TensorFlow(2)Softmax Regression
Softmax Regression
Chapter
Basics
- generate random Tensors
- Three usual activation function in Neural Network
- Softmax funcion
Softmax Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Softmax Regression
- Examples
Basics
- generate random Tensors
- Three usual activation function in Neural Network
- Softmax funcion
generate random Tensors
Two generally type of random distribute:
- uniform
- normal
In TensorFlow, they come in tf.random_normal() and tf.random_uniform() funcion.
Example:
import tensorflow as tf
# 正态分布
# tf.random_normal(shape,mean=0.0,stddev=1.0,dtype=tf.float32,seed=None,name=None)
b = tf.random_normal([5, 5],seed = 1234)
# 平均分布
# tf.random_uniform(shape,minval=0.0,maxval=1.0,dtype=tf.flaot32,seed=None,name=None)
c = tf.random_uniform([5,5], seed=12)
with tf.Session() as sees:
mat1, mat2 = sees.run([b,c])
print(mat1)
print(mat2)
output:
[[ 0.51340485 -0.25581399 0.65199131 1.39236379 0.37256798]
[ 0.20336303 1.24701834 -0.98333126 0.50439858 0.98600131]
[-1.70049322 1.51739979 0.06326418 1.07656693 0.03294745]
[-2.32479048 -1.44697022 0.56703895 0.10577387 -0.90796399]
[-1.05107033 -1.63305104 1.22501576 0.83072805 1.28771544]]
[[ 0.63615251 0.92409146 0.67627728 0.50212514 0.96114957]
[ 0.88567221 0.04360652 0.29879451 0.46695721 0.05440903]
[ 0.82479727 0.28480017 0.98824406 0.67999697 0.66409671]
[ 0.75018144 0.31693625 0.51552784 0.75187266 0.44445455]
[ 0.07454526 0.04856801 0.35572827 0.2670846 0.4779768 ]]
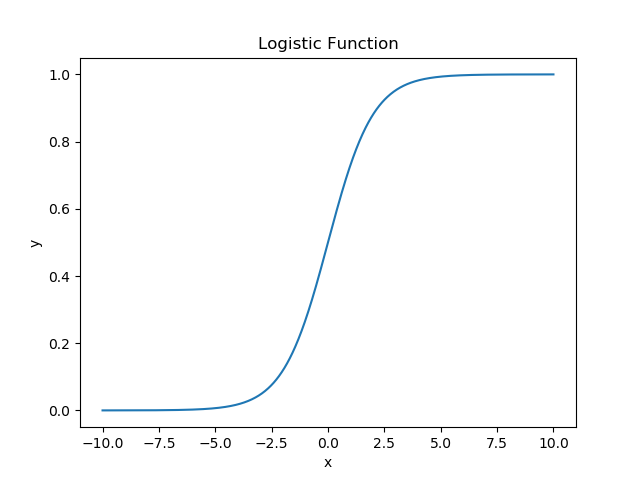
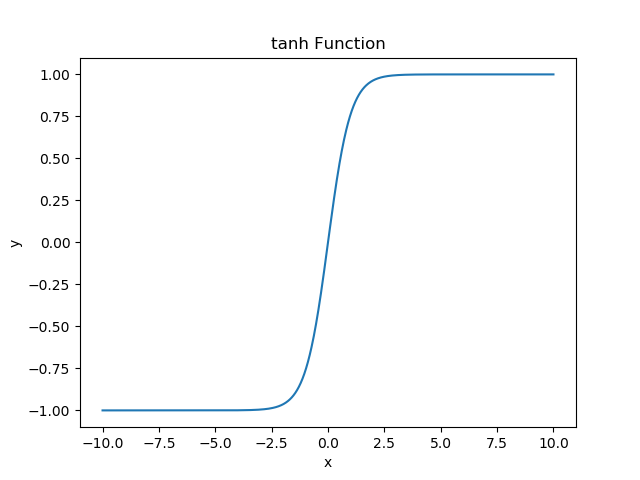
Three usual activation function in Neural Network
- logistic function: (sigmoid function)
\]
- tanh function
\]
- ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) function
\begin{cases}
0, & \text{if x $\le$ 0} \\
x, & \text{if $x$ $\gt$ 0}
\end{cases}
\]
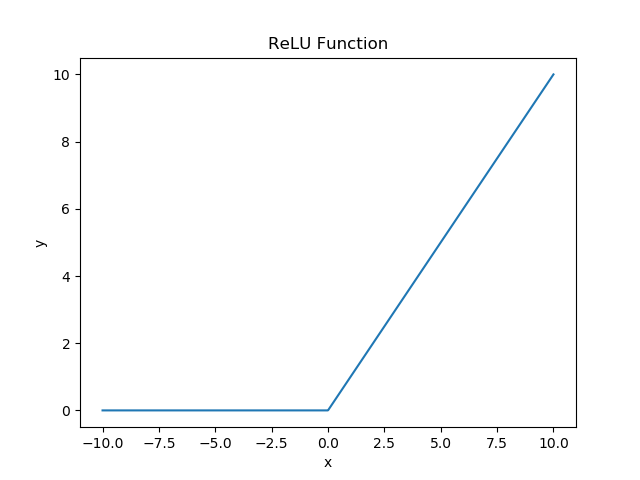
TensorFlow Code:
# 常用的神经网络的三种激活函数(sigmoid, tanh, ReLu)
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
g = tf.Graph()
with g.as_default() as g:
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float64)
y = tf.nn.sigmoid(x) # sigmoid函数
# y = tf.nn.tanh(x) # tanh函数
# y = tf.nn.relu(x) # ReLU函数
with tf.Session(graph=g) as sess:
# x的范围为-10到10,均匀地取1000个点
x_value = np.linspace(-10, 10, 1000)
x, y = sess.run([x,y], feed_dict={x: x_value})
# 绘制函数图像
plt.plot(x,y)
plt.title('logistic Function')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
Softmax Function
The softmax function is a generalization of the logistic function that "squashes" a K-dimensional vector of arbitrary real values to a K-dimensional vector of real values, where each entry is in the range (0, 1], and all the entries add up to 1.
The function is :
In TensorFlow, we can use tf.nn.softmax() function.
Python Code:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
A = np.array([1.0,2.0,3.0,4.0,5.0,6.0])
exp_A = np.exp(A)
softmax_A = exp_A/sum(exp_A)
print(softmax_A)
tf_a = tf.constant(A)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(tf.nn.softmax(tf_a)))
output:
[ 0.00426978 0.01160646 0.03154963 0.08576079 0.23312201 0.63369132]
[ 0.00426978 0.01160646 0.03154963 0.08576079 0.23312201 0.63369132]
Softmax Regression
- Logistic Regression
- Softmax Regression
- Examples
Logistic Regression
Think logistic regression in a neural-network way.
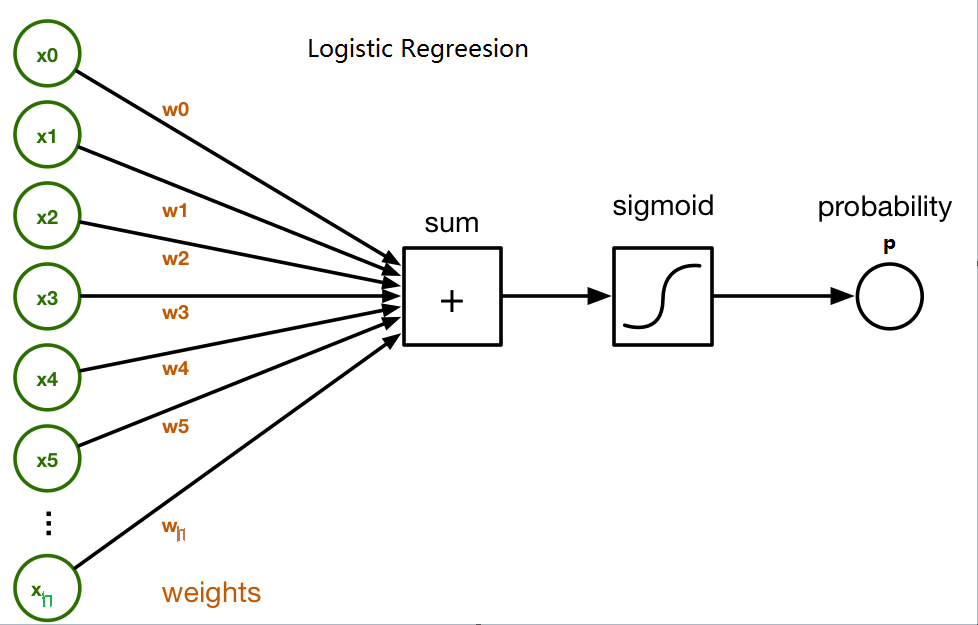
Suppose there are m samples, each sample in n-dimension with label in {0,1}, so the loss function is:
h_{\theta}(x) =\frac{1}{1+e^{-\phi(x)}}
\]
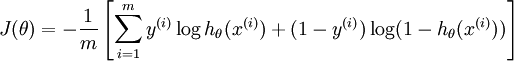
We use gradient descent method to find the optimal parameter \(\theta\) (n+1 parameters: \(w_0,w_1,...,w_n\)) in order to minimize the loss.
Softmax Regression
Softmax Regression is a generalize type of Logistic Function which is useful for multi-class classification.
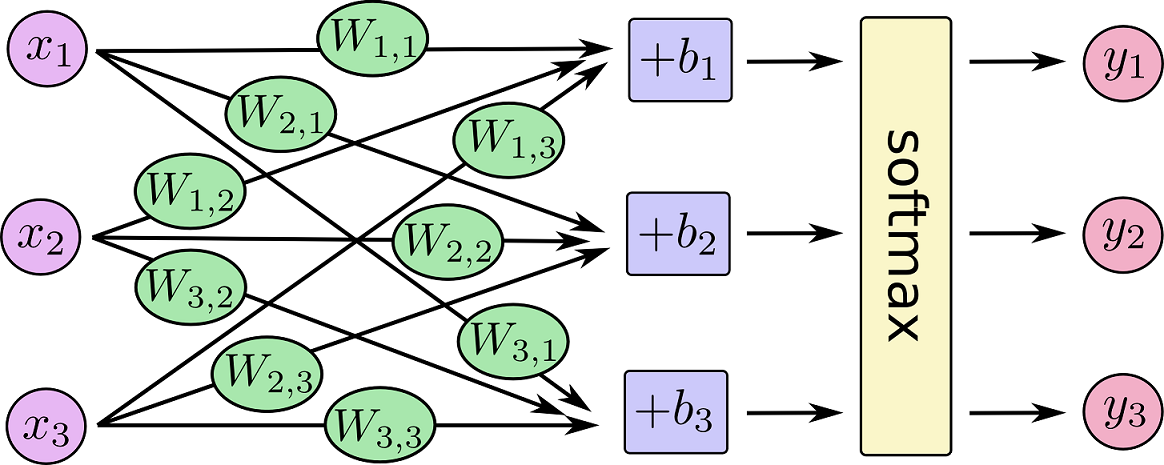
Suppose there are m samples, each sample in n-dimension with label in {1,2,...,k}, so the loss function is:
\]
We use gradient descent method to find the optimal parameter \(\theta\) (\(k\times (n+1)\) parameters) in order to minimize the loss.
TensorFlow Code:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s: %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class Softmax:
def __init__(self, input_size, class_num, epoch = 1000, learning_rate = 0.1, save_model_path='./model.ckpt'):
self.save_model_path = save_model_path # 模型保存目录
self.epoch = epoch # 循环次数
self.learning_rate = learning_rate # 学习率
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, input_size]) # 特征
y_true = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, class_num]) # 标签
# 定义softmax回归的网络结构
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([input_size, class_num]), name='weight')
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([class_num]), name='bias')
# tf.nn.softmax computes softmax activations
# softmax = exp(logits) / reduce_sum(exp(logits), dim)
self.hypothesis = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b)
self.x = x
self.y_true = y_true
# Cross entropy loss
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(self.y_true * tf.log(self.hypothesis), axis=1))
# 选择optimizer使loss达到最小, 使用梯度下降法减少 loss,学习率是self.learning_rate
self.train_model = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss)
self.saver = tf.train.Saver()
logger.info('Initialize the model...')
# 训练并保存模型
def train(self, x_data, y_data):
logger.info('Training the model...')
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 对所有变量进行初始化
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
feed_dict = {self.x: x_data, self.y_true: y_data}
# 进行迭代学习
for i in range(self.epoch+1):
sess.run(self.train_model, feed_dict=feed_dict)
if i % int(self.epoch/10) == 0:
# to see the step improvement
print('已训练%d次, loss: %s.' % (i, sess.run(self.loss, feed_dict=feed_dict)))
# 保存ANN模型
logger.info('Saving the model...')
self.saver.save(sess, self.save_model_path) # E
# 预测数据
def predict(self, data):
with tf.Session() as sess:
logger.info('Restoring the model...')
self.saver.restore(sess, self.save_model_path) # A
predict = sess.run(self.hypothesis, feed_dict={self.x: data}) # B
predict_class = sess.run(tf.argmax(predict,1))
print("预测值为:%s." % predict_class)
return predict
# 使用Softmax类
# 样本数据
x_data = np.array([[1, 2, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 3, 2],
[3, 1, 3, 4],
[4, 1, 5, 5],
[1, 7, 5, 5],
[1, 2, 5, 6],
[1, 6, 6, 6],
[1, 7, 7, 7]])
y_data = np.array([[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0]])
input_size = x_data.shape[1]
class_num = y_data.shape[1]
save_path = 'E://logs/model.ckpt'
st = Softmax(input_size, class_num, 1000, 0.1, save_path)
st.train(x_data, y_data)
st.predict(np.array([[1, 3, 4, 3]]))
output:
2018-08-17 17:01:37,854 - INFO: Initialize the model...
2018-08-17 17:01:37,854 - INFO: Training the model...
已训练0次, loss: 5.31073.
已训练100次, loss: 0.624064.
已训练200次, loss: 0.559649.
已训练300次, loss: 0.511522.
已训练400次, loss: 0.470231.
已训练500次, loss: 0.432752.
已训练600次, loss: 0.397538.
已训练700次, loss: 0.363444.
已训练800次, loss: 0.329436.
已训练900次, loss: 0.294607.
已训练1000次, loss: 0.259079.
2018-08-17 17:01:38,289 - INFO: Saving the model...
2018-08-17 17:01:39,062 - INFO: Restoring the model...
INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from E://logs/model.ckpt
2018-08-17 17:01:39,062 - INFO: Restoring parameters from E://logs/model.ckpt
预测值为:[0].
Examples
iris.csv: https://github.com/percent4/Storing_pictures/blob/master/iris.csv
TensorFlow Code:
Softmax 类:TF_Softmax.py
import tensorflow as tf
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level = logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s: %(message)s')
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
class Softmax:
def __init__(self, input_size, class_num, epoch = 1000, learning_rate = 0.1, save_model_path='./model.ckpt'):
self.save_model_path = save_model_path # 模型保存目录
self.epoch = epoch # 循环次数
self.learning_rate = learning_rate # 学习率
x = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, input_size]) # 特征
y_true = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None, class_num]) # 标签
# 定义softmax回归的网络结构
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([input_size, class_num], name='weight'))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([class_num], name='bias'))
# tf.nn.softmax computes softmax activations
# softmax = exp(logits) / reduce_sum(exp(logits), dim)
self.hypothesis = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x, W) + b)
self.x = x
self.y_true = y_true
# Cross entropy loss
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(self.y_true * tf.log(self.hypothesis), axis=1))
# 选择optimizer使loss达到最小, 使用梯度下降法减少 loss,学习率是self.learning_rate
self.train_model = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(self.learning_rate).minimize(self.loss)
self.saver = tf.train.Saver()
logger.info('Initialize the model...')
# 训练并保存模型
def train(self, x_data, y_data):
logger.info('Training the model...')
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 对所有变量进行初始化
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
feed_dict = {self.x: x_data, self.y_true: y_data}
# 进行迭代学习
for i in range(self.epoch+1):
sess.run(self.train_model, feed_dict=feed_dict)
if i % int(self.epoch/10) == 0:
# to see the step improvement
print('已训练%d次, loss: %s.' % (i, sess.run(self.loss, feed_dict=feed_dict)))
# 保存ANN模型
logger.info('Saving the model...')
self.saver.save(sess, self.save_model_path) # E
# 预测数据
def predict(self, data):
with tf.Session() as sess:
logger.info('Restoring the model...')
self.saver.restore(sess, self.save_model_path) # A
predict = sess.run(self.hypothesis, feed_dict={self.x: data}) # B
# print("预测值为:%s." % predict)
return predict
预测数据:test_softmax.py
"""
利用Softmax对IRIS数据集进行多分类
"""
from TF_Softmax import Softmax
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelBinarizer
CSV_FILE_PATH = 'E://iris.csv' # CSV 文件路径
IRIS = pd.read_csv(CSV_FILE_PATH) # 读取CSV文件
target_variable = 'class' # 目标变量
# 数据集的特征
features = list(IRIS.columns)
features.remove(target_variable)
# 目标变量的类别
Class = IRIS[target_variable].unique()
# 对目标变量进行重新编码
# 目标变量的类别字典
Class_dict = {}
for i, clf in enumerate(Class):
Class_dict[clf] = i+1
# 增加一列target, 将目标变量进行编码
IRIS['target'] = IRIS[target_variable].apply(lambda x: Class_dict[x])
# 对目标变量进行0-1编码
lb = LabelBinarizer()
lb.fit(list(Class_dict.values()))
transformed_labels = lb.transform(IRIS['target'])
y_bin_labels = [] # 对多分类进行0-1编码的变量
for i in range(transformed_labels.shape[1]):
y_bin_labels.append('y'+str(i))
IRIS['y'+str(i)] = transformed_labels[:, i]
# print(IRIS.head(100))
# 数据是否标准化
# x_bar = (x-mean)/std
IS_STANDARD = 'no'
if IS_STANDARD == 'yes':
for feature in features:
mean = IRIS[feature].mean()
std = IRIS[feature].std()
IRIS[feature] = (IRIS[feature]-mean)/std
# print(IRIS.head())
# 将数据集分为训练集和测试集,训练集80%, 测试集20%
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(IRIS[features], IRIS[y_bin_labels], \
train_size = 0.8, test_size=0.2, random_state=123)
# 使用Softmax进行预测
# 构建Softmax网络
input_size = x_train.shape[1]
class_num = y_train.shape[1]
# 模型保存地址
MODEL_SAVE_PATH = 'E://logs/softmax.ckpt'
# Softmax初始化
ann = Softmax(input_size, class_num, 10000, 0.5, MODEL_SAVE_PATH)
ann.train(x_train, y_train) # 训练ANN
y_pred = ann.predict(x_test) # 预测数据
# 预测分类
prediction = []
for pred in y_pred:
prediction.append(list(pred).index(max(pred))+1)
# 计算预测的准确率
x_test['prediction'] = prediction
x_test['label'] = IRIS['target'][y_test.index]
print(x_test.head())
accuracy = accuracy_score(x_test['prediction'], x_test['label'])
print('Softmax预测准确率为%.2f%%.'%(accuracy*100))
output:
2018-08-17 21:36:33,373 - INFO: Initialize the model...
2018-08-17 21:36:33,373 - INFO: Training the model...
已训练0次, loss: 8.691852.
已训练1000次, loss: 0.060822684.
已训练2000次, loss: 0.053384975.
已训练3000次, loss: 0.04848685.
已训练4000次, loss: 0.044897027.
已训练5000次, loss: 0.042198572.
已训练6000次, loss: 0.040111676.
已训练7000次, loss: 0.038444195.
已训练8000次, loss: 0.037071057.
已训练9000次, loss: 0.035911743.
已训练10000次, loss: 0.034913346.
2018-08-17 21:36:37,012 - INFO: Saving the model...
2018-08-17 21:36:37,215 - INFO: Restoring the model...
INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from E://logs/softmax.ckpt
2018-08-17 21:36:37,230 - INFO: Restoring parameters from E://logs/softmax.ckpt
sepal_length sepal_width petal_length petal_width prediction label
72 6.3 2.5 4.9 1.5 2 2
112 6.8 3.0 5.5 2.1 3 3
132 6.4 2.8 5.6 2.2 3 3
88 5.6 3.0 4.1 1.3 2 2
37 4.9 3.1 1.5 0.1 1 1
Softmax预测准确率为96.67%.
TensorFlow(2)Softmax Regression的更多相关文章
- 学习笔记TF024:TensorFlow实现Softmax Regression(回归)识别手写数字
TensorFlow实现Softmax Regression(回归)识别手写数字.MNIST(Mixed National Institute of Standards and Technology ...
- TensorFlow实现Softmax Regression识别手写数字
本章已机器学习领域的Hello World任务----MNIST手写识别做为TensorFlow的开始.MNIST是一个非常简单的机器视觉数据集,是由几万张28像素*28像素的手写数字组成,这些图片只 ...
- TensorFlow实现Softmax Regression识别手写数字中"TimeoutError: [WinError 10060] 由于连接方在一段时间后没有正确答复或连接的主机没有反应,连接尝试失败”问题
出现问题: 在使用TensorFlow实现MNIST手写数字识别时,出现"TimeoutError: [WinError 10060] 由于连接方在一段时间后没有正确答复或连接的主机没有反应 ...
- TensorFlow实战之Softmax Regression识别手写数字
关于本文说明,本人原博客地址位于http://blog.csdn.net/qq_37608890,本文来自笔者于2018年02月21日 23:10:04所撰写内容(http://blog.c ...
- Tensorflow - Implement for a Softmax Regression Model on MNIST.
Coding according to TensorFlow 官方文档中文版 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mn ...
- 【TensorFlow-windows】(一)实现Softmax Regression进行手写数字识别(mnist)
博文主要内容有: 1.softmax regression的TensorFlow实现代码(教科书级的代码注释) 2.该实现中的函数总结 平台: 1.windows 10 64位 2.Anaconda3 ...
- 基于MNIST数据的softmax regression
跟着tensorflow上mnist基本机器学习教程联系 首先了解sklearn接口: sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression In the multiclas ...
- Softmax回归(Softmax Regression)
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/ 多分类问题 在一个多分类问题中,因变量y有k个取值,即.例如在邮件分类问题中,我们要把邮件分为垃圾邮件.个人邮件.工作邮件 ...
- (六)6.10 Neurons Networks implements of softmax regression
softmax可以看做只有输入和输出的Neurons Networks,如下图: 其参数数量为k*(n+1) ,但在本实现中没有加入截距项,所以参数为k*n的矩阵. 对损失函数J(θ)的形式有: 算法 ...
随机推荐
- iptables简单用法
iptables -t 表名 <-A/I/D/R> 规则链名 [规则号] <-i/o 网卡名> -p 协议名 <-s 源IP/源子网> --sport 源端口 &l ...
- spark入门
这一两年Spark技术很火,自己也凑热闹,反复的试验.研究,有痛苦万分也有欣喜若狂,抽空把这些整理成文章共享给大家.这个系列基本上围绕了Spark生态圈进行介绍,从Spark的简介.编译.部署,再到编 ...
- 12 week work
调用一个地图API <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/ ...
- CS61B HW0
The Enhanced For Loop public class EnhancedForBreakDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { S ...
- html input file accept 上传文件类型限制格式 MIME 类型列表
例: <input type="file" accept="application/vnd.openxmlformats-officedocument.spread ...
- Android 视频播放器 (三):使用NBPlayer播放直播视频
一.前言 在 Android 音视频开发学习思路 中,我们不断的学习和了解音视频相关的知识,随着知识点不断的学习,我们现在应该做的事情,就是将知识点不断的串联起来.这样才能得到更深层次的领悟.通过整理 ...
- Javascript高级编程学习笔记(28)—— BOM(2)window对象2
今天讲一下window对象和浏览器导航,弹窗等有关的内容 导航和打开窗口 window.open() 用于导航到某个特定 url 该方法接收四个参数 1.url 2.窗口目标(当页面中有多个框架fra ...
- 解决mysql插入数据报错[Err] 1146 - Table 'performance_schema.session_status' doesn't exist
解决办法:1.打开cmd 执行命令cd/ 进入C盘根目录2.dir 查看C盘根目录下文件夹 找到 Program Files文件夹3.cd Program Files 进入该文件夹下 再输入dir ...
- Docker学习笔记-CentOS7镜像
前言: 环境:centos7.5 64 位 正文: 第一步:下载centos7镜像 docker pull centos 第二步:建立centos7的容器 sudo docker run --priv ...
- Docker学习笔记-Redis 安装
拉取官方的镜像 docker pull redis:3.2 查看 docker images redis 运行容器 docker run -p 6379:6379 -v $PWD/data:/data ...


