#【Python】【基础知识】【内置对象常用方法】
数字
数字的常用方法:
>>> dir(int)
['__abs__', '__add__', '__and__', '__bool__', '__ceil__', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__divmod__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__float__', '__floor__', '__floordiv__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__index__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__int__', '__invert__', '__le__', '__lshift__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__neg__', '__new__', '__or__', '__pos__', '__pow__', '__radd__', '__rand__', '__rdivmod__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rfloordiv__', '__rlshift__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__ror__', '__round__', '__rpow__', '__rrshift__', '__rshift__', '__rsub__', '__rtruediv__', '__rxor__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__sub__', '__subclasshook__', '__truediv__', '__trunc__', '__xor__', 'bit_length', 'conjugate', 'denominator', 'from_bytes', 'imag', 'numerator', 'real', 'to_bytes']
第一组常用方法:
'bit_length', 'conjugate', 'denominator', 'from_bytes', 'imag', 'numerator', 'real', 'to_bytes'
第二组常用方法:
(内置函数)
math模块的方法:
>>> import math
>>> dir(math)
['__doc__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', 'acos', 'acosh', 'asin', 'asinh', 'atan', 'atan2', 'atanh', 'ceil', 'copysign', 'cos', 'cosh', 'degrees', 'e', 'erf', 'erfc', 'exp', 'expm1', 'fabs', 'factorial', 'floor', 'fmod', 'frexp', 'fsum', 'gamma', 'gcd', 'hypot', 'inf', 'isclose', 'isfinite', 'isinf', 'isnan', 'ldexp', 'lgamma', 'log', 'log10', 'log1p', 'log2', 'modf', 'nan', 'pi', 'pow', 'radians', 'remainder', 'sin', 'sinh', 'sqrt', 'tan', 'tanh', 'tau', 'trunc']
第三组常用方法:
'acos', 'acosh', 'asin', 'asinh', 'atan', 'atan2', 'atanh', 'ceil', 'copysign', 'cos', 'cosh', 'degrees', 'e', 'erf', 'erfc', 'exp', 'expm1', 'fabs', 'factorial', 'floor', 'fmod', 'frexp', 'fsum', 'gamma', 'gcd', 'hypot', 'inf', 'isclose', 'isfinite', 'isinf', 'isnan', 'ldexp', 'lgamma', 'log', 'log10', 'log1p', 'log2', 'modf', 'nan', 'pi', 'pow', 'radians', 'remainder', 'sin', 'sinh', 'sqrt', 'tan', 'tanh', 'tau', 'trunc'
字符串
字符串的常用方法:
>>> dir(str)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
第一组常用方法:
'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isascii', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill'
string模块的方法:
>>> import string
>>> dir(string)
['Formatter', 'Template', '_ChainMap', '_TemplateMetaclass', '__all__', '__builtins__', '__cached__', '__doc__', '__file__', '__loader__', '__name__', '__package__', '__spec__', '_re', '_string', 'ascii_letters', 'ascii_lowercase', 'ascii_uppercase', 'capwords', 'digits', 'hexdigits', 'octdigits', 'printable', 'punctuation', 'whitespace']
第二组常用方法:
'ascii_letters', 'ascii_lowercase', 'ascii_uppercase', 'capwords', 'digits', 'hexdigits', 'octdigits', 'printable', 'punctuation', 'whitespace'
str.join()
>>> l
[1, 3, 4, 5]
>>> "#".join(str(n) for n in l)
'1#3#4#5'
列表
列表的常用方法:
>>> dir(list)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort']
第一组常用方法:
'append',
'clear',
'copy',
'count',
'extend',
'index',
'insert',
语法:
list.insert(index, obj)
返回值:无返回值
示例:
>>>
>>> l = [1,6,3,4,7]
>>> l
[1, 6, 3, 4, 7]
>>>
>>>
>>>
>>> l.insert(3,99)
>>> l
[1, 6, 3, 99, 4, 7]
>>>
'pop',
'remove',
'reverse',
'sort'
元组
元组的常用方法:
>>> dir(tuple)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'count', 'index']
第一组常用方法:
'count', 'index'
字典
字典的常用方法:
>>> dir(dict)
['__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'clear', 'copy', 'fromkeys', 'get', 'items', 'keys', 'pop', 'popitem', 'setdefault', 'update', 'values']
第一组常用方法:
'clear', 'copy', 'fromkeys', 'get', 'items', 'keys', 'pop', 'popitem', 'setdefault', 'update', 'values'
文件
文件的常用方法:
集合
集合的常用方法:
>>> dir(set) ['__and__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iand__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__ior__', '__isub__', '__iter__', '__ixor__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__or__', '__rand__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__ror__', '__rsub__', '__rxor__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__sub__', '__subclasshook__', '__xor__', 'add', 'clear', 'copy', 'difference', 'difference_update', 'discard', 'intersection', 'intersection_update', 'isdisjoint', 'issubset', 'issuperset', 'pop', 'remove', 'symmetric_difference', 'symmetric_difference_update', 'union', 'update'] >>>
布尔
布尔的常用方法:
>>> dir(bool)
['__abs__', '__add__', '__and__', '__bool__', '__ceil__', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__divmod__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__float__', '__floor__', '__floordiv__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__index__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__int__', '__invert__', '__le__', '__lshift__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__neg__', '__new__', '__or__', '__pos__', '__pow__', '__radd__', '__rand__', '__rdivmod__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rfloordiv__', '__rlshift__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__ror__', '__round__', '__rpow__', '__rrshift__', '__rshift__', '__rsub__', '__rtruediv__', '__rxor__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__sub__', '__subclasshook__', '__truediv__', '__trunc__', '__xor__', 'bit_length', 'conjugate', 'denominator', 'from_bytes', 'imag', 'numerator', 'real', 'to_bytes']
第一组常用方法:
'bit_length', 'conjugate', 'denominator', 'from_bytes', 'imag', 'numerator', 'real', 'to_bytes'
类型相互转换:
字符串转换为列表
字符串转换为数字
字符串转换为集合
列表转换为字典
使用dict:
列表内有两个元素,一个作为键名,一个作为键值:
>>> s = ["m","n"]
>>> dict([s])
{'m': 'n'}
>>>
>>> >>> >>> s = ["m","n"]
>>> ll = [3,4]
>>> dict([s,ll])
{'m': 'n', 3: 4}
若一个列表作为键名,另外一个列表作为键值,将这两个列表转换为字典:
#!/usr/bin/python
# encoding=utf-8
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*- # 将两个列表转换为字典,一个键名,另外一个作为键值; p = ["a","b","c","d","e","f","g","h","i"]
q = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
r = []
for i in range(len(p)):
r.append([p[i],q[i]])
print(r) print(dict(r))
输出结果:

需要注意的是,必须保证两个列表的长度相同,若两个列表不一样长,对于索引值超过一个列表的长度,则会报错:(不超过则不会报错)
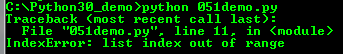
如果列表有三个元素,则会报错;
>>> t = ["s","d","f"]
>>> dict(t)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<pyshell#23>", line 1, in <module>
dict(t)
ValueError: dictionary update sequence element #0 has length 1; 2 is required
>>>
字典转换为列表
————————(我是分割线)————————
参考:
None
备注:
初次编辑时间:2019年10月6日11:34:19
第1次修改时间:2019年10月6日15:01:22 /添加列表insert说明
第2次修改时间:2019年10月6日19:07:00 /添加列表转换为字典的Python代码示例;
环境:Windows 7 / Python 3.7.2
#【Python】【基础知识】【内置对象常用方法】的更多相关文章
- 十六. Python基础(16)--内置函数-2
十六. Python基础(16)--内置函数-2 1 ● 内置函数format() Convert a value to a "formatted" representation. ...
- 十五. Python基础(15)--内置函数-1
十五. Python基础(15)--内置函数-1 1 ● eval(), exec(), compile() 执行字符串数据类型的python代码 检测#import os 'import' in c ...
- js内置对象常用方法
JS内置对象: ● String对象:处理所有的字符串操作 ● Math对象:处理所有的数学运算 ● Date对象:处理日期和时间的存储.转化和表达 ● Array对象:提供一个数组的模型.存储大量有 ...
- js 内置对象常用方法
1 内容概述 js包含一些内置对象,如Array,Function,String等,这些是基本的,常用的js类,所以了解它们十分重要:把他们的方法,用例子和文字简要的记录下来,方便今后参看. 2 Ar ...
- JS基础语法---内置对象
js学习中三种对象: 内置对象----js系统自带的对象 自定义对象---自己定义的构造函数创建的对象 浏览器对象---BOM的时候讲 内置对象: Math Date String Array Obj ...
- python基础(15):内置函数(一)
1. 内置函数 什么是内置函数? 就是python给你提供的,拿来直接⽤的函数,比如print,input等等,截⽌到python版本3.6.2 python⼀共提供了68个内置函数.他们就是pyth ...
- python基础(内置函数+文件操作+lambda)
一.内置函数 注:查看详细猛击这里 常用内置函数代码说明: # abs绝对值 # i = abs(-123) # print(i) #返回123,绝对值 # #all,循环参数,如果每个元素为真,那么 ...
- JavaWeb基础-Jsp内置对象
request对象 客户端的请求信息被封装在request对象中,通过它才能了解到客户的需求,然后做出响应,它是HttpServlteRequest类的实例.Request对象具有请求域,即完成客户端 ...
- python基础知识13---函数对象、函数嵌套、名称空间与作用域、装饰器
阅读目录 一 函数对象 二 函数嵌套 三 名称空间与作用域 四 闭包函数 五 装饰器 六 练习题 一 函数对象 1 函数是第一类对象,即函数可以当作数据传递 #1 可以被引用 #2 可以当作参数传递 ...
随机推荐
- Til the Cows Come Home ( POJ 2387) (简单最短路 Dijkstra)
problem Bessie is out in the field and wants to get back to the barn to get as much sleep as possibl ...
- mapreduce 倒序 排序 最简单 易上手
对于mapreduce倒序只需要建立一个类,然后继承WritableComparator 在重写 Compare函数最后在main里调用一下,就可以实现倒序排序: 代码: public static ...
- 一台服务器配置多个mysql实例
在公司资源紧张的情况下,需要在一台服务器上部署多个数据库实例,现在就来实战一下该情况. 需要启动两个不同的端口,分别是3306和3307 [root@node1 ~]# mkdir /u01/mysq ...
- redhat7.4安装svn
1.使用yum install subversion出错 已加载插件:langpacks, product-id, search-disabled-repos, subscription-manage ...
- html文字两行后,就用省略号代替剩下的
html文字两行后,就用省略号代替剩下的 一.总结 一句话总结: 实现原理很简单,将box的高度设置为行高的两倍,超出之后隐藏,这样就只有两行了,然后再用after属性绝对定位在第二行后面加几个点 . ...
- Flutter移动电商实战 --(26)列表页_使用Provide控制子类-2
主要实现功能,点击一级分类,二级分类跟着变.这里主要用我们的provide 新建provide provide文件夹下创建:child_category.dart 事件上就是这个实体:BxMallSu ...
- 高并发实时弹幕系统 并发数一定是可以进行控制的 每个需要异步处理开启的 Goroutine(Go 协程)都必须预先创建好固定的个数,如果不提前进行控制,那么 Goroutine 就随时存在爆发的可能。
小结: 1.内存优化1.一个消息一定只有一块内存使用 Job 聚合消息,Comet 指针引用. 2.一个用户的内存尽量放到栈上内存创建在对应的用户 Goroutine(Go 程)中. 3.内存由自己控 ...
- 19.网络插件calico
19.网络插件calico 官网: https://docs.projectcalico.org/v3.8/introduction/ calico默认工作在192.168.0.0/16 的网络 ca ...
- Flask中路由参数
Flask中路由参数.请求方式设置 一.参数设置 1.参数类型 Flask中参数的使用 @app.route('/parames/<username>/') def hello_world ...
- spring常用模式--模板模式
引入:这几天在看一本讲spring源码的书<SPRING技术内幕>里面在讲加载配置文件的时候,可以有不同的加载方式,如根据文件系统目录加载配置文件(FileSystemXmlApplica ...
