1、自动化运维之SaltStack实践
自动化运维之SaltStack实践
| linux-node1(master服务端) | 192.168.0.15 |
| linux-node2(minion客户端) | 192.168.0.16 |
| Local | 本地 |
| Master/Minion | 传统运行方式(server端跟agent端) |
| Salt SSH | SSH |
[root@linux-node1 yum.repos.d]# ping linux-node1.zhurui.comPING linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15)56(84) bytes of data.64 bytes from linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15): icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.087 ms64 bytes from linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15): icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.060 ms64 bytes from linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15): icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.053 ms64 bytes from linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15): icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.060 ms64 bytes from linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15): icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.053 ms64 bytes from linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15): icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.052 ms64 bytes from linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15): icmp_seq=7 ttl=64 time=0.214 ms64 bytes from linux-node1.zhurui.com (192.168.0.15): icmp_seq=8 ttl=64 time=0.061 ms

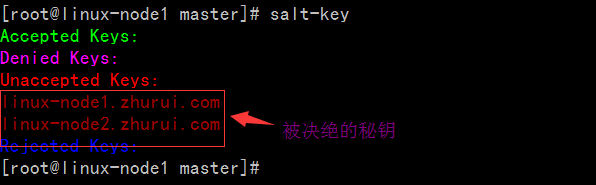
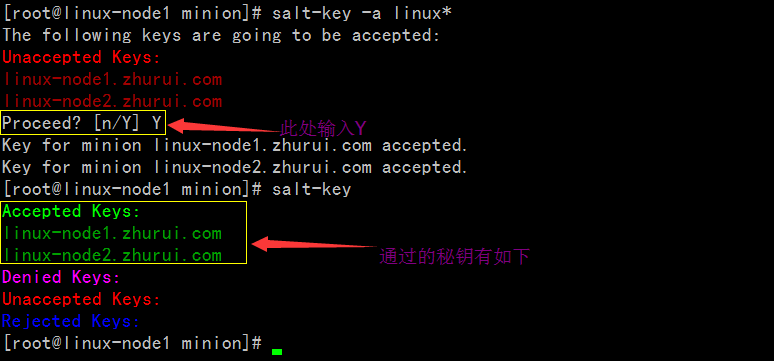
[root@linux-node1 minion]# salt-key -a linux*The following keys are going to be accepted:UnacceptedKeys:linux-node1.zhurui.comlinux-node2.zhurui.comProceed?[n/Y] YKeyfor minion linux-node1.zhurui.com accepted.Keyfor minion linux-node2.zhurui.com accepted.[root@linux-node1 minion]# salt-keyAcceptedKeys:linux-node1.zhurui.comlinux-node2.zhurui.comDeniedKeys:UnacceptedKeys:RejectedKeys:
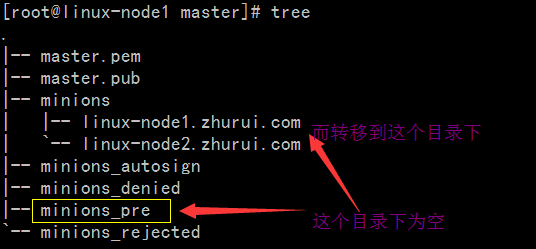

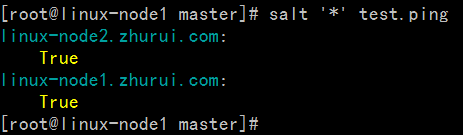




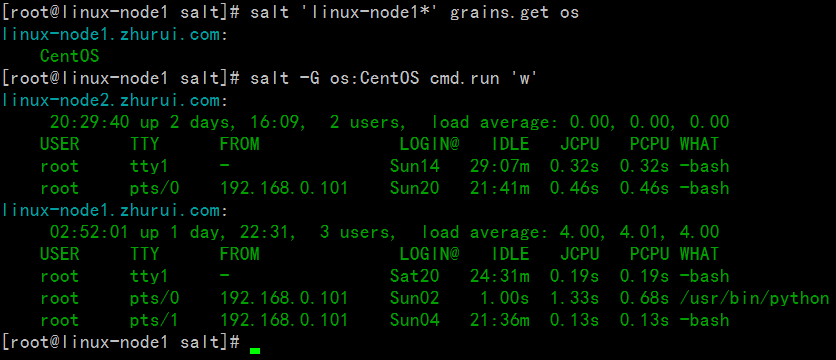
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt '*' state.sls apachelinux-node2.zhurui.com:----------ID: apache-installFunction: pkg.installedName: httpdResult:TrueComment:Package httpd is already installed.Started:22:38:52.954973Duration:1102.909 msChanges:----------ID: apache-installFunction: pkg.installedName: httpd-develResult:TrueComment:Package httpd-devel is already installed.Started:22:38:54.058190Duration:0.629 msChanges:----------ID: apache-serviceFunction: service.runningName: httpdResult:TrueComment:Service httpd has been enabled, and is runningStarted:22:38:54.059569Duration:1630.938 msChanges:----------httpd:TrueSummary------------Succeeded:3(changed=1)Failed:0------------Total states run:3linux-node1.zhurui.com:----------ID: apache-installFunction: pkg.installedName: httpdResult:TrueComment:Package httpd is already installed.Started:05:01:17.491217Duration:1305.282 msChanges:----------ID: apache-installFunction: pkg.installedName: httpd-develResult:TrueComment:Package httpd-devel is already installed.Started:05:01:18.796746Duration:0.64 msChanges:----------ID: apache-serviceFunction: service.runningName: httpdResult:TrueComment:Service httpd has been enabled, and is runningStarted:05:01:18.798131Duration:1719.618 msChanges:----------httpd:TrueSummary------------Succeeded:3(changed=1)Failed:0------------Total states run:3[root@linux-node1 salt]#
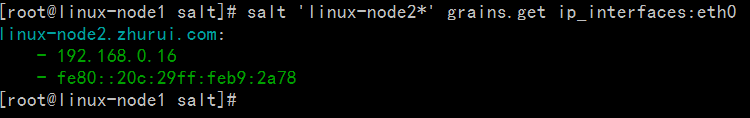
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node1*' grains.lslinux-node1.zhurui.com:-SSDs- biosreleasedate- biosversion- cpu_flags- cpu_model- cpuarch- domain- fqdn- fqdn_ip4- fqdn_ip6- gpus- host- hwaddr_interfaces- id- init- ip4_interfaces- ip6_interfaces- ip_interfaces- ipv4- ipv6- kernel- kernelrelease- locale_info- localhost- lsb_distrib_codename- lsb_distrib_id- lsb_distrib_release- machine_id- manufacturer- master- mdadm- mem_total- nodename- num_cpus- num_gpus- os- os_family- osarch- oscodename- osfinger- osfullname- osmajorrelease- osrelease- osrelease_info- path- productname- ps- pythonexecutable- pythonpath- pythonversion- saltpath- saltversion- saltversioninfo- selinux- serialnumber- server_id- shell- virtual- zmqversion[root@linux-node1 salt]#
[root@linux-node1 salt]# salt 'linux-node1*' grains.itemslinux-node1.zhurui.com:----------SSDs:biosreleasedate:07/31/2013biosversion:6.00cpu_flags:- fpu- vme- de- pse- tsc- msr- pae- mce- cx8- apic- sep- mtrr- pge- mca- cmov- pat- pse36- clflush- dts- mmx- fxsr- sse- sse2- ss- syscall- nx- rdtscp- lm- constant_tsc- up- arch_perfmon- pebs- bts- xtopology- tsc_reliable- nonstop_tsc- aperfmperf- unfair_spinlock- pni- ssse3- cx16- sse4_1- sse4_2- x2apic- popcnt- hypervisor- lahf_lm- arat- dtscpu_model:Intel(R)Core(TM) i3 CPU M 380@2.53GHzcpuarch:x86_64domain:zhurui.comfqdn:linux-node1.zhurui.comfqdn_ip4:-192.168.0.15fqdn_ip6:gpus:|_----------model:SVGA II Adaptervendor:unknownhost:linux-node1hwaddr_interfaces:----------eth0:00:0c:29:fc:ba:90lo:00:00:00:00:00:00id:linux-node1.zhurui.cominit:upstartip4_interfaces:----------eth0:-192.168.0.15lo:-127.0.0.1ip6_interfaces:----------eth0:- fe80::20c:29ff:fefc:ba90lo:-::1ip_interfaces:----------eth0:-192.168.0.15- fe80::20c:29ff:fefc:ba90lo:-127.0.0.1-::1ipv4:-127.0.0.1-192.168.0.15ipv6:-::1- fe80::20c:29ff:fefc:ba90kernel:Linuxkernelrelease:2.6.32-573.el6.x86_64locale_info:----------defaultencoding:UTF8defaultlanguage:en_USdetectedencoding:UTF-8localhost:linux-node1.zhurui.comlsb_distrib_codename:Finallsb_distrib_id:CentOSlsb_distrib_release:6.7machine_id:da5383e82ce4b8d8a76b5a3e00000010manufacturer:VMware,Inc.master:192.168.0.15mdadm:mem_total:556nodename:linux-node1.zhurui.comnum_cpus:1num_gpus:1os:CentOSos_family:RedHatosarch:x86_64oscodename:Finalosfinger:CentOS-6osfullname:CentOSosmajorrelease:6osrelease:6.7osrelease_info:-6-7path:/sbin:/usr/sbin:/bin:/usr/binproductname:VMwareVirtualPlatformps:ps -efHpythonexecutable:/usr/bin/python2.6pythonpath:-/usr/bin-/usr/lib64/python26.zip-/usr/lib64/python2.6-/usr/lib64/python2.6/plat-linux2-/usr/lib64/python2.6/lib-tk-/usr/lib64/python2.6/lib-old-/usr/lib64/python2.6/lib-dynload-/usr/lib64/python2.6/site-packages-/usr/lib64/python2.6/site-packages/gtk-2.0-/usr/lib/python2.6/site-packagespythonversion:-2-6-6- final-0saltpath:/usr/lib/python2.6/site-packages/saltsaltversion:2015.5.10saltversioninfo:-2015-5-10-0selinux:----------enabled:Trueenforced:Permissiveserialnumber:VMware-564d8f43912d3a99-eb c4 3b a9 34 fc ba 90server_id:295577080shell:/bin/bashvirtual:VMwarezmqversion:3.2.5
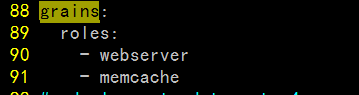
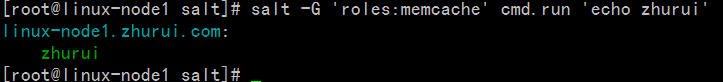








| 名称 | 存储位置 | 数据类型 | 数据采集更新方式 | 应用 |
| Grains | minion端 | 静态数据 | minion启动时收集,也可以使用saltutil.sync_grains进行刷新。 | 存储minion基本数据,比如用于匹配minion,自身数据可以用来做资产管理等。 |
| Pillar | master端 | 动态数据 | 在master端定义,指定给对应的minion,可以使用saltutil.refresh_pillar刷新 | 存储Master指定的数据,只有指定的minion可以看到,用于敏感数据保存。 |
1、自动化运维之SaltStack实践的更多相关文章
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑧SaltStack实践配置管理安装nginx-1.10.3
saltstack自动化运维系列⑧SaltStack实践配置管理安装nginx-1.10.3 安装nginx-1.10.3.tar.gz # mkdir -p /srv/salt/prod/pkg / ...
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑦SaltStack实践配置管理安装zabbix
saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践配置管理安装zabbix 1.添加管理zabbix的sls文件# vim /srv/salt/base/init/zabbix_agent.sl ...
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践安装配置HAproxy的Keepalived
saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践安装配置HAproxy的Keepalived 安装配置Keepalived 1.编写功能模块 #创建keepalived目录# mkdir -p ...
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践安装配置HAproxy
saltstack自动化运维系列⑥SaltStack实践安装配置HAproxy 下载haproxy1.6.2.tar.gz下载地址:http://www.haproxy.org/download/1. ...
- 自动化运维之SaltStack实践
自动化运维之SaltStack实践 1.1.环境 linux-node1(master服务端) 192.168.0.15 linux-node2(minion客户端) 192.168.0.16 1.2 ...
- 自动化运维之Saltstack
第三十八课 自动化运维之Saltstack 目录 一.自动化运维介绍 二. saltstack安装 三. 启动saltstack服务 四. saltstack配置认证 五. saltstack远程执行 ...
- saltstack自动化运维系列⑩SaltStack二次开发初探
saltstack自动化运维系列⑩SaltStack二次开发初探 1.当salt运行在公网或者网络环境较差的条件下,需要配置timeout时间vim /etc/salt/master timeout: ...
- 自动化运维工具 SaltStack 搭建
原文地址:https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-devops-saltstack-in-cloud/index.html#N10072 ...
- 自动化运维工具SaltStack详细部署【转】
==========================================================================================一.基础介绍==== ...
随机推荐
- C++相关:动态内存和智能指针
前言 在C++中,动态内存的管理是通过运算符new和delete来完成的.但使用动态内存很容易出现问题,因为确保在正确的时间释放内存是及其困难的.有时候我们会忘记内存的的释放,这种情况下就会产生内存泄 ...
- Linux修改本机/etc/hosts的hostName
1.Linux修改本机别名/etc/hosts的hostName后经常不生效解决 Linux修改本机别名/etc/hosts的hostName后经常不生效, 比如我们/etc/hosts的内容如下: ...
- cmd登录系统用户
1. sqlplus /nolog 2. conn system/密码 as sysdba 或conn / as sysdba 或conn sys/密码 as sysdba 注:system系 ...
- 如何通俗的理解spring的控制反转、依赖注入、面向切面编程等等
之前一直不理解spring的一些基础特性是什么意思,虽然网上的解释也很多,但是由于我比较笨,就是看不懂,知道最近才稍微了解,下面就以通俗讲解的方式记录下来. 前言 假设我是一个没有开店经验的小老板,准 ...
- PAT1011:World Cup Betting
1011. World Cup Betting (20) 时间限制 400 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue Wit ...
- Spring的两种任务调度Scheduled和Async
Spring提供了两种后台任务的方法,分别是: 调度任务,@Schedule 异步任务,@Async 当然,使用这两个是有条件的,需要在spring应用的上下文中声明<task:annotati ...
- Android 超高仿微信图片选择器 图片该这么加载
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/39943731,本文出自:[张鸿洋的博客] 1.概述 关于手机图片加载器,在当今像 ...
- .Net Core版开源跨平台框架SkyMallCore
相互学习提升,有不足之处请指教!有需要急速开发的朋友可以拿来用哦! SkyMallCore 该项目目前放在github上,功能仍在完善,已Fork的园友已给了一些建议, 我会继续完善,并将开发过程遇到 ...
- python生产环境部署
Python部署web开发程序的几种方法 fastcgi ,通过flup模块来支持,在nginx里对应的配置指令是 fastcgi_pass http,nginx使用proxy_pass转发,这个要求 ...
- C++中“wchar_t* ”和“ char * ”之间的相互转换
把char*转换为wchar_t* 用stdlib.h中的mbstowcs_s函数,可以通过下面的例子了解其用法: char *CStr = "string to convert" ...
