Angular1组件通讯方式总结
这里需要将Angular1分为Angular1.5之前和Angular1.5两个不同的阶段来讲,两者虽然同属Angular1,但是在开发模式上还是有较大区别的。在Angular1.4及以前,主要是基于HTML的,将所有view划分为不同的HTML片段,通过路由,transclude,include等方式,按照用户行为切换显示不同界面。对于每个template内部来讲,可以是纯HTML,也可以是自定义的directive。directive之间可以有层级关系,也可以没有层级关系。在Angular1.5中,引入了Component API,鼓励使用单向数据流及Component tree 开发模式,在这种情况下,整个应用完全是基于组件的,除了root Component,其他Component都有自己的父级组件,组件之间主要是靠由上到下的单向数据流动来通信的,在这种模式下,directive不允许有自己的template,只能够来封装DOM操作。
在Angular1中提供了很多组件(指令)之间的通讯方式,本文主要来将这些方式一一列举出来,便于总结和使用。
directive通讯方式1-共享Service
在Angular1中,所有service都是单例的,这意味着一旦应用启动之后,在内存中会维护一些注册的service实例,在代码中任意地方对这些service的操作,都会导致其发生改变,而其他controller或者directive获取该service的值,也是发生改变之后的值。在这种情况下,一个directive对service进行写操作,另外一个directive对它进行读操作,两者就能通过该service进行通讯。
service定义
class HomeService {
constructor() {
this.names = [];
}
addName(name){
this.names.push(name);
}
}
10 export default HomeService;
directiveA定义
function aDirective(homeService) {
"ngInject";
return {
restrict: 'E',
template: `name:<input type='text' ng-model='showValue'>
<br><button ng-click="addName()">addName</button>`,
link: (scope, element, attrs) => {
scope.addName = () => {
if (scope.showValue) {
homeService.addName(scope.showValue);
}
}
}
};
}
export default aDirective;
directiveB定义
function bDirective(homeService) {
"ngInject";
return {
restrict: 'E',
template: `<ul>
<li ng-repeat="list in lists">{{list}}</li>
</ul>`,
link: (scope, element, attrs) => {
scope.lists=homeService.names;
}
};
}
export default bDirective;
HTML
<main class="home">
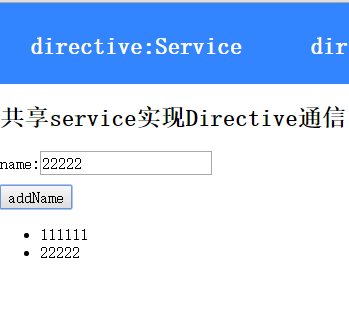
<h2>共享service实现Directive通信</h2>
<div>
<a-directive></a-directive>
<b-directive></b-directive>
</div>
</main>
在这里,我们在homeService中定义了一个addName方法,用来给该service的names中添加元素,然后让directiveA调用addName方法添加元素,随着names属性的变化,directiveB的list也会显示添加的内容,结果如下:
directive通讯方式2-自定义事件$broadcast及$emit
Angular1提供了scope之间事件的传播机制,使用scope.$emit可以往父级scope传播自定义事件并携带数据,使用scope.$broadcast可以给所有子scope广播事件和数据,所有需要接收到的scope需要使用scope.$on(eventName,callback)方法来监听事件。该机制很有用,但是我认为能不用就不用,主要是在实际开发中大多数是使用$rootScope来广播事件,每广播一次,整个scope下面的$$listeners都要去检测是否有对应的事件监听从而执行,如果scope层级较深,那么效率不会很高。除此之外,在各种directive,controller中监听自定义事件会导致混乱,代码不好去追踪,而且有可能引发命名冲突。
directiveA定义
function aDirective(homeService,$rootScope) {
"ngInject";
return {
restrict: 'E',
template: `name:<input type='text' ng-model='showValue' class='about'>
<br><button ng-click="addName()">addName</button>`,
link: (scope, element, attrs) => {
scope.addName = () => {
if(scope.showValue){
$rootScope.$broadcast('addName',scope.showValue);
}
}
}
};
}
export default aDirective;
directiveB定义
function bDirective(homeService) {
"ngInject";
return {
restrict: 'E',
template: `<ul>
<li ng-repeat="list in lists">{{list}}</li>
</ul>`,
link: (scope, element, attrs) => {
scope.lists=[];
scope.$on('addName',(...params)=>{
scope.lists.push(params[1]);
});
}
};
}
export default bDirective;
HTML
<section>
2 <event-adirective class="about"></event-adirective>
3 <event-bdirective></event-bdirective>
4 </section>
在这里,DirectiveA使用rootScope来广播事件,directiveB来监听事件,然后将事件传递的参数添加到lists数组当中去,结果同上。
directive通讯方式3-在link函数中使用attrs通讯
每个directive在定义的时候都有一个link函数,函数签名的第三个参数是attrs,代表在该directive上面的所有atrributes数组,attrs提供了一些方法,比较有用的是$set和$observe,前者可以自定义attr或修改已经有的attr的值,后者可以监听到该值的变化。利用这种方式,我们可以让在位于同一个dom元素上的两个directive进行通讯,因为它们之间共享一个attrs数组。
directiveA定义
function aDirective($interval) {
"ngInject";
return {
restrict: 'A',
link: (scope, element, attrs) => {
let deInterval=$interval(()=>{
attrs.$set('showValue', new Date().getTime());
},1000);
scope.$on('$destroy',()=>{
$interval.cancel(deInterval);
});
}
};
}
export default aDirective;
directiveB定义
function bDirective() {
"ngInject";
return {
restrict: 'E',
template: `<span>{{time|date:'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss'}}</span>`,
link: (scope, element, attrs) => {
attrs.$observe('showValue', (newVal)=>{
scope.time=newVal;
console.log(newVal);
});
}
};
}
export default bDirective;
HTML
1 <div>
2 <h2>{{ $ctrl.name }}</h2>
3 <directive-b directive-a></directive-b>
4 </div>
这里让directiveA不断修改showValue的值,让directiveB来observe该值并显示在template中,结果如下:

directive通讯方式4-使用directive的Controller+require来进行通讯
在directive中,可以在自己的controller中定义一些方法或属性,这些方法或者属性可以在其他directive中使用require来引入目标directive,然后在自己的link函数中的第四个参数中就可以拿到目标directive的实例,从而操作该实例,进行两者通讯。
directiveA定义
function aDirective() {
"ngInject";
return {
restrict: 'E',
transclude: true,
scope: {},
template: `<div><div ng-transclude></div><ul>
<li ng-repeat="list in lists">{{list}}</li>
</ul></div>`,
controller: function($scope) {
"ngInject";
$scope.lists = [];
this.addName = (item) => {
$scope.lists.push(item);
}
}
};
}
export default aDirective;
directiveB定义
function bDirective() {
"ngInject";
return {
restrict: 'E',
require:'^^aCtrlDirective',
template: `name:<input type='text' ng-model='showValue'>
<br><button ng-click="addName()">addName</button>
`,
link: (scope, element, attrs,ctrls) => {
scope.addName=function(){
if(scope.showValue){
ctrls.addName(scope.showValue);
}
}
}
};
}
export default bDirective;
HTML
<a-ctrl-directive>
<div>
<div>
<b-ctrl-directive class='ctrls'></b-ctrl-directive>
</div>
</div>
</a-ctrl-directive>
在directiveA中定义自己的controller,暴露addName方法给外部,然后再directiveB中require引用directiveA,在directiveB的link函数中调用addName方法,从而操作directiveA的lists数组,lists并没有在directiveB中定义。
Component通讯方式-单向数据流+$onChanges hook方法
在Angular1.5之后,为了更好的升级到Angular2,引入了Component API,并鼓励使用单向数据流加组件树开发模式,这和之前的directive相比,开发模式发生了比较大的变化。虽然component本身仅仅是directive语法糖,但是其巨大意义在于让开发者脱离之前的HTML为核心,转而适应组件树开发方式,这种模式也是目前主流前端框架都鼓励使用的模式,如Angular2,React及Vue。在这种模式下,上述几种通讯方式仍然有效,但是并不是最佳实践,Component由于天生具有层级关系,所以更鼓励使用单向数据流+生命周期Hook方法来进行通讯。
这里我们模拟一个查询的场景,使用三个组件来完成该功能,最外层的一个searchBody组件,用来作为该功能的根组件,searchFiled组件用来接收用户输入,并提供查询按钮,searchList组件用来显示查询结果。
searchList定义(为了便于查看,我将该组件的HTMl及核心js一起展示)
import template from './searchList.html';
import controller from './searchList.controller'; let searchListComponent = {
restrict: 'E',
bindings: {
searchMessages:'<',
searchText:'<'
},
template,
controller
}; class SearchListController {
constructor() {
this.name = 'searchList';
}
$onInit() {
this.initialMessages = angular.copy(this.searchMessages);
}
$onChanges(changesObj) {
if (changesObj.searchText && changesObj.searchText.currentValue) {
this.searchMessages = this.initialMessages.filter((message) => {
return message.key.indexOf(this.searchText) !== -1;
})
}
} } export default SearchListController; <div>
<ul class="search-ul">
<li ng-repeat="item in $ctrl.searchMessages">
{{item.key+"-"+item.val}}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
这里定义了一个controller,将searchList的所有逻辑都放在该controller中,6-9行在component定义中使用单向绑定<来定义来将其父组件上的数据绑定到controller上。18-20行在$onInit方法中初始化保留一份原始数据供查询使用。21-27行使用Angular1.5中Component的生命周期hook方法,当父组件中绑定的数据发生变化之后,都会触发该方法,该方法有一个参数,changesObj代表本次发生变化的对象,我们需要监听changesObj.searchText的变化,并按照searchText的最新值来过滤searchMessages.
searchField定义
import template from './searchField.html';
import controller from './searchField.controller'; let searchFieldComponent = {
restrict: 'E',
bindings: {},
template,
controller,
require:{
searchBody:'^searchBody'
}
}; class SearchFieldController {
constructor() {
this.searchWords = '';
} doSearch(){
if(!this.searchWords) return;
this.searchBody.doSearch(this.searchWords);
} } export default SearchFieldController; <div>
<input type="text" name="" value="" ng-model="$ctrl.searchWords">
<button ng-click="$ctrl.doSearch()">search</button>
</div>
searchField的作用是使用input接受用户输入的查询参数,然后在点击button的时候调用searchBody的doSearch方法,来通知最外层的searchBody更新searchText。
searchBody定义
import template from './searchBody.html';
import controller from './searchBody.controller'; let searchBodyComponent = {
restrict: 'E',
bindings: {},
template,
controller
};
class SearchBodyController {
constructor() {
this.searchTitle = 'searchBody';
}
$onInit(){
this.messages=[
{key:"erer",val:"ererererererere"},
{key:"1111",val:"111111111111111"},
{key:"2222",val:"222222222222222"},
{key:"3333",val:"333333333333333"},
{key:"4444",val:"444444444444444"},
{key:"5555",val:"555555555555555"},
{key:"6666",val:"666666666666666"},
{key:"7777",val:"777777777777777"},
{key:"8888",val:"888888888888888"}
]
} doSearch(text){
this.searchText=text;
}
} export default SearchBodyController; <div>
<h1>{{ $ctrl.searchTitle }}</h1>
<search-field></search-field>
<search-list search-messages="$ctrl.messages" search-text="$ctrl.searchText"></search-list>
</div>
在上述代码中的37-38行,引用searchField和searchList两个组件,并将searchBody的messages及searchText作为最初的数据源传递给searchList组件,然后再searchField中点击查询按钮,会调用searchBody的doSearch方法,改变searchBody的searchText的值,然后触发searchList中的$onChanges方法,从而过滤相关结果,可以看到所有数据都是从上到下单向流动的,组件之间都是靠数据来通信的。
Angular1组件通讯方式总结的更多相关文章
- vue 组件通讯方式到底有多少种 ?
前置 做大小 vue 项目都离不开组件通讯, 自己也收藏了很多关于 vue 组件通讯的文章. 今天自己全部试了试, 并查了文档, 在这里总结一下并全部列出, 都是简单的例子. 如有错误欢迎指正. 温馨 ...
- Angular1.x组件通讯方式总结
Angular1开发模式 这里需要将Angular1分为Angular1.5之前和Angular1.5两个不同的阶段来讲,两者虽然同属Angular1,但是在开发模式上还是有较大区别的.在Angula ...
- Angular 组件通讯方式
(一)父子组件 输入/输出属性 关键词 Input,Output,EventEmitter. 父子组件信息信息,分为 (1)子组件向父组件传递 (2)父组件向子组件传递 (二)模版变量与 @V ...
- vue组件通讯之provide / inject
什么是 provide / inject [传送门] vue的组件通讯方式我们熟知的有 props $emit bus vuex ,另外就是 provide/inject provide/inject ...
- android ipc通信机制之之三,进程通讯方式。
IPC通讯方式的优缺点: IPC通讯方式的对比 名称 优点 缺点 适用场景 Bundle 简单易用 只能传输Bundle支持的数据类型 四大组件的进程通信 文件共享 简单易用 不适合高并发场景,并无法 ...
- Omi教程-组件通讯
组件通讯 Omi框架组建间的通讯非常遍历灵活,因为有许多可选方案进行通讯: 通过在组件上声明 data-* 传递给子节点 通过在组件上声明 data 传递给子节点 父容器设置 childrenData ...
- Angular4 组件通讯方法大全
组件通讯,意在不同的指令和组件之间共享信息.如何在两个多个组件之间共享信息呢. 最近在项目上,组件跟组件之间可能是父子关系,兄弟关系,爷孙关系都有.....我也找找了很多关于组件之间通讯的方法,不同的 ...
- 【Vue】Vue中的父子组件通讯以及使用sync同步父子组件数据
前言: 之前写过一篇文章<在不同场景下Vue组件间的数据交流>,但现在来看,其中关于“父子组件通信”的介绍仍有诸多缺漏或者不当之处, 正好这几天学习了关于用sync修饰符做父子组件数据双向 ...
- Omi教程-组件通讯攻略大全
组件通讯 Omi框架组建间的通讯非常遍历灵活,因为有许多可选方案进行通讯: 通过在组件上声明 data-* 传递给子节点 通过在组件上声明 data 传递给子节点 (支持复杂数据类型的映射) 父容器设 ...
随机推荐
- Rstudio常用快捷键 “原版+中文” 整理
- 【实战】sqlmap显示有注入却无法爆出库名
sqlmap爆mssql数据库时采用的语句如下图: 从语句中不难看出,如果关键字select被“(非tamper绕过)处理”了,那sqlmap是无法爆出数据库的,这时我们可以使用原始的猜解法, #判断 ...
- 1-----Docker实例-安装Nginx
Docker 安装 Nginx 方法一.docker pull nginx(推荐) 查找 Docker Hub 上的 nginx 镜像 runoob@runoob:~/nginx$ docker se ...
- redis在Linux上的安装
1 安装redis编译的c环境 输入命令: 注意yum安装必须联网 yum install gcc-c++ 如果提示是否需要下载输入y就可以开始下载. 2 redis安装 1 上传文件 2 解压文件 ...
- 【LESS系列】一些常用的Mixins
在我们平时的开发中,对于一些使用频率很高的方法函数,我们一般都会将其归纳到一起,整理出一个核心库来. 其实这个思想,借助 LESS 也可以在 CSS 中得以实现. 下面是几个在 W3CPLUS 中偷过 ...
- Hibernate 多对一映射
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBL ...
- git 自己创建了一个项目A,我的同事fork一个B,当我的项目更新的时候,怎么样在他fork的repo上进行相应的更新?
先把B clone到本地 git clone B_REPOSITORY_URL 再cd到本地B的目录,把A作为一个remote加到本地的B中(一般命名为upstream) git remote add ...
- addEventListener()和removeEventListener()
作用: addEventListener()与removeEventListener()用于处理指定和删除事件处理程序操作. 它们都接受3个参数:事件名.事件处理的函数和布尔值. 布尔值参数是true ...
- grep常用命令总结与基础正则
grep 'str'用来选取含有str的行 参数: -v 反向选取 -n 显示行号 -c 计算查找到字符串的次数 -i 选取时不区分大小写 基础正则表达式符: [list] 从字符集合里选出任意一个字 ...
- step7: 输出到json文件
调用scrapy自身的Exporter输出 编辑pipeline文件 import json from scrapy.exporters import JsonItemExporter #引入Expo ...
