LCA cogs 2450 2048 1588
t1 2450距离 链接:http://cogs.pro:8081/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=vSNNNVqga
【题目描述】
在一个村子里有N个房子,一些双向的路连接着他们。人们总喜欢问这个“如果1想从房子A走到房子B有多远?”这个通常很难回答。但幸运的是在这个村里答案总是唯一的,自从道路修建以来这只有唯一的一条路(意思是你不能去一个地方两次)在每两座房子之间。你的工作是回答所有好奇的人。
【输入格式】
输入文件第一行有两个数n(2≤n≤10000)和m(1≤m≤20000),即房子数和问题数。后面n-1行每行由3个数构成i,j,k,由空格隔开,意思是房子i和房子j之间距离为k(0<k≤100)。房子以1到n标记。
下面m行每行有两个不同的整数i和j,你需要回答房子i和房子j之间的距离。
【输出格式】
输出有n行。每行表示个一个问题的答案。
【样例1】
输入样例1:
3 2
1 2 10
3 1 15
1 2
2 3
输出样例1:
10
25
【样例2】
输入样例2:
2 2
1 2 100
1 2
2 1
输出样例2:
100
100 思路:一道带边权的LCA,tarjan离线算法即可,将query读进来作为一种结构,同边一样记录,dfs的时候同时维护一个栈,栈元素的x为查询的from,i为边序号,维护这个栈即可,同时
距离dis[x]表示树根到x的距离,每次递归处理,ans[q[i].id]即为第几次询问的答案, 理解ans = dis_x + dis_y - 2 * dis_LCA,通过函数找到x和y的LCA
代码
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "iostream"
#include "cstdio"
#include "cstring"
#define maxn 10010
using namespace std;
int n, m, from, to, k;
struct Edge
{
int to, val, pre;
}e[maxn << ]; struct query
{
int to, id, pre;
}q[maxn << ]; struct AA
{
int x, i;
}a[maxn]; int lastE[maxn] = { };
int lastQ[maxn] = { };
int p[maxn] = { };
int dis[maxn], anc[maxn], ans[maxn << ];
bool vis[maxn << ] = { };
int cnt = , cnt1 = , cnt2 = , top = ; void inserte(int from, int to, int val)
{
e[++cnt1].to = to;
e[cnt1].val = val;
e[cnt1].pre = lastE[from];
lastE[from] = cnt1;
} void insertq(int from, int to, int i)
{
q[++cnt2].to = to;
q[cnt2].id = i;
q[cnt2].pre = lastQ[from];
lastQ[from] = cnt2;
} int findRoot(int x)
{
static int y, root;
root = anc[x];
while (anc[root] != root)
root = anc[root];
while (anc[x] != x)
{
y = anc[x];
anc[x] = root;
x = y;
}
return root;
} void dfs(int x)
{
int y, i;
a[++top].x = x;
a[top].i = lastE[x];
while (top)
{
x = a[top].x;
i = a[top].i;
if (e[i].to == p[x])
i = e[i].pre;
if (i)
{
a[top].i = e[i].pre;
y = e[i].to;
p[y] = x;
dis[y] = dis[x] + e[i].val;
a[++top].x = y;
a[top].i = lastE[y];
anc[y] = y;
}
else
{
vis[x] = ;
for (int i = lastQ[x]; i; i = q[i].pre)
{
y = q[i].to;
if (vis[y])
{
ans[q[i].id] = dis[x] + dis[y] - (dis[findRoot(y)] << );
}
}
anc[x] = p[x];
top--;
}
}
} int main()
{
freopen("distance.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("distance.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = ; i < n - ; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &from, &to, &k);
inserte(from, to, k);
inserte(to, from, k);
}
for (int i = ; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &from, &to);
insertq(from, to, i);
insertq(to, from, i);
}
dis[] = p[] = ;
dfs(); for (int i = ; i < m; i++)
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return ;
}
t2 cogs 1588 题目链接:http://cogs.pro:8081/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=vxmxQkgUU
【题目描述】
农夫约翰有N(2<=N<=40000)个农场,标号1到N。M(2<=M<=40000)条的不同的垂直或水平的道路连结着农场,道路的长度不超过1000.这些农场的分布就像下面的地图一样,图中农场用F1..F7表示:
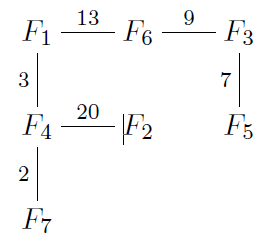
每个农场最多能在东西南北四个方向连结4个不同的农场。此外,农场只处在道路的两端。道路不会交叉而且每对农场间有且仅有一条路径。邻居鲍伯要约翰来导航,但约翰丢了农场的地图,他只得从电脑的备份中修复率。每一条道路的信息如下:
从农场23往南经距离10到达农场17
从农场1往东经距离7到达农场17
. . .
最近美国过度肥胖非常普遍。农夫约翰为了让他的奶牛多做运动,举办了奶牛马拉松。马拉松路线要尽量长。
奶牛们拒绝跑马拉松,因为她们悠闲的生活无法承受约翰选择的如此长的赛道。因此约翰决心找一条更合理的赛道。他打算咨询你。读入地图之后会有K个问题,每个问题包括2个整数,就是约翰感兴趣的2个农场的编号,请尽快算出这2个农场间的距离。
【输入格式】
第1行:两个分开的整数N和M。
第2到M+1行:每行包括4个分开的内容,F1,F2,L,D分别描述两个农场的编号,道路的长度,F1到F2的方向N,E,S,W。
第2+M行:一个整数K(1<=K<=10000).
第3+M到2+M+K行:每行输入2个整数,代表2个农场。
【输出格式】
对每个问题,输出单独的一个整数,给出正确的距离。
【样例输入】
7 6
1 6 13 E
6 3 9 E
3 5 7 S
4 1 3 N
2 4 20 W
4 7 2 S
3
1 6
1 4
2 6
【样例输出】
13
3
36
【提示】
农场2到农场6有20+3+13=36的距离。
同t1,读入的时候读方向但是忽略即可。
代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "iostream"
#include "cstdio"
#include "cstring"
#define maxn 40010
using namespace std;
int n, m, from, to, k, sumQ;
struct Edge
{
int to, val, pre;
}e[maxn << ]; struct query
{
int to, id, pre;
}q[maxn << ]; struct AA
{
int x, i;
}a[maxn]; int lastE[maxn] = { };
int lastQ[maxn] = { };
int p[maxn] = { };
int dis[maxn], anc[maxn], ans[maxn << ];
bool vis[maxn << ] = { };
int cnt = , cnt1 = , cnt2 = , top = ; void inserte(int from, int to, int val)
{
e[++cnt1].to = to;
e[cnt1].val = val;
e[cnt1].pre = lastE[from];
lastE[from] = cnt1;
} void insertq(int from, int to, int i)
{
q[++cnt2].to = to;
q[cnt2].id = i;
q[cnt2].pre = lastQ[from];
lastQ[from] = cnt2;
} int findRoot(int x)
{
static int y, root;
root = anc[x];
while (anc[root] != root)
root = anc[root];
while (anc[x] != x)
{
y = anc[x];
anc[x] = root;
x = y;
}
return root;
} void dfs(int x)
{
int y, i;
a[++top].x = x;
a[top].i = lastE[x];
while (top)
{
x = a[top].x;
i = a[top].i;
if (e[i].to == p[x])
i = e[i].pre;
if (i)
{
a[top].i = e[i].pre;
y = e[i].to;
p[y] = x;
dis[y] = dis[x] + e[i].val;
a[++top].x = y;
a[top].i = lastE[y];
anc[y] = y;
}
else
{
vis[x] = ;
for (int i = lastQ[x]; i; i = q[i].pre)
{
y = q[i].to;
if (vis[y])
{
ans[q[i].id] = dis[x] + dis[y] - (dis[findRoot(y)] << );
}
}
anc[x] = p[x];
top--;
}
}
} int main()
{
freopen("dquery.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("dquery.out", "w", stdout);
char c;
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for (int i = ; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d %d %c", &from, &to, &k, &c);
inserte(from, to, k);
inserte(to, from, k);
}
scanf("%d", &sumQ);
for (int i = ; i < sumQ; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &from, &to);
insertq(from, to, i);
insertq(to, from, i);
}
dis[] = p[] = ;
dfs(); for (int i = ; i < sumQ; i++)
printf("%d\n", ans[i]);
return ;
}
t3 cogs
2084. [SYOI 2015] Asm.Def的基本算法
链接:http://cogs.pro:8081/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=vyiJNVaUq
【题目描述】
“有句美国俗语说,如果走起来像鸭子,叫起来像鸭子,那就是一只鸭子。”斯科特·华莱士看着Asm.Def面前屏幕上滚动的绿色字符,若有所思地说。
“什么意思?”
“你的数据。看上去是一棵树。”
“按照保密条令,我什么也不说这是最好的——但见你这么热情,一句话不说也不好。”Asm.Def停下手中的快速数论变换,“确实是树。”
“然后你怎么算出来目标的位置?”
“都需要按照基本算法,按照图论的那一套理论,去产生。听说过LCA吗?不是那个印度飞机,我是说最近公共祖先……
Asm.Def通过分析无线电信号得到了一棵有n个节点,以1为根的树。除1之外,节点i的父亲是p_i。节点带有权值,节点i的权值是w_i。
我们定义某点的祖先为从根到它路径上的所有点(包括它本身),而两个节点a、b的最近公共祖先是某个点p,使得p同时是a、b的祖先,而且p离根最远。
Asm.Def想要求出

(文字:∑∑w_i*w_j*w_LCA(i,j)),
其中LCA(i,j)是i、j的最近公共祖先,他认为这个值至关重要。由于这个值可能很大,Asm.Def只需要知道它模1,000,000,007(即10^9+7)的结果。
【输入格式】
第1行两个整数:n和w_1.
第2行到第n行,第i行有两个整数p_i和w_i。
【输出格式】
一行一个整数,即答案模1,000,000,007的值。
【样例输入】
2 2
1 1
【样例输出】
17
【提示】
1×1×1+1×2×2+2×1×2+2×2×2=17。
对于30%的数据,n<=100,w_i<=10。
对于60%的数据,n<=1000,w_i<=1000.
对于100%的数据,1<=n<=10^5,0<=w_i<=10^9,1<=p_i<i.
思路:递归遍历,以每个节点为一个根 为单位,维护以此节点为根的子树的权值sum,乘积求和,见注释
代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "iostream"
#include "cstdio"
#include "cstring" #define ll long long
#define maxn 100100
using namespace std; struct Edge
{
ll to, pre;
Edge() :to(), pre() {};
}e[maxn << ];
bool vis[maxn << ];
int prt[maxn], n, w[maxn], last[maxn << ];
int cnt = ;
ll sum = ;
int s[maxn]; //以x为根的点的权值和
//int sz[maxn]; //子孙节点个数 void insert(int from, int to)
{
e[++cnt].to = to;
e[cnt].pre = last[from];
last[from] = cnt;
} void dfs(int x)
{
//sz[x] = 1; //从x开始,子孙节点个数为1
s[x] = w[x]; //包含自己,子节点权值和为w_x
int y;
for (int i = last[x]; i; i = e[i].pre)
{
y = e[i].to;
if (y == prt[x])
continue;
prt[y] = x;
dfs(y);
s[x] = (s[x] + s[y]) % ; //回溯后,子节点和累加上来
//sz[x] += sz[y]; //子节点个数累加
} ll ss = s[x], tmp = ;
for (int i = last[x]; i; i = e[i].pre)
{
y = e[i].to;
if (y == prt[x])
continue;
//ss-s_y即为除了y和它的子节点权值和 其余节点的权值和,乘积满足Σwi*wj
tmp = (tmp + ((ll)s[y] * ((ss - s[y] + ) % ) % )) % ;
//每个乘积会被算两次但父节点和子节点不会,因此再加上s_y * wx
tmp = (tmp + ((ll)s[y] * w[x] % )) % ;
}
//对每个x,都有i==j的时候,x和自己的乘积以及LCA也是它自己
tmp = (tmp + ((ll)w[x] * w[x] % )) % ;
//前边只有wi wj,统一乘wLCA
tmp = ((ll)tmp * w[x]) % ;
sum = (sum + tmp) % ;
} int main()
{
freopen("asm_algo.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("asm_algo.out", "w", stdout);
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &w[]);
for (int i = ; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
w[i] = y;
insert(x, i);
} dfs();
printf("%lld\n", sum);
return ;
}
LCA cogs 2450 2048 1588的更多相关文章
- cogs 2450. 距离 树链剖分求LCA最近公共祖先 快速求树上两点距离 详细讲解 带注释!
2450. 距离 ★★ 输入文件:distance.in 输出文件:distance.out 简单对比时间限制:1 s 内存限制:256 MB [题目描述] 在一个村子里有N个房子,一 ...
- [SinGuLaRiTy] 树链问题
[SinGuLaRiTy-1035] Copyright (c) SinGuLaRiTy 2017. All Rights Reserved. 关于树链 树链是什么?这个乍一看似乎很陌生的词汇表达的其 ...
- cogs 1588. [USACO Feb04]距离咨询 倍增LCA
1588. [USACO Feb04]距离咨询 ★★ 输入文件:dquery.in 输出文件:dquery.out 简单对比时间限制:1 s 内存限制:256 MB [题目描述] 农夫 ...
- 【COGS 2434】 暗之链锁 树上差分+LCA
差分就是把一个值拆成许多差的和如 1 2 4 6 9 那么 把这个东西拆成 1 1 2 2 3 就是了,当然也可以理解为对一个问题分解为多个子问题并对其进行操作来得到原问题的答案. 树上差分就更玄妙了 ...
- cogs 2098. [SYOI 2015] Asm.Def的病毒 LCA 求两条路径是否相交
2098. [SYOI 2015] Asm.Def的病毒 ★☆ 输入文件:asm_virus.in 输出文件:asm_virus.out 简单对比时间限制:1 s 内存限制:256 M ...
- cogs 186. [USACO Oct08] 牧场旅行 树链剖分 LCA
186. [USACO Oct08] 牧场旅行 ★★☆ 输入文件:pwalk.in 输出文件:pwalk.out 逐字节对比时间限制:1 s 内存限制:128 MB n个被自然地编号为 ...
- cogs 2109. [NOIP 2015] 运输计划 提高组Day2T3 树链剖分求LCA 二分答案 差分
2109. [NOIP 2015] 运输计划 ★★★☆ 输入文件:transport.in 输出文件:transport.out 简单对比时间限制:3 s 内存限制:256 MB [题 ...
- COGS——T1588. [USACO FEB04]距离咨询
http://cogs.pro/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=1588 ★★ 输入文件:dquery.in 输出文件:dquery.out 简单对比时间限制:1 ...
- Cogs 1583. [POJ3237]树的维护 LCT,树链剖分
题目:http://cojs.tk/cogs/problem/problem.php?pid=1583 1583. [POJ3237]树的维护 ★★★☆ 输入文件:maintaintree.in ...
随机推荐
- IDEA 2019.1版本 永久激活(假装是永久激活,其实还是有时间的,不过这个时间比较长)
先下载 一个 jar 包 链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/12eC8OZzMrUve2xC7aRUKLQ 提取码: bavi 将下载下来的jar包,放置你安装idea的目录的b ...
- Oracle 11 安装教程(桌面类)
准备文件: http://download.oracle.com/otn/nt/oracle11g/112010/win64_11gR2_database_1of2.zip http://downlo ...
- 入门 uCOS 操作系统的一点建议
原创: 鱼鹰Osprey 鱼鹰谈单片机 3月2日 预计阅读时间: 4 分钟 对于想入门操作系统的读者,我的建议是先学 uCOS II.原因有以下几点: 1.最为重要的原因是网上相关资源非常丰富,这对 ...
- XHTML测试题
1.XHTML 指的是? A.EXtra Hyperlinks and Text Markup Language B.EXtensible HyperText Marking Language C.E ...
- 【原创】洛谷 LUOGU P3372 【模板】线段树1
P3372 [模板]线段树 1 题目描述 如题,已知一个数列,你需要进行下面两种操作: 1.将某区间每一个数加上x 2.求出某区间每一个数的和 输入输出格式 输入格式: 第一行包含两个整数N.M,分别 ...
- 在Postman脚本中发送请求(pm.sendRequest)
Postman的Collection(集合)/Folder(集合的子文件夹)/Request(请求)都有Pre-request script和Tests两个脚本区域, 分别可以在发送请求前和请求后使用 ...
- javaweb和数据库的简易商城系统
这是一个基于Javaweb和数据库的简易商城系统.为大二夏季小学期完成. 目录结构 主要功能截图为: 一.购买用户 1.首页(除此界面其余界面访问需要登录才能进入) 查看商品 添加购物车 查看购物车 ...
- mysql 日期字符串互转
字符串转日期select str_to_date('2008-4-2 15:3:28','%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s');select str_to_date('2008-08-09 08:9 ...
- No Desktop License Servers available to provide a license
远程桌面连接失败,提示:“no Remote Desktop License Servers available to provide a license” 原因:没有remote desktop l ...
- ArcGIS Python 保存lyr
import arcpy ##################my = arcpy.GetParameterAsText(0)mylyrfile = arcpy.GetParameterAsText( ...
