在Android so文件的.init、.init_array上和JNI_OnLoad处下断点
本文博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/qq1084283172/article/details/54233552
移动端Android安全的发展,催生了各种Android加固的诞生,基于ELF文件的特性,很多的加固厂商在进行Android逆向的对抗的时,都会在Android的so文件中进行动态的对抗,对抗的点一般在so文件的.init段和JNI_OnLoad处。因此,我们在逆向分析各种厂商的加固so时,需要在so文件的.init段和JNI_OnLoad处下断点进行分析,过掉这些加固的so对抗。
一、如何向.init和.init_array段添加自定义的函数
so共享库文件的高级特性
在so共享库文件动态加载时,有一次执行代码的机会:
[1] so加载时构造函数,在函数声明时加上"__attribute__((constructor))"属性
void __attribute__((constructor)) init_function(void)
{
// to do
}
对应有so卸载时析构函数,在程序exit()或者dlclose()返回前执行
void __attribute__((destructor)) fini_function(void)
{
// to do
}
[2] c++全局对象初始化,其构造函数(对象)被自动执行在Android NDK编程中,.init段和.init_array段函数的定义方式:
extern "C" void _init(void) { } -------》编译生成后在.init段
__attribute__((constructor)) void _init(void) { } -------》编译生成后在.init_array段
说明下,带构造函数的全局对象生成的时在在.init_array段里面。使用IDA工具查看so库文件中.init段和.init_array段的方法
参考连接:
《UNIX系统编程手册》
【求助】JNI编程,怎么在native中定义_init段呢?
http://www.blogfshare.com/linker-load-so.html
http://blog.csdn.net/qq1084283172/article/details/54095995
http://blog.csdn.net/l173864930/article/details/38456313
二、向Android JNI的JNI_OnLoad添加自定义的代码
在Android的jni编程中,native函数实现的jni映射,既可以根据jni函数的编写协议编写jni函数,让java虚拟机在加载so库文件时,根据函数签名逐一检索,将各个native方法与相应的java本地函数映射起来(增加运行的时间,降低运行的效率)也可以调用jni机制提供的RegisterNatives()函数手动将jni本地方法和java类的本地方法直接映射起来,需要开发者自定义实现JNI_OnLoad()函数;当so库文件被加载时,JNI_OnLoad()函数会被调用,实现jni本地方法和java类的本地方法的直接映射。
根据jni函数的编写协议,实现java本地方法和jni本地方法的映射
使用JNI_OnLoad的执行,调用RegisterNatives()函数实现java本地方法和jni本地方法的映射
三、在so库文件中定义的.init和.init_array段处函数的执行
Android4.4.4r1的源码\bionic\linker\dlfcn.cpp:
// dlopen函数调用do_dlopen函数实现so库文件的加载
void* dlopen(const char* filename, int flags) {
// 信号互斥量(锁)
ScopedPthreadMutexLocker locker(&gDlMutex);
// 调用do_dlopen()函数实现so库文件的加载
soinfo* result = do_dlopen(filename, flags);
// 判断so库文件是否加载成功
if (result == NULL) {
__bionic_format_dlerror("dlopen failed", linker_get_error_buffer());
return NULL;
}
// 返回加载后so库文件的文件句柄
return result;
}Android4.4.4r1的源码\bionic\linker\linker.cpp:
// 实现对so库文件的加载和执行构造函数
soinfo* do_dlopen(const char* name, int flags) {
// 判断加载so文件的flags是否符合要求
if ((flags & ~(RTLD_NOW|RTLD_LAZY|RTLD_LOCAL|RTLD_GLOBAL)) != 0) {
DL_ERR("invalid flags to dlopen: %x", flags);
return NULL;
}
// 修改内存属性为可读可写
set_soinfo_pool_protection(PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE);
// find_library会判断so是否已经加载,
// 如果没有加载,对so进行加载,完成一些初始化工作
soinfo* si = find_library(name);
// 判断so库问价是否加载成功
if (si != NULL) {
// ++++++ so加载成功,调用构造函数 ++++++++
si->CallConstructors();
// ++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++
}
// 设置内存属性为可读
set_soinfo_pool_protection(PROT_READ);
// 返回so内存模块
return si;
}当上面的构造函数 si->CallConstructors() 被调用时,preinit_array-> .init -> .init_array段的函数,会依次按照顺序进行执行并且.init_array段的函数指针数组的执行的实现其实和.init段的函数的执行的实现是一样的。
这里的DT_INIT和DT_INIT_ARRAY到底是什么呢?
init_func和init_array都是结构体soinfo的成员变量,在soinfo_link_image加载so的时候进行赋值。
#define DT_INIT 12 /* Address of initialization function */
#define DT_INIT_ARRAY 25 /* Address of initialization function array */
case DT_INIT:
si->init_func = reinterpret_cast<linker_function_t>(base + d->d_un.d_ptr);
DEBUG(“%s constructors (DT_INIT) found at %p”, si->name, si->init_func);
break;
case DT_INIT_ARRAY:
si->init_array = reinterpret_cast<linker_function_t*>(base + d->d_un.d_ptr);
DEBUG(“%s constructors (DT_INIT_ARRAY) found at %p”, si->name, si->init_array);
break;先调用.init段的构造函数再调用.init_array段的构造函数
// so库文件加载完毕以后调用构造函数
void soinfo::CallConstructors() {
if (constructors_called) {
return;
}
// We set constructors_called before actually calling the constructors, otherwise it doesn't
// protect against recursive constructor calls. One simple example of constructor recursion
// is the libc debug malloc, which is implemented in libc_malloc_debug_leak.so:
// 1. The program depends on libc, so libc's constructor is called here.
// 2. The libc constructor calls dlopen() to load libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.
// 3. dlopen() calls the constructors on the newly created
// soinfo for libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.
// 4. The debug .so depends on libc, so CallConstructors is
// called again with the libc soinfo. If it doesn't trigger the early-
// out above, the libc constructor will be called again (recursively!).
constructors_called = true;
if ((flags & FLAG_EXE) == 0 && preinit_array != NULL) {
// The GNU dynamic linker silently ignores these, but we warn the developer.
PRINT("\"%s\": ignoring %d-entry DT_PREINIT_ARRAY in shared library!",
name, preinit_array_count);
}
// 调用DT_NEEDED类型段的构造函数
if (dynamic != NULL) {
for (Elf32_Dyn* d = dynamic; d->d_tag != DT_NULL; ++d) {
if (d->d_tag == DT_NEEDED) {
const char* library_name = strtab + d->d_un.d_val;
TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors in DT_NEEDED \"%s\"", name, library_name);
find_loaded_library(library_name)->CallConstructors();
}
}
}
TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors", name);
// DT_INIT should be called before DT_INIT_ARRAY if both are present.
// 先调用.init段的构造函数
CallFunction("DT_INIT", init_func);
// 再调用.init_array段的构造函数
CallArray("DT_INIT_ARRAY", init_array, init_array_count, false);
}.init段构造函数的调用实现
// 构造函数调用的实现
void soinfo::CallFunction(const char* function_name UNUSED, linker_function_t function) {
// 判断构造函数的调用地址是否符合要求
if (function == NULL || reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(function) == static_cast<uintptr_t>(-1)) {
return;
}
// function_name被调用的函数名称,function为函数的调用地址
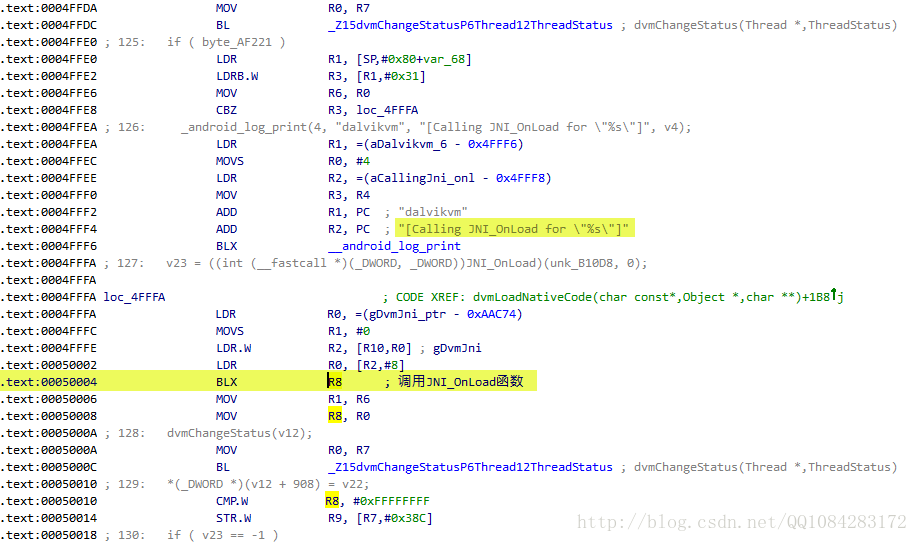
// [ Calling %s @ %p for '%s' ] 字符串为在 /system/bin/linker 中查找.init和.init_array段调用函数的关键
TRACE("[ Calling %s @ %p for '%s' ]", function_name, function, name);
// 调用function函数
function();
TRACE("[ Done calling %s @ %p for '%s' ]", function_name, function, name);
// The function may have called dlopen(3) or dlclose(3), so we need to ensure our data structures
// are still writable. This happens with our debug malloc (see http://b/7941716).
set_soinfo_pool_protection(PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE);
}.init_arrayt段构造函数的调用实现
void soinfo::CallArray(const char* array_name UNUSED, linker_function_t* functions, size_t count, bool reverse) {
if (functions == NULL) {
return;
}
TRACE("[ Calling %s (size %d) @ %p for '%s' ]", array_name, count, functions, name);
int begin = reverse ? (count - 1) : 0;
int end = reverse ? -1 : count;
int step = reverse ? -1 : 1;
// 循环遍历调用.init_arrayt段中每个函数
for (int i = begin; i != end; i += step) {
TRACE("[ %s[%d] == %p ]", array_name, i, functions[i]);
// .init_arrayt段中,每个函数指针的调用和上面的.init段的构造函数的实现是一样的
CallFunction("function", functions[i]);
}
TRACE("[ Done calling %s for '%s' ]", array_name, name);
}从.init段和.init_arrayt段构造函数的调用实现来看,最终都是调用的 void soinfo::CallFunction(const char* function_name UNUSED, linker_function_t function) 函数,因此IDA动态调试so时,只要守住CallFunction函数就可以实现对.init段和.init_arrayt段构造函数调用的监控。
四、Android jni中JNI_OnLoad函数的执行
Android4.4.4r1的源码/libcore/luni/src/main/java/java/lang/System.java
/**
* Loads and links the library with the specified name. The mapping of the
* specified library name to the full path for loading the library is
* implementation-dependent.
*
* @param libName
* the name of the library to load.
* @throws UnsatisfiedLinkError
* if the library could not be loaded.
*/
// System.loadLibrary函数加载libxxx.so库文件
public static void loadLibrary(String libName) {
// 调用Runtime.loadLibrary函数实现libxxx.so库文件的加载
Runtime.getRuntime().loadLibrary(libName, VMStack.getCallingClassLoader());
}Android4.4.4r1的源码/libcore/luni/src/main/java/java/lang/Runtime.java
/**
* Loads and links the library with the specified name. The mapping of the
* specified library name to the full path for loading the library is
* implementation-dependent.
*
* @param libName
* the name of the library to load.
* @throws UnsatisfiedLinkError
* if the library can not be loaded.
*/
public void loadLibrary(String libName) {
loadLibrary(libName, VMStack.getCallingClassLoader());
}
/*
* Searches for a library, then loads and links it without security checks.
*/
void loadLibrary(String libraryName, ClassLoader loader) {
if (loader != null) {
String filename = loader.findLibrary(libraryName);
if (filename == null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Couldn't load " + libraryName +
" from loader " + loader +
": findLibrary returned null");
}
String error = doLoad(filename, loader);
if (error != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(error);
}
return;
}
String filename = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
List<String> candidates = new ArrayList<String>();
String lastError = null;
for (String directory : mLibPaths) {
String candidate = directory + filename;
candidates.add(candidate);
if (IoUtils.canOpenReadOnly(candidate)) {
// 调用doLoad函数加载so库文件
String error = doLoad(candidate, loader);
if (error == null) {
return; // We successfully loaded the library. Job done.
}
lastError = error;
}
}
if (lastError != null) {
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(lastError);
}
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError("Library " + libraryName + " not found; tried " + candidates);
}看下String doLoad(String name, ClassLoader loader)函数的实现,doLoad函数调用native层实现的nativeLoad函数进行so库文件的加载
private String doLoad(String name, ClassLoader loader) {
// Android apps are forked from the zygote, so they can't have a custom LD_LIBRARY_PATH,
// which means that by default an app's shared library directory isn't on LD_LIBRARY_PATH.
// The PathClassLoader set up by frameworks/base knows the appropriate path, so we can load
// libraries with no dependencies just fine, but an app that has multiple libraries that
// depend on each other needed to load them in most-dependent-first order.
// We added API to Android's dynamic linker so we can update the library path used for
// the currently-running process. We pull the desired path out of the ClassLoader here
// and pass it to nativeLoad so that it can call the private dynamic linker API.
// We didn't just change frameworks/base to update the LD_LIBRARY_PATH once at the
// beginning because multiple apks can run in the same process and third party code can
// use its own BaseDexClassLoader.
// We didn't just add a dlopen_with_custom_LD_LIBRARY_PATH call because we wanted any
// dlopen(3) calls made from a .so's JNI_OnLoad to work too.
// So, find out what the native library search path is for the ClassLoader in question...
String ldLibraryPath = null;
if (loader != null && loader instanceof BaseDexClassLoader) {
// so库文件的文件路径
ldLibraryPath = ((BaseDexClassLoader) loader).getLdLibraryPath();
}
// nativeLoad should be synchronized so there's only one LD_LIBRARY_PATH in use regardless
// of how many ClassLoaders are in the system, but dalvik doesn't support synchronized
// internal natives.
synchronized (this) {
// 调用native方法nativeLoad加载so库文件
return nativeLoad(name, loader, ldLibraryPath);
}
}
// TODO: should be synchronized, but dalvik doesn't support synchronized internal natives.
// 函数nativeLoad为native方法实现的
private static native String nativeLoad(String filename, ClassLoader loader, String ldLibraryPath);nativeLoad函数在Android4.4.4r1源码/dalvik/vm/native/java_lang_Runtime.cpp中的实现
/*
* static String nativeLoad(String filename, ClassLoader loader, String ldLibraryPath)
*
* Load the specified full path as a dynamic library filled with
* JNI-compatible methods. Returns null on success, or a failure
* message on failure.
*/
/*
* 参数args[0]保存的是一个Java层的String对象,这个String对象描述的就是要加载的so文件,
* 函数Dalvik_java_lang_Runtime_nativeLoad首先是调用函数dvmCreateCstrFromString来将它转换成一个C++层的字符串fileName,
* 然后再调用函数dvmLoadNativeCode来执行加载so文件的操作。
*/
static void Dalvik_java_lang_Runtime_nativeLoad(const u4* args,
JValue* pResult)
{
StringObject* fileNameObj = (StringObject*) args[0];
Object* classLoader = (Object*) args[1];
StringObject* ldLibraryPathObj = (StringObject*) args[2];
assert(fileNameObj != NULL);
char* fileName = dvmCreateCstrFromString(fileNameObj);
if (ldLibraryPathObj != NULL) {
char* ldLibraryPath = dvmCreateCstrFromString(ldLibraryPathObj);
void* sym = dlsym(RTLD_DEFAULT, "android_update_LD_LIBRARY_PATH");
if (sym != NULL) {
typedef void (*Fn)(const char*);
Fn android_update_LD_LIBRARY_PATH = reinterpret_cast<Fn>(sym);
(*android_update_LD_LIBRARY_PATH)(ldLibraryPath);
} else {
ALOGE("android_update_LD_LIBRARY_PATH not found; .so dependencies will not work!");
}
free(ldLibraryPath);
}
StringObject* result = NULL;
char* reason = NULL;
// 调用dvmLoadNativeCode函数加载so库文件
bool success = dvmLoadNativeCode(fileName, classLoader, &reason);
if (!success) {
const char* msg = (reason != NULL) ? reason : "unknown failure";
result = dvmCreateStringFromCstr(msg);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) result, NULL);
}
free(reason);
free(fileName);
RETURN_PTR(result);
}nativeLoad函数的本地方法实现Dalvik_java_lang_Runtime_nativeLoad()函数最终调用Android4.4.4r1源码/dalvik/vm/Native.cpp中的dvmLoadNativeCode()函数,在该函数中先调用dlopen函数加载so库文件到内存中,然后调用dlsym函数获取so库文件中JNI_OnLoad函数的导出地址,然后调用JNI_OnLoad函数执行开发者自定义的代码和实现jni函数的注册。
typedef int (*OnLoadFunc)(JavaVM*, void*);
/*
* Load native code from the specified absolute pathname. Per the spec,
* if we've already loaded a library with the specified pathname, we
* return without doing anything.
*
* TODO? for better results we should absolutify the pathname. For fully
* correct results we should stat to get the inode and compare that. The
* existing implementation is fine so long as everybody is using
* System.loadLibrary.
*
* The library will be associated with the specified class loader. The JNI
* spec says we can't load the same library into more than one class loader.
*
* Returns "true" on success. On failure, sets *detail to a
* human-readable description of the error or NULL if no detail is
* available; ownership of the string is transferred to the caller.
*/
bool dvmLoadNativeCode(const char* pathName, Object* classLoader,
char** detail)
{
SharedLib* pEntry;
void* handle;
bool verbose;
/* reduce noise by not chattering about system libraries */
verbose = !!strncmp(pathName, "/system", sizeof("/system")-1);
verbose = verbose && !!strncmp(pathName, "/vendor", sizeof("/vendor")-1);
if (verbose)
ALOGD("Trying to load lib %s %p", pathName, classLoader);
*detail = NULL;
/*
* See if we've already loaded it. If we have, and the class loader
* matches, return successfully without doing anything.
*/
pEntry = findSharedLibEntry(pathName);
if (pEntry != NULL) {
if (pEntry->classLoader != classLoader) {
ALOGW("Shared lib '%s' already opened by CL %p; can't open in %p",
pathName, pEntry->classLoader, classLoader);
return false;
}
if (verbose) {
ALOGD("Shared lib '%s' already loaded in same CL %p",
pathName, classLoader);
}
if (!checkOnLoadResult(pEntry))
return false;
return true;
}
/*
* Open the shared library. Because we're using a full path, the system
* doesn't have to search through LD_LIBRARY_PATH. (It may do so to
* resolve this library's dependencies though.)
*
* Failures here are expected when java.library.path has several entries
* and we have to hunt for the lib.
*
* The current version of the dynamic linker prints detailed information
* about dlopen() failures. Some things to check if the message is
* cryptic:
* - make sure the library exists on the device
* - verify that the right path is being opened (the debug log message
* above can help with that)
* - check to see if the library is valid (e.g. not zero bytes long)
* - check config/prelink-linux-arm.map to ensure that the library
* is listed and is not being overrun by the previous entry (if
* loading suddenly stops working on a prelinked library, this is
* a good one to check)
* - write a trivial app that calls sleep() then dlopen(), attach
* to it with "strace -p <pid>" while it sleeps, and watch for
* attempts to open nonexistent dependent shared libs
*
* This can execute slowly for a large library on a busy system, so we
* want to switch from RUNNING to VMWAIT while it executes. This allows
* the GC to ignore us.
*/
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
ThreadStatus oldStatus = dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_VMWAIT);
// 先调用dlopen函数加载so库文件到内存中
handle = dlopen(pathName, RTLD_LAZY);
dvmChangeStatus(self, oldStatus);
if (handle == NULL) {
*detail = strdup(dlerror());
ALOGE("dlopen(\"%s\") failed: %s", pathName, *detail);
return false;
}
/* create a new entry */
SharedLib* pNewEntry;
pNewEntry = (SharedLib*) calloc(1, sizeof(SharedLib));
pNewEntry->pathName = strdup(pathName);
pNewEntry->handle = handle;
pNewEntry->classLoader = classLoader;
dvmInitMutex(&pNewEntry->onLoadLock);
pthread_cond_init(&pNewEntry->onLoadCond, NULL);
pNewEntry->onLoadThreadId = self->threadId;
/* try to add it to the list */
SharedLib* pActualEntry = addSharedLibEntry(pNewEntry);
if (pNewEntry != pActualEntry) {
ALOGI("WOW: we lost a race to add a shared lib (%s CL=%p)",
pathName, classLoader);
freeSharedLibEntry(pNewEntry);
return checkOnLoadResult(pActualEntry);
} else {
if (verbose)
ALOGD("Added shared lib %s %p", pathName, classLoader);
bool result = false;
void* vonLoad;
int version;
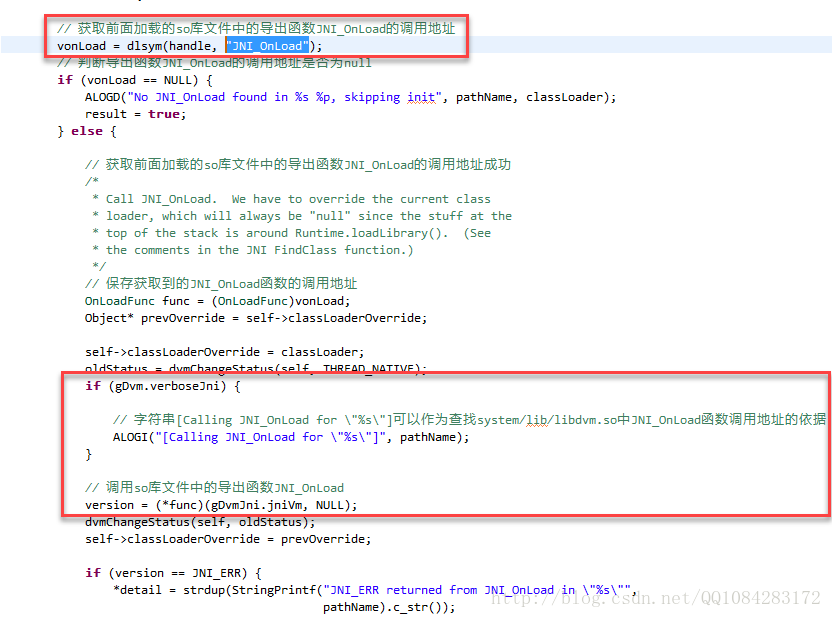
// 获取前面加载的so库文件中的导出函数JNI_OnLoad的调用地址
vonLoad = dlsym(handle, "JNI_OnLoad");
// 判断导出函数JNI_OnLoad的调用地址是否为null
if (vonLoad == NULL) {
ALOGD("No JNI_OnLoad found in %s %p, skipping init", pathName, classLoader);
result = true;
} else {
// 获取前面加载的so库文件中的导出函数JNI_OnLoad的调用地址成功
/*
* Call JNI_OnLoad. We have to override the current class
* loader, which will always be "null" since the stuff at the
* top of the stack is around Runtime.loadLibrary(). (See
* the comments in the JNI FindClass function.)
*/
// 保存获取到的JNI_OnLoad函数的调用地址
OnLoadFunc func = (OnLoadFunc)vonLoad;
Object* prevOverride = self->classLoaderOverride;
self->classLoaderOverride = classLoader;
oldStatus = dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_NATIVE);
if (gDvm.verboseJni) {
// 字符串[Calling JNI_OnLoad for \"%s\"]可以作为查找system/lib/libdvm.so中JNI_OnLoad函数调用地址的依据
ALOGI("[Calling JNI_OnLoad for \"%s\"]", pathName);
}
// 调用so库文件中的导出函数JNI_OnLoad
version = (*func)(gDvmJni.jniVm, NULL);
dvmChangeStatus(self, oldStatus);
self->classLoaderOverride = prevOverride;
if (version == JNI_ERR) {
*detail = strdup(StringPrintf("JNI_ERR returned from JNI_OnLoad in \"%s\"",
pathName).c_str());
} else if (dvmIsBadJniVersion(version)) {
*detail = strdup(StringPrintf("Bad JNI version returned from JNI_OnLoad in \"%s\": %d",
pathName, version).c_str());
/*
* It's unwise to call dlclose() here, but we can mark it
* as bad and ensure that future load attempts will fail.
*
* We don't know how far JNI_OnLoad got, so there could
* be some partially-initialized stuff accessible through
* newly-registered native method calls. We could try to
* unregister them, but that doesn't seem worthwhile.
*/
} else {
result = true;
}
if (gDvm.verboseJni) {
ALOGI("[Returned %s from JNI_OnLoad for \"%s\"]",
(result ? "successfully" : "failure"), pathName);
}
}
if (result)
pNewEntry->onLoadResult = kOnLoadOkay;
else
pNewEntry->onLoadResult = kOnLoadFailed;
pNewEntry->onLoadThreadId = 0;
/*
* Broadcast a wakeup to anybody sleeping on the condition variable.
*/
dvmLockMutex(&pNewEntry->onLoadLock);
pthread_cond_broadcast(&pNewEntry->onLoadCond);
dvmUnlockMutex(&pNewEntry->onLoadLock);
return result;
}
}感谢连接:
http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/8923483
http://blog.csdn.net/myarrow/article/details/9718677
http://www.cnblogs.com/vendanner/p/4979177.html
http://bbs.pediy.com/showthread.php?t=211764
五、在.init和.init_array段的函数上下断点(基于Android4.4.4版本)
方法一:在上面已经分析了.init和.init_array段构造函数的执行,很显然我们想在.init和.init_array段构造函数上下断点也必须根据这些执行的流程来。由于Android系统的/system/bin/linker文件中上面提到的很多so库文件加载过程的函数没有被导出设置为隐藏,在进行so库文件的动态调试后不好通过查找关键流程函数的方法来查找.init和.init_array段构造函数。根据.init和.init_array段构造函数的调用的特点,最终的构造函数的调用都是在CallFunction函数并且在调用.init和.init_array段构造函数之前有明显的特征字符串 [
Calling %s @ %p for '%s' ],因此我们使用IDA工具,通过在/system/bin/linker文件中搜索特征字符串[ Calling %s @ %p for '%s' ] 来查找到 .init和.init_array段构造函数调用的地方。
将手机设备中的/system/bin/linker文件导出来,拖入到IDA中进行分析
adb pull /system/bin/linker通过IDA工具在/system/bin/linker文件中,查找特征字符串 [
Calling %s @ %p for '%s' ]
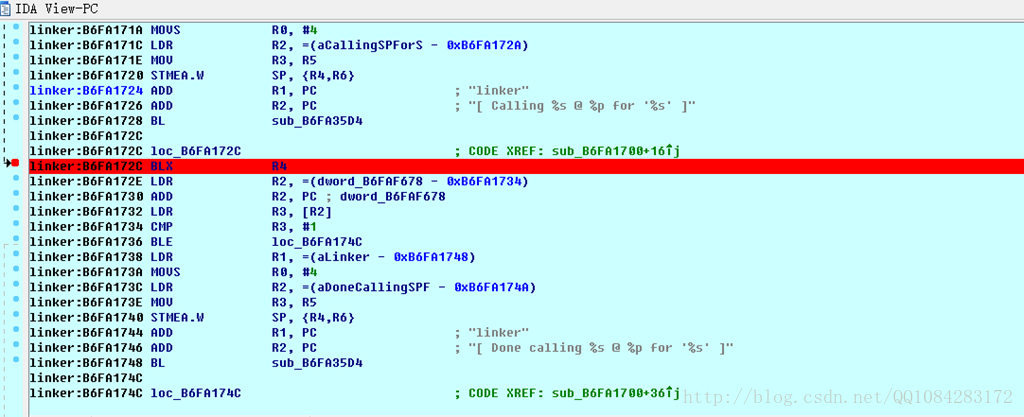
根据字符串 [
Calling %s @ %p for '%s' ] 引用查询到.init和.init_array段构造函数调用的代码调用位置即 0x0000274C BLX R4处,0x0000274C即为.init和.init_array段构造函数调用地址(RVA)。
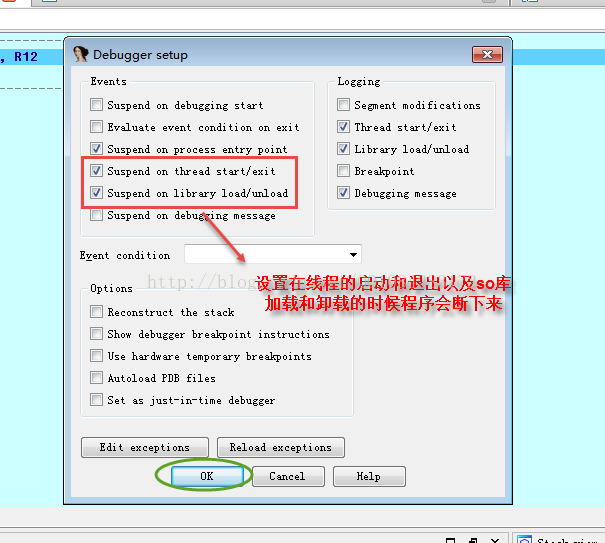
再开一个IDA对该so库文件进行Android应用的附加调试,设置IDA调试时断在so库文件加载的位置,更保险的方法就是
在system/lib/libdvm.so库文件的导出函数dvmLoadNativeCode()处下断点 ,然后通过IDA工具获取/system/bin/linker的模块加载基址linker_base(RA),因此 inker_base+0x0000274C
即为.init和.init_array段构造函数被调用的位置(VA),在此处下断点F7跟进 即可进入.init和.init_array段构造函数的实际调用地址VA处,实现监控.init和.init_array段构造函数的代码行为。
这里就不动态调试操作了,直接网上借一张图片显示效果,下面图即为.init和.init_array段构造函数被调用的位置,
F7 跟进进行分析即可:
方法二:使用作者无名侠 【原创】执行视图
解析init_array 提供的工具,静态的解析so库文件的可执行试图,获取到.init_array段构造函数的调用地址(不是被调用的位置)的相对虚拟地址偏移fun_rva,加上该so模块加载基址so_base即 so_base+fun_rva
即为.init_array段构造函数的直接函数调用地址VA。代码下载地址为:https://github.com/Chenyuxin/elf_initarray.git。
/*
Code By:无名侠
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <elf.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
/***
*
* 需要注意的是Elf32_Dyn中解析出的init_array 地址是RVA,
* 有些时候段装载地址可能和文件偏移不同(也就是p_vaddr!= p_offset),
* 如果想直接从文件解析该数组需要做转换.转换方法是查表.
*
***/
// 将相对地址偏移RVA转换为elf文件的文件偏移FA
Elf32_Addr VaToFa(int fd,Elf32_Addr rva)
{
/*顾名思义
fd - 打开的so文件句柄
rva - 欲转换的地址
return - rva的文件偏移
*/
int old;
int pnum;
Elf32_Ehdr ehdr;
Elf32_Addr result;
old = lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_CUR);
lseek(fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
read(fd,&ehdr,sizeof(Elf32_Ehdr));
pnum = ehdr.e_phnum;
result = rva;
for(int i = 0; i < pnum; i++)
{
Elf32_Phdr phdr;
read(fd,&phdr, sizeof(Elf32_Phdr));
if(rva >= phdr.p_vaddr && rva < phdr.p_vaddr+phdr.p_memsz)
result = rva-phdr.p_vaddr+phdr.p_offset;
}
lseek(fd,old,SEEK_SET);
return result;
}
// elf可执行程序的主函数
int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) {
int fp;
Elf32_Ehdr ehdr;
int phnum;
// 对输入的函数参数的个数进行校验
if(argc!=2)
{
printf("Please input elf file!\n");
return -1;
}
// 打开静态的so文件
fp = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if(!fp)
{
printf("error:can't open %s \n",argv[1] );
return -1;
}
// 读取elf32文件的文件头
read(fp, &ehdr,sizeof(Elf32_Ehdr));
// 对文件的格式进行简单的判断
if(memcmp(ehdr.e_ident, ELFMAG, SELFMAG))
{
printf("bad magic.\n");
close(fp);
return -1;
}
// 获取elf文件中程序头表的个数
phnum = ehdr.e_phnum;
// 遍历程序头表
for(int i = 0; i < phnum; i++)
{
Elf32_Phdr phdr;
// elf文件的文件头的后面就是elf文件的程序头表
// 读取elf文件的程序头表
read(fp, &phdr,sizeof(Elf32_Phdr));
// 对程序头表保存的数据的类型是否为.dynamic段
if(phdr.p_type==PT_DYNAMIC)
{
Elf32_Dyn dyn;
Elf32_Addr initaddr;
Elf32_Word initsize;
// 该程序段为PT_DYNAMIC类型的.dynamic段
int cnt = 0;
// 打印该程序段在elf文件中文件偏移RVA
printf("offset : %x\n",phdr.p_offset);
// 设置文件的偏移,定位到该程序的文件内容处
lseek(fp,phdr.p_offset, SEEK_SET);
// 该程序段的实际数据为多个Elf32_Dyn结构体
// 遍历该程序段的Elf32_Dyn结构体查找到.init_array段
do {
// 读取Elf32_Dyn结构体的数据
read(fp,&dyn,sizeof(Elf32_Dyn));
// 判断Elf32_Dyn结构体保存的数据是否为.init_array段的
if(dyn.d_tag == DT_INIT_ARRAY)
// 获取.init段的初始化函数跳转表起始相对地址
initaddr = dyn.d_un.d_ptr;
else if(dyn.d_tag == DT_INIT_ARRAYSZ)
{
// 获取DT_INIT_ARRAY的大小(占用字节数)
initsize = dyn.d_un.d_val;
break;
}
} while(dyn.d_tag != DT_NULL);
// 获取.init_array段有效初始函数调用地址的个数
initsize/=4;
initsize-=1;
// 打印.init_array段初始化函数的起始相对地址RVA和初始化函数的个数
printf("INIT ARRAY OFFSET:%x(RVA)\nINTI NUM:%d\ninit table:\n", initaddr, initsize);
// 将.init_array段初始化函数的起始相对地址RVA转换为文件偏移的FA
initaddr = VaToFa(fp, initaddr);
// 定位到elf文件的保存.init_array段初始化函数位置
lseek(fp, initaddr, SEEK_SET);
// 遍历读取.init_array段初始化函数的相对调用地址RVA
for(int i = 0;i < initsize;i++)
{
Elf32_Addr fun;
// 读取.init_array段的初始函数的相对调用地址
read(fp, &fun, 4);
// 打印读取到的.init_array段的初始函数的相对调用地址
printf("fun %d :%x\n", i, fun);
}
}
}
return 0;
}作者无名侠的代码使用方法以及测试:
pandaos@pandaos:~/elf1$ gcc main.cpp -o elf1
pandaos@pandaos:~/elf1$ ./elf1 libdanmu.so
offset : 1399f0
INIT ARRAY OFFSET:13a9c0(RVA)
INTI NUM:11
init table:
fun 0 :9eb9
fun 1 :9fa9
fun 2 :a099
fun 3 :a1bd
fun 4 :a2e1
fun 5 :a815
fun 6 :a895
fun 7 :a8d1
fun 8 :a8e1
fun 9 :a9bd
fun 10 :aa99
pandaos@pandaos:~/elf1$ 自己动手的测试的结果:
.init_array段构造函数的调用地址的RVA获取到了,只要通过 方法一 中的IDA调试so库的方法获取到该.init_array段所在so文件的内存加载基址 so_base ,因此 so_base+.init_array段构造函数的调用地址的RVA
即为.init_array段构造函数的调用地址的VA也就是.init_array段构造函数的动态实际调用地址,我们只要在这个地址处下断点即可。
感谢连接:
http://bbs.pediy.com/showthread.php?t=212374
https://github.com/Chenyuxin/elf_initarray.git
六、在so库文件的JNI_OnLoad上下断点(基于Android4.4.4版本的Dalvik模式)
方法一:由于JNI_OnLoad函数在被调用时是在函数dvmLoadNativeCode()中,并且JNI_OnLoad函数在被调用时也有特征字符串,如 [Calling
JNI_OnLoad for \"%s\"] 和 "JNI_OnLoad" 等根据自己的喜欢选一个就行。因此,我们可以将手机设备中的system/lib/libdvm.so文件导出来,拖到IDA中进行分析,然后使用特征字符串搜索的方法进行定位。
adb pull system/lib/libdvm.so详细的步骤可以参考作者【原创】JNI_OnLoad与init_array下断方法整理 的帖子
方法二:前面的作者可能是已经被特征字符串搜索的方法思维定式了,其实在JNI_OnLoad上下断点很容易的,不需要这么麻烦。
adb
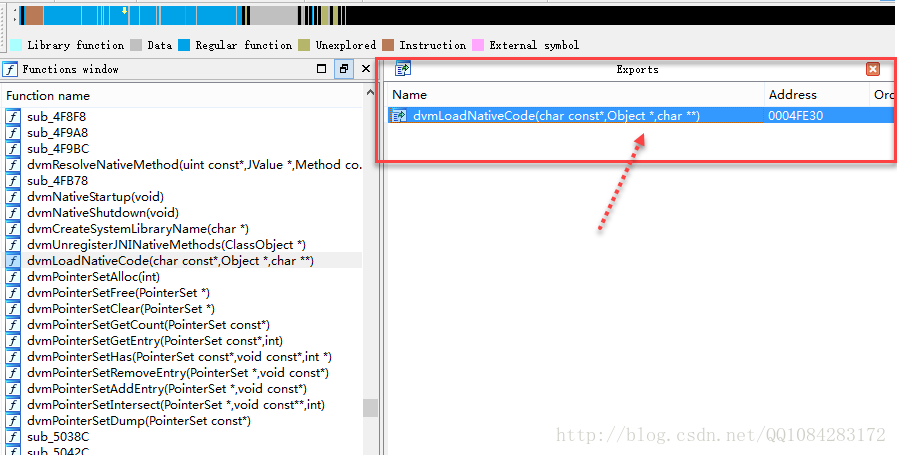
pull system/lib/libdvm.so将Android手机设备的libdvm.so文件导出来,拖到IDA中进行分析,可以发现libdvm.so库文件中 dvmLoadNativeCode() 是导出的,意味着我们在使用IDA动态调试so库文件时,可以在函数dvmLoadNativeCode()上下断点,很高兴的是JNI_OnLoad函数的调用就是在函数dvmLoadNativeCode()中,因此通过 _Z17dvmLoadNativeCodePKcP6ObjectPPc
即dvmLoadNativeCode()函数就可以定位到JNI_OnLoad函数的调用的位置。
通过 _Z17dvmLoadNativeCodePKcP6ObjectPPc
即dvmLoadNativeCode()函数就可以定位到JNI_OnLoad函数的调用的位置(这里是静态的查找示意图,动态查找的方法一样,等目标App应用的so库文件加载了,然后在动态加载的system/lib/libdvm.so中查找 _Z17dvmLoadNativeCodePKcP6ObjectPPc
函数,然后在函数_Z17dvmLoadNativeCodePKcP6ObjectPPc中查找到JNI_OnLoad函数的调用位置[ BLX R8 ]),F7 跟进JNI_OnLoad函数的实现即可分析JNI_OnLoad函数的代码行为。
这里给出的实例是Dalvik模式下的,Art模式下在JNI_OnLoad函数上下断点方法一样。
七、在Android
so文件的.init、.init_array上和JNI_OnLoad处下断点的方法总结
由用于调试的Android设备的Androd系统的版本,找到该Android系统版本对应的Android源码,查看和弄明白.init、.init_array和JNI_OnLoad的执行流程和原理,找到能用于搜索的有效特征字符串,导出用于调试的Android设备的Androd系统的/system/bin/linker文件、system/lib/libdvm.so或system/lib/libartso文件,使用IDA工具进行分析,通过前面的特征字符串搜索找到.init、.init_array和JNI_OnLoad被调用位置的RVA,然后IDA调试so获取相应的system/lib/libdvm.so或system/lib/libartso文件的动态内存加载基址linker_base、libdvm_base或者libartso_base,因此IDA动态调试时.init、.init_array被调用的位置VA为 linker_base+RVA;JNI_OnLoad被调用的位置的VA为 libdvm_base或者libartso_base
+ RVA,我们在动态调试分析的时候,只要在这两个关键点处下断点即可。
感谢连接:
http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/8923483
http://blog.csdn.net/myarrow/article/details/9718677
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-1835494-id-2831799.html
http://bbs.pediy.com/showthread.php?t=211764
http://bbs.pediy.com/showthread.php?t=212374
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-elf/part1/
http://bbs.pediy.com/showthread.php?p=1365423
http://www.blogfshare.com/linker-load-so.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/vendanner/p/4979177.html
https://github.com/Chenyuxin/elf_initarray
在Android so文件的.init、.init_array上和JNI_OnLoad处下断点的更多相关文章
- ida动态调试so,在init_array和JNI_ONLOAD处下断点
本文涉及到的apk.请在github下载https://github.com/jltxgcy/AliCrack/AliCrackme_2.apk. 0x00 怎样在JNI_ONLOAD下断点.參考安卓 ...
- IDA调试android so文件.init_array和JNI_OnLoad
我们知道so文件在被加载的时候会首先执行.init_array中的函数,然后再执行JNI_OnLoad()函数.JNI_Onload()函数因为有符号表所以非常容易找到,但是.init_array里的 ...
- Android C语言_init函数和constructor属性及.init/.init_array节探索
本篇文章主要介绍了"Android C语言_init函数和constructor属性及.init/.init_array节探索",主要涉及到Android C语言_init函数和c ...
- Android 用adb pull或push 拷贝手机文件到到电脑上,拷贝手机数据库到电脑上,拷贝电脑数据库到手机上
先说一下adb命令配置,如果遇到adb不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序或批量文件.配置下环境变量 1.adb不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序或批量文件. 解决办法:在我的电脑-属性-高级计 ...
- 使用.NET框架、Web service实现Android的文件上传(二)
aaarticlea/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAYUAAAKpCAIAAADcx6fPAAAgAElEQVR4nOydd1hT5+LHg1attbfr1t ...
- Android和FTP服务器交互,上传下载文件(实例demo)
今天同学说他备份了联系人的数据放在一个文件里,想把它存到服务器上,以便之后可以进行下载恢复..于是帮他写了个上传,下载文件的demo 主要是 跟FTP服务器打交道-因为这个东东有免费的可以身亲哈 1. ...
- 分析cocos2d-x在Android上的编译过程(1):cocco2d-x是怎样生成的Android的文件夹结构
当新建完一个cocos2d-x的项目后.进入到项目中的proj.android中,会看到例如以下的文件夹结构 在VS先把它编译,然后导入到Eclipse中,导入完后会看到多了几个文件 watermar ...
- Android OkHttp文件上传与下载的进度监听扩展
http://www.loongwind.com/archives/290.html 上一篇文章介绍了用Retrofit实现文件的上传与下载,但是我们发现没办法监听上传下载的进度,毕竟我们在做开发的时 ...
- android中的文件(图片)上传
android中的文件(图片)上传其实没什么复杂的,主要是对 multipart/form-data 协议要有所了解. 关于 multipart/form-data 协议,在 RFC文档中有详细的描述 ...
随机推荐
- Docker系列——InfluxDB+Grafana+Jmeter性能监控平台搭建(一)
在做性能测试的时候,重点关注点是各项性能指标,用Jmeter工具,查看指标数据,就是借助于聚合报告,但查看时也并不方便.那如何能更直观的查看各项数据呢?可以通过InfluxDB+Grafana+Jme ...
- Hi3559AV100 NNIE开发(2)-RFCN(.wk)LoadModel及NNIE Init函数运行过程分析
之后随笔将更多笔墨着重于NNIE开发系列,下文是关于Hi3559AV100 NNIE开发(2)-RFCN(.wk)LoadModel及NNIE Init函数运行过程分析,通过对LoadModel函数及 ...
- C# 读取Word文本框中的文本、图片和表格(附VB.NET代码)
[概述] Word中可插入文本框,在文本框中可添加文本.图片.表格等内容.本篇文章通过C#程序代码介绍如何来读取文本框中的文本.图片和表格等内容.附VB.NET代码,有需要可作参考. [程序环境] 程 ...
- Nebula Storage 2.0 存储格式
随着 2.0 各版本的陆续发布,Nebula Graph 迎来了一系列的改动,在存储方面,影响最大的改动就是底层编码格式进行了修改.Nebula Graph 的底层存储是基于 KV 保存在 Rocks ...
- 社区 正式发布了 CoreWCF 0.1.0 GA
CoreWCF 项目在2021.2.19 正式发布了0.1.0 GA版本:https://github.com/CoreWCF/CoreWCF/releases/tag/v0.1.0 ,这个版本号虽然 ...
- github个人主页 阿里云域名的绑定
域名解析 我在阿里云上买了一个新域名:gaolu.name,我已经在GitHub Pages上建立了自己的博客:http://gaolu1215.github.io.现在我希望将gaolu.name映 ...
- python列表,元组,字典,集合的比较总结
这四个都是python中的序列,用于存放数据,他们区别总结如下: 列表list 元组tuple 字典dictionary 集合set 是否可变 可变 不可变 可变 可变 是否有序 有序 有序 无序 ...
- 当红开发语言Go,真的是未来的技术主流吗?
摘要:文将详细介绍 Golang 的语言特点以及它的优缺点和适用场景,带着上述几个疑问,为读者分析 Go 语言的各个方面,以帮助初入 IT 行业的程序员以及对 Go 感兴趣的开发者进一步了解这个热门语 ...
- Kubernetes,kubectl常用命令详解
kubectl概述 祭出一张图,转载至 kubernetes-handbook/kubectl命令概述 ,可以对命令族有个整体的概念. 环境准备 允许master节点部署pod,使用命令如下: kub ...
- Python-Tkinter 使用for循环生成列表式Button及函数调用
Tkinter是轻量级的图形化界面,在使用中我们可能遇到需要生成一串Button按钮的情况,如图: 如果一个一个操作就太麻烦了,但我们可以通过for循环列表的形式来实现 来看看以下例子: from t ...