【读书笔记《Android游戏编程之从零开始》】3.Android 游戏开发常用的系统控件(Button、Layout、ImageButton)
3.1 Button
Button这控件不用多说,就是一个按钮,主要是点击后进行相应事件的响应。
给组件添加ID属性:定义格式为 android:id="@+id/name",这里的name是自定义的,不是索引变量。“@+”表示新声明,"@"表示引用,例如:
"@+id/tv" 表示新声明一个id,是id名为tv的组件;
"@id/tv" 表示引用id名为tv的组件。
给按钮添加点击事件响应
想知道按钮是否被用户点击,就需要一个“点击监听器”来对其进行监听,然后通过监听器来获取点击的事件,就可以判断关注的按钮是否被用户所点击。
使用监听器有两种方式:
1.当前类使用点击监听器接口,修改后源码如下:
//使用点击监听器
public class ButtonProject extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private Button btn_submit,btn_cancel;
private TextView tv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.button_project_layout);
btn_submit = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_submit);
btn_cancel = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_cancel);
tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
btn_submit.setOnClickListener(this);
btn_cancel.setOnClickListener(this);
} //使用点击监听器必须重写其抽象函数,
//@Override 表示重写函数
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(v == btn_submit)
{
tv.setText("确定按钮触发事件!");
}else if(v==btn_cancel)
{
tv.setText("取消按钮触发事件!");
}
}
}
先用当前类使用点击监听器接口(onClickListner),重写点击监听器的抽象函数(onClick);然后对需要监听的按钮进行按钮绑定监听器操作,这样监听器才能对绑定的按钮进行监听,以判断其是否被用户点击,一旦按钮被点击,就会自动响应onClick函数,并将点击的button(button也是 1个view)传入;最后就可以在onClick函数中书写点击会触发的事件(因为定义了多个按钮,所以在onClick函数中对系统传入的view进行按钮匹配的判断,让不同的按钮做不通的处理事件)。
2.使用内部类实现监听器进行监听,修改后源代码如下:
public class ButtonProject extends Activity {
private Button btn_submit,btn_cancel;
private TextView tv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.button_project_layout);
btn_submit = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_submit);
btn_cancel = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_cancel);
tv = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tv);
//将btn_submit按钮绑定点击监听器
btn_submit.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
tv.setText("确定按钮触发事件!");
}
});
btn_cancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
tv.setText("取消按钮触发事件!");
}
});
}
}
利用内部类的形式也需要重写监听器的抽象函数,然后在onClick里进行处理事件,这里不用判断view了,因为一个Button对应了一个监听器。
Button类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/Button.html
其中有说明,如果不用OnClickListener监听器的话,现在可以在XML布局按钮控件中使用android:onClick属性。然后在类中调用你设置的onClick方法。代码如下:
<Button
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/self_destruct"
android:onClick="selfDestruct" />
当用户单击按钮时,Android系统调用selfDestruct方法。该方法必须是公开并接受一个视图作为其唯一的参数。
public void selfDestruct(View view) {
// 按钮响应事件
}
3.2 Layout
1.线性布局 LinearLayout
LinearLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/LinearLayout.html
LinearLayout(线性布局)是5中布局中最常用的一种,此布局在显示组件的时候会默认保持组件的间隔以及组件之间的相互对其(相对一个组件的右对齐、中间对齐或者左对齐)。线性布局显示组件的方式有垂直与水平两种,可以通过orienrarion进行设定。
orientation属性表示设置布局中的控件的方向,其属性值有两种,一种是“vertical”垂直排列(见下图左),另一种是“horizontal”水平排列(见下图右)。
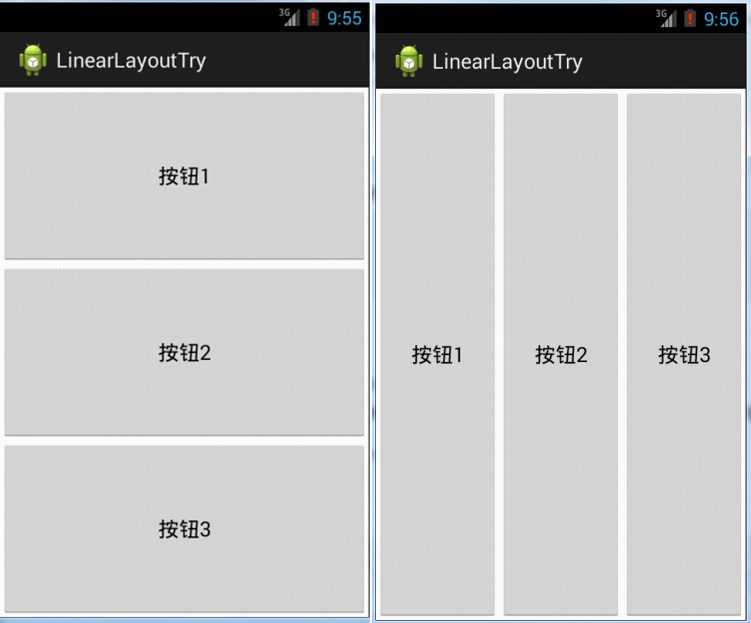
(1)gravity:每个组件默认其值为左上角对齐,其属性可以调整组件对齐方式,比如向左、向右、或者居中对齐等。
(2)padding:边距的填充,也称内边距。其边距属性有:
android:paddingTop,设置上边距;
android:paddingBottom,设置下边距;
android:paddingLeft,设置左边距;
android:paddingRight,设置右边距;
android:padding则表示周围四方向各内边距统一调整。
边距属性值为具体数字。
(3)layout_margn:外边距,其上下左右边距属性类似内边距。
padding内边距指的是当前布局与包含的组件之间的边距;layout_margn外边距指的是与其他组件之间的边距。
2.相对布局 RelativeLayout
RelativeLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/RelativeLayout.html
RelativeLayout(相对布局):除了最常用的LinearLayout之外,相对布局则是另一种常用的布局。与线性布局不同之处在于,线性布局如果需要将一组件对齐另外一个组件就必须将所有的组件进行对齐,或者使用嵌套布局才可以完成;但是相对布局不必这么麻烦。因为在相对布局中,每个组件都可以指定相对于其他组件或父组件的位置,只是必须通过ID来进行指定。修改main.xml布局如下;
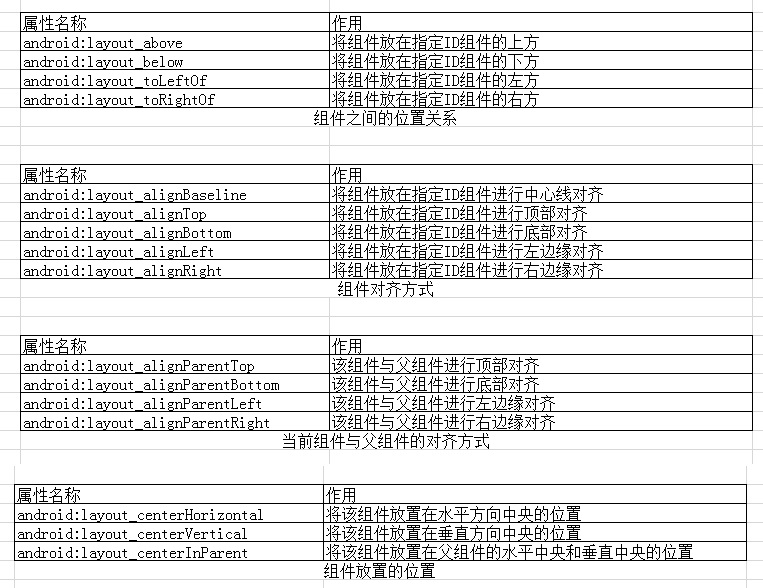
所以在相对布局中,如果想固定一个组件的位置,至少要确定组件“左右”与“上下”两个位置才可以准确固定组件的位置。
3.表格布局 TableLayout
TableLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/TableLayout.html
Tablelayout(表格布局)的样式如同一个表格。通常情况下,TableLayout有多个TableRow组成,每个TableRow就是一行,定义几个TableRow就是定义几行:TableLayout不会显示行列号,也没有分割线。其行数和列数也是有自己来操作和确定的。
下面来介绍在TableLayout中常用的几个属性:
(1)shrinkColumns属性:以0为序,当TableRow里面的控件布满布局时,指定列自动延伸以填充可用部分;当TableRow里面的控件还没有布满布局时,不起作用。
(2)strechColumns属性:以第0行为序,指定列对空白部分进行填充。
(3)collapseColumns属性:以第0行为序,隐藏指定的列。
(4)layout_column属性:以第0行为序,设置组件显示在指定列。
(5)layout_span属性:以第0行为序,设置组件显示占用的列数。
4.绝对布局 AbsoluteLayout
AbsoluteLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/AbsoluteLayout.html
AbsoluteLayout(绝对布局)布局用法如其名,组件的位置可以准确的指定其在屏幕的x/y坐标位置。虽然可以精确的去规定坐标,但是由于代码的书写过于刚硬,使在不同的设备,不同分辨率的手机移动设备上不能很好的显示应有的效果,此布局设定组件位置都是用x/y来进行调整,又使得整体布局格式代码很不灵活,所以此布局不推荐使用。
5.单帧布局 FrameLayout
FrameLayout类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/FrameLayout.htm
FrameLayout(单帧布局)是5中布局中最简单的一种,因为单帧布局在新定义组件的时候永远都会将组件放在屏幕的左上角,即使在此布局中定义多个组件,后一个组件总会将前一个组件覆盖,除非最后一个组件是透明的。
3.3 ImageButton
ImageButton类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/ImageButton.html
ImageButton与Button类似 ,区别在于ImageButton可以自定义一张图片作为一个按钮;也正因为使用图片代替了按钮,所以ImageButton按下与抬起的样式效果需要自定义。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" > <ImageButton
android:id="@+id/btn_ImageButton"
android:layout_marginLeft="100dp"
android:layout_marginTop="100dp"
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@drawable/dsfvsdf" /> </LinearLayout>
public class ImageButtonProject extends Activity {
private ImageButton btn_ImageButton;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.imagebutton_layout);
btn_ImageButton = (ImageButton)findViewById(R.id.btn_ImageButton);
//为图片按钮添加触屏监听
btn_ImageButton.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
//第一个参数:表示触发触屏事件的事件源view
//第二个参数:表示触屏事件的类型,如按下、抬起、移动等。
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(event.getAction()==MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN)//按下事件
{
//设置图片按钮背景
//getResources().getDrawable(int ID) 传入图片ID得到一个Drawable对象。
btn_ImageButton.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.dsfvsdf_bg));
}else if(event.getAction()==MotionEvent.ACTION_UP)//抬起事件
{
btn_ImageButton.setBackgroundDrawable(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.dsfvsdf));
}
return false;
}
});
}
}
显示不同的按钮状态官方文档中有提到可以在单独在xml文件中配置,然后布局文件中引用就可以了,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:state_pressed="true"
android:drawable="@drawable/button_pressed" /> <!-- pressed 按下状态-->
<item android:state_focused="true"
android:drawable="@drawable/button_focused" /> <!-- focused 聚焦状态-->
<item android:drawable="@drawable/button_normal" /> <!-- default 默认状态-->
</selector>
【读书笔记《Android游戏编程之从零开始》】3.Android 游戏开发常用的系统控件(Button、Layout、ImageButton)的更多相关文章
- 【读书笔记《Android游戏编程之从零开始》】6.Android 游戏开发常用的系统控件(TabHost、ListView)
3.9 TabSpec与TabHost TabHost类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/TabHost.htm ...
- 【读书笔记《Android游戏编程之从零开始》】7.Android 游戏开发常用的系统控件(Dialog)
在Android应用开发中,Dialog(对话框)创建简单且易于管理因而经常用到,对话框默认样式类似创建样式的Activity.首先介绍android.app.AlertDialog下的Builder ...
- 【读书笔记《Android游戏编程之从零开始》】5.Android 游戏开发常用的系统控件(ProgressBar、Seekbar)
3.7 ProgressBar ProgressBar类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/ProgressBar ...
- 【读书笔记《Android游戏编程之从零开始》】4.Android 游戏开发常用的系统控件(EditText、CheckBox、Radiobutton)
3.4 EditText EditText类官方文档地址:http://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/EditText.html Edi ...
- 【读书笔记《Android游戏编程之从零开始》】8.Android 游戏开发常用的系统控件(系统控件常见问题)
Android 中常用的计量单位Android有时候需要一些计量单位,比如在布局Layout文件中可能需要指定具体单位等.常用的计量单位有:px.dip(dp).sp,以及一些不常用的pt.in.mm ...
- Android控件——Button与ImageButton
1.简单介绍
- Windows游戏编程之从零开始d
Windows游戏编程之从零开始d I'm back~~恩,几个月不见,大家还好吗? 这段时间真的好多童鞋在博客里留言说或者发邮件说浅墨你回来继续更新博客吧. woxiangnifrr童鞋说每天都在来 ...
- Java并发编程的艺术读书笔记(2)-并发编程模型
title: Java并发编程的艺术读书笔记(2)-并发编程模型 date: 2017-05-05 23:37:20 tags: ['多线程','并发'] categories: 读书笔记 --- 1 ...
- Java并发编程的艺术读书笔记(1)-并发编程的挑战
title: Java并发编程的艺术读书笔记(1)-并发编程的挑战 date: 2017-05-03 23:28:45 tags: ['多线程','并发'] categories: 读书笔记 --- ...
随机推荐
- Hadoop Pipes Exception: Illegal text protocol command
Hadoop Pipes Exception: Illegal text protocol command 对于Hadoop pipes 出现这样的错误,基本上编译代码依赖的.so和.a 版本不匹配 ...
- [moka同学笔记]yii2场景的使用(摘录)
前半部分为自己使用的过程,下边为转载的,具体地址见:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_88a65c1b0101j717.html 1.在model中 public func ...
- 总结一下SQL的全局变量
SQL Server 2008中的全局变量及其用法 T-SQL程序中的变量分为全局变量和局部变量两类,全局变量是由SQL Server系统定义和使用的变量.DBA和用户可以使用全局变量的值,但不能自己 ...
- jQuery pgwslideshow 空间相册
一个响应式相册插件,你可以自定义幻灯片最大高度,滑动效果,是否显示控制按钮,自动轮播或间隔时间. pgwslideshow相册插件有以下特点 支持响应式 支持桌面和移动设备 代码简单 ...
- mybatis hellworld
用maven来进行搭建项目的~~ 1. 搭建环境 pom.xml <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" x ...
- eclipse导入svn项目,项目却没有svn的标记
现象: eclipse(已经装有svn插件)导入svn项目,项目没有svn的标记. 原因: 1.可能是由于你的svn eclipse插件,也就是subclipse,与svn的客户端版本不匹配. 解决 ...
- 移位操作<<和>>,是逻辑数字上的移动(和大端小端无关)
问题描述 这几天帮同事调试DSP TMS320F28335,这鬼东西蛋疼死了.char是16bit的,16位就是他的最小内存单元.但是PC机串口发过来的有8bit的数据,然后转换就出问题. 一开始不知 ...
- Level 4 A10: 飞张?
看来庄家的红桃2个输张没法解决,只能寄希望于飞K了. 但如果将牌2-2分布,还有更稳的打法.在下面这种东家3张黑桃的情况时,庄家只需垫到红桃2就行了. 如果东家有4张黑桃,那就只有飞红桃K这一条路了.
- 安卓问题集-Installation error: INSTALL_PARSE_FAILED_MANIFEST_MALFORMED
错误出现原因: 1.没有 AndroidManifest.xml file文件(出现几率较小) 2. 是你在外面修改了包名而在 AndroidManifest.xml file.文件中没有同步过去导致 ...
- 【读书笔记】iOS-KVC
一,KVC即键/值编码. 二,KVC的基本调用包括-valueForKey:和-setValue:forKey:. 三,对于KVC,Cocoa自动放入和取出标量值.也就是说,当使用setValueFo ...
