Android 布局方式学习
一.LinearLayout线性布局:
线性布局是程序中最常见的一种布局方式,线性布局可以分为水平线性布局和垂直线性布局两种, 通过android:orientation属性可以设置线性布局的方向
1.在LinearLayout中设置排列方式为水平时只有垂直方向的设置是有效的,水平方向的设置是无效的:即left,right,center_horizontal 是不生效的
2.在LinearLayout中设置排列方式为垂直时只有水平方向设置是有效的,垂直方向的设置是无效的是无效的:即top,bottom,center_vertical 是无效的;
布局一源码:
android:orientation="vertical" 表示竖直方式对齐
android:orientation="horizontal"表示水平方式对齐
LinearLayout布局方式一布局源码:

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".LinearLayoutOneActivity" >
<EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登陆"/>
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="退出"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>

效果图:

3.LinearLayout 布局中 android:gravity:
该属性用于控制布局中控件的对齐方式。如果是没有子控件的控件设置此属性,表示其内容的对齐方式,比如说TextView里面文字的对齐方式;若是有子控件的控件设置此属性,则表示其子控件的对齐方式。 4.android: layout_weight
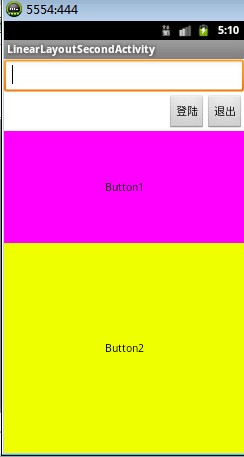
通过设置控件的layout_weight属性以控制各个控件在布局中的相对大小。layout_weight属性是一个非负整数值。线性布局会根据该控件layout_weight值与其所处布局中所有控件layout_weight值之和的比值为该控件分配占用的区域。例如,在水平布局的LinearLayout中有两个Button,这两个Button的layout_weight属性值都为1,那么这两个按钮都会被拉伸到整个屏幕宽度的一半。如果layout_weight指为0,控件会按原大小显示,不会被拉伸;对于其余layout_weight属性值大于0的控件,系统将会减去layout_weight属性值为0的控件的宽度或者高度,再用剩余的宽度或高度按相应的比例来分配每一个控件显示的宽度或高度 LinearLayoutSecond布局显示图
布局源码:

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".LinearLayoutOneActivity" >
<EditText android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="right">
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="登陆"/>
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="退出"/>
</LinearLayout>
<Button android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ff00ff"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="Button1"/>
<Button android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#eeff00"
android:layout_weight="2"
android:text="Button2"/>
</LinearLayout>

5.LinearLayout综合应用 效果图

布局源码:

<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".LinearLayoutThirdActivity" >
<LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_weight="1">
<!-- 文本水平垂直居中 -->
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
android:background="#aa0000"
android:text="红色"/>
<!-- 水平居中 顶部对齐 -->
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="top|center_horizontal"
android:background="#00aa00"
android:text="绿色"/>
<!-- 水平居中顶部对齐 -->
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#0000aa"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|bottom"
android:text="蓝色"/>
<!-- 垂直居中 水平靠左 -->
<TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#aaaa00"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center_vertical|left"
android:text="黄色"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"> <Button android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="left"
android:text="第一行"/>
<Button android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="第二行"/>
<Button android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="第三行"/>
<Button android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="第四行"/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>

二.AbsoluteLayout绝对位置布局:
指定子控件的xy精确坐标的布局。绝对布局缺乏灵活性,在没有绝对定位的情况下相比其他类型的布局更难维护。
布局效果图:
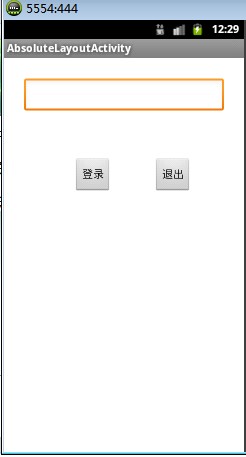
布局源码:

<AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".AbsoluteLayoutActivity" >
<EditText android:layout_width="200px"
android:layout_x="20px"
android:layout_y="20px"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="70px"
android:layout_y="100px"
android:text="登录"/>
<Button android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_x="150px"
android:layout_y="100px"
android:text="退出"/>
</AbsoluteLayout>

三.AbsoluteLayout绝对位置布局:
所有添加到这个布局中的视图都以层叠的方式显示。第一个添加的组件放到最底层,最后添加到框架中的视图显示在最上面。上一层的会覆盖下一层的控件
java.lang.Object
↳ android.view.View
↳ android.view.ViewGroup
↳ android.widget.FrameLayout
布局效果一:

布局源码:

<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".FrameLayoutOneActivity" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#aa0000"
android:gravity="right"
android:text="布局一" />
<TextView android:layout_width="150px"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#00aa00"
android:gravity="bottom"
android:text="布局二"/>
<TextView android:layout_width="190px"
android:layout_height="300px"
android:gravity="bottom"
android:background="#0000aa"
android:text="布局三"/> </FrameLayout>

android:gravity / android:layout_gravity区别:
android:gravity 是设置该view里面的内容相对于该view的位置,例如设置button里面的text相对于view的靠左,居中等位置。(也可以在Layout布局属性中添加,设置Layout中组件的位置)
android:layout_gravity 是用来设置该view相对与父view的位置,例如设置button在layout里面的相对位置:屏幕居中,水平居中等。 即android:gravity用于设置View中内容相对于View组件的对齐方式,而android:layout_gravity用于设置View组件相对于Container的对齐方式。 说的再直白点,就是android:gravity只对该组件内的东西有效,android:layout_gravity只对组件自身有效
布局效果二:
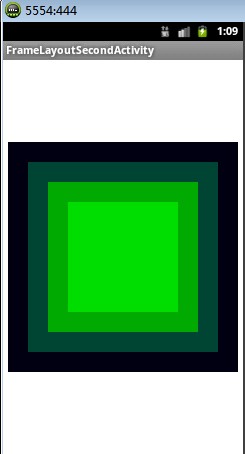
布局源码:

<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".FrameLayoutSecondActivity" > <TextView
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="230px"
android:layout_height="230px"
android:background="#000011" /> <TextView android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="190px"
android:layout_height="190px"
android:background="#004433"/>
<TextView android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="150px"
android:layout_height="150px"
android:background="#00aa00"/>
<TextView android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="110px"
android:layout_height="110px"
android:background="#00dd00"/>
</FrameLayout>

Android 布局方式学习的更多相关文章
- 五大Android布局方式浅析
Android布局是应用界面开发的重要一环,在Android中,共有五种布局方式,分别是:FrameLayout(框架布局),LinearLayout (线性布局),AbsoluteLayout(绝对 ...
- Android布局方式总结
Android的布局分别是:线性布局LinearLayout.相对布局RelativeLayout.帧布局FrameLayout.网格布局GridLayout.约束布局ConstraintLayout ...
- Android 布局优化 -- 学习笔记
通过一些惯用.有效的布局原则,我们可以制作出加载效率高并且复用性高的UI.简单来说,在Android UI布局过程中,需要遵守的原则包括如下几点: 尽量多使用RelativeLayout,不要使用绝对 ...
- Android布局方式_RelativeLayout
RelativeLayout(相对布局)允许子元素指定它们相对于其他元素或父元素的位置(通过ID指定),因此用户可以右对齐,或上下对齐,或置于屏幕中央的形式来排列两个元素. RelativeLayou ...
- Android布局方式
1. LinearLayout(线性布局) android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="wra ...
- kivy八种布局方式学习
kivy八种布局:FloatLayout.BoxLayout.AnchorLayout.GridLayout.PageLayout.RelativeLayout.ScatterLayout.Stack ...
- 【Android学习】四种布局方式
一.LinearLayout 线性布局,即一行展开或者一列展开,也可以嵌套,需要注意的属性如下: android:orentation //对齐方式 二.FrameLayout 帧布局,即一层层叠起 ...
- Android学习笔记④——页面的布局方式
FrameLayout(帧布局) 这个布局的特点是简单的默认把每一个视图组件都放在边框内且放在左上角,即使添加多个视图组件,他们也都是重叠在左上角,新的视图会遮挡住旧的视图.可以根据gravity来改 ...
- 【转】Android开发学习笔记:5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种: 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件. 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件. 表格布局(Tabl ...
随机推荐
- C# 截取屏幕图像
#region 截取屏幕图像 private static Bitmap GetScreenCapture() { Rectangle tScreenRect = , , Screen.Primary ...
- FPGA基础知识,应用,ASIC、ASSP区别(四)
一.ASIC与ASSP区别? 专用应用集成电路( ASIC) 是一种由电子组件组成的集成电路,例如 :晶体管.电容器.电阻器等,这些组件被植入到晶元上 :晶元由硅或其他半导体材料组成,并可按照特定用途 ...
- LeetCode初级算法的Python实现--链表
LeetCode初级算法的Python实现--链表 之前没有接触过Python编写的链表,所以这里记录一下思路.这里前面的代码是和leetcode中的一样,因为做题需要调用,所以下面会给出. 首先定义 ...
- JavaScript基础part1
JavaScript介绍 你不知道它是什么就学?这就是一个网页嵌入式脚本语言...仅此而已 JavaScript组成 一个完整的 JavaScript 实现是由以下 3 个不同部分组成的: 核心(EC ...
- BZOJ1879_Bill的挑战_KEY
题目传送门 第一次看题目感觉毫无还手之力,一看M的范围≤15,果断状压. 但是状压的想法比较新奇. 先想到的状压是设f[i][j]表示前i个状态为j时的方案总数,但是后来想了一想不行,会超时. 于是以 ...
- 【springboot-01】整合quartz
1.什么是quartz? quartz是一个开源的定时任务框架,具备将定时任务持久化至数据库以及分布式环境下多节点调度的能力.当当的elastic-job便是以quartz为基础,结合zookeepe ...
- lesson 18 Electric currents in modern art
lesson18 Electric currents in modern art electricity n. 电力:电流; electric adj. 电的:电动的; electronic adj. ...
- Windows下PHP安全环境的搭建
笔者一直在Windows环境下搭建PHP的运行环境,大大小小的运行环境用过不少,从开始的WAMP到后来的XAMPP以及PHPnow.WAMP和XAMPP都是继承mysql apache以及PHP库的运 ...
- 深度学习图像分割——U-net网络
写在前面: 一直没有整理的习惯,导致很多东西会有所遗忘,遗漏.借着这个机会,养成一个习惯. 对现有东西做一个整理.记录,对新事物去探索.分享. 因此博客主要内容为我做过的,所学的整理记录以及新的算法. ...
- LeetCode - 566. Reshape the Matrix (C++) O(n)
1. 题目大意 根据给定矩阵,重塑一个矩阵,r是所求矩阵的行数,c是所求矩阵的列数.如果给定矩阵和所求矩阵的数据个数不一样,那么返回原矩阵.否则,重塑矩阵.其中两个矩阵中的数据顺序不变(先行后列). ...