scala(二) Future执行逻辑解读
在scala中是没有原生线程的,其底层使用的是java的Thread机制。但是在scala中对java Thread进行了封装,实现了更便于操作线程的Future。
官方文档: Futures provide a way to reason about performing many operations in parallel– in an efficient and non-blocking way.
在使用的时候只需要通过object Future 的apply方法传入执行体即可启动,那么future是如何开始运行的呢?又是如何把运行体加入到线程的执行体中的呢?其底层运行机制又是什么呢?下面就逐步看一下。
先看一段代码.注意在代码中导入的global,其类型为global: ExecutionContext,这里暂时不进行解释,留意一下后面会用到。
package zpj.future import org.scalatest.FunSuite import scala.concurrent.Future
import scala.concurrent.ExecutionContext.Implicits.global /**
* Created by PerkinsZhu on 2018/3/18 11:34
**/
class Test extends FunSuite { test("future demo 1") {
Future {
println("hello world !!!")
}
sleep
} val sleep = Thread.sleep(1000)
}
直接运行代码会打印出“hello world !!!”。我们知道,如果使用java的Thread,则必须调用.start()方法来启动线程的运行,可是在这里我们并没有主动触发start()方法,而线程体却执行了。下面进入源码中看一下。在这之前注意打开idea的Structure窗口,留意每个方法是属于哪个class、object或者trait中。这样便于理解整个Future 的结构关系。
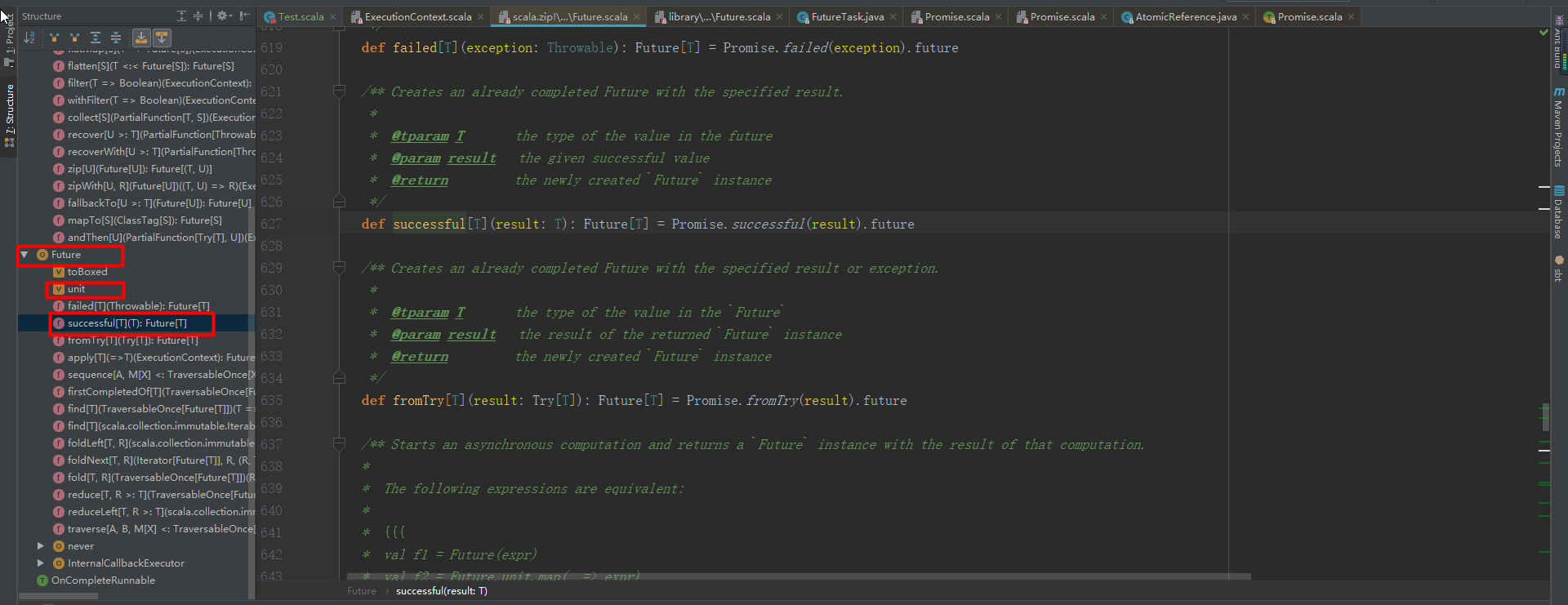
进入Future.apply()函数:
def apply[T](body: =>T)(implicit @deprecatedName('execctx) executor: ExecutionContext): Future[T] =
unit.map(_ => body)
可以看到在body便是传入的线程体,在这里使用unit调用了map方法,那么这个unit又是什么呢?
/** A Future which is always completed with the Unit value.
*/
val unit: Future[Unit] = successful(())
一个值为unit 的已完成future。这里调用的successful(())函数。注意传入的() ,这个就是该future的值:Unit 。可以看一下()的类型:
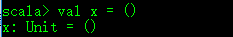
很明显()就是上面注释所说的 Unit value.
继续我们进入successful(())看一下是怎么实现的:
/** Creates an already completed Future with the specified result.
*
* @tparam T the type of the value in the future
* @param result the given successful value
* @return the newly created `Future` instance
*/
def successful[T](result: T): Future[T] = Promise.successful(result).future
先看一下参数部分,result:T,还记得上面传入的()吗,在这里便赋值给result。那么后面的Promise.successful(result).future
又是什么意思呢?我们先看前半部分Promise.successful(result),这里调用的是Promise的succeful(),进入看一下:
/** Creates an already completed Promise with the specified result.
*
* @tparam T the type of the value in the promise
* @return the newly created `Promise` object
*/
def successful[T](result: T): Promise[T] = fromTry(Success(result))
到这里看到Success(result)大概就明白了,这就是用来构建future的结果值,其结果便是Success(()) 。【疑问1】同时注意一下这里返回的结果类型为Promise[T],而其调用出接收的却是Future,这两处是如何对接的呢?我们暂时放一下,先看下面。那fromTry又是做什么呢?
/** Creates an already completed Promise with the specified result or exception.
*
* @tparam T the type of the value in the promise
* @return the newly created `Promise` object
*/
def fromTry[T](result: Try[T]): Promise[T] = impl.Promise.KeptPromise[T](result)
这里通过KeptPromise创建了一个Promise的实例,继续进入KeptPromise.apply():
def apply[T](result: Try[T]): scala.concurrent.Promise[T] =
resolveTry(result) match {
case s @ Success(_) => new Successful(s)
case f @ Failure(_) => new Failed(f)
}
1、注意这里的Successful(s)和Failed(f),这两个是继承了Promise的私有类,看一下这里的继承结构:
private[this] sealed trait Kept[T] extends Promise[T]
private[this] final class Successful[T](val result: Success[T]) extends Kept[T]
private[this] final class Failed[T](val result: Failure[T]) extends Kept[T]
2、resolveTry是对result进行进一步处理,判断result是否失败,并解析出其Exception,只是对future中的结果做一个细分化。
private def resolveTry[T](source: Try[T]): Try[T] = source match {
case Failure(t) => resolver(t)
case _ => source
}
private def resolver[T](throwable: Throwable): Try[T] = throwable match {
case t: scala.runtime.NonLocalReturnControl[_] => Success(t.value.asInstanceOf[T])
case t: scala.util.control.ControlThrowable => Failure(new ExecutionException("Boxed ControlThrowable", t))
case t: InterruptedException => Failure(new ExecutionException("Boxed InterruptedException", t))
case e: Error => Failure(new ExecutionException("Boxed Error", e))
case t => Failure(t)
}
走到这里,就明白了Promise.successful(result).future中的 前半部分的执行机。还记得上面抛出的一个疑问吗?这里就对【疑问1】解释一下。
def successful[T](result: T): Future[T] = Promise.successful(result).future接收的是Future,而Promise.successful(result)返回的是一个Promise,这两个类型怎么对接呢?后面调用了future ,我们进入看一下
trait Promise[T] {
def future: Future[T]
...
...
该函数是定义在特质scala.concurrent.Promise中的一个抽象函数(注意这里的包路径)。上面我们知道Promise.successful(result)返回的是一个Successful,那么future应该会在Successful中进行实现了:
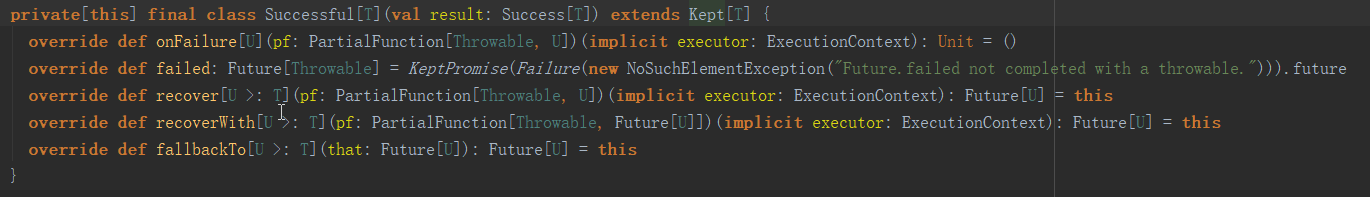
进去之后发现并没有,那么会不会在其父类中实现了呢?我们继续进入Kept看看:

发现Kept中也没有,那么久继续向上找,private[this] sealed trait Kept[T] extends Promise[T],(注意这里的Promise是scala.concurrent.impl中的Promise,不是刚才的scala.concurrent.Promis)这里我们进入scala.concurrent.Promise看一下:
private[concurrent] trait Promise[T] extends scala.concurrent.Promise[T] with scala.concurrent.Future[T] {
def future: this.type = this
会发现在 scala.concurrent.impl.Promise[T] extends scala.concurrent.Promise[T],且两者都是特质(注意区分这两个Promise)。在下面可以看到 future 在这里被实现了def future: this.type = this。对于这里该如何理解呢?
future返回的结果应该是Future[T]类型的,那么这里的this.type 应该就是Promise类型,而this就应该是上面的Successful(())。这里可能有些不太容易理解,事实上 scala.concurrent.impl.Promise继承了Promise 混合了Future ,注意看上面的继承关系:
private[concurrent] trait Promise[T] extends scala.concurrent.Promise[T] with scala.concurrent.Future[T]
这里的with混合了scala.concurrent.Future特质,通过def future: this.type = this把Promise类型转化为Future返回给了调用处。
走到这里unit的构建就清晰了,其实质就是一个已经完成了的Future
回到Future.apply()方法中,unit就明白了其构建过程,而对于map呢?该如何理解?
def apply[T](body: =>T)(implicit @deprecatedName('execctx) executor: ExecutionContext): Future[T] =
unit.map(_ => body)
继续进入map的实现源码:
def map[S](f: T => S)(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S] = transform(_ map f)
def transform[S](f: Try[T] => Try[S])(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S]
一路跟进来之后会进入scala.concurrent.Future#transform的抽象方法中。上面我们知道这里的unit是scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Successful的实例,根据上面的经验一层一层的向上找transform的实现位置,会发现在scala.concurrent.impl.Promise#transform中进行了实现。看一下这里的实现代码:
override def transform[S](f: Try[T] => Try[S])(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S] = {
val p = new DefaultPromise[S]()
onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) }
p.future
}
在这里我们逐一分析一下这三行代码:
1、val p = new DefaultPromise[S]()。创建了 一个scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.DefaultPromise实例,进入DefaultPromise的构造器中看一下:
class DefaultPromise[T] extends AtomicReference[AnyRef](Nil) with Promise[T]
会发现DefaultPromise依旧混合了scala.concurrent.impl.Promise特质,同时还继承了java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference且向其构造器中传入了Nil空列表。这里先挂起,分析第二行代码。
2、onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) },在理解这行代码的时候需要注意scala的参数类型,明确其传入的是函数还是参数值。
我们进入onComplete 发现是一个scala.concurrent.Future#onComplete的抽象方法。那么找到其实现处:scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Kept#onComplete,看一下源码:
override def onComplete[U](func: Try[T] => U)(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Unit =
(new CallbackRunnable(executor.prepare(), func)).executeWithValue(result)
这里终于看到开启线程的代码了,每个future开启一个线程的代码应该就是这里了。
注意这里new CallbackRunnable(executor.prepare(), func)) 传入的对象 executor,和func,这里的executor是从上面一路带过来的(implicit executor: ExecutionContext),也就是我们上面刚开始导入的import scala.concurrent.ExecutionContext.Implicits.global;在看func,回溯上面会发现func就是scala.concurrent.Promise#complete方法,根据名字可以指定是在Future 完成之后的回调,接收的参数就是Future.apply()的函数体。
进入scala.concurrent.impl.CallbackRunnable看一起源码:
private final class CallbackRunnable[T](val executor: ExecutionContext, val onComplete: Try[T] => Any) extends Runnable with OnCompleteRunnable {
// must be filled in before running it
var value: Try[T] = null
override def run() = {
require(value ne null) // must set value to non-null before running!
try onComplete(value) catch { case NonFatal(e) => executor reportFailure e }
}
def executeWithValue(v: Try[T]): Unit = {
require(value eq null) // can't complete it twice
value = v
// Note that we cannot prepare the ExecutionContext at this point, since we might
// already be running on a different thread!
try executor.execute(this) catch { case NonFatal(t) => executor reportFailure t }
}
}
注意如下几点:
1、继承关系可以发现CallbackRunnable是java.lang.Runnable的实现类,因此其实一个可以在java Threa中运行的线程。 CallbackRunnable[T](val executor: ExecutionContext, val onComplete: Try[T] => Any) extends Runnable
2、注意其构造器参数,executor是一个全局线程池,onComplete: Try[T] => Any是一个函数。函数是可以调用的代码块,可以传参的(理解scala的函数式编程)。
3、注意其run方法中执行的代码块,其中是调用了onComplete的,且传入的结果是一个Value。
4、注意executeWithValue的参数v,其把v赋值给Value。赋值之后调用了 executor.execute(this);该命令再熟悉不过了,调用线程池执行线程,这里的this就是CallbackRunnable实例。
通过这四点可以明白:
scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Kept#onComplete 是在单独的线程中执行的,结合上面的 onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) }这块代码,发现onComplete执行的就是scala.concurrent.Promise#complete的代码逻辑。
再看一下scala.concurrent.impl.Promise#transform的源码:
override def transform[S](f: Try[T] => Try[S])(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S] = {
val p = new DefaultPromise[S]()
onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) }
p.future
}
注意这里面的参数类型,f: Try[T] => Try[S]是一个函数,然而注意这里: p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) ,看一下 p.complete()方法接收的参数类型是什么:
def complete(result: Try[T]): this.type =
if (tryComplete(result)) this else throw new IllegalStateException("Promise already completed.")
一个结果参数,不是一个函数。再看上面的f(result),其实质在调用f()函数,传入的参数就是result,然后计算出结果之后把结果值传入scala.concurrent.Promise#complete。仔细体会一下这里的调用逻辑。也就是说在调用scala.concurrent.Promise#complete之前f()函数已经进行了调用,这里的f()函数也就是Future.apply()的函数体。
汇总上面再理一下调用逻辑:
override def transform[S](f: Try[T] => Try[S])(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S] = {
val p = new DefaultPromise[S]()
onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) }
p.future
}
在onComplete ()中开启线程,并执行线程体。在线程执行过程中,调用p.complete()函数,而在调用p.complete()之前会触发f()函数的调用,这样便触发了Future.apply()的执行,于是便执行了 println("hello world !!!") 代码块。
因此Future.apply()中的代码块是在单独的一个线程中执行的,这便是scala 中Future自动开启线程执行代码块的机制。
这里不太容易理解的就是这个函数的调用时机。搞清楚Future是如何把Future.apply()代码块加载到java Thread中运行之后,Future的核心便易于理解了。
注意这里还有一个result的传入时机:
onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) }
这个result 是从哪里过来的呢?我们知道future是可以组合上一个future的结果的。例如:
Future { 10 }.map( _ + 10).map(_ * 10)
这里执行逻辑时机上是(10+10)* 10 结果就是200 ,那么这里的10如何传给第二个map函数的呢?又是如何把20传给第三个map函数的呢?
我们再看一下scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Kept#onComplete的实现源码:
override def onComplete[U](func: Try[T] => U)(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Unit =
(new CallbackRunnable(executor.prepare(), func)).executeWithValue(result)
注意这里的result,调用executeWithValue()之后会把该result赋值给scala.concurrent.impl.CallbackRunnable#value的参数,在run运行过程中,调用onComlete会把该继续把该result传给p.complete()
override def run() = {
require(value ne null) // must set value to non-null before running!
try onComplete(value) catch { case NonFatal(e) => executor reportFailure e }
}
override def transform[S](f: Try[T] => Try[S])(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S] = {
val p = new DefaultPromise[S]()
onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) }
p.future
}
这里的result便是线程run方法中传入的Value,那么在(new CallbackRunnable(executor.prepare(), func)).executeWithValue(result)这里的result又是哪里来的呢?
看一下onComplete的源码:
private[this] sealed trait Kept[T] extends Promise[T] {
def result: Try[T]
override def onComplete[U](func: Try[T] => U)(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Unit =
(new CallbackRunnable(executor.prepare(), func)).executeWithValue(result)
发现result是一个抽象值,那么我们就去找Kept的实现类scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Successful。看一下构造器:
private[this] final class Successful[T](val result: Success[T]) extends Kept[T]
在这里可以发现其实result是通过构造器传入的,那么是哪里调用构造器传入的呢?还记得我们看unit实现逻辑吗?其中有一部分这样的代码:
def apply[T](result: Try[T]): scala.concurrent.Promise[T] =
resolveTry(result) match {
case s @ Success(_) => new Successful(s)
case f @ Failure(_) => new Failed(f)
}
这里的S便是传入的result,而在构建unit的时候,这里的S是一个Unit值,这也是初始Future的值。
那么我们上面说的10、20分别是如何通过map传入的呢?
这里我们回想一下前面的unit,unit是通过scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Successful构造的,其混入的是scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Kept因此看下面
override def transform[S](f: Try[T] => Try[S])(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S] = {
val p = new DefaultPromise[S]()
onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) }
p.future
}
unit在调用transform的时候,执行的 onComplete 是scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Kept#onComplete。而看第三行返回的结果: p.future,也即是说第一个Future返回的对象是DefaultPromise()实例的future。结合代码:
Future { 10 }.map( _ + 10).map(_ * 10)
这里返回的future是DefaultPromise()的future,所以调用map的也是DefaultPromise()的future。那么,进入map方法之后,我们会发现又进入了scala.concurrent.Future#transform
def transform[S](f: Try[T] => Try[S])(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S]
override def transform[S](f: Try[T] => Try[S])(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Future[S] = {
val p = new DefaultPromise[S]()
onComplete { result => p.complete(try f(result) catch { case NonFatal(t) => Failure(t) }) }
p.future
}
注意这里调用transform的不再是KeptPromise()了,而是DefaultPromise()的实例在调用。所以 在调用onComplete()的时候进入的就是scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.DefaultPromise#onComplete,而不再是scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.KeptPromise.Kept#onComplete了
下面看一下scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.DefaultPromise#onComplete的源码:
final def onComplete[U](func: Try[T] => U)(implicit executor: ExecutionContext): Unit =
dispatchOrAddCallback(new CallbackRunnable[T](executor.prepare(), func))
注意这里只是new 了一个CallbackRunnable,并没有启动。不启动的原因就是不确定上一个Future是否执行成功。可能需要等待,由此可以猜到dispatchOrAddCallback()的目的就是对调用者future进行判断和等待的逻辑。看一下scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.DefaultPromise#dispatchOrAddCallback的源码:
/** Tries to add the callback, if already completed, it dispatches the callback to be executed.
* Used by `onComplete()` to add callbacks to a promise and by `link()` to transfer callbacks
* to the root promise when linking two promises together.
*/
@tailrec
private def dispatchOrAddCallback(runnable: CallbackRunnable[T]): Unit = {
get() match {
case r: Try[_] => runnable.executeWithValue(r.asInstanceOf[Try[T]])
case dp: DefaultPromise[_] => compressedRoot(dp).dispatchOrAddCallback(runnable)
case listeners: List[_] => if (compareAndSet(listeners, runnable :: listeners)) ()
else dispatchOrAddCallback(runnable)
}
}
/**
* Gets the current value.
*
* @return the current value
*/
public final V get() {// 注意该方法的路径:java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference#get
return value;
}
注意如下几点:
1、scala.concurrent.impl.Promise.DefaultPromise#dispatchOrAddCallback是一个递归方法,注意注释@tailrec
2、case r: Try[_] 该分支说明调用者future已经结束,启动该future的线程,执行map中的操作。
3、为什么会调用的get()方法呢?因为DefaultPromise混入了AtomicReference:
class DefaultPromise[T] extends AtomicReference[AnyRef](Nil) with Promise[T]
注意这里传入的是Nil ,这也是为什么会有case listeners: List[_]分支的原因。
scala在进行debug的时候不像java那么方便,需要深入理解函数式编程的逻辑,函数的调用逻辑。
=========================================
=========================================
-------end
scala(二) Future执行逻辑解读的更多相关文章
- scala akka Future 顺序执行 sequential execution
对于 A => B => C 这种 future 之间的操作,akka 默认会自动的按照顺序执行,但对于数据库操作来说,我们希望几个操作顺序执行,就需要使用语法来声明 有两种声明 futu ...
- Scala之Future
一.简介 Future提供了一套高效便捷的非阻塞并行操作管理方案.其基本思想很简单,所谓Future,指的是一类占位符对象,用于指代某些尚未完成的计算的结果.一般来说,由Future指代的计算都是并行 ...
- ETL-kettle 核心执行逻辑
一.大数据下的ETL工具是否还使用Kettle kettle 作为通用的ETL工具,非常成熟,应用也很广泛,这里主要讲一下 目前我们如何使用kettle的? 在进行大数据处理时,ETL也是大数据处理的 ...
- defer、return、返回值,这三者的执行逻辑
defer.return.返回值,这三者的执行逻辑是: return 最先执行,return 负责将结果写入返回值中:接着defer执行,可能修改返回值:最后函数携带当前返回值退出.
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(二)之逻辑回归
Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记(二)之逻辑回归 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请指明转载地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/fydeblog/p/7364636.html 前言 ...
- 手把手带你阅读Mybatis源码(二)执行篇
前言 上一篇文章提到了MyBatis是如何构建配置类的,也说了MyBatis在运行过程中主要分为两个阶段,第一是构建,第二就是执行,所以这篇文章会带大家来了解一下MyBatis是如何从构建完毕,到执行 ...
- scala的trait执行报错: 错误: 找不到或无法加载主类 cn.itcast.scala.`trait`
scala的trait执行报错: 错误: 找不到或无法加载主类 cn.itcast.scala.`trait`.Children 原因:包名写成了trait,与trait关键字重名了: package ...
- Springboot中mybatis执行逻辑源码分析
Springboot中mybatis执行逻辑源码分析 在上一篇springboot整合mybatis源码分析已经讲了我们的Mapper接口,userMapper是通过MapperProxy实现的一个动 ...
- MySQL Update执行流程解读
GreatSQL社区原创内容未经授权不得随意使用,转载请联系小编并注明来源. 一.update跟踪执行配置 使用内部程序堆栈跟踪工具path_viewer,跟踪mysql update 一行数据的执行 ...
随机推荐
- 在 ASP.NET Core 项目中实现小写的路由URL
在 ASP.NET MVC 早期版本中,我们可以通过在应用的 RegisterRoutes 方法中设置 routes.LowercaseUrls = true ; 来将页面的 URL 链接转小写.在 ...
- Mysql根据指定字段的int值查出在当前列表的排名
先看表结构和数据: DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `ndb_record`; CREATE TABLE `ndb_record` ( `id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AU ...
- PHP封装的一个单例模式Mysql操作类
掌握满足单例模式的必要条件----三私一公. ①私有的构造方法-为了防止在类外使用new关键字实例化对象. ②私有的成员属性-为了防止在类外引入这个存放对象的属性. ③私有的克隆方法-为了防止在类外通 ...
- 关于C/S框架网单表绑定,查询
这种绑定暂时支持单表,并且不支持主键自增长!保存,删除,查看,修改用框架现成的. 1.先生成tb.bll.dal三个类.框架有生成工具,在debug文件里面有个叫CSFramework.Tools.C ...
- JS Cookie丢失问题
JS Cookie丢失问题 前些天有人问我vue中使用proxy发送请求,为什么请求时cookie丢失,首先说一下我对cookie的理解: 1.cookie在正常情况下是会在每次请求时自动携带, 2. ...
- react+react-router+react-redux+nodejs+mongodb项目
一个实际项目(OA系统)中的部分功能.这个demo中引入了数据库,数据库使用了mongodb.安装mongodb才能运行完整的功能.要看完整的项目可以移步我的github 技术栈 React v15. ...
- <CEPH中国-深圳站-技术交流会演讲PPT> YY云平台Ceph Block应用实践 & 我写的书 《CEPH实战》
YY云平台Ceph Block应用实践 http://s3.yyclouds.com/public/YY%E4%BA%91%E5%B9%B3%E5%8F%B0Ceph%E5%AE%9E%E8%B7%B ...
- 使用WinDbg内核调试
首先你要配置好测试环境:参考VMware+Windgb+Win7 内核驱动调试 在你的主机上配置Symbols 配置sympath,C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\first\objch ...
- 关于用wubi安装Ubuntu,总是提示“没有定义根文件系统”的问题
用diskgenius测试一下分区问题,就发现一些错误,所以怀疑可能就是因为这个分区参数错误导致WUBI安装不成功,费了大力气转移数据后,重新对硬盘分区,这里称赞一下diskgenius,的确不错,当 ...
- 引导加载程序之争: LILO 和 GRUB
在不考虑他们的工作或专业情况下,所有 Linux 用户都会使用的是哪个工具?引导加载程序.通过本文了解引导加载程序的工作原理,认识两个流行的引导加载程序 LILO(LInux LOader)和 GNU ...
