DeepLearning.ai-Week4-Face Recognition for the Happy House
1 - Task
- Implement the triplet loss function
- Use a pretrained model to map face images into 128-dimensional encodings
- Use these encodings to perform face verification and face recognition
2 - Import Packages
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Conv2D, ZeroPadding2D, Activation, Input, concatenate
from keras.models import Model
from keras.layers.normalization import BatchNormalization
from keras.layers.pooling import MaxPooling2D, AveragePooling2D
from keras.layers.merge import Concatenate
from keras.layers.core import Lambda, Flatten, Dense
from keras.initializers import glorot_uniform
from keras.engine.topology import Layer
from keras import backend as K
K.set_image_data_format('channels_first')
import cv2
import os
import numpy as np
from numpy import genfromtxt
import pandas as pd
import tensorflow as tf
from fr_utils import *
from inception_blocks_v2 import * %matplotlib inline
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2 np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.nan)
3 - Naive Face Verification
在人脸验证任务中,我们需要判断两张图片中的人脸是否为同一个人。最简单的做法是逐个像素点比较,如果总共的距离低于给定的某一个阈值,则判断为同一个人。这种方法效果会很差。所以我们可以通过学习一个模型,可以将人脸图片提取出特征向量,再比较特征向量的距离来判断是否为同一个人。

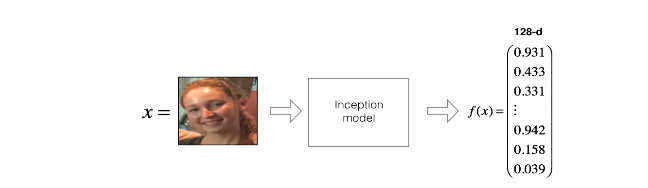
4 - Encoding face images into a 128-dimensional vector
4.1 - Using an ConvNet to compute encodings
注意到
- 这个网络的输入的批次图像维度为$(m,3,96,96)$
- 网络的输出为$(m,128)$的编码,网络是对每一个输入编码成一个128维度向量的输出
FRmodel = faceRecoModel(input_shape=(3, 96, 96))
print("Total Params:", FRmodel.count_params())
Result:
Total Params: 3743280

好的编码应该具有如下性质:
- 同一个人的两张图片的编码应该尽可能的相似
- 不同人的两张图片的编码要非常不同
$triplet loss$损失函数便是描述上述性质的,并且尽量使得同一个人的两张图片的编码更加相似,不同人的两张图片的编码更具有区分性。
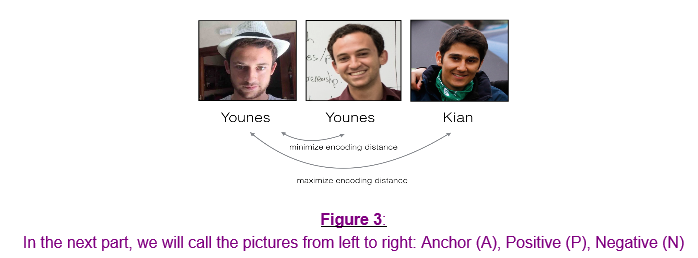
4.2 - The Triplet Loss
训练用于编码的神经网络(对应上面f映射),需要三元组图片$(A,P,N)$:
- A is an "Anchor" image--a picture of a person.
- P is a "Positive" image--a picture of the same person as the Anchor image.
- N is a "Negative" image--a picture of a different person than the Anchor image.
它们之间具有下式所示关系:
$$\mid \mid f(A^{(i)}) - f(P^{(i)}) \mid \mid_2^2 + \alpha < \mid \mid f(A^{(i)}) - f(N^{(i)}) \mid \mid_2^2$$
所以我们要最小化的"$triplet cost$"如下:
- Compute the distance between the encodings of "anchor" and "positive": $\begin{Vmatrix} f(A^{(i)}) - f(P^{(i)}) \end{Vmatrix}_2^2$
- Compute the distance between the encodings of "anchor" and "negative": $\begin{Vmatrix} f(A^{(i)}) - f(N^{(i)}) \end{Vmatrix}_2^2$
- Compute the formula per training example: $\begin{Vmatrix} f(A^{(i)}) - f(P^{(i)}) \end{Vmatrix} - \begin{Vmatrix} f(A^{(i)}) - f(N^{(i)}) \end{Vmatrix}_2^2 + \alpha$
- Compute the full formula by taking the max with zero and summing over the training examples:$$\mathcal{J} = \sum^{m}_{i=1} \large[ \small \mid \mid f(A^{(i)}) - f(P^{(i)}) \mid \mid_2^2 - \mid \mid f(A^{(i)}) - f(N^{(i)}) \mid \mid_2^2+ \alpha \large ] \small_+ \tag{3}$$
# GRADED FUNCTION: triplet_loss def triplet_loss(y_true, y_pred, alpha = 0.2):
"""
Implementation of the triplet loss as defined by formula (3) Arguments:
y_true -- true labels, required when you define a loss in Keras, you don't need it in this function.
y_pred -- python list containing three objects:
anchor -- the encodings for the anchor images, of shape (None, 128)
positive -- the encodings for the positive images, of shape (None, 128)
negative -- the encodings for the negative images, of shape (None, 128) Returns:
loss -- real number, value of the loss
""" anchor, positive, negative = y_pred[0], y_pred[1], y_pred[2] ### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines)
# Step 1: Compute the (encoding) distance between the anchor and the positive, you will need to sum over axis=-1
pos_dist = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(anchor, positive)))
# Step 2: Compute the (encoding) distance between the anchor and the negative, you will need to sum over axis=-1
neg_dist = tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(tf.subtract(anchor, negative)))
# Step 3: subtract the two previous distances and add alpha.
basic_loss = tf.add(tf.subtract(pos_dist, neg_dist), alpha)
# Step 4: Take the maximum of basic_loss and 0.0. Sum over the training examples.
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.maximum(basic_loss, 0.0))
### END CODE HERE ### return loss
with tf.Session() as test:
tf.set_random_seed(1)
y_true = (None, None, None)
y_pred = (tf.random_normal([3, 128], mean=6, stddev=0.1, seed = 1),
tf.random_normal([3, 128], mean=1, stddev=1, seed = 1),
tf.random_normal([3, 128], mean=3, stddev=4, seed = 1))
loss = triplet_loss(y_true, y_pred) print("loss = " + str(loss.eval()))
Result: //和答案不一样,但我找到别人能出正确答案的代码也跟我一样,所以我认为应该是随机种子的问题
loss = 350.027
5 - Loading the trained model
因为训练FaceNet需要大量的数据和计算,因此此作业不打算训练该模型,而是直接加载已经训练好的模型。
FRmodel.compile(optimizer = 'adam', loss = triplet_loss, metrics = ['accuracy'])
load_weights_from_FaceNet(FRmodel)

6 - Applying the model
6.1 - Face Verification
使用方法$img_to_encoding(image_path, model)$建立一个人脸特征库,只有识别到其中的人脸才能通过验证。
database = {}
database["danielle"] = img_to_encoding("images/danielle.png", FRmodel)
database["younes"] = img_to_encoding("images/younes.jpg", FRmodel)
database["tian"] = img_to_encoding("images/tian.jpg", FRmodel)
database["andrew"] = img_to_encoding("images/andrew.jpg", FRmodel)
database["kian"] = img_to_encoding("images/kian.jpg", FRmodel)
database["dan"] = img_to_encoding("images/dan.jpg", FRmodel)
database["sebastiano"] = img_to_encoding("images/sebastiano.jpg", FRmodel)
database["bertrand"] = img_to_encoding("images/bertrand.jpg", FRmodel)
database["kevin"] = img_to_encoding("images/kevin.jpg", FRmodel)
database["felix"] = img_to_encoding("images/felix.jpg", FRmodel)
database["benoit"] = img_to_encoding("images/benoit.jpg", FRmodel)
database["arnaud"] = img_to_encoding("images/arnaud.jpg", FRmodel)
实现$verify()$方法去识别这个人是否能够通过验证,有如下几步:
- Compute the encoding of the image from image_path
- Compute the distance about this encoding and the encoding of the identity image stored in the database
- Open the door if the distance is less than 0.7, else do not open.
# GRADED FUNCTION: verify def verify(image_path, identity, database, model):
"""
Function that verifies if the person on the "image_path" image is "identity". Arguments:
image_path -- path to an image
identity -- string, name of the person you'd like to verify the identity. Has to be a resident of the Happy house.
database -- python dictionary mapping names of allowed people's names (strings) to their encodings (vectors).
model -- your Inception model instance in Keras Returns:
dist -- distance between the image_path and the image of "identity" in the database.
door_open -- True, if the door should open. False otherwise.
""" ### START CODE HERE ### # Step 1: Compute the encoding for the image. Use img_to_encoding() see example above. (≈ 1 line)
encoding = img_to_encoding(image_path, model) # Step 2: Compute distance with identity's image (≈ 1 line)
dist = np.linalg.norm(encoding-database[identity]) # Step 3: Open the door if dist < 0.7, else don't open (≈ 3 lines)
if dist<0.7:
print("It's " + str(identity) + ", welcome home!")
door_open = True
else:
print("It's not " + str(identity) + ", please go away")
door_open = False ### END CODE HERE ### return dist, door_open
verify("images/camera_0.jpg", "younes", database, FRmodel)

verify("images/camera_2.jpg", "kian", database, FRmodel)

6.2 - Face Recognition
实现$who\_is\_it()$方法需要以下几步:
- Compute the target encoding of the image from image_path
- Find the encoding from the database that has smallest distance with the target encoding.
- Initialize the
min_distvariable to a large enough number (100). It will help you keep track of what is the closest encoding to the input's encoding. - Loop over the database dictionary's names and encodings. To loop use
for (name, db_enc) in database.items().- Compute L2 distance between the target "encoding" and the current "encoding" from the database.
- If this distance is less than the min_dist, then set min_dist to dist, and identity to name.
- Initialize the
# GRADED FUNCTION: who_is_it def who_is_it(image_path, database, model):
"""
Implements face recognition for the happy house by finding who is the person on the image_path image. Arguments:
image_path -- path to an image
database -- database containing image encodings along with the name of the person on the image
model -- your Inception model instance in Keras Returns:
min_dist -- the minimum distance between image_path encoding and the encodings from the database
identity -- string, the name prediction for the person on image_path
""" ### START CODE HERE ### ## Step 1: Compute the target "encoding" for the image. Use img_to_encoding() see example above. ## (≈ 1 line)
encoding = img_to_encoding(image_path, model) ## Step 2: Find the closest encoding ## # Initialize "min_dist" to a large value, say 100 (≈1 line)
min_dist = 100 # Loop over the database dictionary's names and encodings.
for (name, db_enc) in dataset: # Compute L2 distance between the target "encoding" and the current "emb" from the database. (≈ 1 line)
dist = np.linalg.norm(encoding-db_enc) # If this distance is less than the min_dist, then set min_dist to dist, and identity to name. (≈ 3 lines)
if dist < min_dist:
min_dist = dist
identity = name ### END CODE HERE ### if min_dist > 0.7:
print("Not in the database.")
else:
print ("it's " + str(identity) + ", the distance is " + str(min_dist)) return min_dist, identity
who_is_it("images/camera_0.jpg", database, FRmodel)
7 - Summary
虽然我们没有实现和训练神经网络,但是可以通过下面两种方法来提高算法的准确性:
- Put more images of each person (under different lighting conditions, taken on different days, etc.) into the database. Then given a new image, compare the new face to multiple pictures of the person. This would increae accuracy.(增加数据集)
- Crop the images to just contain the face, and less of the "border" region around the face. This preprocessing removes some of the irrelevant pixels around the face, and also makes the algorithm more robust.(降低噪声)
8 - References
https://web.stanford.edu/class/cs230/
DeepLearning.ai-Week4-Face Recognition for the Happy House的更多相关文章
- Coursera机器学习+deeplearning.ai+斯坦福CS231n
日志 20170410 Coursera机器学习 2017.11.28 update deeplearning 台大的机器学习课程:台湾大学林轩田和李宏毅机器学习课程 Coursera机器学习 Wee ...
- DeepLearning.ai学习笔记汇总
第一章 神经网络与深度学习(Neural Network & Deeplearning) DeepLearning.ai学习笔记(一)神经网络和深度学习--Week3浅层神经网络 DeepLe ...
- Coursera深度学习(DeepLearning.ai)编程题&笔记
因为是Jupyter Notebook的形式,所以不方便在博客中展示,具体可在我的github上查看. 第一章 Neural Network & DeepLearning week2 Logi ...
- DeepLearning.ai学习笔记(三)结构化机器学习项目--week2机器学习策略(2)
一.进行误差分析 很多时候我们发现训练出来的模型有误差后,就会一股脑的想着法子去减少误差.想法固然好,但是有点headlong~ 这节视频中吴大大介绍了一个比较科学的方法,具体的看下面的例子 还是以猫 ...
- Coursera DeepLearning.ai Logistic Regression逻辑回归总结
既<Machine Learning>课程后,Andrew Ng又推出了新一系列的课程<DeepLearning.ai>,注册了一下可以试听7天.之后每个月要$49,想想还是有 ...
- Deeplearning.ai课程笔记--汇总
从接触机器学习就了解到Andrew Ng的机器学习课程,后来发现又出来深度学习课程,就开始在网易云课堂上学习deeplearning.ai的课程,Andrew 的课真是的把深入浅出.当然学习这些课程还 ...
- deeplearning.ai学习RNN
一.RNN基本结构 普通神经网络不能处理时间序列的信息,只能割裂的单个处理,同时普通神经网络如果用来处理文本信息的话,参数数目将是非常庞大,因为如果采用one-hot表示词的话,维度非常大. RNN可 ...
- deeplearning.ai 旁听如何做课后编程作业
在上吴恩达老师的深度学习课程,在coursera上. 我觉得课程绝对值的49刀,但是确实没有额外的钱来上课.而且课程提供了旁听和助学金. 之前在coursera上算法和机器学习都是直接旁听的,这些课旁 ...
- deeplearning.ai课程学习(1)
本系列主要是我对吴恩达的deeplearning.ai课程的理解和记录,完整的课程笔记已经有很多了,因此只记录我认为重要的东西和自己的一些理解. 第一门课 神经网络和深度学习(Neural Netwo ...
- 吴恩达deepLearning.ai循环神经网络RNN学习笔记_看图就懂了!!!(理论篇)
前言 目录: RNN提出的背景 - 一个问题 - 为什么不用标准神经网络 - RNN模型怎么解决这个问题 - RNN模型适用的数据特征 - RNN几种类型 RNN模型结构 - RNN block - ...
随机推荐
- Serlect的笔记二(request 、 ersponse)
Web服务器收到客户端的http请求,会针对每一次请求,分别创建一个用于代表请求的request对象.和代表响应的response对象. 下面这两个对象的基本理解: 一.HttpServletRequ ...
- JDBC 增、改、删 MySQL中的表
在数据库test里先创建表school,内容如下 通过JDBC增加第五人tom,修改他的生日,最后删除tom import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.D ...
- gdb带参调试
第一种方法:为程序传递参数5 root@guo-virtual-machine:~/debug# gdb --args factorial 5 第二种方法:为程序传递参数5 (gdb) run 5 方 ...
- css: position的使用;
position有四种模式: static, relative, position, fixed; 1.static(静态定位):默认值.没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中(忽略 top, bottom, ...
- 【转载】Qt之JSON生成与解析
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.它基于JavaScript(Standard ECMA-262 3rd Edition - December ...
- M1-Flask-Day2
内容概要: 1.flask - 蓝图 - 中间件 - 闪现 2.扩展 - session - wtfrom 3.上下文管理 - local-threading 4.websocket - 轮训 - 长 ...
- python自动化开发-[第十六天]-bootstrap和django
今日概要: 1.bootstrap使用 2.栅格系统 3.orm简介 4.路由系统 5.mvc和mtv模式 6.django框架 1.bootstrap的引用方式 1.Bootstrap 专门构建了免 ...
- poi读取写入word【未完,待续】
, [项目实战]Java POI之Word导出经典案例一 Java POI 读取word文件 POI-对于WORD的操作(一)
- Gerrit的安装和使用说明
Gerrit安装和使用说明 搞了几天,资料也查了不少,终于磨出来了.有什么不对的地方,大家及时提出来...,开始吧 系统 Centos6.5 x64 内存 2G 硬盘 20G 数据库 Mysql5.1 ...
- 原生JavaScript运动功能系列(四):多物体多值链式运动
原生JavaScript运动功能系列(一):运动功能剖析与匀速运动实现 原生JavaScript运动功能系列(二):缓冲运动 原生JavaScript运动功能系列(三):多物体多值运动 多物体多值链式 ...
