Spring源码解析二:IOC容器初始化过程详解
IOC容器初始化分为三个步骤,分别是:
1、Resource定位,即BeanDefinition的资源定位。
2、BeanDefinition的载入
3、向IOC容器注册BeanDefinition
下面我们来详细展开这三部分的内容
一、Resource定位
以ApplicationContext的具体实现FileSystemXmlApplicationContext来介绍Resource定位的过程:
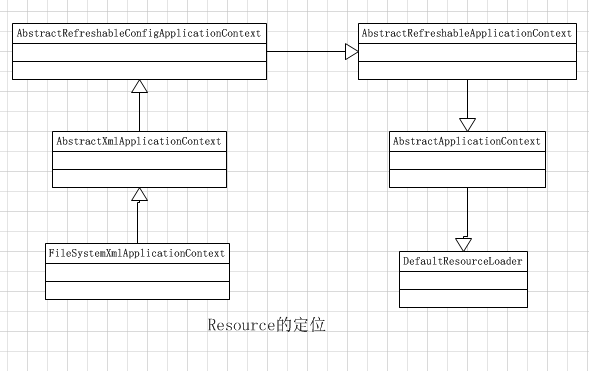
IOC容器初始化类比为用木桶来装水,Resource的定位过程就是寻找水的过程。
它是由ResourceLoader通过统一的Resource接口来完成的,Resource对各种形式的BeanDefinition的使用都提供了统一的接口。
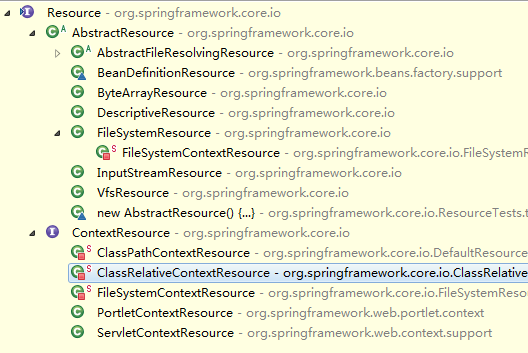
Resource接口有许多实现类,针对不同的BeanDefinition,如:
在文件系统中的Bean定义信息可以使用FileSystemResource来进行抽象。
在类路径中的Bean定义信息可以使用ClassPathResource来进行抽象。
我们来看下FileSystemXmlApplicationContext其中的一个构造函数:
- public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
- throws BeansException {
- super(parent);
- setConfigLocations(configLocations);
- if (refresh) {
- refresh();
- }
- }
这里有个refresh()方法,这个方法非常重要,可以说是IOC容器启动的入口,该方法的实现在AbstractApplicationContext中。
在AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法中,最终对调用到AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory,在这里会创建一个基础的IOC容器供ApplicationContext使用,这个基础的BeanFactory就是DefaultListableBeanFactory。
- protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
- if (hasBeanFactory()) {
- destroyBeans();
- closeBeanFactory();
- }
- try {
- DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
- beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
- customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
- loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
- synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
- this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
- }
- }
- catch (IOException ex) {
- throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
- }
- }
再根据loadBeanDefinitions方法一直往下查找,最终会找到DefaultResourceLoader类的getResource方法:
- public Resource getResource(String location) {
- Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
- if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
- return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
- }
- else {
- try {
- // Try to parse the location as a URL...
- URL url = new URL(location);
- return new UrlResource(url);
- }
- catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
- // No URL -> resolve as resource path.
- return getResourceByPath(location);
- }
- }
- }
这里的getResourceByPath方法最终被子类重写,该场景下重写该方法的类就是FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
- protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
- if (path != null && path.startsWith("/")) {
- path = path.substring(1);
- }
- return new FileSystemResource(path);
- }
这样我们从FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的构造函数中的refresh方法开始,最终到getResourceByPath结束,完成了资源定位的解析。但是这个只是容器启动中的一部分,还有载入和解析也是糅合在一起的,只是为了思路清晰,故意对这些地方视而不见。
二、BeanDefinition的载入和解析
在第一部分资源的定位中,我们是以getResourceByPath()结束的,接下来我们要通过该方法返回的Resource对象来进行BeanDefinition的载入了。现在我们已经知道水在哪里了,就可以现在打水和装水之旅了。
这个过程就是将定义的BeanDefinition在IOC容器中转化成一个Spring内部表示的数据结构的过程。我们紧接着前面的源码往下梳理:
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的方法refreshBeanFactory中调用loadBeanDefinitions(),往下梳理找到类AbstractXmlApplicationContext,源码片段如下;
- protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
- // Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
- XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
- // Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
- // resource loading environment.
- beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
- beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
- // Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
- // then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
- initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
- loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
- }
其中第7行是为读取器设置ResourceLoader,为后面的资源读取做准备;第13行就是启动Bean定义信息载入的开始。
- protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
- Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
- if (configResources != null) {
- reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
- }
- String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
- if (configLocations != null) {
- reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
- }
- }
第2行是以Resource的方式获取配置文件的资源位置,而第6行是以String的形式获取配置文件的位置。
reader.loadBeanDefinitions()的实现见XmlBeanDefinitionReader的父类AbstractBeanDefinitionReader
- public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
- Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
- int counter = 0;
- for (String location : locations) {
- counter += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
- }
- return counter;
- }
这里如果Resource为空,则停止BeanDefinition的载入。在启动BeanDefinition的过程中,会遍历整个Resource集合所包含的BeanDefinition的信息。
这里面调用的loadBeanDefinitions()方法具体实现并不在AbstractBeanDefinitionReader,而是在子类里:
- public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
- Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
- if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
- logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
- }
- Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
- if (currentResources == null) {
- currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
- this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
- }
- if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
- throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
- "Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
- }
- try {
- InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
- try {
- InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
- if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
- inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
- }
- return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
- }
- finally {
- inputStream.close();
- }
- }
在这里可以拿到代表XML文件的Resource,读取器在打开I/O流后就可以得到XML的文件对象,接下来的事情就是按照Spring的Bean定义规则对这个XML文件做解析并封装了。而这个解析的过程是在类BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
在调用doLoadBeanDefinitions过程中,代码会走到类XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的doLoadBeanDefinitions的方法
- protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
- throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
- try {
- int validationMode = getValidationModeForResource(resource);
- Document doc = this.documentLoader.loadDocument(
- inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler, validationMode, isNamespaceAware());
- return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
- }
这里第5行就是Document对象生成的入口,具体实现在DefaultDocumentLoader中。
第7行就是BeanDefinition解析的入口,我们接着往下走,最终的解析过程在类BeanDefinitionParserDelegate中,源码如下:
- public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
- String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
- String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
- List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>();
- if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
- String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, BEAN_NAME_DELIMITERS);
- aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
- }
- String beanName = id;
- if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
- beanName = aliases.remove(0);
- if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
- "' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
- }
- }
- if (containingBean == null) {
- checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
- }
- AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
- if (beanDefinition != null) {
- if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
- try {
- if (containingBean != null) {
- beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
- beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
- }
- else {
- beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
- // Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
- // if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
- // This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
- String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
- if (beanClassName != null &&
- beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
- !this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
- aliases.add(beanClassName);
- }
- }
- if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
- logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
- "using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
- }
- }
- catch (Exception ex) {
- error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
- return null;
- }
- }
- String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
- return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
- }
- return null;
- }
其中 第24行会触发对Bean元素的详细解析,解析完成后会返回一个AbstractBeanDefinition对象,可以看下这个对象的属性,基本上都是Spring配置文件中的常用属性。
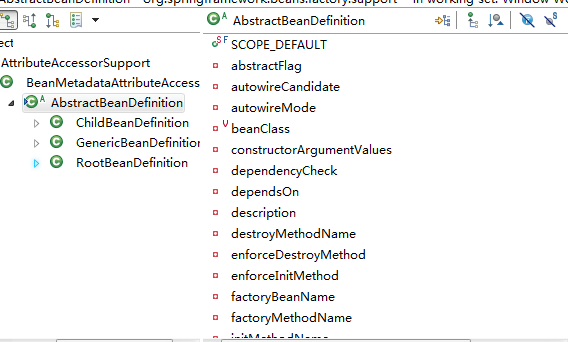
解析方法的具体内容如下:
- public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
- Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
- this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
- String className = null;
- if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
- className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
- }
- try {
- String parent = null;
- if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
- parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
- }
- AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
- parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
- bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
- parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
- parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
- parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
- parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
- parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
- parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
- bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
- bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
- return bd;
- }
其中第18行-27行,都是对Spring配置文件中不同<Bean>节点的解析,可以每个都深入去研究下。最终返回一个AbstractBeanDefinition对象。
到这里,XML文件中定义的BeanDefinition就被整个载入到IOC容器中,建立了对应的数据结构,可以看成是POJO在容器中的抽象。但是这个时候容器中还只是有一些静态的配置信息,完成了管理Bean对象的数据准备工作,但是容器还没有完全发挥作用。
三、BeanDefinition注册过程
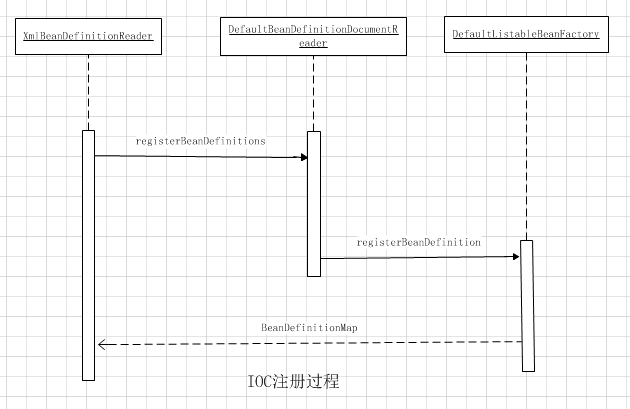
这个源码中方法调用过程比较简单,我们直接来看注册的核心代码:
- public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
- throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
- Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
- Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
- if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
- try {
- ((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
- }
- catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
- throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
- "Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
- }
- }
- synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
- Object oldBeanDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
- if (oldBeanDefinition != null) {
- if (!this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding) {
- throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
- "Cannot register bean definition [" + beanDefinition + "] for bean '" + beanName +
- "': There is already [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] bound.");
- }
- else {
- if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
- this.logger.info("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
- "': replacing [" + oldBeanDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
- }
- }
- }
- else {
- this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
- this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
- }
- this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
- resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
- }
- }
最关键的一步就是第36行,所谓的注册就是将解析得到的BeanDefinition设置到hashMap中去。至此就完成了整个IOC容器初始化的工作,这样一来就可以在beanDefinition里检索和使用已经配置好的Bean了。ICO容器的作用就是维护和处理里面的Bean。
最后,我们来回答下这个问题,spring 容器中bean是什么时候被初始化的?
通过前面的分析,我们知道bean的实例化是伴随着容器的初始化而同时进行的(但是也有特例),并且默认情况下是单例的。
Spring源码解析二:IOC容器初始化过程详解的更多相关文章
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(二)
前言:在[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(一)文末中已经提出loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory)的重要性,本文将以此为切入点继续分析. ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化——查漏补缺(二)
前言:在[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(八)中多次提到了前置处理与后置处理,本篇文章针对此问题进行分析.Spring对前置处理或后置处理主要通过BeanPostProcessor进行实现. ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(总结)
前言:在经过前面十二篇文章的分析,对bean的加载流程大致梳理清楚了.因为内容过多,因此需要进行一个小总结. 经过前面十二篇文章的漫长分析,终于将xml配置文件中的bean,转换成我们实际所需要的真正 ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(三)
前言:在[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(二)中已经得到了XML配置文件的Document实例,下面分析bean的注册过程. XmlBeanDefinitionReader#registerB ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(四)
前言:在[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(三)中已经分析了BeanDefinition注册之前的一些准备工作,下面将进入BeanDefinition注册的核心流程. //DefaultBean ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(十)
前言:前文[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(九)中分析了AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#createBeanInstance方法中通过工厂方法创建bean ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化——查漏补缺(五)
前言:我们知道在Spring中经常使用配置文件的形式对进行属性的赋值,那配置文件的值是怎么赋值到属性上的呢,本文将对其进行分析. 首先了解一个类:PropertySourcesPlaceholderC ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(七)
前言:在[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(六)中分析了从单例缓存中加载bean对象,由于篇幅原因其核心函数 FactoryBeanRegistrySupport#getObjectFromFa ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化——查漏补缺(一)
前言:在[spring源码分析]IOC容器初始化(十一)中提到了初始化bean的三个步骤: 激活Aware方法. 后置处理器应用(before/after). 激活自定义的init方法. 这里我们就来 ...
- Spring源码分析专题 —— IOC容器启动过程(上篇)
声明 1.建议先阅读<Spring源码分析专题 -- 阅读指引> 2.强烈建议阅读过程中要参照调用过程图,每篇都有其对应的调用过程图 3.写文不易,转载请标明出处 前言 关于 IOC 容器 ...
随机推荐
- 乐视4.14硬件免费日de用户体验
此贴用于记录2016年4月14日乐视硬件免费日购买X65超级电视的用户体验.后续将动态更新 我是乐视电视的第一批用户,从乐视上市第一批超级电视,我先后帮助家人.同事.朋友买了6台乐视超级电视,也算是乐 ...
- java通过反射调用有参数的方法
public static void eachCfg(Class Initclass,String taskType){ Field[] fields = Initclass.getDeclaredF ...
- docker构建Java环境
FROM java:7 COPY . /usr/src/javaapp WORKDIR /usr/src/javaapp RUN javac HelloWorld.java CMD ["ja ...
- shiro实战系列(十三)之单元测试
由于我们已经涉及到了 Subject reference,我们知道 Subject 是“当前执行”用户的特定安全视图,且该 Subject 实 例绑定到一个线程来确保我们知道在线程执行期间的任何时间是 ...
- Dubbo -- 系统学习 笔记 -- 安装手册
安装手册 示例提供者安装 示例消费者安装 Zookeeper注册中心安装 Redis注册中心安装 简易注册中心安装 简易监控中心安装 管理控制台安装 推荐使用Zookeeper注册中心 你可以只运行D ...
- 爬虫header和cookie
def on_start(self): self.crawl('http://bbs.byr.cn/board/Python', headers={'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHt ...
- 用BCP从SQL Server 数据库中导出Excel文件
BCP(Bulk Copy Program)是一种简单高效的数据传输方式在SQL Server中,其他数据传输方式还有SSIS和DTS. 这个程序的主要功能是从数据库中查询Job中指定step的执行信 ...
- js基础知识整理
一.javaScript,也称之为js,是专为网页交互设计的脚本语言.主要由以下三部分组成: 1)ECMAScript 由ECMA-262定义,提供核心语言功能. 2)DOM对象(document ...
- python获取文件扩展名的方法(转)
主要介绍了python获取文件扩展名的方法,涉及Python针对文件路径的相关操作技巧.具体实现方法如下: 1 2 3 4 import os.path def file_extension(path ...
- Swift与OC代码转换实例
1. Objectice-C code: NSShadow *shadow = [NSShadow new]; [shadow setShadowColor:[UIColor colorWithRed ...
