视音频数据处理入门:FLV封装格式解析
=====================================================
视音频数据处理入门系列文章:
=====================================================
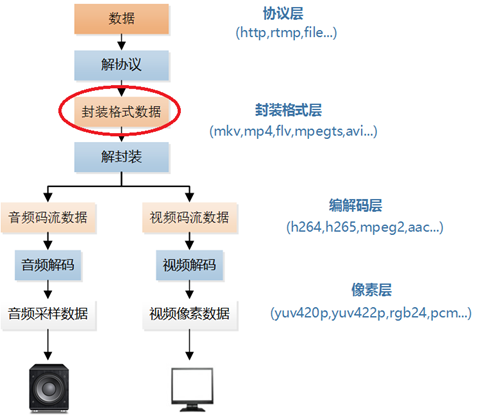
前两篇文章介绍了音频码流处理程序和视频码流处理程序,本文介绍将他们打包到一起后的数据——封装格式数据的处理程序。封装格式数据在视频播放器中的位置如下所示。
本文中的程序是一个FLV封装格式解析程序。该程序可以从FLV中分析得到它的基本单元Tag,并且可以简单解析Tag首部的字段。通过修改该程序可以实现不同的FLV格式数据处理功能。
原理
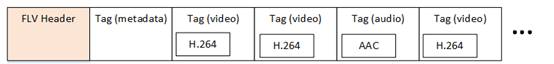
FLV封装格式是由一个FLV Header文件头和一个一个的Tag组成的。Tag中包含了音频数据以及视频数据。FLV的结构如下图所示。
有关FLV的格式本文不再做记录。可以参考文章《视音频编解码学习工程:FLV封装格式分析器》。本文的程序实现了FLV中的FLV Header和Tag的解析,并可以分离出其中的音频流。
代码
整个程序位于simplest_flv_parser()函数中,如下所示。
- /**
- * 最简单的视音频数据处理示例
- * Simplest MediaData Test
- *
- * 雷霄骅 Lei Xiaohua
- * leixiaohua1020@126.com
- * 中国传媒大学/数字电视技术
- * Communication University of China / Digital TV Technology
- * http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
- *
- * 本项目包含如下几种视音频测试示例:
- * (1)像素数据处理程序。包含RGB和YUV像素格式处理的函数。
- * (2)音频采样数据处理程序。包含PCM音频采样格式处理的函数。
- * (3)H.264码流分析程序。可以分离并解析NALU。
- * (4)AAC码流分析程序。可以分离并解析ADTS帧。
- * (5)FLV封装格式分析程序。可以将FLV中的MP3音频码流分离出来。
- * (6)UDP-RTP协议分析程序。可以将分析UDP/RTP/MPEG-TS数据包。
- *
- * This project contains following samples to handling multimedia data:
- * (1) Video pixel data handling program. It contains several examples to handle RGB and YUV data.
- * (2) Audio sample data handling program. It contains several examples to handle PCM data.
- * (3) H.264 stream analysis program. It can parse H.264 bitstream and analysis NALU of stream.
- * (4) AAC stream analysis program. It can parse AAC bitstream and analysis ADTS frame of stream.
- * (5) FLV format analysis program. It can analysis FLV file and extract MP3 audio stream.
- * (6) UDP-RTP protocol analysis program. It can analysis UDP/RTP/MPEG-TS Packet.
- *
- */
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <string.h>
- //Important!
- #pragma pack(1)
- #define TAG_TYPE_SCRIPT 18
- #define TAG_TYPE_AUDIO 8
- #define TAG_TYPE_VIDEO 9
- typedef unsigned char byte;
- typedef unsigned int uint;
- typedef struct {
- byte Signature[3];
- byte Version;
- byte Flags;
- uint DataOffset;
- } FLV_HEADER;
- typedef struct {
- byte TagType;
- byte DataSize[3];
- byte Timestamp[3];
- uint Reserved;
- } TAG_HEADER;
- //reverse_bytes - turn a BigEndian byte array into a LittleEndian integer
- uint reverse_bytes(byte *p, char c) {
- int r = 0;
- int i;
- for (i=0; i<c; i++)
- r |= ( *(p+i) << (((c-1)*8)-8*i));
- return r;
- }
- /**
- * Analysis FLV file
- * @param url Location of input FLV file.
- */
- int simplest_flv_parser(char *url){
- //whether output audio/video stream
- int output_a=1;
- int output_v=1;
- //-------------
- FILE *ifh=NULL,*vfh=NULL, *afh = NULL;
- //FILE *myout=fopen("output_log.txt","wb+");
- FILE *myout=stdout;
- FLV_HEADER flv;
- TAG_HEADER tagheader;
- uint previoustagsize, previoustagsize_z=0;
- uint ts=0, ts_new=0;
- ifh = fopen(url, "rb+");
- if ( ifh== NULL) {
- printf("Failed to open files!");
- return -1;
- }
- //FLV file header
- fread((char *)&flv,1,sizeof(FLV_HEADER),ifh);
- fprintf(myout,"============== FLV Header ==============\n");
- fprintf(myout,"Signature: 0x %c %c %c\n",flv.Signature[0],flv.Signature[1],flv.Signature[2]);
- fprintf(myout,"Version: 0x %X\n",flv.Version);
- fprintf(myout,"Flags : 0x %X\n",flv.Flags);
- fprintf(myout,"HeaderSize: 0x %X\n",reverse_bytes((byte *)&flv.DataOffset, sizeof(flv.DataOffset)));
- fprintf(myout,"========================================\n");
- //move the file pointer to the end of the header
- fseek(ifh, reverse_bytes((byte *)&flv.DataOffset, sizeof(flv.DataOffset)), SEEK_SET);
- //process each tag
- do {
- previoustagsize = _getw(ifh);
- fread((void *)&tagheader,sizeof(TAG_HEADER),1,ifh);
- //int temp_datasize1=reverse_bytes((byte *)&tagheader.DataSize, sizeof(tagheader.DataSize));
- int tagheader_datasize=tagheader.DataSize[0]*65536+tagheader.DataSize[1]*256+tagheader.DataSize[2];
- int tagheader_timestamp=tagheader.Timestamp[0]*65536+tagheader.Timestamp[1]*256+tagheader.Timestamp[2];
- char tagtype_str[10];
- switch(tagheader.TagType){
- case TAG_TYPE_AUDIO:sprintf(tagtype_str,"AUDIO");break;
- case TAG_TYPE_VIDEO:sprintf(tagtype_str,"VIDEO");break;
- case TAG_TYPE_SCRIPT:sprintf(tagtype_str,"SCRIPT");break;
- default:sprintf(tagtype_str,"UNKNOWN");break;
- }
- fprintf(myout,"[%6s] %6d %6d |",tagtype_str,tagheader_datasize,tagheader_timestamp);
- //if we are not past the end of file, process the tag
- if (feof(ifh)) {
- break;
- }
- //process tag by type
- switch (tagheader.TagType) {
- case TAG_TYPE_AUDIO:{
- char audiotag_str[100]={0};
- strcat(audiotag_str,"| ");
- char tagdata_first_byte;
- tagdata_first_byte=fgetc(ifh);
- int x=tagdata_first_byte&0xF0;
- x=x>>4;
- switch (x)
- {
- case 0:strcat(audiotag_str,"Linear PCM, platform endian");break;
- case 1:strcat(audiotag_str,"ADPCM");break;
- case 2:strcat(audiotag_str,"MP3");break;
- case 3:strcat(audiotag_str,"Linear PCM, little endian");break;
- case 4:strcat(audiotag_str,"Nellymoser 16-kHz mono");break;
- case 5:strcat(audiotag_str,"Nellymoser 8-kHz mono");break;
- case 6:strcat(audiotag_str,"Nellymoser");break;
- case 7:strcat(audiotag_str,"G.711 A-law logarithmic PCM");break;
- case 8:strcat(audiotag_str,"G.711 mu-law logarithmic PCM");break;
- case 9:strcat(audiotag_str,"reserved");break;
- case 10:strcat(audiotag_str,"AAC");break;
- case 11:strcat(audiotag_str,"Speex");break;
- case 14:strcat(audiotag_str,"MP3 8-Khz");break;
- case 15:strcat(audiotag_str,"Device-specific sound");break;
- default:strcat(audiotag_str,"UNKNOWN");break;
- }
- strcat(audiotag_str,"| ");
- x=tagdata_first_byte&0x0C;
- x=x>>2;
- switch (x)
- {
- case 0:strcat(audiotag_str,"5.5-kHz");break;
- case 1:strcat(audiotag_str,"1-kHz");break;
- case 2:strcat(audiotag_str,"22-kHz");break;
- case 3:strcat(audiotag_str,"44-kHz");break;
- default:strcat(audiotag_str,"UNKNOWN");break;
- }
- strcat(audiotag_str,"| ");
- x=tagdata_first_byte&0x02;
- x=x>>1;
- switch (x)
- {
- case 0:strcat(audiotag_str,"8Bit");break;
- case 1:strcat(audiotag_str,"16Bit");break;
- default:strcat(audiotag_str,"UNKNOWN");break;
- }
- strcat(audiotag_str,"| ");
- x=tagdata_first_byte&0x01;
- switch (x)
- {
- case 0:strcat(audiotag_str,"Mono");break;
- case 1:strcat(audiotag_str,"Stereo");break;
- default:strcat(audiotag_str,"UNKNOWN");break;
- }
- fprintf(myout,"%s",audiotag_str);
- //if the output file hasn't been opened, open it.
- if(output_a!=0&&afh == NULL){
- afh = fopen("output.mp3", "wb");
- }
- //TagData - First Byte Data
- int data_size=reverse_bytes((byte *)&tagheader.DataSize, sizeof(tagheader.DataSize))-1;
- if(output_a!=0){
- //TagData+1
- for (int i=0; i<data_size; i++)
- fputc(fgetc(ifh),afh);
- }else{
- for (int i=0; i<data_size; i++)
- fgetc(ifh);
- }
- break;
- }
- case TAG_TYPE_VIDEO:{
- char videotag_str[100]={0};
- strcat(videotag_str,"| ");
- char tagdata_first_byte;
- tagdata_first_byte=fgetc(ifh);
- int x=tagdata_first_byte&0xF0;
- x=x>>4;
- switch (x)
- {
- case 1:strcat(videotag_str,"key frame ");break;
- case 2:strcat(videotag_str,"inter frame");break;
- case 3:strcat(videotag_str,"disposable inter frame");break;
- case 4:strcat(videotag_str,"generated keyframe");break;
- case 5:strcat(videotag_str,"video info/command frame");break;
- default:strcat(videotag_str,"UNKNOWN");break;
- }
- strcat(videotag_str,"| ");
- x=tagdata_first_byte&0x0F;
- switch (x)
- {
- case 1:strcat(videotag_str,"JPEG (currently unused)");break;
- case 2:strcat(videotag_str,"Sorenson H.263");break;
- case 3:strcat(videotag_str,"Screen video");break;
- case 4:strcat(videotag_str,"On2 VP6");break;
- case 5:strcat(videotag_str,"On2 VP6 with alpha channel");break;
- case 6:strcat(videotag_str,"Screen video version 2");break;
- case 7:strcat(videotag_str,"AVC");break;
- default:strcat(videotag_str,"UNKNOWN");break;
- }
- fprintf(myout,"%s",videotag_str);
- fseek(ifh, -1, SEEK_CUR);
- //if the output file hasn't been opened, open it.
- if (vfh == NULL&&output_v!=0) {
- //write the flv header (reuse the original file's hdr) and first previoustagsize
- vfh = fopen("output.flv", "wb");
- fwrite((char *)&flv,1, sizeof(flv),vfh);
- fwrite((char *)&previoustagsize_z,1,sizeof(previoustagsize_z),vfh);
- }
- #if 0
- //Change Timestamp
- //Get Timestamp
- ts = reverse_bytes((byte *)&tagheader.Timestamp, sizeof(tagheader.Timestamp));
- ts=ts*2;
- //Writeback Timestamp
- ts_new = reverse_bytes((byte *)&ts, sizeof(ts));
- memcpy(&tagheader.Timestamp, ((char *)&ts_new) + 1, sizeof(tagheader.Timestamp));
- #endif
- //TagData + Previous Tag Size
- int data_size=reverse_bytes((byte *)&tagheader.DataSize, sizeof(tagheader.DataSize))+4;
- if(output_v!=0){
- //TagHeader
- fwrite((char *)&tagheader,1, sizeof(tagheader),vfh);
- //TagData
- for (int i=0; i<data_size; i++)
- fputc(fgetc(ifh),vfh);
- }else{
- for (int i=0; i<data_size; i++)
- fgetc(ifh);
- }
- //rewind 4 bytes, because we need to read the previoustagsize again for the loop's sake
- fseek(ifh, -4, SEEK_CUR);
- break;
- }
- default:
- //skip the data of this tag
- fseek(ifh, reverse_bytes((byte *)&tagheader.DataSize, sizeof(tagheader.DataSize)), SEEK_CUR);
- }
- fprintf(myout,"\n");
- } while (!feof(ifh));
- _fcloseall();
- return 0;
- }
上文中的函数调用方法如下所示。
- simplest_flv_parser("cuc_ieschool.flv");
结果
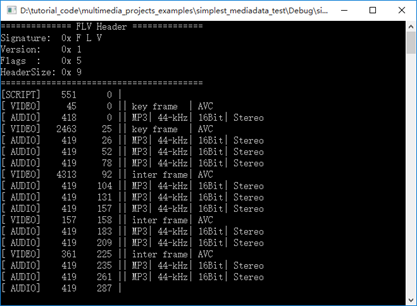
本程序的输入为一个FLV的文件路径,输出为FLV的统计数据,如下图所示。
此外本程序还可以分离FLV中的视频码流和音频码流。需要注意的是本程序并不能分离一些特定类型的音频(例如AAC)和视频,这一工作有待以后有时间再完成。
下载
Simplest mediadata test
项目主页
SourceForge:https://sourceforge.net/projects/simplest-mediadata-test/
Github:https://github.com/leixiaohua1020/simplest_mediadata_test
开源中国:http://git.oschina.net/leixiaohua1020/simplest_mediadata_test
CSDN下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/leixiaohua1020/9422409
本项目包含如下几种视音频数据解析示例:
(1)像素数据处理程序。包含RGB和YUV像素格式处理的函数。
(2)音频采样数据处理程序。包含PCM音频采样格式处理的函数。
(3)H.264码流分析程序。可以分离并解析NALU。
(4)AAC码流分析程序。可以分离并解析ADTS帧。
(5)FLV封装格式分析程序。可以将FLV中的MP3音频码流分离出来。
(6)UDP-RTP协议分析程序。可以将分析UDP/RTP/MPEG-TS数据包。
视音频数据处理入门:FLV封装格式解析的更多相关文章
- 视音频数据处理入门:UDP-RTP协议解析
===================================================== 视音频数据处理入门系列文章: 视音频数据处理入门:RGB.YUV像素数据处理 视音频数据处理 ...
- 视音频数据处理入门:AAC音频码流解析
===================================================== 视音频数据处理入门系列文章: 视音频数据处理入门:RGB.YUV像素数据处理 视音频数据处理 ...
- 视音频数据处理入门:H.264视频码流解析
===================================================== 视音频数据处理入门系列文章: 视音频数据处理入门:RGB.YUV像素数据处理 视音频数据处理 ...
- 视音频数据处理入门:PCM音频采样数据处理
===================================================== 视音频数据处理入门系列文章: 视音频数据处理入门:RGB.YUV像素数据处理 视音频数据处理 ...
- 视音频数据处理入门:RGB、YUV像素数据处理
===================================================== 视音频数据处理入门系列文章: 视音频数据处理入门:RGB.YUV像素数据处理 视音频数据处理 ...
- [转载] 视音频数据处理入门:RGB、YUV像素数据处理
===================================================== 视音频数据处理入门系列文章: 视音频数据处理入门:RGB.YUV像素数据处理 视音频数据处理 ...
- 视音频数据处理入门:RGB、YUV像素数据处理【转】
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020/article/details/50534150 ==================================== ...
- FLV 封装格式解析
本文为作者原创,转载请注明出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/leisure_chn/p/10662941.html FLV (Flash Video) 是由 Adobe 公司推出的 ...
- 视音频编解码学习工程:FLV封装格式分析器
===================================================== 视音频编解码学习工程系列文章列表: 视音频编解码学习工程:H.264分析器 视音频编解码学习 ...
随机推荐
- CMD命令操作符
cmd command的缩写,是windows环境下的虚拟DOS窗口,提供有DOS命令,功能强大 mstsc 远程 inetmgr ...
- Codeforces Round #299 (Div. 2) D. Tavas and Malekas kmp
题目链接: http://codeforces.com/problemset/problem/535/D D. Tavas and Malekas time limit per test2 secon ...
- 解决tomcat登录需要给角色授权
1:编辑/usr/local/tomcat/conf/tomcat-users.xml文件,在没有注释的内容中添加: <role rolename="manager-gui" ...
- Hadoop 2.6.0 HIVE 2.1.1配置
我用的hadoop 是2.6.0 版本 ,hive 是 2.1.1版本进入:/home/zkpk/apache-hive-2.1.1-bin/执行hive 后报错: (1)Exception in t ...
- springMVC 访问静态资源
问题描述 使用SpringMVC时遇到静态资源无法加载的问题,报404 问题原因 如果SpringMVC的映射模式采用的是后缀名匹配,如[*.do]或者[*.action]则不会出现该问题,因为静态资 ...
- oracle 慢查询
一.查询执行最慢的sql select * from (select sa.SQL_TEXT, sa.SQL_FULLTEXT, sa.EXECUTIONS "执行次数", , ) ...
- winrar 授权破解过期解决
RAR registration data Federal Agency for Education 1000000 PC usage license UID=b621cca9a84bc5deffbf ...
- 批量更新 A表的PK_ID字段
UPDATE ASET PK_ID=(SELECT ID FROM B WHERE A.TAB_NAME=B.TAB_NAME AND B.IS_KEY='1' ) AB表 以TAB_NAME 做 ...
- poj2761 feed the dog
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=2761 Description Wind loves pretty dogs very much, and she has n pet ...
- 前端学习 --Css -- 子元素的伪类
:first-child 寻找父元素的第一个子元素,在所有的子元素中排序: :last-child 寻找父元素的最后一个子元素,在所有的子元素中排序: :nth-child 寻找父元素中的指定位置子元 ...