Flume案例Ganglia监控
Flume案例和Flume监控系统的使用:
安装
- 将apache-flume-1.7.0-bin.tar.gz上传到linux的/opt/software目录下
解压apache-flume-1.7.0-bin.tar.gz到/opt/module/目录下
[hadoop@datanode1 software]$ tar -zxf apache-flume-1.7.0-bin.tar.gz -C /opt/module/
3. 修改apache-flume-1.7.0-bin的名称为flume
[hadoop@datanode1 module]$ mv apache-flume-1.7.0-bin flume
将flume/conf下的flume-env.sh.template文件修改为flume-env.sh,并配置flume-env.sh文件
[hadoop@datanode1 module]$ mv flume-env.sh.template flume-env.sh
[hadoop@datanode1 module]$ vi flume-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/module/jdk1.8.0_162
案例实操
监控端口数据
案例需求:首先,Flume监控本机44444端口,然后通过telnet工具向本机44444端口发送消息,最后Flume将监听的数据实时显示在控制台。
判断端口是否被占用
sudo netstat -tunlp | grep 44444
功能描述:netstat命令是一个监控TCP/IP网络的非常有用的工具,它可以显示路由表、实际的网络连接以及每一个网络接口设备的状态信息。
基本语法:netstat [选项]
选项参数:
-t或—tcp:显示TCP传输协议的连线状况;
-u或—udp:显示UDP传输协议的连线状况;
-n或—numeric:直接使用ip地址,而不通过域名服务器;
-l或—listening:显示监控中的服务器的Socket;
-p或—programs:显示正在使用Socket的程序识别码和程序名称;
配置
hadoop@datanode1 job]$ vim flume-telnet-logger.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1 #r1:表示a1的输入源
a1.sinks = k1 #k1表示a1的输出目的地
a1.channels = c1 #C1表示a1的缓冲区 # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat #表示a1的输入源类型为netcat类型
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost #标识a1的监听的主机
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 #标识a1监听的端口号 # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger #标识a1的输出目的地是logger类型 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory #表示a1的channel类型是memory内存型
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000 #表示a1的channel总容量1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 #表示a1的channel传输总容量100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 #表示将r1和c1连接起来
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1 #表示将k1和c1连接起来
启动
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/flume-telnet-logger.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console 参数说明:
--conf conf/ :表示配置文件存储在conf/目录
--name a1 :表示给agent起名为a1
--conf-file job/flume-telnet.conf :flume本次启动读取的配置文件是在job文件夹下的flume-telnet.conf文件。
-Dflume.root.logger==INFO,console :-D表示flume运行时动态修改flume.root.logger参数属性值,并将控制台日志打印级别设置为INFO级别。
日志级别包括:log、info、warn、error。
telnet localhost 44444

实时读取本地文件到HDFS案例
测试脚本
[hadoop@datanode1 data]$ vim test.sh
#!bin/bash
i=1
while [ true ]
let i+=1
d=$( date +%Y-%m-%d\ %H\:%M\:%S )
do
echo "data:$d $i"
done
flume-file-hdfs.conf
[hadoop@datanode1 job]$ vim flume-file-hdfs.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r2
a2.sinks = k2
a2.channels = c2 # Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r2.type = exec
a2.sources.r2.command = tail -F /opt/module/flume/job/data/data1.log
a2.sources.r2.shell = /bin/bash -c # Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k2.type = hdfs
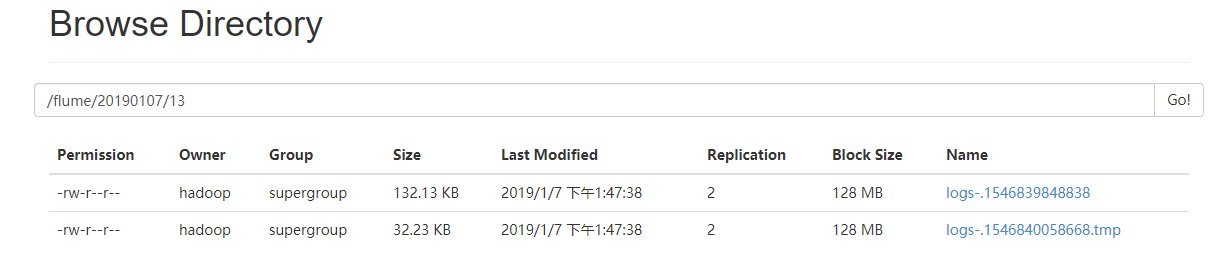
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.path = hdfs://datanode1:9000/flume/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.filePrefix = logs-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.batchSize = 1000
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollInterval = 600
#设置每个文件的滚动大小
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#最小冗余数
a2.sinks.k2.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a2.channels.c2.type = memory
a2.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r2.channels = c2
a2.sinks.k2.channel = c2
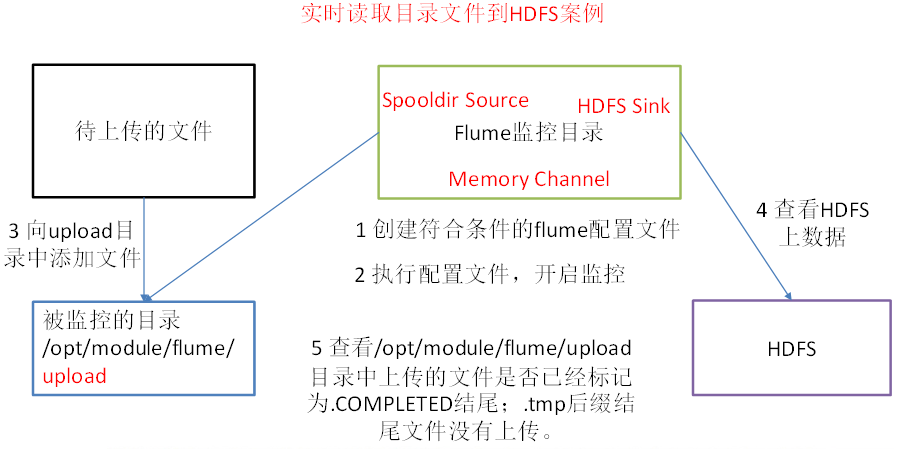
实时读取目录文件到HDFS案例
需求分析
配置
[hadoop@datanode1 job]$ vim flume-dir-hdfs.conf
[hadoop@datanode1 job]$ vim flume-dir-hdfs.conf
a3.sources = r3
a3.sinks = k3
a3.channels = c3 # Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r3.type = spooldir
a3.sources.r3.spoolDir = /opt/module/flume/upload
a3.sources.r3.fileSuffix = .COMPLETED
a3.sources.r3.fileHeader = true
#忽略所有以.tmp结尾的文件,不上传
a3.sources.r3.ignorePattern = ([^ ]*\.tmp) # Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k3.type = hdfs
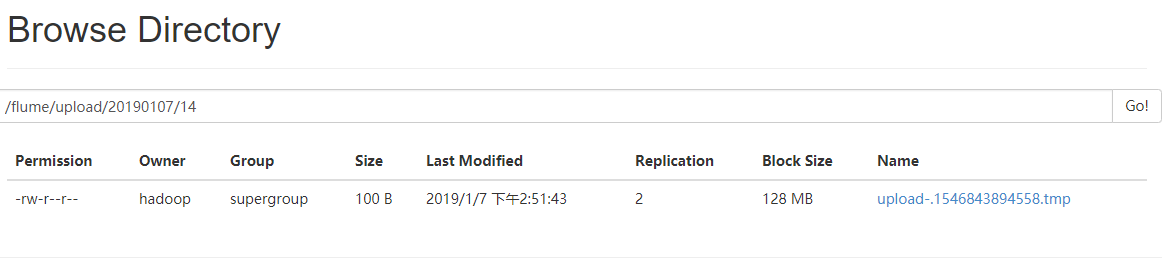
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.path = hdfs://datanode1:9000/flume/upload/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.filePrefix = upload-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollInterval = 600
#设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是128M
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#最小冗余数
a3.sinks.k3.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1 # Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a3.channels.c3.type = memory
a3.channels.c3.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c3.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a3.sources.r3.channels = c3
a3.sinks.k3.channel = c3
测试脚本
#!bin/bash
i=1
cd /opt/module/flume/upload
while [ true ]
let i+=1
d=$( date +%Y-%m-%d\ %H\:%M\:%S )
do
touch "文档$i.txt"
touch "$d-$i.log"
touch "$i.tmp"
sleep 1
done
启动
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/flume-dir-hdfs.conf
注意
- 在使用Spooling Directory Source时
- 不要在监控目录中创建并持续修改文件
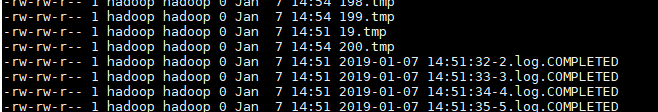
- 上传完成的文件会以.COMPLETED结尾
- 被监控文件夹每600毫秒扫描一次文件变动
查看
查看本地文件
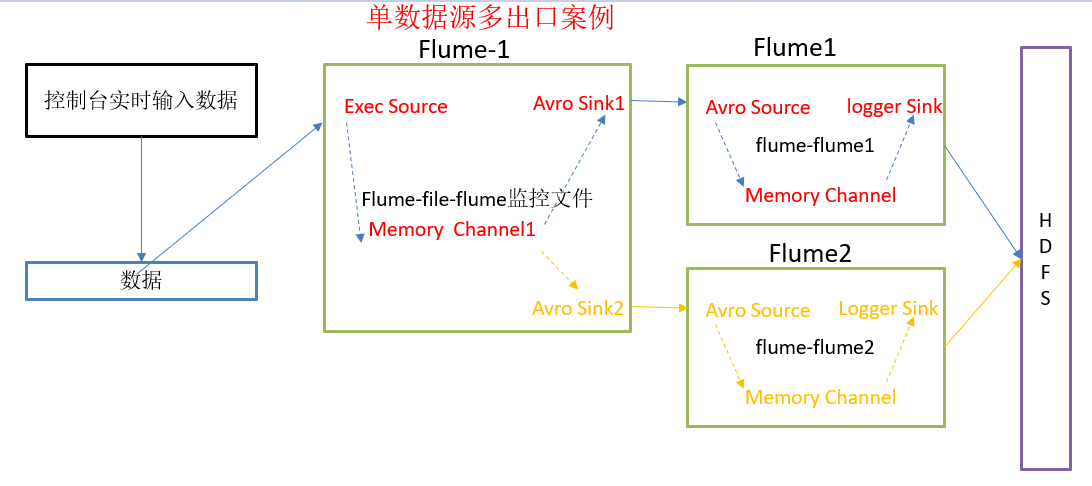
单数据源多出口案例(一)

分析
案例需求:使用flume-1监控文件变动,flume-1将变动内容传递给flume-2,flume-2负责存储到HDFS。同时flume-1将变动内容传递给flume-3,flume-3负责输出到local filesystem。
需求分析:

步骤
在/opt/module/flume/job目录下创建group1文件夹
[hadoop@datanode1 job]$ cd group1/
在datanode3节点上/opt/module/datas/目录下创建flume3文件夹
[hadoop@datanode3 datas]$ mkdir flume3/
配置1个接收日志文件的source和两个channel、两个sink,分别输送给flume-flume-hdfs和flume-flume-dir。
datanode1配置文件
[hadoop@datanode1 group1]$ vim flume-file-flume.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
# 将数据流复制给多个channel
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = replicating # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/module/datas/logs.log
a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = datanode2
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141 a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = datanode3
a1.sinks.k2.port = 4142 # Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
datanode2配置文件
[hadoop@datanode2 group1]$ vim flume-flume-hdfs.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = datanode2
a2.sources.r1.port = 4141 # Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.path = hdfs://datanode1:9000/flume2/%Y%m%d/%H
#上传文件的前缀
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.filePrefix = flume2-
#是否按照时间滚动文件夹
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.round = true
#多少时间单位创建一个新的文件夹
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundValue = 1
#重新定义时间单位
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.roundUnit = hour
#是否使用本地时间戳
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp = true
#积攒多少个Event才flush到HDFS一次
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.batchSize = 100
#设置文件类型,可支持压缩
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType = DataStream
#多久生成一个新的文件
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval = 600
#设置每个文件的滚动大小大概是128M
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize = 134217700
#文件的滚动与Event数量无关
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount = 0
#最小冗余数
a2.sinks.k1.hdfs.minBlockReplicas = 1 # Describe the channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
datanode3配置文件
[hadoop@datanode3 group1]$ vim flume-flume-dir.conf
me the components on this agent
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c2 # Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = datanode3
a3.sources.r1.port = 4142 # Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = file_roll
a3.sinks.k1.sink.directory = /opt/module/datas/flume3 # Describe the channel
a3.channels.c2.type = memory
a3.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a3.sources.r1.channels = c2
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c2启动
启动
datanode1
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/group1/flume-file-flume.conf
datanode2
[hadoop@datanode2 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/group1/flume-flume-hdfs.conf
datanode3
[hadoop@datanode3 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/group1/flume-flume-dir.conf
单数据源多出口案例(二)
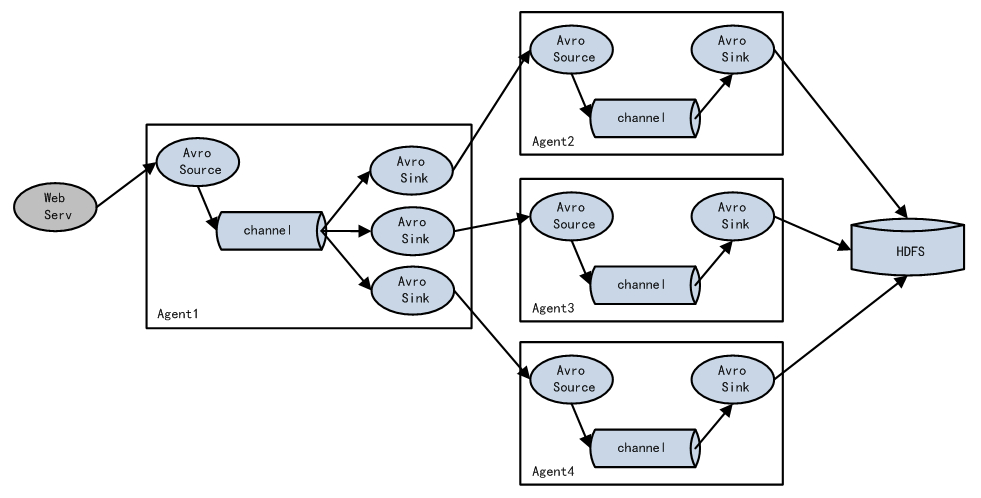
需求
案例需求:使用flume-1监控文件变动,flume-1将变动内容传递给flume-2,flume-2负责存储到HDFS。同时flume-1将变动内容传递给flume-3,flume-3也负责存储到HDFS
实现
datanode1
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ vim job/group1/flume-netcat-flume.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinkgroups = g1
a1.sinks = k1 k2 # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = datanode1
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444 a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.type = load_balance
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.backoff = true
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector = round_robin
a1.sinkgroups.g1.processor.selector.maxTimeOut=10000 # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = datanode2
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141 a1.sinks.k2.type = avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = datanode3
a1.sinks.k2.port = 4142 # Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinkgroups.g1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c1
datanode2
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = datanode2
a2.sources.r1.port = 4141 # Describe the sink
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger # Describe the channel
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
datanode3
[hadoop@datanode3 flume]$ vim job/group1/flume-flume2.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c2 # Describe/configure the source
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = datanode3
a3.sources.r1.port = 4142 # Describe the sink
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger # Describe the channel
a3.channels.c2.type = memory
a3.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a3.sources.r1.channels = c2
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c2
启动
datanode1
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/group1/flume-netcat-flume.conf
datanode2
[hadoop@datanode2 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/group1/flume-flume1.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
datanod3
[hadoop@datanode3 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/group1/flume-flume2.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
多数据源汇总案例
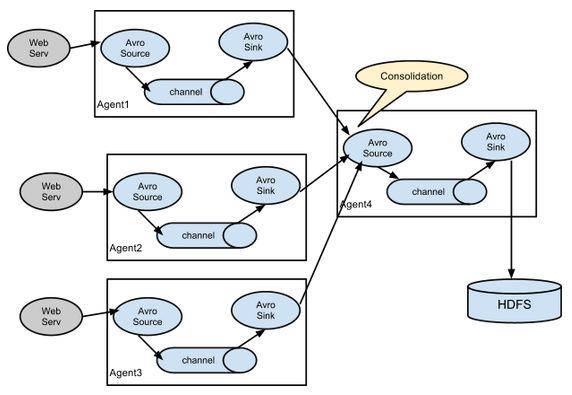
datanode1上的flume-1监控一个软件的log日志,
datanode2上的flume-2监控某一个端口的数据流,
flume-1与flume-2将数据发送给datanode3上的flume-3,flume-3将最终数据打印到控制台
步骤
- 分发flume
[hadoop@datanode2 job]$ mkdir group2
[hadoop@datanode2 job]$ xsync /opt/module/flume/
datanode1配置source用于监控hive.log文件,配置sink输出数据到下一级flume。
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = exec
a1.sources.r1.command = tail -F /opt/module/datas/logs.log
a1.sources.r1.shell = /bin/bash -c # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = datanode1
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141 # Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
启动
[hadoop@datanode3 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/group2/flume3.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[hadoop@datanode2 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/group2/flume2.conf
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/group2/flume1.conf
自定义MYSQLSource
SQLSourceHelper
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.conf.ConfigurationException;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.*;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties; public class SQLSourceHelper { private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SQLSourceHelper.class); private int runQueryDelay, //两次查询的时间间隔
startFrom, //开始id
currentIndex, //当前id
recordSixe = 0, //每次查询返回结果的条数
maxRow; //每次查询的最大条数 private String table, //要操作的表
columnsToSelect, //用户传入的查询的列
customQuery, //用户传入的查询语句
query, //构建的查询语句
defaultCharsetResultSet;//编码集 //上下文,用来获取配置文件
private Context context; //为定义的变量赋值(默认值),可在flume任务的配置文件中修改
private static final int DEFAULT_QUERY_DELAY = 10000;
private static final int DEFAULT_START_VALUE = 0;
private static final int DEFAULT_MAX_ROWS = 2000;
private static final String DEFAULT_COLUMNS_SELECT = "*";
private static final String DEFAULT_CHARSET_RESULTSET = "UTF-8"; private static Connection conn = null;
private static PreparedStatement ps = null;
private static String connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword; //加载静态资源
static {
Properties p = new Properties();
try {
p.load(SQLSourceHelper.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"));
connectionURL = p.getProperty("dbUrl");
connectionUserName = p.getProperty("dbUser");
connectionPassword = p.getProperty("dbPassword");
Class.forName(p.getProperty("dbDriver"));
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException e) {
LOG.error(e.toString());
}
} //获取JDBC连接
private static Connection InitConnection(String url, String user, String pw) {
try {
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, pw);
if (conn == null)
throw new SQLException();
return conn;
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
} //构造方法
SQLSourceHelper(Context context) throws ParseException {
//初始化上下文
this.context = context; //有默认值参数:获取flume任务配置文件中的参数,读不到的采用默认值
this.columnsToSelect = context.getString("columns.to.select", DEFAULT_COLUMNS_SELECT);
this.runQueryDelay = context.getInteger("run.query.delay", DEFAULT_QUERY_DELAY);
this.startFrom = context.getInteger("start.from", DEFAULT_START_VALUE);
this.defaultCharsetResultSet = context.getString("default.charset.resultset", DEFAULT_CHARSET_RESULTSET); //无默认值参数:获取flume任务配置文件中的参数
this.table = context.getString("table");
this.customQuery = context.getString("custom.query");
connectionURL = context.getString("connection.url");
connectionUserName = context.getString("connection.user");
connectionPassword = context.getString("connection.password");
conn = InitConnection(connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword); //校验相应的配置信息,如果没有默认值的参数也没赋值,抛出异常
checkMandatoryProperties();
//获取当前的id
currentIndex = getStatusDBIndex(startFrom);
//构建查询语句
query = buildQuery();
} //校验相应的配置信息(表,查询语句以及数据库连接的参数)
private void checkMandatoryProperties() {
if (table == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("property table not set");
}
if (connectionURL == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("connection.url property not set");
}
if (connectionUserName == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("connection.user property not set");
}
if (connectionPassword == null) {
throw new ConfigurationException("connection.password property not set");
}
} //构建sql语句
private String buildQuery() {
String sql = "";
//获取当前id
currentIndex = getStatusDBIndex(startFrom);
LOG.info(currentIndex + "");
if (customQuery == null) {
sql = "SELECT " + columnsToSelect + " FROM " + table;
} else {
sql = customQuery;
}
StringBuilder execSql = new StringBuilder(sql);
//以id作为offset
if (!sql.contains("where")) {
execSql.append(" where ");
execSql.append("id").append(">").append(currentIndex);
return execSql.toString();
} else {
int length = execSql.toString().length();
return execSql.toString().substring(0, length - String.valueOf(currentIndex).length()) + currentIndex;
}
} //执行查询
List<List<Object>> executeQuery() {
try {
//每次执行查询时都要重新生成sql,因为id不同
customQuery = buildQuery();
//存放结果的集合
List<List<Object>> results = new ArrayList<>();
if (ps == null) {
//
ps = conn.prepareStatement(customQuery);
}
ResultSet result = ps.executeQuery(customQuery);
while (result.next()) {
//存放一条数据的集合(多个列)
List<Object> row = new ArrayList<>();
//将返回结果放入集合
for (int i = 1; i <= result.getMetaData().getColumnCount(); i++) {
row.add(result.getObject(i));
}
results.add(row);
}
LOG.info("execSql:" + customQuery + "\nresultSize:" + results.size());
return results;
} catch (SQLException e) {
LOG.error(e.toString());
// 重新连接
conn = InitConnection(connectionURL, connectionUserName, connectionPassword);
}
return null;
} //将结果集转化为字符串,每一条数据是一个list集合,将每一个小的list集合转化为字符串
List<String> getAllRows(List<List<Object>> queryResult) {
List<String> allRows = new ArrayList<>();
if (queryResult == null || queryResult.isEmpty())
return allRows;
StringBuilder row = new StringBuilder();
for (List<Object> rawRow : queryResult) {
Object value = null;
for (Object aRawRow : rawRow) {
value = aRawRow;
if (value == null) {
row.append(",");
} else {
row.append(aRawRow.toString()).append(",");
}
}
allRows.add(row.toString());
row = new StringBuilder();
}
return allRows;
} //更新offset元数据状态,每次返回结果集后调用。必须记录每次查询的offset值,为程序中断续跑数据时使用,以id为offset
void updateOffset2DB(int size) {
//以source_tab做为KEY,如果不存在则插入,存在则更新(每个源表对应一条记录)
String sql = "insert into flume_meta(source_tab,currentIndex) VALUES('"
+ this.table
+ "','" + (recordSixe += size)
+ "') on DUPLICATE key update source_tab=values(source_tab),currentIndex=values(currentIndex)";
LOG.info("updateStatus Sql:" + sql);
execSql(sql);
} //执行sql语句
private void execSql(String sql) {
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
LOG.info("exec::" + sql);
ps.execute();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} //获取当前id的offset
private Integer getStatusDBIndex(int startFrom) {
//从flume_meta表中查询出当前的id是多少
String dbIndex = queryOne("select currentIndex from flume_meta where source_tab='" + table + "'");
if (dbIndex != null) {
return Integer.parseInt(dbIndex);
}
//如果没有数据,则说明是第一次查询或者数据表中还没有存入数据,返回最初传入的值
return startFrom;
} //查询一条数据的执行语句(当前id)
private String queryOne(String sql) {
ResultSet result = null;
try {
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
result = ps.executeQuery();
while (result.next()) {
return result.getString(1);
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
} //关闭相关资源
void close() {
try {
ps.close();
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} int getCurrentIndex() {
return currentIndex;
} void setCurrentIndex(int newValue) {
currentIndex = newValue;
} int getRunQueryDelay() {
return runQueryDelay;
} String getQuery() {
return query;
} String getConnectionURL() {
return connectionURL;
} private boolean isCustomQuerySet() {
return (customQuery != null);
} Context getContext() {
return context;
} public String getConnectionUserName() {
return connectionUserName;
} public String getConnectionPassword() {
return connectionPassword;
}
}
SQLSource
| 属性 | 说明(括号中为默认值) |
|---|---|
| runQueryDelay | 查询时间间隔(10000) |
| batchSize | 缓存大小(100) |
| startFrom | 查询语句开始id(0) |
| currentIndex | 查询语句当前id,每次查询之前需要查元数据表 |
| recordSixe | 查询返回条数 |
| table | 监控的表名 |
| columnsToSelect | 查询字段(*) |
| customQuery | 用户传入的查询语句 |
| query | 查询语句 |
| defaultCharsetResultSet | 编码格式(UTF-8) |
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.Event;
import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;
import org.apache.flume.PollableSource;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent;
import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import java.text.ParseException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List; public class SQLSource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource { //打印日志
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SQLSource.class);
//定义sqlHelper
private SQLSourceHelper sqlSourceHelper; @Override
public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {
return 0;
} @Override
public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {
return 0;
} @Override
public void configure(Context context) {
try {
//初始化
sqlSourceHelper = new SQLSourceHelper(context);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} @Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
try {
//查询数据表
List<List<Object>> result = sqlSourceHelper.executeQuery();
//存放event的集合
List<Event> events = new ArrayList<>();
//存放event头集合
HashMap<String, String> header = new HashMap<>();
//如果有返回数据,则将数据封装为event
if (!result.isEmpty()) {
List<String> allRows = sqlSourceHelper.getAllRows(result);
Event event = null;
for (String row : allRows) {
event = new SimpleEvent();
event.setBody(row.getBytes());
event.setHeaders(header);
events.add(event);
}
//将event写入channel
this.getChannelProcessor().processEventBatch(events);
//更新数据表中的offset信息
sqlSourceHelper.updateOffset2DB(result.size());
}
//等待时长
Thread.sleep(sqlSourceHelper.getRunQueryDelay());
return Status.READY;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.error("Error procesing row", e);
return Status.BACKOFF;
}
} @Override
public synchronized void stop() {
LOG.info("Stopping sql source {} ...", getName());
try {
//关闭资源
sqlSourceHelper.close();
} finally {
super.stop();
}
}
}
| SQLSourceHelper(Context context) | 构造方法,初始化属性及获取JDBC连接 |
|---|---|
| InitConnection(String url, String user, String pw) | 获取JDBC连接 |
| checkMandatoryProperties() | 校验相关属性是否设置(实际开发中可增加内容) |
| buildQuery() | 根据实际情况构建sql语句,返回值String |
| executeQuery() | 执行sql语句的查询操作,返回值List> |
| getAllRows(List> queryResult) | 将查询结果转换为String,方便后续操作 |
| updateOffset2DB(int size) | 根据每次查询结果将offset写入元数据表 |
| execSql(String sql) | 具体执行sql语句方法 |
| getStatusDBIndex(int startFrom) | 获取元数据表中的offset |
| queryOne(String sql) | 获取元数据表中的offset实际sql语句执行方法 |
| close() | 关闭资源 |
测试准备
驱动包
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ cp \
/opt/sorfware/mysql-libs/mysql-connector-java-5.1.27/mysql-connector-java-5.1.27-bin.jar \
/opt/module/flume/lib/
打包项目并将jar放入flume的lib目录下
配置文件
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ vim job/mysql.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1 # Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = com.hph.SQLSource
a1.sources.r1.connection.url = jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.101:3306/mysqlsource
a1.sources.r1.connection.user = root
a1.sources.r1.connection.password = 123456
a1.sources.r1.table = student
a1.sources.r1.columns.to.select = *
a1.sources.r1.incremental.column.name = id
a1.sources.r1.incremental.value = 0
a1.sources.r1.run.query.delay=5000 # Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger # Describe the channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100 # Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
Mysql表准备
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
CREATE TABLE `flume_meta` (
`source_tab` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`currentIndex` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`source_tab`)
);
测试脚本
#!/bin/bash HOSTNAME="192.168.1.101" #数据库信息
PORT="3306"
USERNAME="root"
PASSWORD="123456" DBNAME="mysqlsource" #数据库名称
TABLENAME="student" #数据库中表的名称 i=0
while [true]
let i+=1;
do
insert_sql="insert into ${TABLENAME}(id,name) values($i,'student$i')"
mysql -h${HOSTNAME} -P${PORT} -u${USERNAME} -p${PASSWORD} ${DBNAME} -e "${insert_sql}"
sleep 5
done
测试并查看
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/mysql.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console #启动agent
[hadoop@datanode1 job]$ sh mysql.sh #启动测试脚本

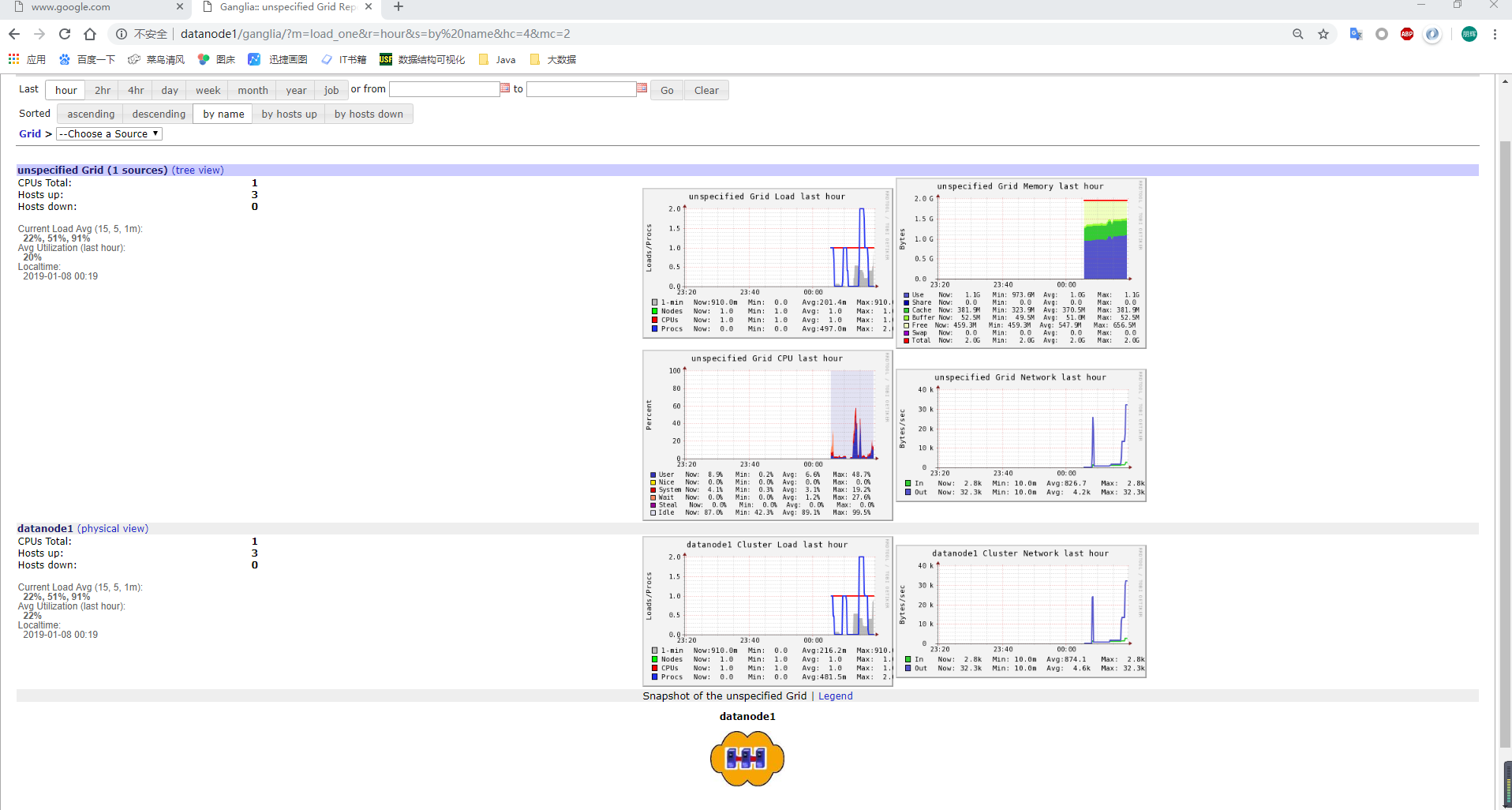
Flume监控Ganglia
步骤
1.安装httpd服务与php
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo yum -y install httpd php
- 安装其他依赖
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo yum -y install rrdtool perl-rrdtool rrdtool-devel
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo yum -y install apr-devel
安装ganglia
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmetad
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo yum -y install ganglia-web
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo yum install -y ganglia-gmond
修改ganglia
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf
# Ganglia monitoring system php web frontend
Alias /ganglia /usr/share/ganglia
<Location /ganglia>
Order deny,allow
Deny from all
Allow from all
# Allow from 127.0.0.1
# Allow from ::1
# Allow from .example.com
</Location>
修改配置文件gmetad.conf
data_source "datanode1" 192.168.1.101
修改配置文件gmond.conf
cluster {
name = "datanode1" #自己的主机名
owner = "unspecified"
latlong = "unspecified"
url = "unspecified"
}
udp_send_channel {
#bind_hostname = yes # Highly recommended, soon to be default.
# This option tells gmond to use a source address
# that resolves to the machine's hostname. Without
# this, the metrics may appear to come from any
# interface and the DNS names associated with
# those IPs will be used to create the RRDs.
#mcast_join = 239.2.11.71 #注释掉
host=192.168.1.101 #自己的主机IP
port = 8649 #端口号
ttl = 1
}
修改配置文件config
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo vim /etc/selinux/config # This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - No SELinux policy is loaded.
SELINUX=disabled
# SELINUXTYPE= can take one of these two values:
# targeted - Targeted processes are protected,
# mls - Multi Level Security protection.
SELINUXTYPE=targeted
注意selinux本次生效关闭必须重启,如果此时不想重启,可以临时生效之:
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo setenforce 0
启动ganglia
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo service httpd start
Starting httpd:
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo service gmetad start
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo service gmond start
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$
如果完成以上操作依然出现权限不足错误,请修改/var/lib/ganglia目录的权限
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ sudo chmod -R 777 /var/lib/ganglia
操作Flume测试监控
1.修改/opt/module/flume/conf目录下的flume-env.sh配置:
[hadoop@datanode1 conf]$ vim flume-env.sh
JAVA_OPTS="-Dflume.monitoring.type=ganglia
-Dflume.monitoring.hosts=192.168.1.101:8649
-Xms100m
-Xmx200m"
[hadoop@datanode1 conf]$ xsync flume-env.sh
启动flume任务
[hadoop@datanode3 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a3 --conf-file job/group2/flume3.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
[hadoop@datanode2 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a2 --conf-file job/group2/flume2.conf
[hadoop@datanode1 flume]$ bin/flume-ng agent --conf conf/ --name a1 --conf-file job/group2/flume1.conf

| 字段(图表名称) | 字段含义 |
|---|---|
| EventPutAttemptCount | source尝试写入channel的事件总数量 |
| EventPutSuccessCount | 成功写入channel且提交的事件总数量 |
| EventTakeAttemptCount | sink尝试从channel拉取事件的总数量。这不意味着每次事件都被返回,因为sink拉取的时候channel可能没有任何数据。 |
| EventTakeSuccessCount | sink成功读取的事件的总数量 |
| StartTime | channel启动的时间(毫秒) |
| StopTime | channel停止的时间(毫秒) |
| ChannelSize | 目前channel中事件的总数量 |
| ChannelFillPercentage | channel占用百分比 |
| ChannelCapacity | channel的容量 |
Flume案例Ganglia监控的更多相关文章
- Flume(5)-Ganglia监控
一. 安装Ganglia 1. 安装httpd服务与php sudo yum -y install httpd php 2. 安装其他依赖 sudo yum -y install rrdtool pe ...
- Hadoop生态圈-使用Ganglia监控flume中间件
Hadoop生态圈-使用Ganglia监控flume中间件 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.Ganglia监控简介 加州伯克利大学千禧计划的其中一个开源项目.是一 ...
- 第1节 flume:13、14、更多flume案例一,通过拦截器实现不同类型的数据区分
1.6.flume案例一 1. 案例场景 A.B两台日志服务机器实时生产日志主要类型为access.log.nginx.log.web.log 现在要求: 把A.B 机器中的access.log.ng ...
- 使用ganglia监控hadoop及hbase集群
一.Ganglia简介 Ganglia 是 UC Berkeley 发起的一个开源监视项目,设计用于测量数以千计的节点.每台计算机都运行一个收集和发送度量数据(如处理器速度.内存使用量等)的名为 gm ...
- Ganglia监控Hadoop集群的安装部署[转]
Ganglia监控Hadoop集群的安装部署 一. 安装环境 Ubuntu server 12.04 安装gmetad的机器:192.168.52.105 安装gmond的机 器:192.168.52 ...
- ganglia监控hadoop2.0配置方法
ganglia监控hadoop2.0配置方法前提:hadoop2.0集群已安装ganglia监控工具第一步:Hadoop用户登录集群每一个节点,修改文件:vi /opt/hadoop-2.0.0-cd ...
- Ganglia监控搭建
一.Ganglia介绍: Ganglia是一个监控服务器.集群的开源软件,能够用曲线图表现最近一个小时,最近一天,最近一周,最近一月,最近一年的服务器或者集群的cpu负载,内存,网络,硬盘等指标.Ga ...
- Ganglia 监控Hadoop
Ganglia监控Hadoop集群的安装部署 一. 安装环境 Ubuntu server 12.04 安装gmetad的机器:192.168.52.105 安装gmond的机 器:192.168.52 ...
- Ganglia监控扩展实现机制
Ganglia监控扩展实现机制 默认安装完成的Ganglia仅向我们提供基础的系统监控信息,通过Ganglia插件可以实现两种扩展Ganglia监控功能的方法.1.添加带内(in-band)插件,主要 ...
随机推荐
- 设置 IntelliJ IDEA 的彩色代码主题
首先,给出一系列 IntelliJ IDEA 代码的彩色主题,供大家选择: VibrantUnknown(Darcula) FadeComments NicePython Solarized Have ...
- VS 中的几种注释方法
在代码的后面添加形如下面注释: //TODO: (未实现)…… //UNDONE:(没有做完)…… //HACK:(修改)…… 等到再次打开VS的时候,找到 :视图>任务列表 即可显示所有带有T ...
- 将数据挂载到 docker 容器中的3种方式:volume、bind mount、tmpfs
出处:https://deepzz.com/post/the-docker-volumes-basic.html
- 第一个appium的Demo
原文来自:一颗糖果 http://www.cnblogs.com/linglingyuese/articles/8418311.html 一.环境搭建 略(后期补) 二.创建一个测试apk包的项目 ...
- win10 + VS2015 + 64位OSG3.4.0
一.下载 1.osg源码 2.整理好的第三方库 3.cmake3.7.1绿色版 4.osg3.4.0数据包 二.编译前的准备工作 在D:\下新建一个OSG文件夹,在其下再新建4个文件夹 D:\OSG\ ...
- Qsys 设计流程---Qsys System Design Tutorial
Qsys 设计流程 ---Qsys System Design Tutorial 1.Avalon-MM Pipeline Bridge Avalon-MM Pipeline Bridge在slave ...
- DynArrayToVariant DynArrayFromVariant复制动态数
type intArr=array of Integer; procedure TfrmMainDA.Button2Click(Sender: TObject);var aa:intArr;bb:in ...
- 坑人的 Javascript 模块化编程 sea.js
坑人的 Javascript 模块化编程 sea.js 忧伤 加 蛋疼的 开始了 看文档 Sea.js 进行配置 seajs.config({ // 设置路径,方便跨目录调用 paths: { 'ar ...
- 关于此实现不是 Windows 平台 FIPS 验证的加密算法的一部分。
注册表进入如下路径中 HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\FipsAlgorithmPolicy 将 enable设置为0 ...
- WPF Demo15 MVVM
项目结构如下: <Window x:Class="MVVMDemo.MainWindow" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/ ...
