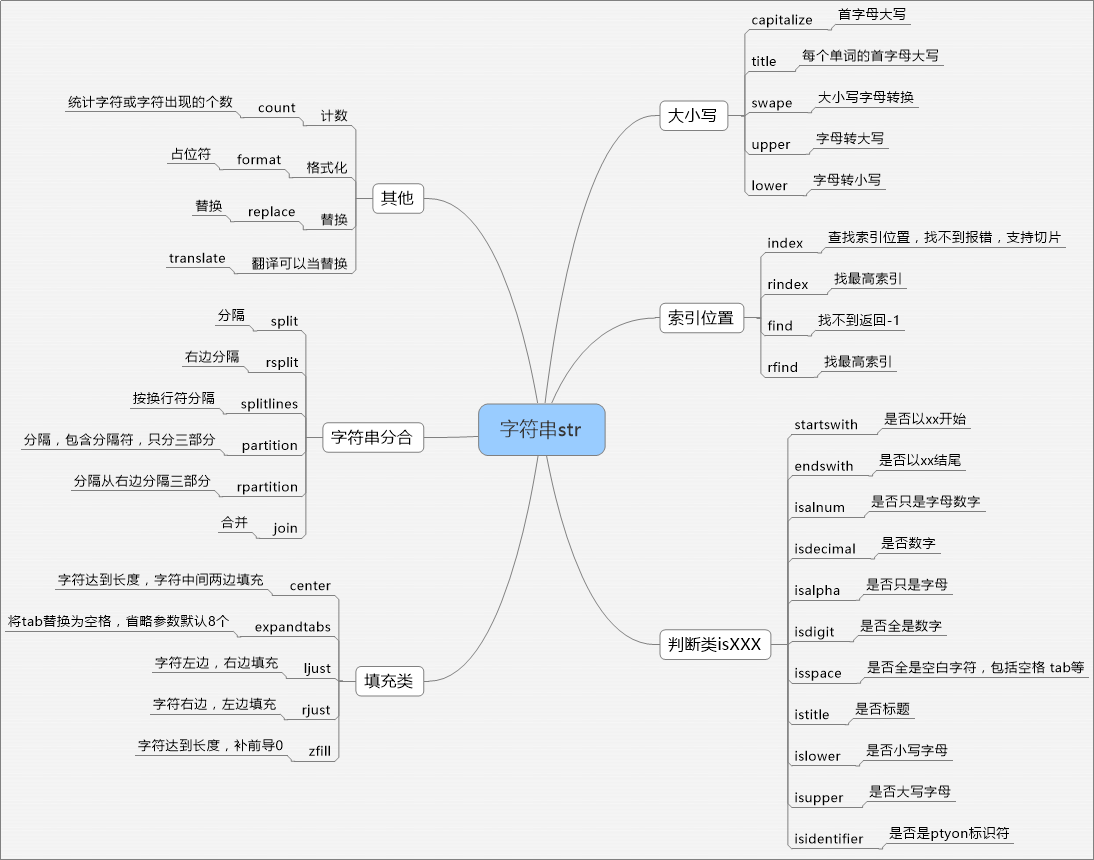
2)所有字符串功能简介代码如下:
- str1.capitalize() #首字母大写
- 'the title is good'.title()#返回The Title Is Good,每个单词开头的第一个字母变为大写
- "YouAre".swapcase() #结果返回yOUaRE,大写变小写,小写变大写
- str1.count('u')#字符串str1中u的个数,后面可以加strt参数和end参数
- str_unicode = str1.decode('utf-8')#str1从utf-8解码为unicode
- str_gbk = str_unicode.encode('gbk') #strr_unicode编码为gbk
- str1.find('s')#查询s在str1中的索引位置,可以选择start和end范围,找不到返回-1
- 'aa_bb_cc'.rfind('_') #结果返回5,返回最高的索引,后面可以加start和end参数
- str1.index('s')#查询s在str1中的索引位置,可以选择start和end范围,找不到返回报错
- 'aa_bb_cc'.rindex('_') #结果返回5,返回最高的索引,后面可以加start和end参数,如果查询不到则抛出异常
- 'your name is {0} and your age is {1}'.format('sunshuhai','30') #结果your name is sunshuhai and your age is 30
- str1.endswith('i')#以字符串i结束,返回True或False,参数可以是元组,元组中的任何一个结束则返回True,后面可以加strt参数和end参数
- str1.startswith('i')#以字符串i结束,返回True或False,参数可以是元组,元组中的任何一个结束则返回True,后面可以加strt参数和end参数
- str1.isalnum()#(alphanumeric字母数字的)判断是否是字母或数字,至少有一个字符。返回True或False
- str1.isalpha()#(alphabetic字母的)判断是否全是字母,至少有一个字符。返回True或False
- str1.isdigit()#判断是否全是数字,至少有一个字符。返回True或False
- str1.isspace()#判断是否全是空白的(包含换行,tab等),至少有一个字符。返回True或False
- 'The Title Is Good'.istitle()#判断是否是否是标题字符串(首字母大写),至少有一个字符。返回True或False
- str1.islower()#判断是否全是小写字母,至少有一个字符。返回True或False
- str1.isupper()#判断是否全是大写字母,至少有一个字符。返回True或False
- 'abc'.upper() #全部转化为大写
- str1.lower() #字符串str1全部转化为小写
- 'tttTitle'.lstrip('t') #剥除字符串左边的字符t,如果没有参数则删除空格
- 'tttTitle'.rstrip('t') #剥除字符串右边的字符t,如果没有参数则删除空格
- 'tttTitle'.strip('t') #剥除字符串两边的字符t,如果没有参数则删除空格
- str1.center(20,"*") #sun在中间剩余的17个字符用*号填充,如果*s省略则默认空格
- str1.expandtabs(20)#将tab替换为20个空格,如果省略则默认8个空格
- str1.ljust(20,'*') #(justified)str1显示在左边,20个字符剩余的位置全部用*填充,*省略默认空格
- str1.rjust(20,'*') #(justified)str1显示在右边,20个字符剩余的位置全部用*填充,*省略默认空格
- 'abc'.zfill(10) #返回0000000abc,如果参数是2返回abc,原字符串不会被截取
- 'aa_bb_cc'.split('_') #分隔,返回['aa', 'bb', 'cc'],返回列表,不包含分隔符本身,如果省略则用任意空白符分隔
- 'aa_bb_cc'.rsplit('_') #分隔,返回['aa', 'bb', 'cc'],返回列表,不包含分隔符本身,如果省略则用任意空白符分隔
- str1.splitlines(True) #按换行符进行分隔,如果参数省略则列表结果中不包含换行符,如果为True则表示结果包含换行符['zhang\n', 'li\n', 'sun\n', 'zhao\n', 'qian\n']
- 'aa_bb_cc'.partition('_') #分隔,返回('aa', '_', 'bb_cc'),返回元组包含前,自己,中,自己,后几部分
- 'aa_bb_cc'.rpartition('_') #分隔,返回('aa_bb', '_', 'cc'),返回元组包含前,自己,中,自己,后几部分
- '|'.join(['sun','li','zhao','qian']) #将列表中的元素以|为分隔符连接起来,参数必须是可迭代的
- 'aa_bb_cc'.replace('_','-',1) #结果返回aa-bb_cc,如果第3个参数表示从左边开始替换几个,不提供,则表示全部替换
- translate 需扩展用法
3)补充
isdecimal
- python中str函数isdigit、isdecimal、isnumeric的区别
- num = "1" #unicode
- num.isdigit() # True
- num.isdecimal() # True
- num.isnumeric() # True
- num = "1" # 全角
- num.isdigit() # True
- num.isdecimal() # True
- num.isnumeric() # True
- num = b"1" # byte
- num.isdigit() # True
- num.isdecimal() # AttributeError 'bytes' object has no attribute 'isdecimal'
- num.isnumeric() # AttributeError 'bytes' object has no attribute 'isnumeric'
- num = "IV" # 罗马数字
- num.isdigit() # True
- num.isdecimal() # False
- num.isnumeric() # True
- num = "四" # 汉字
- num.isdigit() # False
- num.isdecimal() # False
- num.isnumeric() # True
isidentifier() :如果字符串是有效的 Python 标识符返回 True,否则返回 False。
- #!/usr/bin/env python
- #-*- encoding:utf-8 -*-
- print( "if".isidentifier() )
- print( "def".isidentifier() )
- print( "class".isidentifier() )
- print( "_a".isidentifier() )
- print( "中国123a".isidentifier() )
- print( "123".isidentifier() )
- print( "3a".isidentifier() )
- print( "".isidentifier() )
- 输出结果为:
- True
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
translate
- #!/usr/bin/python
- from string import maketrans # 引用 maketrans 函数。
- intab = "aeiou"
- outtab = "12345"
- trantab = maketrans(intab, outtab)
- str = "this is string example....wow!!!"
- print str.translate(trantab)
- #输出结果:th3s 3s str3ng 2x1mpl2....w4w!!!
- 注:Python3.4已经没有string.maketrans()了,取而代之的是内建函数: bytearray.maketrans()、bytes.maketrans()、str.maketrans()
4)字符串归整
遗漏:rstrip lstrip strip
输出中文姓名的2进制编码
- name = '张三' #utf-8一个汉字是3个字节,gbk一个汉字是2个字节,一个字节是8个bit
- for i in name:
- print(i)
- byte_list = bytes(i,'utf-8') #bytes('张','utf-8')将张转化为16进制的utf-8字节码列表(集合)
print(str(byte_list,'utf-8')) #将utf-8的字节转化为字符串- print(byte_list) #b'\xe5\xbc\xa0' b'\xe4\xb8\x89',\x表示16禁止,一个16禁止表示4个2进制
- for i in byte_list: #循环每个字节时返回每个字节10进制数
- print(i,bin(i)) #bin(i) 将10进制转化为2进制
3)、所有str类的函数详细功能,如下代码
- class str(basestring):
- """
- str(object='') -> string
- Return a nice string representation of the object.
- If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object.
- """
- def capitalize(self):
- """ 首字母变大写 """
- """
- S.capitalize() -> string
- Return a copy of the string S with only its first character
- capitalized['k?pit?laizd]大写的
- 返回一个复制的只是第一个字符大写的字符串
- """ return ""
- def center(self, width, fillchar=None):
- """ 内容居中,width:总长度;fillchar:空白处填充内容,默认无 """
- """
- S.center(width[, fillchar]) -> string
- Return S centered in a string of length width. Padding is
- done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
- 返回S字符串参数width长度的中间,用规定的字符进行填补(默认是空格)
- """
- return ""
- def count(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
- """ 子序列个数 """
- """
- S.count(sub[, start[, end]]) -> int
- Return the number of non-overlapping occurrences of substring sub in
- string S[start:end]. Optional arguments start and end are interpreted
- as in slice notation.
- 返回非重叠发生的子字符串序列sub在字符串范围start和end参数之间的个数,可选择参数start和end可以理解为切片
- """
- return 0
- def decode(self, encoding=None, errors=None):
- """ 解码 """
- """
- S.decode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object
- Decodes S using the codec registered for encoding. encoding defaults
- to the default encoding. errors may be given to set a different error
- handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
- a UnicodeDecodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore' and 'replace'
- as well as any other name registered with codecs.register_error that is
- able to handle UnicodeDecodeErrors.
- """
- return object()
- def encode(self, encoding=None, errors=None):
- """ 编码,针对unicode """
- """
- S.encode([encoding[,errors]]) -> object
- Encodes S using the codec registered for encoding. encoding defaults
- to the default encoding. errors may be given to set a different error
- handling scheme. Default is 'strict' meaning that encoding errors raise
- a UnicodeEncodeError. Other possible values are 'ignore', 'replace' and
- 'xmlcharrefreplace' as well as any other name registered with
- codecs.register_error that is able to handle UnicodeEncodeErrors.
- """
- return object()
- def endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None):
- """ 是否以 xxx 结束 """
- """
- S.endswith(suffix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
- Return True if S ends with the specified suffix, False otherwise.
- With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
- With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
- suffix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
- 返回True如果以规定的参数suffix结束,否则返回False
- 选择参数start,那么字符串从这个位置开始
- 选择参数end,那么从这个位置停止比较字符串
- suffix可能是一个字符串类型的元祖
- """
- return False
- def expandtabs(self, tabsize=None):
- """ 将tab转换成空格,默认一个tab转换成8个空格 """
- """
- S.expandtabs([tabsize]) -> string
- Return a copy of S where all tab characters are expanded using spaces.
- If tabsize is not given, a tab size of 8 characters is assumed.
- 返回一个赋值的字符串,该字符串所有的tab字符全部扩展为空格
- 如果tabsize没提供,自动嘉定一个tab大小为8个字符
- """
- return ""
- def find(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
- """ 寻找子序列位置,如果没找到,返回 -1 """
- """
- S.find(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
- Return the lowest index in S where substring sub is found,
- such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
- arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
- 如果那个sub包含在字符串start和end之内。选择
- 参数start和end被理解为切片
- Return -1 on failure.
- 返回在字符串sub被找到的最小索引,
- 失败的话返回-1
- """
- return 0
- def format(*args, **kwargs): # known special case of str.format
- """ 字符串格式化,动态参数,将函数式编程时细说 """
- """
- S.format(*args, **kwargs) -> string
- Return a formatted version of S, using substitutions from args and kwargs.
- The substitutions are identified by braces ('{' and '}').
- 返回格式化版本的字符串,用args和kwargs参数代替。
- 这个替代可以被大括号识别
- """
- pass
- def index(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
- """ 子序列位置,如果没找到,报错 """
- S.index(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
- """
- Like S.find() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
- 像find函数,但是当子字符串找不到时会抛出ValueError是我错误
- """
- return 0
- def isalnum(self):
- """ 是否是字母和数字 """
- """
- S.isalnum() -> bool
- Return True if all characters in S are alphanumeric
- and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
- 返回真,如果所有在字符串中的字符是字母或数字的
- 并且至少在字符串中有一个字符,否则返回False
- """
- return False
- def isalpha(self):
- """ 是否是字母 """
- """
- S.isalpha() -> bool
- Return True if all characters in S are alphabetic
- and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
- 返回True,如果所有的字符都是字母
- 并且至少有一个字符在字符串中,否则返回False
- """
- return False
- def isdigit(self):
- """ 是否是数字 """
- """
- S.isdigit() -> bool
- Return True if all characters in S are digits
- and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
- 返回True如果所有的字符都是数字
- 并且至少有一个字符,否则返回False
- """
- return False
- def islower(self):
- """ 是否小写 """
- """
- S.islower() -> bool
- Return True if all cased characters in S are lowercase and there is
- at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
- 返回True如果所有的字母字符都是小写字母并且
- 至少有一个字符字母在字符串中,否则返回False
- """
- return False
- def isspace(self):
- """
- S.isspace() -> bool
- Return True if all characters in S are whitespace
- and there is at least one character in S, False otherwise.
- 返回True如果所有的字符都是空白的(包含换行,tab等)
- 并且失少有一个字符,否则返回False
- """
- return False
- def istitle(self):
- """
- S.istitle() -> bool
- Return True if S is a titlecased string and there is at least one
- character in S, i.e. uppercase characters may only follow uncased
- characters and lowercase characters only cased ones. Return False
- otherwise.
- 返回True如果字符串中是一个标题字母字符串(并且至少一个字符,
- 也就是大写字母可能只是外漏的字母,其他是小写字母(首字母大写)
- """
- return False
- def isupper(self):
- """
- S.isupper() -> bool
- Return True if all cased characters in S are uppercase and there is
- at least one cased character in S, False otherwise.
- 返回True如果所有的字母都是大写字母
- 至少有一个字母字符在字符串中,否则返回False
- """
- return False
- def join(self, iterable):
- """ 连接 """
- """
- S.join(iterable) -> string
- Return a string which is the concatenation of the strings in the
- iterable. The separator between elements is S.
- 返回一个字符串,该字符串连接迭代器中的字符串,元素直接的分隔符是‘S’
- 支持列表 元组之间的连接
- """
- return ""
- def ljust(self, width, fillchar=None):
- """ 内容左对齐,右侧填充 """
- """
- S.ljust(width[, fillchar]) -> string
- Return S left-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
- done using the specified fill character (default is a space).
- 返回左调整在字符串width的长度中,用规定的字符进行填充(默认是空格)
- 字符显示在左边,其余全部被填充
- """
- return ""
- def lower(self):
- """ 变小写 """
- """
- S.lower() -> string
- Return a copy of the string S converted to lowercase.
- 返回一个赋值的字符串转为小写
- """
- return ""
- def lstrip(self, chars=None):
- """ 移除左侧空白 """
- """
- S.lstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode
- Return a copy of the string S with leading whitespace removed.
- If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
- If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
- 返回一个赋值的字符串,该字符串开头空格被移除
- 如果chars参数被给予并且不是None值,那么删除参数chars代指的字符
- 如果chars是unicode,S 将转化成unicode在删除之前
- """
- return ""
- def partition(self, sep):
- """ 分割,前,中,后三部分 """
- """
- S.partition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
- Search for the separator sep in S, and return the part before it,
- the separator itself, and the part after it. If the separator is not
- found, return S and two empty strings.
- 查找分隔符参数sep,并返回它之前的部分,
- 分隔符自己,和分隔符之后的部分。如果分隔符找不到,
- 返回两个空字符串
- """
- pass
- def replace(self, old, new, count=None):
- """ 替换 """
- """
- S.replace(old, new[, count]) -> string
- Return a copy of string S with all occurrences of substring
- old replaced by new. If the optional argument count is
- given, only the first count occurrences are replaced.
- 返回一个赋值的字符串,已经发生的老字符串被新字符串替换。如果选择参数count被提供了,
- 只有第一个count已发生的被替换
- """
- return ""
- def rfind(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
- """
- S.rfind(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
- Return the highest index in S where substring sub is found,
- such that sub is contained within S[start:end]. Optional
- arguments start and end are interpreted as in slice notation.
- Return -1 on failure.
- 返回最高的索引如果sub在子字符串中被找到
- 如果sub参数包含在start和end之间,选择参数start和end被理解为切片
- 如果查找不到则返回-1
- """
- return 0
- def rindex(self, sub, start=None, end=None):
- """
- S.rindex(sub [,start [,end]]) -> int
- Like S.rfind() but raise ValueError when the substring is not found.
- 和rfind()函数一行,但是当在字符串中找不到的是否抛出ValueError异常
- """
- return 0
- def rjust(self, width, fillchar=None):
- """
- S.rjust(width[, fillchar]) -> string
- Return S right-justified in a string of length width. Padding is
- done using the specified fill character (default is a space)
- 返回字符串长度在参数width中的右调整字符串
- 用规定的字符填补(默认是空格)
- 字符显示在右边,其余全部被填充
- """
- return ""
- def rpartition(self, sep):
- """
- S.rpartition(sep) -> (head, sep, tail)
- Search for the separator sep in S, starting at the end of S, and return
- the part before it, the separator itself, and the part after it. If the
- separator is not found, return two empty strings and S.
- 查找分隔符参数set,从字符串的末尾开始,返回之前的部分,返回分隔符本身,返回后半部分,
- 如果分隔符找不到,返回两个空的字符串
- """
- pass
- def rsplit(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None):
- """
- S.rsplit([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings
- Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the
- delimiter string, starting at the end of the string and working
- to the front. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit splits are
- done. If sep is not specified or is None, any whitespace string
- is a separator.
- 返回一个单词列表在字符串中,把sep用做分隔符,起始于字符创的末尾,并且作用于
- 前面。如果maxsplit参数提供了,最多分隔几次被设定,
- 如果sep没有规定或者是None,任何空白字符就是这个分隔符
- """
- return []
- def rstrip(self, chars=None):
- """
- S.rstrip([chars]) -> string or unicode
- Return a copy of the string S with trailing whitespace removed.
- If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
- If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
- 返回一个复制的字符串,该字符串后面的空格符被移除。
- 如果chars参数被给予并且不是None值,移除字符chars代替
- 如果chars是unicode,字符串将转为unicode在剥除之前
- """
- return ""
- def split(self, sep=None, maxsplit=None):
- """ 分割, maxsplit最多分割几次 """
- """
- S.split([sep [,maxsplit]]) -> list of strings
- Return a list of the words in the string S, using sep as the
- delimiter string. If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit
- splits are done. If sep is not specified or is None, any
- whitespace string is a separator and empty strings are removed
- from the result.
- 返回一个单词列表在字符串中,把sep用做分隔符,如果maxsplit参数提供了,
- 最多分隔此时确定。如果sep参数没有指定或者为None,
- 任何空白符就是分隔符并且空字符串从结果中移除
- """
- return []
- def splitlines(self, keepends=False):
- """ 根据换行分割 """
- """
- S.splitlines(keepends=False) -> list of strings
- Return a list of the lines in S, breaking at line boundaries.
- Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends
- is given and true.
- 返回一个行的列表,阻断在行边界。
- 行中断不包含列表结果中,除非keepends参数提供了并且为True
- """
- return []
- def startswith(self, prefix, start=None, end=None):
- """ 是否起始 """
- """
- S.startswith(prefix[, start[, end]]) -> bool
- Return True if S starts with the specified prefix, False otherwise.
- With optional start, test S beginning at that position.
- With optional end, stop comparing S at that position.
- prefix can also be a tuple of strings to try.
- 返回True 如果开始于指定的参数prefix否则返回False
- 带start参数,从那个位置开始检测
- 带end参数,至那个位置停止比较
- """
- return False
- def strip(self, chars=None):
- """ 移除两段空白 """
- """
- S.strip([chars]) -> string or unicode
- Return a copy of the string S with leading and trailing
- whitespace removed.
- If chars is given and not None, remove characters in chars instead.
- If chars is unicode, S will be converted to unicode before stripping
- 返回一个复制的字符串,该字符串头部和尾部
- 的空白字符被移除
- 如果chars参数被提供并且不为None,移除字符用参数chars代替
- 如果chars是unicode,字符串将被转化为unicode在剥除之前
- """
- return ""
- def swapcase(self):
- """ 大写变小写,小写变大写 """
- """
- S.swapcase() -> string
- Return a copy of the string S with uppercase characters
- converted to lowercase and vice versa.
- 返回一个复制的字符串,改字符串大写字母字符转化为小写字母,
- 反之亦然
- """
- return ""
- def title(self):
- """
- S.title() -> string
- Return a titlecased version of S, i.e. words start with uppercase
- characters, all remaining cased characters have lowercase.
- 返回一个标题版本字符串,也是就单词开始是大写字符,所有剩余的字符字符都是小写
- """
- return ""
- def translate(self, table, deletechars=None):
- """
- 转换,需要先做一个对应表,最后一个表示删除字符集合
- intab = "aeiou"
- outtab = "12345"
- trantab = maketrans(intab, outtab)
- str = "this is string example....wow!!!"
- print str.translate(trantab, 'xm')
- """
- """
- S.translate(table [,deletechars]) -> string
- Return a copy of the string S, where all characters occurring
- in the optional argument deletechars are removed, and the
- remaining characters have been mapped through the given
- translation table, which must be a string of length 256 or None.
- If the table argument is None, no translation is applied and
- the operation simply removes the characters in deletechars.
- 返回一个复制的字符串,该字符串所有的字符
- 出现在选择参数deletechars中被移除,并且
- 剩余的字符已经通过映射规定的翻译表,该表必须是个长度为256的字符串或者是None。
- 如果表的参数为None,没有翻译表应用并且简单的操作移除了在deletechars中的字符
- """
- return ""
- def upper(self):
- """
- S.upper() -> string
- Return a copy of the string S converted to uppercase.
- 返回一个复制的转化为大写的字符串
- """
- return ""
- def zfill(self, width):
- """方法返回指定长度的字符串,原字符串右对齐,前面填充0。"""
- """
- S.zfill(width) -> string
- Pad a numeric string S with zeros on the left, to fill a field
- of the specified width. The string S is never truncated.
- 在左边填补0,填充制定参数width的制定宽度。原字符串不会截取
- """
- return ""
- def _formatter_field_name_split(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
- pass
- def _formatter_parser(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
- pass
- def __add__(self, y):
- """ x.__add__(y) <==> x+y """
- pass
- def __contains__(self, y):
- """ x.__contains__(y) <==> y in x """
- pass
- def __eq__(self, y):
- """ x.__eq__(y) <==> x==y """
- pass
- def __format__(self, format_spec):
- """
- S.__format__(format_spec) -> string
- Return a formatted version of S as described by format_spec.
- """
- return ""
- def __getattribute__(self, name):
- """ x.__getattribute__('name') <==> x.name """
- pass
- def __getitem__(self, y):
- """ x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y] """
- pass
- def __getnewargs__(self, *args, **kwargs): # real signature unknown
- pass
- def __getslice__(self, i, j):
- """
- x.__getslice__(i, j) <==> x[i:j]
- Use of negative indices is not supported.
- """
- pass
- def __ge__(self, y):
- """ x.__ge__(y) <==> x>=y """
- pass
- def __gt__(self, y):
- """ x.__gt__(y) <==> x>y """
- pass
- def __hash__(self):
- """ x.__hash__() <==> hash(x) """
- pass
- def __init__(self, string=''): # known special case of str.__init__
- """
- str(object='') -> string
- Return a nice string representation of the object.
- If the argument is a string, the return value is the same object.
- # (copied from class doc)
- """
- pass
- def __len__(self):
- """ x.__len__() <==> len(x) """
- pass
- def __le__(self, y):
- """ x.__le__(y) <==> x<=y """
- pass
- def __lt__(self, y):
- """ x.__lt__(y) <==> x<y """
- pass
- def __mod__(self, y):
- """ x.__mod__(y) <==> x%y """
- pass
- def __mul__(self, n):
- """ x.__mul__(n) <==> x*n """
- pass
- @staticmethod # known case of __new__
- def __new__(S, *more):
- """ T.__new__(S, ...) -> a new object with type S, a subtype of T """
- pass
- def __ne__(self, y):
- """ x.__ne__(y) <==> x!=y """
- pass
- def __repr__(self):
- """ x.__repr__() <==> repr(x) """
- pass
- def __rmod__(self, y):
- """ x.__rmod__(y) <==> y%x """
- pass
- def __rmul__(self, n):
- """ x.__rmul__(n) <==> n*x """
- pass
- def __sizeof__(self):
- """ S.__sizeof__() -> size of S in memory, in bytes """
- pass
- def __str__(self):
- """ x.__str__() <==> str(x) """
- pass
- str
【python之路7】python基本数据类型(一)的更多相关文章
- Python之路,Day4 - Python基础4 (new版)
Python之路,Day4 - Python基础4 (new版) 本节内容 迭代器&生成器 装饰器 Json & pickle 数据序列化 软件目录结构规范 作业:ATM项目开发 ...
- Python之路,Day1 - Python基础1
本节内容 Python介绍 发展史 Python 2 or 3? 安装 Hello World程序 变量 用户输入 模块初识 .pyc是个什么鬼? 数据类型初识 数据运算 表达式if ...else语 ...
- Python之路:Python操作 RabbitMQ、Redis、Memcache、SQLAlchemy
Memcached Memcached 是一个高性能的分布式内存对象缓存系统,用于动态Web应用以减轻数据库负载.它通过在内存中缓存数据和对象来减少读取数据库的次数,从而提高动态.数据库驱动网站的速度 ...
- 【Python之路】Python目录
Python基础1 -- Python由来.Python种类.编码方式, Python基础2 -- Python运算符.数据类型.enumerate.range.for循环 python基础3 -- ...
- Python之路,Day1 - Python基础1(转载Alex)
本节内容 Python介绍 发展史 Python 2 or 3? 安装 Hello World程序 变量 用户输入 模块初识 .pyc是个什么鬼? 数据类型初识 数据运算 表达式if ...else语 ...
- Python之路,Day1 - Python基础1 --转自金角大王
本节内容 Python介绍 发展史 Python 2 or 3? 安装 Hello World程序 变量 用户输入 模块初识 .pyc是个什么鬼? 数据类型初识 数据运算 表达式if ...else语 ...
- Python之路,Day1 - Python基础1 介绍、基本语法、流程控制
本节内容 1.python介绍 2.发展史 3.python 2.x or python 3.x ? 4.python 安装 5.第一个程序 Hello World 程序 6.变量 7.用户输入 8. ...
- Python之路:Python简介
Python前世今生 python的创始人为吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum).1989年的圣诞节期间他为了在阿姆斯特丹打发时间,决心开发一个新的脚本解释程序,作为ABC语言的一种继承 ...
- Python之路-初识python及环境搭建与测试(Python安装、Anaconda安装、PyCharm安装)
一.认识Python 起源 Python的作者是著名的“龟叔”Guido van Rossum,他希望有一种语言,这种语言能够像C语言那样,能够全面调用计算机的功能接口,又可以像shell那样,可以轻 ...
- Python之路----------基础 一(数据类型、变量、基本语法、流程控制)
一. 数据类型与变量 1.数据类型 整数 #Python在程序中的表示方法和数学上的写法一模一样,-1,0,1都是整数. 浮点数 1 #浮点数就是小数. 字符串 1 #在Python中字符串是以 ...
随机推荐
- 数据绑定(八)使用Binding的RelativeSource
当一个Binding有明白的数据来源时能够通过为Source或ElementName赋值的办法让Binding与之关联,有的时候因为不能确定Source的对象叫什么名字,但知道它与作为Binding目 ...
- PHP【第一篇】安装
一.准备 1.环境 系统平台:Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 7.3 (Maipo) 内核版本:3.10.0-514.el7.x86_64 2.下载安装 ...
- 不支持的关键字:“provider connection string”报错信息及解决方案
今天在部署公司开发框架的时候 ,登录系统之后调用代办列表的时候就报错了 总线调用契约XX.Service.Contracts.IXXService上的GetXXCount方法时出错. Resoluti ...
- SpringMVC——项目启动时从数据库查询数据
SpringMVC项目中遇到这样的问题: 1.很多数据字典需要从数据库中查询: 2.懒得修改SQL语句: 3.想在项目中声明静态变量存储数据字典,但是希望这个字典可以在项目启动时进行加载. 当遇到这样 ...
- Leetcode Python Solution(continue update)
leetcode python solution 1. two sum (easy) Given an array of integers, return indices of the two num ...
- Scala函数字面量简化写法
Scala提供了多种方法来简化函数字面量中多余的部分,比如前面例子中filter方法中使用的函数字面量,完整的写法如下: (x :Int ) => x +1 首先可以省略到参数的类型,Scala ...
- java 用eclipse j2ee写的servlet 程序,WEB-INF下的配置文件web.xml在哪啊?谢谢!
我用的版本是tomcat7.0,在webcontent\web-inf里只有一个空文件夹lib,写完servlet 类程序,就可以运行了,我想知道自动生成的配置文件在哪里?或者说从哪里能够看出来配置内 ...
- win7系统玩游戏不能全屏的解决办法
1.修改注册表中的显示器的参数设置 Win键+R键,打开运行窗口,输入regedit回车,这样就打开了注册表编辑器,然后,定位到以下位置: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ ...
- 不需要软件让Windows7变身WIFI热点
很简单,就是把一台装有windows 7操作系统,并配有无线网卡的电脑变成一台无线路由器或无线AP,以便在没有路由器的环境中实现多台无线终端(比如支持wifi的手机.电脑等设备)共享无线网络.那么我们 ...
- 那天有个小孩跟我说LINQ(六)转载
2 LINQ TO SQL完结(代码下载) 我们还是接着上次那个简单的销售的业务数据库为例子,打开上次那个例子linq_Ch5 2.1 当数据库中的表建立了主外键 ①根据主键获取子表信息 ...
