gpio模拟I2C,驱动pcf8574T
一、pcf8574T介绍
查看pcf8574T的数据手册,
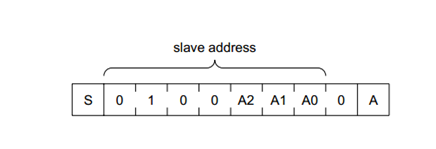
A表示读或写,当A为1的时候表示读,当A为0的时候表示写。现把地址控制线,即A2、A1、A0全部接地,可以得到读控制指令为0x41,写控制指令为0x40。
二、I2C介绍
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/ce123_zhouwei/article/details/6882221
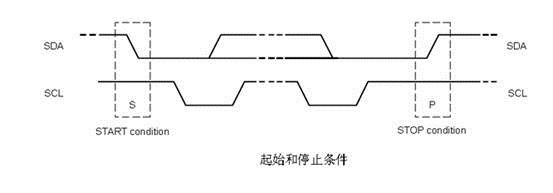
1、起始和停止时序
2、数据位的传输
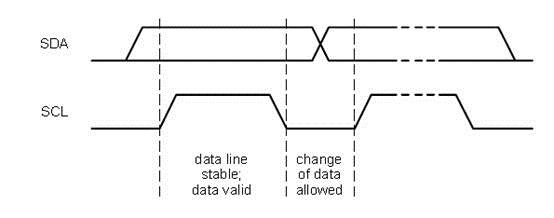
也就是在SCL的下降沿将数据位传出。
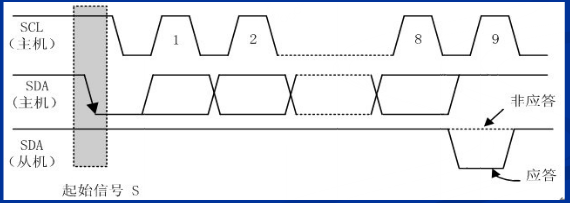
3、主控制器为写的时候,接收应答
当传输完数据的第8位,第9位要发送一个接收应答信号,将SDA拉高,设为输入模式,在SCL为低电平之前将总线上的数据读取过来,如果为1表示从设备接收数据失败,如果为0表示从设备接收数据成功,可以继续发送下一个字节。
代码片段:
// 接收应答信号
static int i2c_recv_ack(void)
{
int tmp;
//SDA=1;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//F0=SDA;
gpio_direction_input(sda_pin);
tmp = gpio_get_value(sda_pin);
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//if(F0==1) return 1;
if (tmp == ) return ; return ;
}
4、主控制器为读的时候,发送应答
第9位发送0,表示接收成功,发送1表示接收失败。如果到最后一个字节后,发送一个NACK信号(1),以通知被控发送器结束数据发送,并释放SDA线,以便主控接收器发送一个停止信号P。
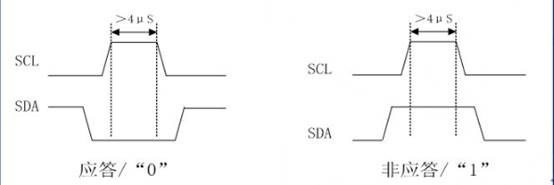
代码片段:
// 发送应答信号
static void i2c_send_ack()
{
//SDA=0;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SDA=0;
gpio_set_value(sda_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
} static void i2c_send_noack()
{
//SDA=1;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SDA=1;
gpio_set_value(sda_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
}
5、写过程完整数据传输
代码片段:
// 控制PCF8574引脚电平
static int pcf8574_write(u8 val)
{
int acktmp = ;
i2c_start();
i2c_write_byte(0x40);//写控制指令 0x20<<1 R/W
acktmp = i2c_recv_ack();
if (acktmp == ) {
PRK("i2c_recv_ack fail\n");
//return -1;
}
i2c_write_byte(val);
acktmp = i2c_recv_ack();
if (acktmp == ) {
PRK("i2c_recv_ack fail\n");
//return -1;
}
i2c_stop();
if (acktmp == ) return -;
return ;
}
6、读过程完整数据传输
代码片段:
// 读出PCF8574引脚电平
static u8 pcf8574_read()
{
int acktemp = ;
u8 rddata = ;
i2c_start();
i2c_write_byte(0x41);//读控制指令
i2c_send_ack();
rddata = i2c_read_byte();
i2c_send_noack();
i2c_stop();
return rddata;
}
三、示例代码:
1、驱动
/*
* Copyright (c) 2015 tingpan
* Copyright 2012-2015 Senscom.cn
* tingpan <smbx-ztbz@cnblog.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
* published by the Free Software Foundation.
*
*/ #include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/miscdevice.h> //混杂设备
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/delay.h> //mdelay
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi_gpio.h> #include <linux/kfifo.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h> #include <linux/types.h> //u8 #include <linux/ioctl.h> #define PCF8574_DEBUG 1 #if (PCF8574_DEBUG == 1)
#define PRK(...) printk(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define PRK(...)
#endif #define DRV_NAME "pcf8574"
#define DRV_DESC "use i2c to extend i/o"
#define DRV_VERSION "0.1.0" //#define PCF8574_NODE_NAME DRV_NAME #define scl_pin 17
#define sda_pin 14 static struct mutex pcf8574_lock; static DEFINE_MUTEX(pcf8574_lock); //pcf8574
// 发送I2C启动位
static void i2c_start(void)
{
//sda_pin=1;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//scl_pin=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SDA=0;
gpio_set_value(sda_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
} // 发送I2C停止位
static void i2c_stop(void)
{
//SDA=0;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SDA=1;
gpio_set_value(sda_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
} // 发送BIT0
static void i2c_send_bit_0(void)
{
//SDA=0;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
} // 发送BIT1
static void i2c_send_bit_1(void)
{
//SDA=1;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
} // 接收应答信号
static int i2c_recv_ack(void)
{
int tmp;
//SDA=1;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//F0=SDA;
gpio_direction_input(sda_pin);
tmp = gpio_get_value(sda_pin);
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//if(F0==1) return 1;
if (tmp == ) return ; return ;
} // 发送应答信号
static void i2c_send_ack()
{
//SDA=0;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SDA=0;
gpio_set_value(sda_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
} static void i2c_send_noack()
{
//SDA=1;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SDA=1;
gpio_set_value(sda_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
} // 写一个字节
static void i2c_write_byte(u8 data)
{
u8 i;
for (i=; i<; i++) {
if ((data<<i) & 0x80)
i2c_send_bit_1();
else
i2c_send_bit_0();
}
} // 接收一个字节
static u8 i2c_read_byte(void)
{
u8 data = ;
u8 i;
int tmp;
for (i=; i<; i++) {
//SDA=1;
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );
//SCL=1;
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//F0=SDA;
gpio_direction_input(sda_pin);
tmp = gpio_get_value(sda_pin);
//delay_us(5);
udelay();
//SCL=0;
gpio_set_value(scl_pin, );
if (tmp == ) {
data = data<<;
data = data | 0x01;
} else
data = data<<;
}
return data;
} // 控制PCF8574引脚电平
static int pcf8574_write(u8 val)
{
int acktmp = ;
i2c_start();
i2c_write_byte(0x40);//写控制指令 0x20<<1 R/W
acktmp = i2c_recv_ack();
if (acktmp == ) {
PRK("i2c_recv_ack fail\n");
//return -1;
}
i2c_write_byte(val);
acktmp = i2c_recv_ack();
if (acktmp == ) {
PRK("i2c_recv_ack fail\n");
//return -1;
}
i2c_stop();
if (acktmp == ) return -;
return ;
} // 读出PCF8574引脚电平
static u8 pcf8574_read()
{
int acktemp = ;
u8 rddata = ;
i2c_start();
i2c_write_byte(0x41);//读控制指令
i2c_send_ack();
rddata = i2c_read_byte();
i2c_send_noack();
i2c_stop();
return rddata;
} static ssize_t op_pcf8574_read(struct file *file, char __user * dat,
size_t len, loff_t *loff)
{
int err = ;
u8 result;
err = !access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, (void __user *)dat, _IOC_SIZE(len));//用到len,分配指定大小空间
if (err) {
PRK(KERN_INFO " access not allowed!\n");
return -EFAULT;
}
result = pcf8574_read();
__copy_to_user(dat, &result, );
return ;
} static ssize_t op_pcf8574_write(struct file *file, char __user * dat,
size_t len, loff_t *loff)
{
u8 wrdata = ;
if(!copy_from_user(&wrdata, dat, len))
{
if (!pcf8574_write(wrdata)) {
PRK("op_sensorid_write %d success!\n",wrdata);
return ;
} else {
PRK("op_sensorid_write %d fail!\n",wrdata);
return -;
} }
else
return -;
} static int op_pcf8574_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
int err; err = gpio_request(scl_pin, "scl_pin");//管脚申请
if (err) {
PRK("[%d]gpio_request scl_pin failed.\n", __LINE__);
return -;
}
gpio_direction_output(scl_pin, );//该管脚设为输出,且输出为高电平 err = gpio_request(sda_pin, "sda_pin");//管脚申请
if (err) {
PRK("[%d]gpio_request sda_pin failed.\n", __LINE__);
return -;
}
gpio_direction_output(sda_pin, );//该管脚设为输出,且输出为高电平 PRK(KERN_INFO " op_pcf8574_open\n");
return ;
} static int op_pcf8574_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
gpio_free(sda_pin);//释放IO口
gpio_free(scl_pin);//释放IO口 PRK(KERN_INFO " op_pcf8574_release\n"); return ;
} static const struct file_operations pcf8574_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE, .open = op_pcf8574_open,
.read = op_pcf8574_read,
.write = op_pcf8574_write,
.release = op_pcf8574_release,
}; static struct miscdevice pcf8574_miscdev =
{
//次设备号,驱动注册时,如果次号指定MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,则进行动态分配。
.minor = MISC_DYNAMIC_MINOR,
.name = DRV_NAME,//设备名称,将在/dev文件夹下显示
.fops = &pcf8574_fops,
};
static int __init pcf8574_init(void)//放后面,因为 misc_register 要包含前面的内容
{
int ret; ret = misc_register(&pcf8574_miscdev);
if (ret) {
printk("misc_register error\n");
return ret;
} printk(KERN_INFO DRV_NAME " ver " DRV_VERSION" init\n"); return ;
} module_init(pcf8574_init); static void __exit pcf8574_exit(void)
{
int ret; ret = misc_deregister(&pcf8574_miscdev);//注销
if (ret) {
printk("misc_deregister error\n");
return ;
} printk(KERN_INFO DRV_NAME " ver " DRV_VERSION" exit\n");
}
module_exit(pcf8574_exit); MODULE_DESCRIPTION(DRV_DESC);//描述
MODULE_VERSION(DRV_VERSION);//版本
MODULE_AUTHOR("tingpan <smbx-ztbz@cnblogs.com>");//作者
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");//协议
2、应用程序
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h> #include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h> #include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <sys/time.h> #include <linux/types.h> #include <syslog.h> #include <uci.h> #include <time.h>
#include <math.h> #include <sys/select.h> #include <pthread.h> #define PCF8574_DTEST 1 #if (PCF8574_DTEST == 1)
#define PRT(...) printf(__VA_ARGS__)
#else
#define PRT(...)
#endif #define USAGE_MESSAGE \
"Usage: pcf8574-dtest MODE [data]\n" \
"MODE is r or w\n" \
"data is the value want to write when MODE is w\n" int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd,ret;
unsigned char data = ;
//if (argc<2 || (argv[1]=='r')) {
//PRT(USAGE_MESSAGE);
//return -1;
//}
//memset(data, 0, sizeof(data));
//PRT("Compile Time %s %s\n", __DATE__, __TIME__);//打印出最后的编译日期
fd = open("/dev/pcf8574", O_RDWR); //打开设备文件
if (fd < ) {
perror("Open device file err:");
close(fd);
return -;
} if(argc > && !strcmp(argv[], "w")) {
data = atoi(argv[]);
ret = write(fd, &data, ); //第三个参数没用上,先固定为1
if (ret) perror("write");
} else if (argc > && !strcmp(argv[], "r")) {
ret = read(fd, &data, );
if (ret) perror("write");
PRT("read data is %d\n",data);
} else {
PRT(USAGE_MESSAGE);
return -;
}
return ;
}
四、问题
试过用pcf8574读取ds2431的序列号,但初始化就失败了,这是因为这样做就类似于用I2C通讯每控制一个IO空的电平,即约每传输20位就要把单总线通讯的管脚电平拉高或拉低,这样的话就要求I2C的通讯速度要大于单总线通讯的二十多倍(可能更多),才能正常控制ds2431。
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/xukai871105/article/details/18273653
源码下载:
http://pan.baidu.com/s/1qXyQJ3Q
gpio模拟I2C,驱动pcf8574T的更多相关文章
- gpio模拟i2c驱动
前段时间做项目,需要gpio模拟i2c通信,最后参考了一些资料,然后编写了一个程序.现在发出来,以免以后忘记,也为一些需要的朋友提供参考.不喜勿喷哈. /* 说明:该程序是基于atmel公司的sama ...
- S5PV210之GPIO模拟I2c时序之pcf8591与at24xx linux3.0.8驱动
目录:一. 说明 二. 驱动程序说明及问题 三. 案例一 四. 案例二 一. 说明 mini210开发板上带了at24c08, 看了linux内核自带的at24.c的驱动程序,编译下载到看 ...
- LPC4370使用学习:GPIO的引脚功能使用,和12864OLED模拟I2C驱动
一: 手中有块LPC4370的开发板,因为便宜,所以引脚引出的不多,而且只有基本的底板资源驱动代码和例程. 看着手册和例程看了老半天,写程序写了半天,结果GPIO老是驱动不起来,因为引脚配置寄存器中有 ...
- STM32F207 两路ADC连续转换及GPIO模拟I2C给MT9V024初始化参数
1.为了更好的方便调试,串口必须要有的,主要打印一些信息,当前时钟.转换后的电压值和I2C读出的数据. 2.通过GPIO 模拟I2C对镁光的MT9V024进行参数初始化.之前用我以前公司SP0A19芯 ...
- openwrt 模拟i2c驱动(一)
一:加载i2c driver kmod-i2c-core................................................ I2C support kmod-i2c-al ...
- 【转载】GPIO模拟i2c通信
I2C总线的通信过程(见图4-8)主要包含三个主要阶段:起始阶段.数据传输阶段和终止阶段. 1. 起始阶段 在I2C总线不工作的情况下,SDA(数据线)和SCL(时钟线)上的信号均为高电平.如果此时主 ...
- linux SPI驱动——gpio模拟spi驱动(三)
一:首先在我的平台注册platform_device,保证能让spi-gpio.c能执行到probe函数. 1: struct spi_gpio_platform_data { 2: unsigned ...
- I2C总线以及GPIO模拟I2C
·I2C总线的一些特征: 1. 只要求两条总线,一条串行数据线(SDA),一条串行时钟线(SCL) 2. 两个连接到总线的器件都可以通过唯一的地址和一直存在的简单的主机/从机系统软件设定的地址:主机可 ...
- am335x gpio 模拟 spi 驱动添加
kernel 内 make menuconfig // make menuconfig Device Drivers ---> [*] SPI support ---> <*> ...
随机推荐
- js 回车键事件
document.onkeydown = function (event) { var e = event || window.event || arguments.callee.caller.arg ...
- Java学习笔记31(IO:Properties类)
Properties类,表示一个持久的j集,可以存在流中,或者从流中加载 是Hashtable的子类 map集合的方法都能用 用途之一:在开发项目中,我们最后交给客户的是一个编译过的class文件,客 ...
- python day04 作业答案
1. 1) li=['alex','WuSir','ritian','barry','wenzhou'] print(len(li)) 2) li=['alex','WuSir','ritian',' ...
- 某些浏览器没有canvas.toBlob 方法的解决方案
var dataURLtoBlob = require('blueimp-canvas-to-blob'); // 80x60px GIF image (color black, base64 dat ...
- 何时使用SUM()与SUMX()
概述 SUM()是一个聚合函数.在应用将影响公式的所有过滤器后,它会将您指定的单个列中的所有值相加.SUM()不知道行的存在(它不能逐行求值) - 它所能做的就是在应用过滤器之后将所有内容添加到它所呈 ...
- JAVA (StringBuffer/StringBuilder)常用API
public class Copy3 { public static void main(String[] args) { //构造实例化 StringBuffer strbu = new Strin ...
- 【opencv基础】图像的几何变换
参考 1. 图像的几何变换-平移和镜像: 2.图像的几何变换-缩放和旋转: 3. opencv图像旋转实现: 完
- tensorboard 可视化
#coding = utf8 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mn ...
- each的break
$.each var arr = [1, 2, 'test', 3, 4, 5, 6] // break $.each(arr, function(index, value) { if (value ...
- xdoj--1077: (循环节长度)
1077: 循环节长度 时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB提交: 103 解决: 37[提交][状态][讨论版] 题目描述 数一有很多的有理数,然而有的是有限小数,如1/2=0.5, ...
