【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(一)
前言:spring主要就是对bean进行管理,因此IOC容器的初始化过程非常重要,搞清楚其原理不管在实际生产或面试过程中都十分的有用。在【spring源码分析】准备工作中已经搭建好spring的环境,并利用xml配置形式对类进行了实例化。在test代码中有一个非常关键的类ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,在这个类中实现了IOC容器的初始化,因此我们从ClassPathXmlApplicationContext着手开始研究IOC的初始化过程。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类继承关系
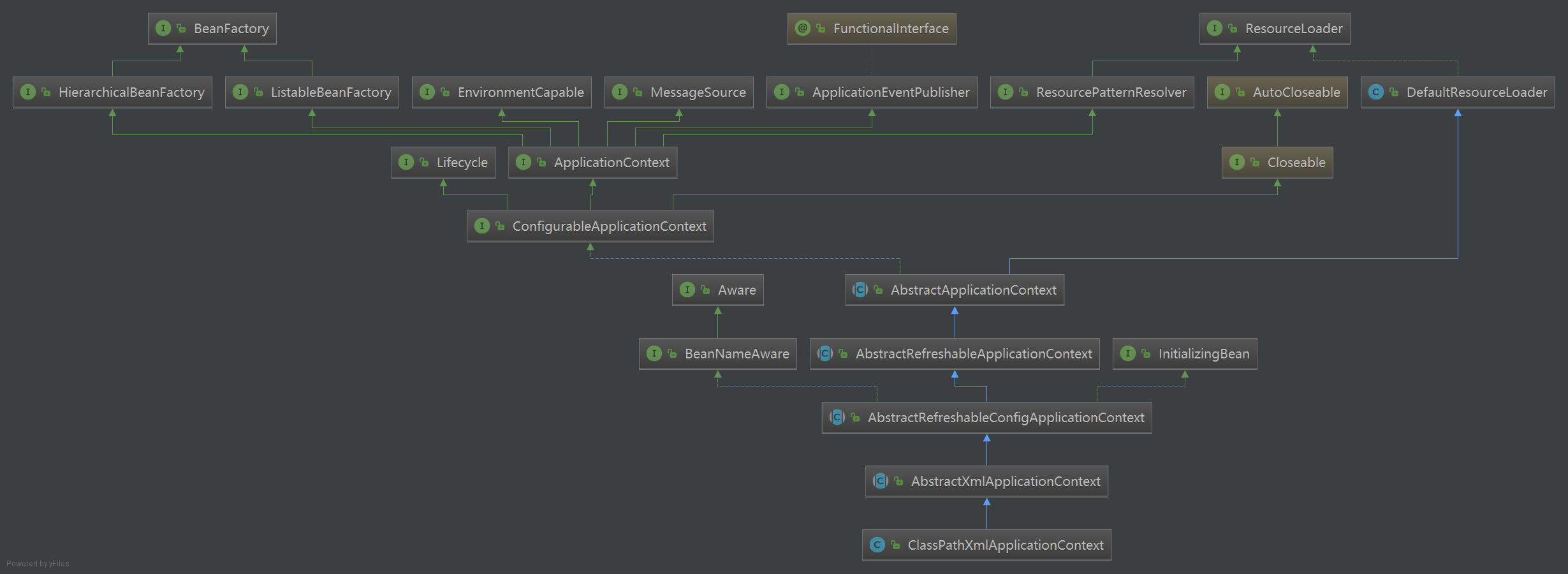
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext类的继承关系非常的庞大,在IOC容器初始化的过程中,经常使用委派的方式进行函数的调用,因此需特别注意类之间的继承关系。通过阅读源码,可粗略的将IOC容器初始化过程分为两步:
① 解析xml文件,导入bean
② 通过反射生成bean
因此下面将从这两大步对IOC初始化进行分析。
导入bean阶段程序调用链
首先给出导入bean的调用链:
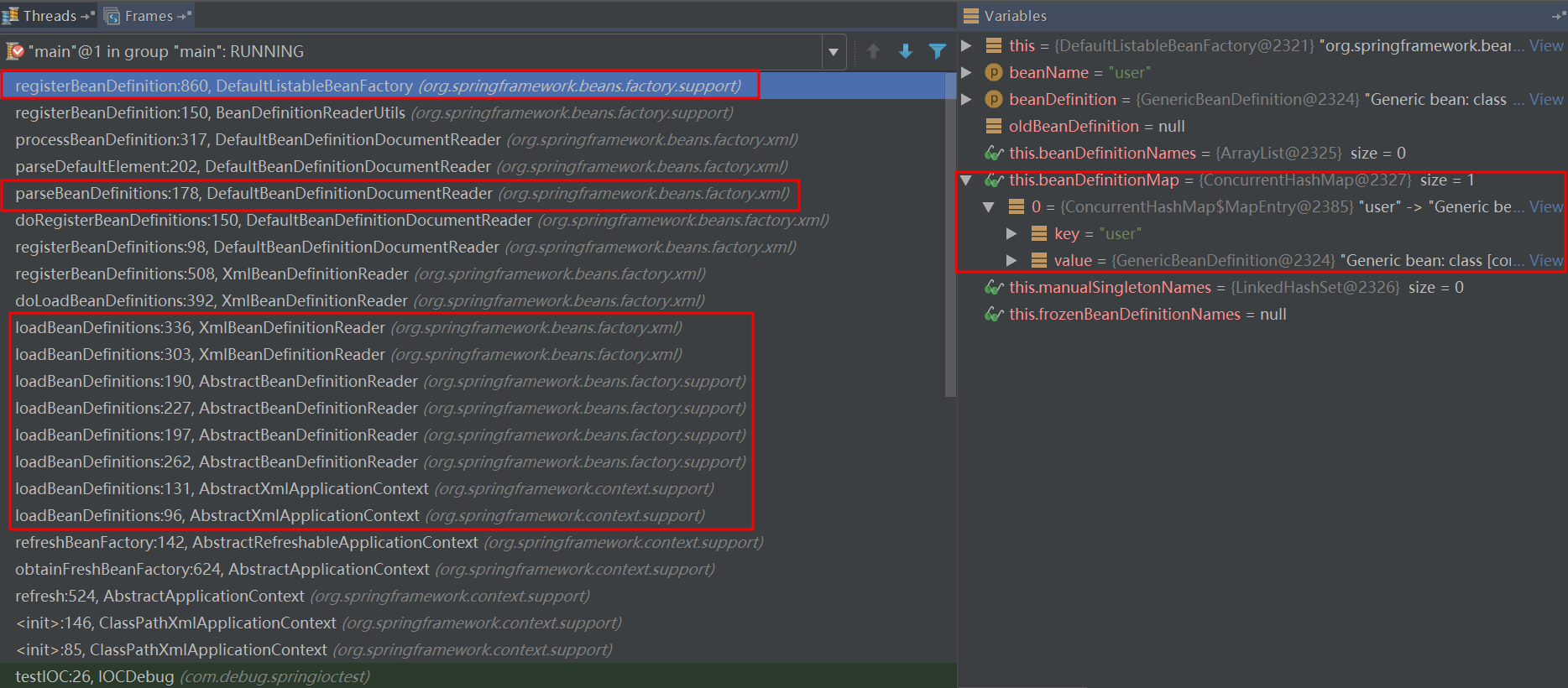
通过程序调用链可知:
#1.导入bean的过程大致分为三个阶段:
①导入bean(loadBeanDefinitions)
②解析bean(parseBeanDefinition)
③注册bean(registerBeanDefinition)
#2.最终bean是存储在beanDefinitionMap中:键为类名(beanName),值为GenericBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition)。
下面对导入bean的三个阶段进行分析。
导入bean阶段源码分析
首先来看ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造函数,具体代码如下:
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
// 初始化父类相关资源
super(parent);
// 解析配置文件路径,并设置资源路径
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
// 核心方法 ioc容器初始化在此方法中实现
refresh();
}
}
看似寥寥的几行代码,其实也非常重要,从这里我们可以了解到spring是如何解析配置文件中的占位符信息的,这里关注PropertyResolver接口。
首先我们看PropertyResolver接口源码:
public interface PropertyResolver {
/**
* 是否包含某个属性<br/>
* Return whether the given property key is available for resolution,
* i.e. if the value for the given key is not {@code null}.
*/
boolean containsProperty(String key);
/**
* 获取属性值 如果找不到则返回null<br/>
* Return the property value associated with the given key,
* or {@code null} if the key cannot be resolved.
*
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @see #getProperty(String, String)
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String)
*/
@Nullable
String getProperty(String key);
/**
* 获取属性值,如果找不到则返回默认值<br/>
* Return the property value associated with the given key, or
* {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved.
*
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String)
* @see #getProperty(String, Class)
*/
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
/**
* 获取指定类型的属性值,找不到则返回null<br/>
* Return the property value associated with the given key,
* or {@code null} if the key cannot be resolved.
*
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
@Nullable
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* 获取指定类型的属性值,找不到则返回默认值<br/>
* Return the property value associated with the given key,
* or {@code defaultValue} if the key cannot be resolved.
*
* @param key the property name to resolve
* @param targetType the expected type of the property value
* @param defaultValue the default value to return if no value is found
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
/**
* 获取属性值,找不到则抛出异常IllegalStateException<br/>
* Return the property value associated with the given key (never {@code null}).
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if the key cannot be resolved
* @see #getRequiredProperty(String, Class)
*/
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 获取指定类型的属性值,找不到则抛出异常IllegalStateException<br/>
* Return the property value associated with the given key, converted to the given
* targetType (never {@code null}).
*
* @throws IllegalStateException if the given key cannot be resolved
*/
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 替换文本中的占位符(${key})到属性值,找不到则不解析
* Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding
* property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with
* no default value are ignored and passed through unchanged.
*
* @param text the String to resolve
* @return the resolved String (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null}
* @see #resolveRequiredPlaceholders
* @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String)
*/
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
/**
* 替换文本中占位符(${key})到属性值,找不到则抛出异常IllegalArgumentException
* Resolve ${...} placeholders in the given text, replacing them with corresponding
* property values as resolved by {@link #getProperty}. Unresolvable placeholders with
* no default value will cause an IllegalArgumentException to be thrown.
*
* @return the resolved String (never {@code null})
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if given text is {@code null}
* or if any placeholders are unresolvable
* @see org.springframework.util.SystemPropertyUtils#resolvePlaceholders(String, boolean)
*/
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
该接口定义了一些与属性(解析占位符/获取属性)相关的方法,以ClassPathXmlApplicationContext构造函数的第7行代码为Debug入口,下面会通过调试的形式进行分析。
PropertyResolver继承关系如下,注意AbstractPropertyResolver与StandardEnvironment都间接的实现了PropertyResolver接口。
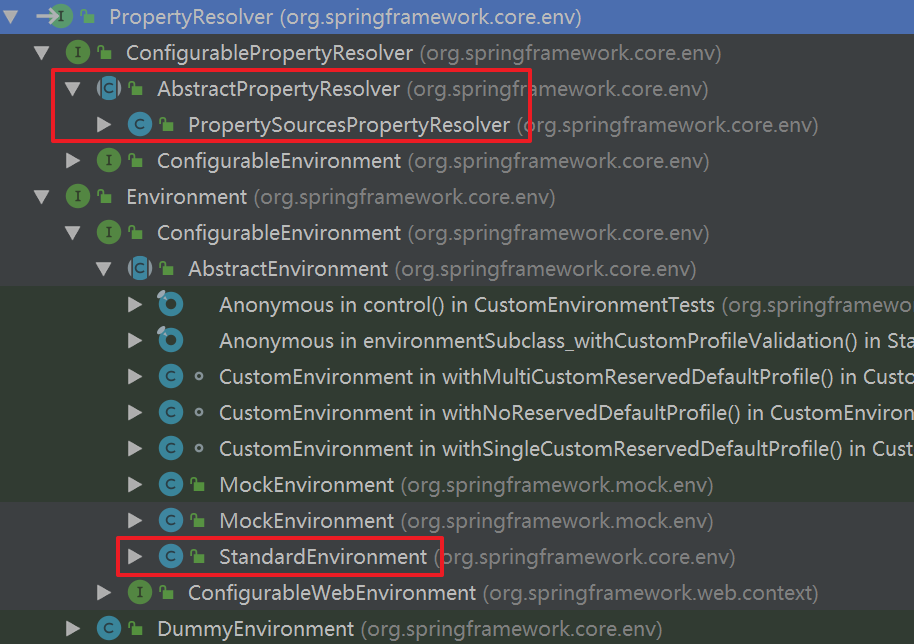
在setConfigLocations(String)打断点,进行Debug,会走到AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext#resolvePath处:
protected String resolvePath(String path) {
return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path);
}
这里getEnvironment()调用的是父类AbstractApplicationContext的方法:
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
// 创建一个ConfigurableEnvironment对象
this.environment = createEnvironment();
}
return this.environment;
}
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardEnvironment();
}
注意这里返回的是一个ConfigurableEnvironment 对象,继续debug,进入resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String)函数:
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver =new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
// 委派给AbstractPropertyResolver执行
return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
由于函数调用过程太细,所以这里给出解析配置文件中占位符的最终核心点:PropertyPlaceholderHelper#parseStringValue方法上:
protected String parseStringValue(
String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) { StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value);
// 获取前缀"${"的索引位置
int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
while (startIndex != -1) {
// 获取后缀"}"的索引位置
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
// 截取"${"和"}"中间的内容,即配置文件中对应的值
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions");
}
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key.
// 解析占位符键中包含的占位符,真正的值
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key...
// 从Properties中获取placeHolder对应的propVal
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
// 如果不存在
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
// 查询":"的位置
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
// 如果存在
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
// 截取":"前面部分的actualPlaceholder
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
// 截取":"后面的defaulValue
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
// 从Properties中获取actualPlaceholder对应的值
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
// 如果不存在,则返回defaultValue
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the
// previously resolved placeholder value.
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
// 忽略值
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in value \"" + value + "\"");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
}
// 返回propVal,就是替换之后的值
return result.toString();
}
分析:
该函数的主要作用就是取占位符"${}"或":"中的值进行赋值,比如在配置文件中直接使用xxx="${xxx.xx.xx}"或使用注解扫描时使用@Value("${xxx.xx.xx}")进行属性值注入的时候,都会走该函数进行解析。
接下来看非常重要的AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()函数:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
// 准备刷新上下文环境
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 创建并初始化BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
// 填充BeanFactory
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 提供子类覆盖的额外处理,即子类处理定义的BeanFactoryPostProcess
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 激活各种BeanFactory处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册拦截Bean创建的Bean处理器,即注册BeanPostProcessor
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 初始化上下文中的资源文件,如国际化文件的处理
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化上下文事件广播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 给子类扩展初始化其他bean
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 在所有bean中查找listener bean,然后注册到广播器中
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 初始化剩下的单例Bean(非延迟加载的)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 完成刷新过程,通知声明周期处理器lifecycleProcessor刷新过程,同时发出ContextRefreshEvent事件通知别人
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
// 销毁已经创建的bean
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
// 重置容器激活标签
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
分析:
该函数中进行了IOC容器的初始化工作,以该函数为切入点,进行相应源码的分析,一步一步来力求搞清楚。
AbstractApplicationContext#prepareRefresh()
protected void prepareRefresh() {
// Switch to active.
// 设置启动时间
this.startupDate = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 设置context当前状态
this.closed.set(false);
this.active.set(true);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Refreshing " + this);
} else {
logger.debug("Refreshing " + getDisplayName());
}
}
// Initialize any placeholder property sources in the context environment.
// 初始化context environment(上下文环境)中的占位符属性来源,该函数主要提供给子类进行扩展使用
initPropertySources();
// Validate that all properties marked as required are resolvable:
// see ConfigurablePropertyResolver#setRequiredProperties
// 对属性值进行必要的验证
getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();
// Store pre-refresh ApplicationListeners...
if (this.earlyApplicationListeners == null) {
this.earlyApplicationListeners = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.applicationListeners);
} else {
// Reset local application listeners to pre-refresh state.
this.applicationListeners.clear();
this.applicationListeners.addAll(this.earlyApplicationListeners);
}
// Allow for the collection of early ApplicationEvents,
// to be published once the multicaster is available...
this.earlyApplicationEvents = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
分析:
prepareRefresh()函数,作用较为简单,主要是做一些设置操作,这里不做过多赘述。
AbstractApplicationContext#obtainFreshBeanFactory()
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
// 刷新BeanFactory
refreshBeanFactory();
// 返回BeanFactory
return getBeanFactory();
}
分析:
该函数主要作用:创建并初始化BeanFactory。
这里简单介绍一下BeanFactory:它是一个基本的Bean容器,其中BeanDefinition是它的基本结构,BeanFactory内部维护了一个BeanDefinitionMap(要点),BeanFactory可根据BeanDefinition的描述进行bean的创建与管理。
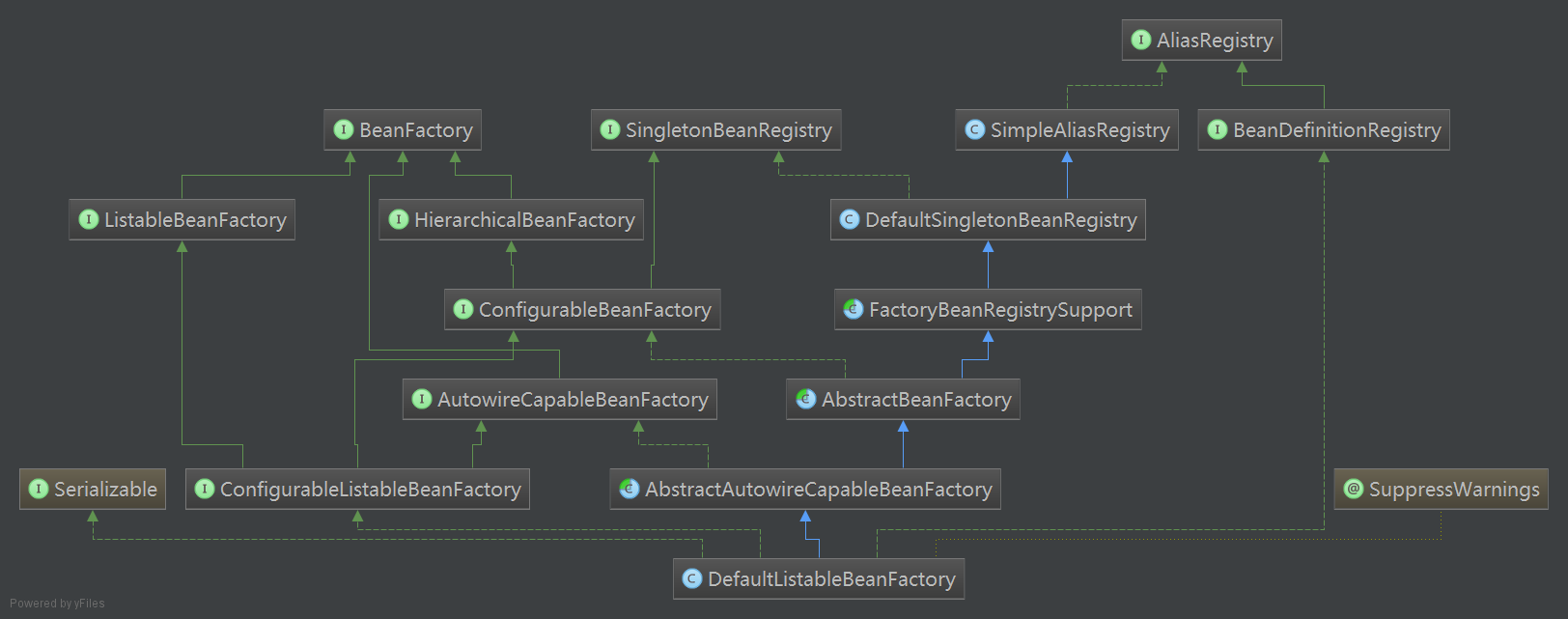
注:DefaultListableBeanFactory为最终默认实现,它实现了所有接口。
进入AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext#refreshBeanFactory()函数
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
// 若已有BeanFactory,则销毁bean,并销毁BeanFactory
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 创建BeanFactory对象
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
// 指定序列化编号
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 定制BeanFactory 设置相关属性
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 加载BeanDefinition
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
// 设置Context的BeanFactory
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
分析:
相应代码已经给出了基本注释,这里我们主要关注第16行代码:loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory),从该函数可引申非常多重要的知识点,介于篇幅原因,将在后面进行详细分析。
总结
这里再次总结本文重点:
- PropertyResolver,以及引申出来的PropertyPlaceholderHelper#parseStringValue(占位符解析重要函数)与日常开发也息息相关。
- BeanFactory以及其最终实现类DefaultListableBeanFactory,基础的IoC容器,提供与bean相关的方法。
- loadBeanDefinitions方法,这里再次强调一下,该方法非常重要。
by Shawn Chen,2018.11.24日,晚。
【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(一)的更多相关文章
- SPRING源码分析:IOC容器
在Spring中,最基本的IOC容器接口是BeanFactory - 这个接口为具体的IOC容器的实现作了最基本的功能规定 - 不管怎么着,作为IOC容器,这些接口你必须要满足应用程序的最基本要求: ...
- Spring源码解析-ioc容器的设计
Spring源码解析-ioc容器的设计 1 IoC容器系列的设计:BeanFactory和ApplicatioContext 在Spring容器中,主要分为两个主要的容器系列,一个是实现BeanFac ...
- spring源码分析---IOC(1)
我们都知道spring有2个最重要的概念,IOC(控制反转)和AOP(依赖注入).今天我就分享一下spring源码的IOC. IOC的定义:直观的来说,就是由spring来负责控制对象的生命周期和对象 ...
- spring 源码之 ioc 容器的初始化和注入简图
IoC最核心就是两个过程:IoC容器初始化和IoC依赖注入,下面通过简单的图示来表述其中的关键过程:
- Spring源码阅读-IoC容器解析
目录 Spring IoC容器 ApplicationContext设计解析 BeanFactory ListableBeanFactory HierarchicalBeanFactory Messa ...
- Spring 源码剖析IOC容器(一)概览
目录 一.容器概述 二.核心类源码解读 三.模拟容器获取Bean ======================= 一.容器概述 spring IOC控制反转,又称为DI依赖注入:大体是先初始化bean ...
- Spring源码解析-IOC容器的实现
1.IOC容器是什么? IOC(Inversion of Control)控制反转:本来是由应用程序管理的对象之间的依赖关系,现在交给了容器管理,这就叫控制反转,即交给了IOC容器,Spring的IO ...
- Spring源码解析-IOC容器的实现-ApplicationContext
上面我们已经知道了IOC的建立的基本步骤了,我们就可以用编码的方式和IOC容器进行建立过程了.其实Spring已经为我们提供了很多实现,想必上面的简单扩展,如XMLBeanFacroty等.我们一般是 ...
- Spring源码之IOC容器创建、BeanDefinition加载和注册和IOC容器依赖注入
总结 在SpringApplication#createApplicationContext()执行时创建IOC容器,默认DefaultListableBeanFactory 在AbstractApp ...
- 【spring源码分析】IOC容器初始化(总结)
前言:在经过前面十二篇文章的分析,对bean的加载流程大致梳理清楚了.因为内容过多,因此需要进行一个小总结. 经过前面十二篇文章的漫长分析,终于将xml配置文件中的bean,转换成我们实际所需要的真正 ...
随机推荐
- gittalk报错Error
最近通过github和jekyll搭了一个博客,申请使用了gittalk的评论. 但是博客的页面一直报Error:Not found,如下 发现是gittalk中的信息填写错了,name随便写:Hom ...
- mapbox.gl源码解析——基本架构与数据渲染流程
加载地图 Mapbox GL JS是一个JavaScript库,使用WebGL渲染交互式矢量瓦片地图和栅格瓦片地图.WebGL渲染意味着高性能,MapboxGL能够渲染大量的地图要素,拥有流畅的交互以 ...
- 【Python实践-1】求一元二次方程的两个解
知识点: import sys, sys模块包含了与Python解释器和它的环境有关的函数. “sys”是“system”的缩写.sys.exit() 中途退出程序, (注:0是正常退出,其他为不正常 ...
- python列表的交、并、差集
#!/usr/bin/env python3 l1 = ['] l2 = ['] # 交集 result1 = [i for i in l1 if i in l2] result2 = list(se ...
- .NET Core微服务之基于Apollo实现统一配置中心
Tip: 此篇已加入.NET Core微服务基础系列文章索引 一.关于统一配置中心与Apollo 在微服务架构环境中,项目中配置文件比较繁杂,而且不同环境的不同配置修改相对频繁,每次发布都需要对应修改 ...
- Vue2.0源码阅读笔记(二):响应式原理
Vue是数据驱动的框架,在修改数据时,视图会进行更新.数据响应式系统使得状态管理变的简单直接,在开发过程中减少与DOM元素的接触.而深入学习其中的原理十分有必要,能够回避一些常见的问题,使开发变的 ...
- Ocelot-基于.NET Core的开源网关实现
写在前面 API网关是系统内部服务暴露在外部的一个访问入口,类似于代理服务器,就像一个公司的门卫承担着寻址.限制进入.安全检查.位置引导等工作,我们可以形象的用下图来表示: 外部设备需要访问内部系统服 ...
- [翻译]在Windows版或MacOS版的Microsoft Edge上安装一个谷歌浏览器拓展
原文:Install a Chrome Web Store extension on Microsoft Edge for Windows and MacOS 拓展阅读:What to expect ...
- EasyUI 使用tabs切换后datagrid显示不了内容
今天刚遇到这个问题,找了下各群的深度合作伙伴,没有好的答案,那就自己研究吧. 问题点在于打开tab1时,快速切到tab2,这时tab1的datagrid渲染未完成,再次回到tab1,因为是在不可见区域 ...
- Eclipse设置全局用户名
-Duser.name=你的名字
