Java8新特性之三:Stream API
Java8的两个重大改变,一个是Lambda表达式,另一个就是本节要讲的Stream API表达式。Stream 是Java8中处理集合的关键抽象概念,它可以对集合进行非常复杂的查找、过滤、筛选等操作,在新版的JPA中,也已经加入了Stream。如:
@Query("select u from User u")
Stream<User> findAllByCustomQueryAndStream();
Stream<User> readAllByFirstnameNotNull();
@Query("select u from User u")
Stream<User> streamAllPaged(Pageable pageable);
Stream API给我们操作集合带来了强大的功用,同时Stream API操作简单,容易上手。
1、Stream的操作步骤
Stream有如下三个操作步骤:
一、创建Stream
从一个数据源,如集合、数组中获取流。
二、中间操作
一个操作的中间链,对数据源的数据进行操作。
三、终止操作
一个终止操作,执行中间操作链,并产生结果。
要注意的是,对流的操作完成后需要进行关闭操作(或者用JAVA7的try-with-resources)。
举个简单的例子:
假设有一个Person类和一个Person列表,现在有两个需求:1)找到年龄大于18岁的人并输出;2)找出所有中国人的数量。
@Data
class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String country;
private char sex; public Person(String name, Integer age, String country, char sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.country = country;
this.sex = sex;
}
}
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add(new Person("欧阳雪",18,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("Tom",24,"美国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("Harley",22,"英国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("向天笑",20,"中国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("李康",22,"中国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("小梅",20,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("何雪",21,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("李康",22,"中国",'M'));
在JDK8以前,我们可以通过遍历列表来完成。但是在有了Stream API后,可以这样来实现:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1)找到年龄大于18岁的人并输出;
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getAge() > 18).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
// 2)找出所有中国人的数量
long chinaPersonNum = personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getCountry().equals("中国")).count();
System.out.println("中国人有:" + chinaPersonNum + "个");
}
输出结果:
Person(name=Tom, age=24, country=美国, sex=M)
Person(name=Harley, age=22, country=英国, sex=F)
Person(name=向天笑, age=20, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=小梅, age=20, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=何雪, age=21, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
-------------------------------------------
中国人有:6
在这个例子中,personList.stream()是创建流,filter()属于中间操作,forEach、count()是终止操作。
2、Stream中间操作--筛选与切片
- filter:接收Lambda,从流中排除某些操作;
- limit:截断流,使其元素不超过给定对象
- skip(n):跳过元素,返回一个扔掉了前n个元素的流,若流中元素不足n个,则返回一个空流,与limit(n)互补
- distinct:筛选,通过流所生成元素的hashCode()和equals()去除重复元素。
2.1 limit举例
需求,从Person列表中取出两个女性。
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'F').limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
输出结果为:
Person(name=欧阳雪, age=18, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=Harley, age=22, country=英国, sex=F)
2.2 skip举例
从Person列表中从第2个女性开始,取出所有的女性。
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'F').skip(1).forEach(System.out::println);
输出结果为:
Person(name=Harley, age=22, country=英国, sex=F)
Person(name=小梅, age=20, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=何雪, age=21, country=中国, sex=F)
2.3 distinct举例
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'M').distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
输出结果为:
Person(name=Tom, age=24, country=美国, sex=M)
Person(name=向天笑, age=20, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
男性中有两个李康,去除掉了一个重复的。
3、Stream中间操作--映射
- map--接收Lambda,将元素转换成其他形式或提取信息。接收一个函数作为参数,该函数会被应用到每个元素上,并将其映射成一个新的元素。
- flatMap--接收一个函数作为参数,将流中的每个值都换成另一个流,然后把所有流连接成一个流
3.1 map举例
例1:比如,我们用一个PersonCountry类来接收所有的国家信息:
@Data
class PersonCountry {
private String country;
} personList.stream().map((p) -> {
PersonCountry personName = new PersonCountry();
personName.setCountry(p.getCountry());
return personName;
}).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
输出结果为:
PersonName(country=中国)
PersonName(country=美国)
PersonName(country=英国)
例2:假如有一个字符列表,需要提出每一个字符
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","ddd");
代码如下:
根据字符串获取字符方法:
public static Stream<Character> getCharacterByString(String str) {
List<Character> characterList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Character character : str.toCharArray()) {
characterList.add(character);
}
return characterList.stream();
}
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","ddd");
final Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream
= list.stream().map(TestStreamAPI::getCharacterByString);
streamStream.forEach(System.out::println);
运行结果:
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@3f91beef
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@1a6c5a9e
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@37bba400
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@179d3b25
java.util.stream.ReferencePipeline$Head@254989ff
从输出结果及返回结果类型(Stream<Stream<Character>>)可以看出这是一个流中流,要想打印出我们想要的结果,需要对流中的每个流进行打印:
streamStream.forEach(sm -> sm.forEach(System.out::print));
运行结果为:
aaabbbcccdddddd
但我们希望的是返回的是一个流,而不是一个包含了多个流的流,而flatMap可以帮助我们做到这一点。
3.2 flatMap举例
改写上面的方法,将map改成flatMap:
final Stream<Character> characterStream = list.stream().flatMap(TestStreamAPI::getCharacterByString);
characterStream.forEach(System.out::print);
运行结果为:
aaabbbcccdddddd
3.3 map和flatMap的图解
map图解:
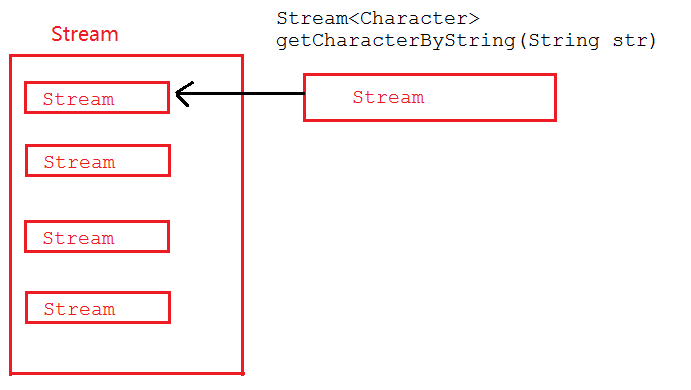
map在接收到流后,直接将Stream放入到一个Stream中,最终整体返回一个包含了多个Stream的Stream。
flatMap图解:
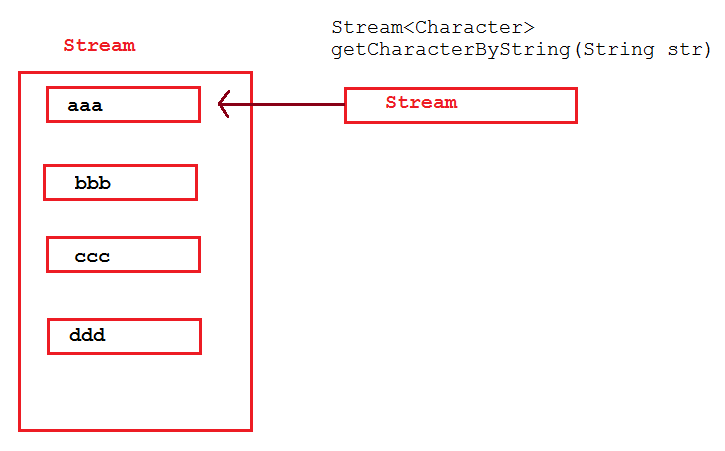
flatMap在接收到Stream后,会将接收到的Stream中的每个元素取出来放入一个Stream中,最后将一个包含多个元素的Stream返回。
ps:图画得丑,将就一下。
4、Stream中间操作--排序
- sorted()--自然排序(Comparable)
- sorted(Comparator com)--定制排序(Comparator)
自然排序比较好理解,这里只讲一下定制排序,对前面的personList按年龄从小到大排序,年龄相同,则再按姓名排序:
final Stream<Person> sorted = personList.stream().sorted((p1, p2) -> {
if (p1.getAge().equals(p2.getAge())) {
return p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
} else {
return p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge());
}
});
sorted.forEach(System.out::println);
运行结果:
Person(name=欧阳雪, age=18, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=向天笑, age=20, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=小梅, age=20, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=何雪, age=21, country=中国, sex=F)
Person(name=Harley, age=22, country=英国, sex=F)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=李康, age=22, country=中国, sex=M)
Person(name=Tom, age=24, country=美国, sex=M)
5、终止操作--查找与匹配
- allMatch--检查是否匹配所有元素
- anyMatch--检查是否至少匹配一个元素
- noneMatch--检查是否没有匹配所有元素
- findFirst--返回第一个元素
- findAny--返回当前流中的任意元素
- count--返回流中元素的总个数
- max--返回流中最大值
- min--返回流中最小值
这些方面在Stream类中都有说明,这里不一一举例,只对allMatch、max各举一例进行说明。
4.1 allMatch
判断personList中的人是否都是成年人:
final boolean adult = personList.stream().allMatch(p -> p.getAge() >= 18);
System.out.println("是否都是成年人:" + adult); final boolean chinaese = personList.stream().allMatch(p -> p.getCountry().equals("中国"));
System.out.println("是否都是中国人:" + chinaese);
运行结果:
是否都是成年人:true
是否都是中国人:false
4.1 max min
final Optional<Person> maxAge = personList.stream().max((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("年龄最大的人信息:" + maxAge.get()); final Optional<Person> minAge = personList.stream().min((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("年龄最小的人信息:" + minAge.get());
运行结果:
年龄最大的人信息:Person(name=Tom, age=24, country=美国, sex=M)
年龄最小的人信息:Person(name=欧阳雪, age=18, country=中国, sex=F)
5、归约
Stream API的归约操作可以将流中元素反复结合起来,得到一个值,有:
Optional<T> reduce(BinaryOperator<T> accumulator); T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator); <U> U reduce(U identity,
BiFunction<U, ? super T, U> accumulator,
BinaryOperator<U> combiner);
5.1 求一个1到100的和
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>(100);
for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {
integerList.add(i);
}
final Integer reduce = integerList.stream().reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println("结果为:" + reduce);
结果为:5050
这个例子用到了reduce第二个方法:T reduce(T identity, BinaryOperator<T> accumulator)
把这个动作拆解一下,其运算步骤模拟如下:
0 (1,2) -> 1 + 2 + 0
3 (3,4) -> 3 + 4 + 3
10 (5,6) -> 5 + 6 + 10
.
.
.
其运算步骤是,每次将列表的两个元素相加,并将结果与前一次的两个元素的相加结果进行累加,因此,在开始时,将identity设为0,因为第1个元素和第2个元素在相加的时候,前面还没有元素操作过。
5.2 求所有人的年龄之和
final Optional<Integer> reduce = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println("年龄总和:" + reduce);
年龄总和:169
6、收集
collect:将流转换为其他形式,接收一个Collector接口实现 ,用于给Stream中汇总的方法
<R, A> R collect(Collector<? super T, A, R> collector); <R> R collect(Supplier<R> supplier,
BiConsumer<R, ? super T> accumulator,
BiConsumer<R, R> combiner);
collect不光可以将流转换成其他集合等形式,还可以进行归约等操作,具体实现也很简单,主要是与Collectors类搭配使用。
6.1 改写3.1 map举例中的的例子,将国家收集起来转换成List
final List<String> collect = personList.stream().map(p -> p.getCountry()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
输出结果:
[中国, 美国, 英国]
6.2 计算出平均年龄
final Double collect1 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(p -> p.getAge()));
2 System.out.println("平均年龄为:" + collect1);
输出结果:
平均年龄为:21.125
6.3 找出最小年龄、最大年龄
final Optional<Integer> maxAge2 = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(maxAge2.get());
最小年龄类型。
还有其他很操作,可以参考java.util.stream.Collectors。
7 注意流的关闭
try(final Stream<Integer> integerStream = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge)) {
final Optional<Integer> minAge = integerStream.collect(Collectors.minBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(minAge.get());
}
最好将流的操作放到try-with-resources,本章前面内容为了方便,没有放到try-with-resources中。
8 完整测试代码
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import java.util.stream.Stream; public class TestStreamAPI { public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Person> personList = new ArrayList<>();
personList.add(new Person("欧阳雪",18,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("Tom",24,"美国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("Harley",22,"英国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("向天笑",20,"中国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("李康",22,"中国",'M'));
personList.add(new Person("小梅",20,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("何雪",21,"中国",'F'));
personList.add(new Person("李康",22,"中国",'M')); // 1)找到年龄大于18岁的人并输出;
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getAge() > 18).forEach(System.out::println); System.out.println("-------------------------------------------"); // 2)找出所有中国人的数量
long chinaPersonNum = personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getCountry().equals("中国")).count();
System.out.println("中国人有:" + chinaPersonNum); // limit
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'F').limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
// skip
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'F').skip(1).forEach(System.out::println); // distinct
personList.stream().filter((p) -> p.getSex() == 'M').distinct().forEach(System.out::println); // map
personList.stream().map((p) -> {
PersonCountry personName = new PersonCountry();
personName.setCountry(p.getCountry());
return personName;
}).distinct().forEach(System.out::println); // map2
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aaa","bbb","ccc","ddd","ddd"); final Stream<Stream<Character>> streamStream
= list.stream().map(TestStreamAPI::getCharacterByString);
// streamStream.forEach(System.out::println);
streamStream.forEach(sm -> sm.forEach(System.out::print)); // flatMap
final Stream<Character> characterStream = list.stream().flatMap(TestStreamAPI::getCharacterByString);
characterStream.forEach(System.out::print); // sort
final Stream<Person> sorted = personList.stream().sorted((p1, p2) -> { if (p1.getAge().equals(p2.getAge())) {
return p1.getName().compareTo(p2.getName());
} else {
return p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge());
}
});
sorted.forEach(System.out::println); // allMatch
final Stream<Person> stream = personList.stream();
final boolean adult = stream.allMatch(p -> p.getAge() >= 18);
System.out.println("是否都是成年人:" + adult); final boolean chinaese = personList.stream().allMatch(p -> p.getCountry().equals("中国"));
System.out.println("是否都是中国人:" + chinaese); // max min
final Optional<Person> maxAge = personList.stream().max((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("年龄最大的人信息:" + maxAge.get()); final Optional<Person> minAge = personList.stream().min((p1, p2) -> p1.getAge().compareTo(p2.getAge()));
System.out.println("年龄最小的人信息:" + minAge.get()); // reduce
List<Integer> integerList = new ArrayList<>(100);
for(int i = 1;i <= 100;i++) {
integerList.add(i);
}
final Integer reduce = integerList.stream().reduce(0, (x, y) -> x + y);
System.out.println("结果为:" + reduce); final Optional<Integer> totalAge = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).reduce(Integer::sum);
System.out.println("年龄总和:" + totalAge); // collect
final List<String> collect = personList.stream().map(p -> p.getCountry()).distinct().collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect); final Double collect1 = personList.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingInt(p -> p.getAge()));
System.out.println("平均年龄为:" + collect1); final Optional<Integer> maxAge2 = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge).collect(Collectors.maxBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(maxAge2.get()); try(final Stream<Integer> integerStream = personList.stream().map(Person::getAge)) {
final Optional<Integer> minAge2 = integerStream.collect(Collectors.minBy(Integer::compareTo));
System.out.println(minAge2.get());
}
} public static Stream<Character> getCharacterByString(String str) { List<Character> characterList = new ArrayList<>(); for (Character character : str.toCharArray()) {
characterList.add(character);
} return characterList.stream();
}
} @Data
class PersonCountry {
private String country;
} @Data
class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String country;
private char sex; public Person(String name, Integer age, String country, char sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.country = country;
this.sex = sex;
}
}
Java8新特性之三:Stream API的更多相关文章
- Java8 新特性之Stream API
1. Stream 概述 Stream 是Java8中处理集合的关键抽象概念,可以对集合执行非常复杂的查找,过滤和映射数据等操作; 使用 Stream API 对集合数据进行操作,就类似于使用 SQL ...
- 【Java8新特性】Stream API有哪些中间操作?看完你也可以吊打面试官!!
写在前面 在上一篇<[Java8新特性]面试官问我:Java8中创建Stream流有哪几种方式?>中,一名读者去面试被面试官暴虐!归根结底,那哥儿们还是对Java8的新特性不是很了解呀!那 ...
- Java8 新特性 Lambda & Stream API
目录 Lambda & Stream API 1 Lambda表达式 1.1 为什么要使用lambda表达式 1.2 Lambda表达式语法 1.3 函数式接口 1.3.1 什么是函数式接口? ...
- 乐字节-Java8新特性之Stream流(上)
上一篇文章,小乐给大家介绍了<Java8新特性之方法引用>,下面接下来小乐将会给大家介绍Java8新特性之Stream,称之为流,本篇文章为上半部分. 1.什么是流? Java Se中对于 ...
- 乐字节-Java8新特性之Date API
上一篇文章,小乐给大家带来了Java8新特性之Optional,接下来本文将会给大家介绍Java8新特性之Date API 前言: Java 8通过发布新的Date-Time API来进一步加强对日期 ...
- 【Java8新特性】- Stream流
Java8新特性 - Stream流的应用 生命不息,写作不止 继续踏上学习之路,学之分享笔记 总有一天我也能像各位大佬一样 一个有梦有戏的人 @怒放吧德德 分享学习心得,欢迎指正,大家一起学习成长! ...
- Java8 新特性 Data Time API
Java8新的日期类型 在Java8以前,Date日期API对我们非常的不友好,它无法表示日期,只能以毫秒的精试来表示时间,并且可以修改,他的线程还不是安全的.所以Java8中引入了全新的日期和时间A ...
- java8 新特性入门 stream/lambda
Java 8 中的 Stream 是对集合(Collection)对象功能的增强,它专注于对集合对象进行各种非常便利.高效的聚合操作(aggregate operation),或者大批量数据操作 (b ...
- Java8新特性之Stream
原文链接:http://ifeve.com/stream/ Java8初体验(二)Stream语法详解 感谢同事[天锦]的投稿.投稿请联系 tengfei@ifeve.com上篇文章Java8初体验( ...
随机推荐
- 搭建centos7的开发环境1-系统安装及Python配置
在公司开发部干活的好处是可以再分配一台高性能的PC,有了新的工作电脑,原来分配的笔记本电脑就可以安装linux系统做开发了,主要有两方面的开发计划,一个是计划中要参与爬虫系统的开发,第二个是大数据环境 ...
- Urlparse模块
urlparse模块主要是把url拆分为6部分,并返回元组.并且可以把拆分后的部分再组成一个url.主要有函数有urljoin.urlsplit.urlunsplit.urlparse等. urlpa ...
- NopCommerce是什么(转自CNSD)
NopCommerce是什么 nopCommerce--最好的免费购物车!nopCommerce是一个开源的解决方案.它是一个具有综合功能.对于新在线业务来说亦易于使用的解决方案,同时它也是一个功能强 ...
- 详解Linux文档属性、拥有者、群组、权限、差异
写在前面 我们都知道Linux是一个支持多用户.多任务的系统,这也是它最优秀的特性,即可能同时有很多人都在系统上进行工作,所以千万不要强制关机,同时,为了保护每个人的隐私和工作环境,针对某一个文档(文 ...
- 聊一聊顺序消息(RocketMQ顺序消息的实现机制)
当我们说顺序时,我们在说什么? 日常思维中,顺序大部分情况会和时间关联起来,即时间的先后表示事件的顺序关系. 比如事件A发生在下午3点一刻,而事件B发生在下午4点,那么我们认为事件A发生在事件B之前, ...
- 超实用的JavaScript代码段 Item2 --伸缩菜单栏
伸缩菜单栏 点击标题时判断该标题下的菜单是否显示,如果是显示的则将其隐藏,如果是隐藏的则将其显示出来. <!doctype html> <html lang="en&quo ...
- CentOS7上解决tomcat不能被外部浏览访问的问题?
在linux上开启的tomcat使用浏览器访问不了.主要原因在于防火墙的存在,导致的端口无法访问. CentOS7使用firewall而不是iptables.所以解决这类问题可以通过添加firewal ...
- poj~1904
Description Once upon a time there lived a king and he had N sons. And there were N beautiful girls ...
- 测试网页时需要添加等待的情形 (Selenium)
测试网页时需要添加等待的情形: 1. 网页跳转 2. DOM结构发生改变.
- java程序运行结果
下面这段代码的运行结果是:AB.B 分析原因:也就是说在你的operate()方法中,参数是引用传递,也就是x,y分别为a,b引用的拷贝,在方法中,你给x追加了值,也就相应的改变了a的值,但是第二条语 ...
