cuda编程-矩阵乘法(2)
采用shared memory加速
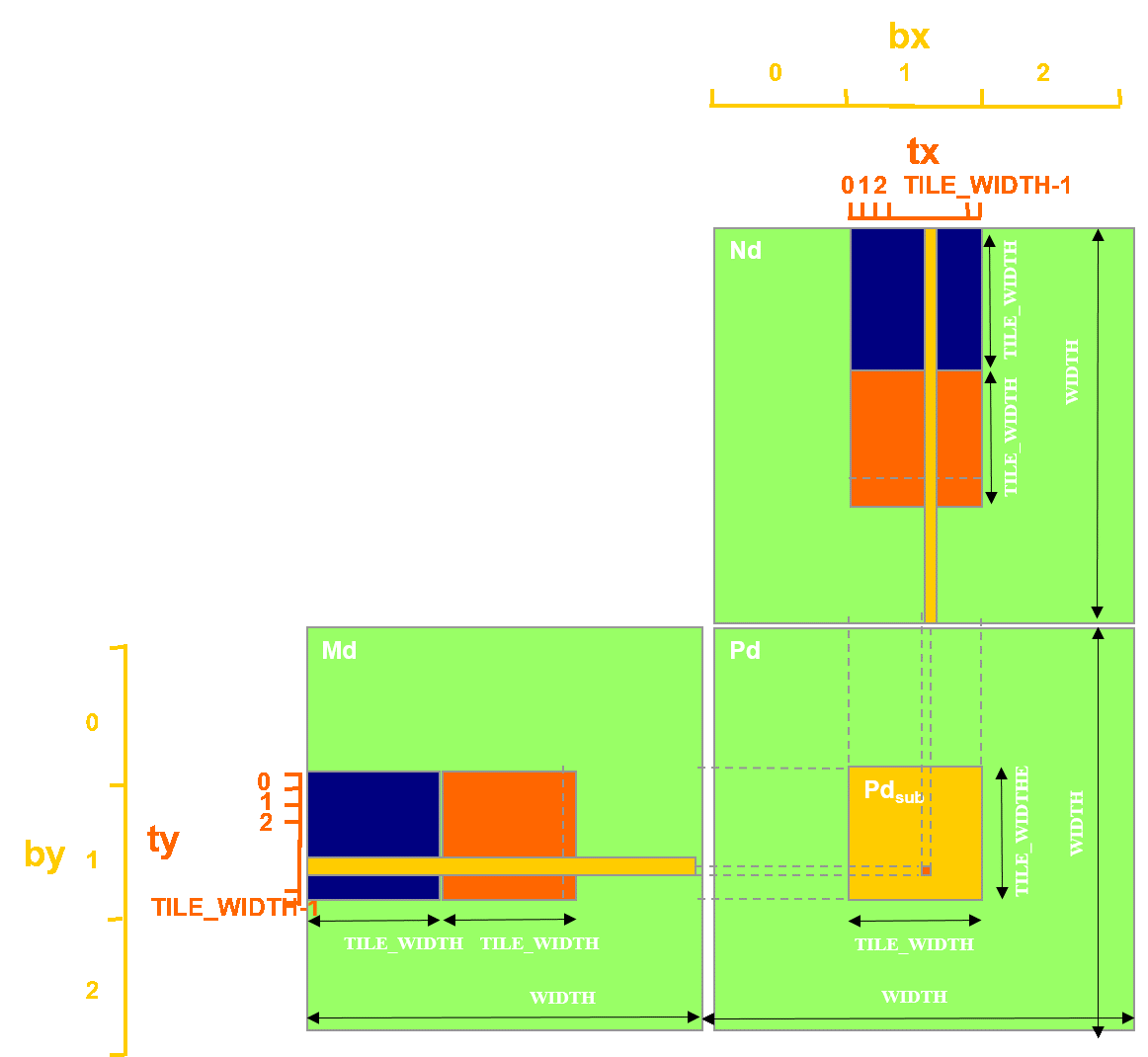
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#include "functions.h" #define TILE_SIZE 16 __global__ void matrixMulKernel(float *C, float *A, float *B, int width, int height){
__shared__ float tile_A[TILE_SIZE][TILE_SIZE];
__shared__ float tile_B[TILE_SIZE][TILE_SIZE];
unsigned int tx = threadIdx.x;
unsigned int ty = threadIdx.y;
unsigned int gx = blockIdx.x * TILE_SIZE + tx;
unsigned int gy = blockIdx.y * TILE_SIZE + ty;
if (gx >= width || gy >= height)
return; // Load shared memory
int tile_num = (width + TILE_SIZE - ) / TILE_SIZE;
float sum = ;
for (int i = ; i < tile_num; ++i){
int bound = min(width, TILE_SIZE);
for (int j = tx; j < bound; j += blockDim.x){
tile_A[ty][j] = A[gy * width + i * bound + j];
}
for (int j = ty; j < bound; j += blockDim.y){
tile_B[j][tx] = B[(i * bound + j) * width + gx];
}
//Synchronize to make sure the sub-matrices are loaded before starting the computation
__syncthreads(); for (int j = ; j < bound; ++j){
sum += tile_A[ty][j] * tile_B[j][tx];
}
//Synchronize to make sure that the preceding computation is done before loading two new
//sub-matrices of M and N in the next iteration
__syncthreads();
}
C[gy*width + gx] = sum;
} void constantInit(float *data, int size, float val){
for (int i = ; i < size; ++i){
data[i] = val;
}
} void matrixMul(){
int dev_id = ;
cudaSetDevice(dev_id); // Allocate host memory for matrices A and B
int width = ;
int height = ;
unsigned int size = width * height;
unsigned int mem_size = sizeof(float)* size;
float *h_A = (float *)malloc(mem_size);
float *h_B = (float *)malloc(mem_size);
float *h_C = (float *)malloc(mem_size); // Initialize host memory
const float valB = 0.01f;
constantInit(h_A, size, 1.0f);
constantInit(h_B, size, valB); // Allocate device memory
float *d_A, *d_B, *d_C;
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_A, mem_size);
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_B, mem_size);
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_C, mem_size); // Memcpy
cudaMemcpy(d_A, h_A, mem_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_B, h_B, mem_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // Config dim
dim3 block(TILE_SIZE, TILE_SIZE);
dim3 grid((width + block.x - ) / block.x, (height + block.y - ) / block.y);
matrixMulKernel <<<grid, block >>>(d_C, d_A, d_B, width, height); // Memcpy device to host
cudaMemcpy(h_C, d_C, mem_size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); // Check
printf("Checking computed result for correctness: ");
bool correct = true;
// test relative error by the formula // |<x, y>_cpu - <x,y>_gpu|/<|x|, |y|> < eps
double eps = .e-;
// machine zero
for (int i = ; i < (int)(width * height); i++) {
double abs_err = fabs(h_C[i] - (width * valB));
double dot_length = width;
double abs_val = fabs(h_C[i]);
double rel_err = abs_err / abs_val / dot_length;
if (abs_err > eps) {
printf("Error! Matrix[%05d]=%.8f, ref=%.8f error term is > %E\n", i, h_C[i], (float)(width*height), eps);
correct = false;
}
}
printf("%s\n", correct ? "Result = PASS" : "Result = FAIL");
}
合并访存:tile_A按行存储,tile_B按列存储,sum=row_tile_A * row_tile_B
__global__ void matrixMulKernel(float *C, float *A, float *B, int width, int height){
__shared__ float tile_A[TILE_SIZE][TILE_SIZE];
__shared__ float tile_B[TILE_SIZE][TILE_SIZE];
unsigned int tx = threadIdx.x;
unsigned int ty = threadIdx.y;
unsigned int gx = blockIdx.x * TILE_SIZE + tx;
unsigned int gy = blockIdx.y * TILE_SIZE + ty;
if (gx >= width || gy >= height)
return;
// Load shared memory
int tile_num = (width + TILE_SIZE - ) / TILE_SIZE;
float sum = ;
for (int i = ; i < tile_num; ++i){
tile_A[tx][ty] = A[gy * width + i * TILE_SIZE + tx];
tile_B[ty][tx] = B[(i * TILE_SIZE + ty) * width + gx];
//Synchronize to make sure the sub-matrices are loaded before starting the computation
__syncthreads();
for (int j = ; j < TILE_SIZE; ++j){
sum += tile_A[j][ty] * tile_B[j][tx];
}
//Synchronize to make sure that the preceding computation is done before loading two new
//sub-matrices of M and N in the next iteration
__syncthreads();
}
C[gy*width + gx] = sum;
}
cuda编程-矩阵乘法(2)的更多相关文章
- cuda编程-矩阵乘法(1)
本方法采用简单的单线程计算每组行和列乘加运算 代码如下: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostrea ...
- cuda(2) 矩阵乘法优化过程
Created on 2013-8-5URL : http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_a502f1a30101mjch.html@author: zhxfl转载请说明出处 # ...
- CUDA编程之快速入门
CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture)的中文全称为计算统一设备架构.做图像视觉领域的同学多多少少都会接触到CUDA,毕竟要做性能速度优化,CUDA是个很重要 ...
- CUDA编程之快速入门【转】
https://www.cnblogs.com/skyfsm/p/9673960.html CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture)的中文全称为计算统一设备架 ...
- 详解CUDA编程
CUDA 是 NVIDIA 的 GPGPU 模型,它使用 C 语言为基础,可以直接以大多数人熟悉的 C 语言,写出在显示芯片上执行的程序,而不需要去学习特定的显示芯片的指令或是特殊的结构.” 编者注: ...
- CUDA 矩阵乘法终极优化指南
作者:马骏 | 旷视 MegEngine 架构师 前言 单精度矩阵乘法(SGEMM)几乎是每一位学习 CUDA 的同学绕不开的案例,这个经典的计算密集型案例可以很好地展示 GPU 编程中常用的优化技巧 ...
- OpenCL 矩阵乘法
▶ 矩阵乘法,按照书里的内容进行了几方面的优化,包括局部内存,矢量数据类型,寄存器,流水线等. ● 最直接的乘法.调用时 main.c 中使用 size_t globalSize[] = { rowA ...
- 【Cuda编程】加法归约
目录 cuda编程并行归约 AtomicAdd调用出错 gpu cpu下时间计算 加法的归约 矩阵乘法 矩阵转置 统计数目 平方和求和 分块处理 线程相邻 多block计算 cuda编程并行归约 At ...
- CUDA编程(十)使用Kahan's Summation Formula提高精度
CUDA编程(十) 使用Kahan's Summation Formula提高精度 上一次我们准备去并行一个矩阵乘法.然后我们在GPU上完毕了这个程序,当然是非常单纯的把任务分配给各个线程.也没有经过 ...
随机推荐
- Apollo内核版本安装
参考:https://github.com/ApolloAuto/apollo/blob/master/docs/quickstart/apollo_software_installation_gui ...
- 欢迎加入.NET Core 技术QQ群一起讨论交流学习
群号:4656606 介绍:本群主要讨论.NET Core及其相关技术,如:IdentityServer4.ABP.Dcoker.Linux.Devops.微服务等,如果你正在使用或者准备使用.NET ...
- 记录一次.Net框架Bug发现和提交过程:.Net Framework和.Net Core均受影响
SmtpClient一处代码编写错误导致异步发送邮件时DeliveryFormat配置项无法正确工作,异步操作已经完全不受我们设置属性控制了,UTF-8内容(如中文)转不转码完全看对方邮件服务器心情! ...
- 【Python撩妹合集】微信聊天机器人,推送天气早报、睡前故事、精美图片分享
福利时间,福利时间,福利时间 如果你还在为不知道怎么撩妹而烦恼,不知道怎么勾搭小仙女而困惑,又或者不知道怎么讨女朋友欢心而长吁短叹. 那么不要犹豫徘徊,往下看.接下来我会分享怎么使用 Python 实 ...
- Spring MVC+ Spring + Mybatis从零开始搭建一个精美且实用的管理后台
点击进入<SSM搭建精美实用的管理系统>达人课页面 SSM 框架即 SpringMVC+Spring+Mybatis,相信各位朋友在投递简历时已直观感受到它的重要性,JavaWeb 相关工 ...
- eclipse maven设置
eclipse 4.4以上版本集成了maven,只需配置一下即可,如果你的eclipse 没有安装maven,可以参考这个文章.http://marketplace.eclipse.org/conte ...
- 关于NETCORE中使用特性Serializable找不到引用的解决方法
升级到netcore后,serializable特性不在命名空间System下了,需要nuget依赖包System.Runtime.Serialization.Formatters
- Podfile语法参考(译)
https://www.jianshu.com/p/8af475c4f717 2015.10.30 19:14* 字数 2496 阅读 35976评论 9喜欢 120 本文翻译自官方的Podfile ...
- Django之在Python中调用Django环境
Django之在Python中调用Django环境 新建一个py文件,在其中写下如下代码: import os if __name__ == '__main__': os.environ.setdef ...
- 【学习总结】Git学习-参考廖雪峰老师教程六-分支管理
学习总结之Git学习-总 目录: 一.Git简介 二.安装Git 三.创建版本库 四.时光机穿梭 五.远程仓库 六.分支管理 七.标签管理 八.使用GitHub 九.使用码云 十.自定义Git 期末总 ...
