【C#】线程之Task
Task开启线程
有两种启动方式:
1.构造创建线程,然后启动
var taskForAction = new Task(() =>
{
//do something
});
taskForAction.Start();
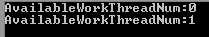
注:构造所有的重载并没有传入Func函数的,而且我们这个时候看线程池中活动线程数会发现改变
//打印线程池中线程活动数
PrintAvailabeWorkThreadNum(); var taskForAction = new Task(() =>
{
//do something
});
taskForAction.Start();
PrintAvailabeWorkThreadNum();
输出结果:
2.直接使用静态方法
//打印线程池中线程活动数
PrintAvailableWorkThreadNum(); var taskForAction = Task.Run(() => Console.WriteLine("print string for Action")); var taskForFunc = Task.Run(() => "return string for Func<string>"); PrintAvailableWorkThreadNum(); //Result内部会调用Wait,所以这里不需要调 Console.WriteLine(taskForFunc.Result);
同样的,直接调用静态方法来创建一个线程,并返回当前正在执行的线程副本以供我们调用,Result只有传递进去的是Func函数才会在返回的Task中存在,如果传入的是Action函数,Result是不存在的, 这个时候线程活动数量也会改变。

取消任务
已经在 【C#】线程协作式取消 这章里面好好讨论过如何去取消了,如何注册回调函数等技术了.
任务完成时重新开启一个任务(ConintueWith)
我们有时候想在执行完一个任务以后,再开始做一个其他的任务,这个时候如果我们用Wait就会堵塞线程,如果我们用线程嵌套的方式去做,会浪费资源并损害的伸缩性。
//这样会堵塞我们的线程
Task.Run(() =>
{
//do something
}).Wait(); Task.Run(() =>
{
//do another thing
}); //虽然不会堵塞线程了,但这样会浪费资源
Task.Run(() =>
{
Task.Run(() =>
{
//do something
}).Wait(); Task.Run(() =>
{
//do another thing
});
});
CLR给我们提供了另一个方法:ContinueWith.
这个方法会不会堵塞当前的线程,并且会等第一个任务做好了以后再做第二个任务(当然可以开启多个)
var t = Task.Run(() =>
{
int index = ;
int count = ;
while (index != )
{
count += index;
Console.WriteLine("Task:" + index++);
Thread.Sleep( * );
}
return count;
}); t.ContinueWith(task =>
{
//这里的参数Task,就是我们上面那个线程对象(t),可以用于获取结果集,状态等数据
Console.WriteLine("First continue task:" + task.Status);
Console.WriteLine("First continue task:" + (task.Result + )+"\n");
}); t.ContinueWith(task =>
{
Console.WriteLine("Second continue task:" + task.Status);
Console.WriteLine("Second continue task:" + (task.Result - ));
}); t.ContinueWith(task =>
{
//Do another thing
});
ContinueWith方法延伸
需求肯定是很复杂的,比如我们希望在各种状态(取消,完成,失败等)情况下执行各种ContinueWith的方法,这个时候我们需要关注一个枚举类型:TaskContinuationOptions, 以下给出官方的定义:
namespace System.Threading.Tasks
{
// Summary:
// Specifies the behavior for a task that is created by using the System.Threading.Tasks.Task.ContinueWith(System.Action<System.Threading.Tasks.Task>,System.Threading.CancellationToken,System.Threading.Tasks.TaskContinuationOptions,System.Threading.Tasks.TaskScheduler)
// or System.Threading.Tasks.Task<TResult>.ContinueWith(System.Action<System.Threading.Tasks.Task<TResult>>,System.Threading.Tasks.TaskContinuationOptions)
// method.
[Serializable]
[Flags]
public enum TaskContinuationOptions
{
// Summary:
// Default = "Continue on any, no task options, run asynchronously" Specifies
// that the default behavior should be used. Continuations, by default, will
// be scheduled when the antecedent task completes, regardless of the task's
// final System.Threading.Tasks.TaskStatus.
None = ,
//
// Summary:
// A hint to a System.Threading.Tasks.TaskScheduler to schedule a task in as
// fair a manner as possible, meaning that tasks scheduled sooner will be more
// likely to be run sooner, and tasks scheduled later will be more likely to
// be run later.
PreferFairness = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that a task will be a long-running, course-grained operation. It
// provides a hint to the System.Threading.Tasks.TaskScheduler that oversubscription
// may be warranted.
LongRunning = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that a task is attached to a parent in the task hierarchy.
AttachedToParent = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that an System.InvalidOperationException will be thrown if an attempt
// is made to attach a child task to the created task.
DenyChildAttach = ,
//
// Summary:
// Prevents the ambient scheduler from being seen as the current scheduler in
// the created task. This means that operations like StartNew or ContinueWith
// that are performed in the created task will see System.Threading.Tasks.TaskScheduler.Default
// as the current scheduler.
HideScheduler = ,
//
// Summary:
// In the case of continuation cancellation, prevents completion of the continuation
// until the antecedent has completed.
LazyCancellation = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that the continuation task should not be scheduled if its antecedent
// ran to completion. This option is not valid for multi-task continuations.
NotOnRanToCompletion = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that the continuation task should not be scheduled if its antecedent
// threw an unhandled exception. This option is not valid for multi-task continuations.
NotOnFaulted = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that the continuation task should be scheduled only if its antecedent
// was canceled. This option is not valid for multi-task continuations.
OnlyOnCanceled = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that the continuation task should not be scheduled if its antecedent
// was canceled. This option is not valid for multi-task continuations.
NotOnCanceled = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that the continuation task should be scheduled only if its antecedent
// threw an unhandled exception. This option is not valid for multi-task continuations.
OnlyOnFaulted = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that the continuation task should be scheduled only if its antecedent
// ran to completion. This option is not valid for multi-task continuations.
OnlyOnRanToCompletion = ,
//
// Summary:
// Specifies that the continuation task should be executed synchronously. With
// this option specified, the continuation will be run on the same thread that
// causes the antecedent task to transition into its final state. If the antecedent
// is already complete when the continuation is created, the continuation will
// run on the thread creating the continuation. Only very short-running continuations
// should be executed synchronously.
ExecuteSynchronously = ,
}
}
这里就不一一解释了,这里面有一些参数只是建议,会不会执行两说,这里我只介绍几个常用的,直接附上代码:
var t = Task.Run(() =>
{ int index = ;
int count = ;
while (index != )
{
count += index;
Console.WriteLine("Task:" + index++);
Thread.Sleep( * );
}
return count;
}); t.ContinueWith(task =>
{
//只有执行成功以后才会继续做
}, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnRanToCompletion); t.ContinueWith(task =>
{
//只有取消的时候才做操作
}, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnCanceled); t.ContinueWith(task =>
{
//只有失败的时候才会运行,抛出未知异常什么的.
AggregateException ex = task.Exception;
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
}, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted);
个人对这个机制是十分喜欢的,即不堵塞我们的线程,又可以按照状态来分别做操作。
任务启动子任务
var t = new Task<Int32[]>(() =>
{
var results = new int[];
new Task(() =>
{
Thread.Sleep( * );
results[] = ; }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start(); new Task(() =>
{
results[] = ; }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start(); new Task(() =>
{
results[] = ; }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start(); return results;
});
t.ContinueWith(task =>
Array.ForEach(task.Result, Console.WriteLine),
TaskContinuationOptions.AttachedToParent); t.Start();
这里主要是用到了TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent枚举标志,用到了这个标志,父线程会等待子线程所有线程都执行完毕以后才会继续往下走(注:这里也不能当前主线程).这里我尝试过用Task.Run这个去建立这样的机制,可惜的是这个没有办法完成(Task.Run没有参数包含TaskCreationOptions的重载),具体的原因还在探索中,如果有朋友知道,请告知,谢谢:)!
任务工厂
关于这个方法,我在网上查到的也都是CLR那本书上的东西,但是关于这个,如果用起来不注意的话,会出现很多的问题,先给出代码:
private static Int32 Sum(CancellationToken ct, Int32 n)
{
Int32 sum = 0;
for (; n > 0; n--)
{
ct.ThrowIfCancellationRequested();
checked { sum += n; }
}
return sum;
} public static void TaskFactory()
{
var parent = new Task(() =>
{
var cts = new CancellationTokenSource();
var tf = new TaskFactory<Int32>(cts.Token,
TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent,
TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously,
TaskScheduler.Default); // This tasks creates and starts 3 child tasks
var childTasks = new[] {
tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, 10000)),
tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, 20000)),
tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, Int32.MaxValue)), // Too big, throws OverflowException
}; //如果有一个线程错误了就暂停所有的任务
Array.ForEach(childTasks,
task => task.ContinueWith(t => cts.Cancel(), TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted)); tf.ContinueWhenAll(
childTasks,
completedTasks => completedTasks.Where(t => t.Status == TaskStatus.RanToCompletion).Max(t => t.Result),
CancellationToken.None)
.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("The maximum is: " + t.Result),
TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously).Wait(); // Wait is for testing only
}); parent.ContinueWith(p =>
{
var sb = new StringBuilder("The following exception(s) occurred:" + Environment.NewLine);
foreach (var e in p.Exception.Flatten().InnerExceptions)
sb.AppendLine(" " + e.GetType().ToString());
Console.WriteLine(sb.ToString());
}, TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted); parent.Start(); try
{
parent.Wait(); // For testing purposes
}
catch (AggregateException)
{
}
}
首先我们看一下
var childTasks = new[] {
tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, 10000)),
tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, 20000)),
tf.StartNew(() => Sum(cts.Token, Int32.MaxValue)), // Too big, throws OverflowException
};
//如果有一个线程错误了就暂停所有的任务
Array.ForEach(childTasks,
task => task.ContinueWith(t => cts.Cancel(), TaskContinuationOptions.OnlyOnFaulted));
这段代码是创建了三个线程放入工厂中,并建立一个会抛出异常的线程,下面那段代码会取消线程的操作(3个线程都取消操作,因为注册了同一个TOKEN),但是这里需要注意的是:如果我其他线程跑的比抛出异常的线程块,这会导致取消不了,因为结束了(这个的确很难做,因为无法控制线程的执行速度和优先级)。
tf.ContinueWhenAll(
childTasks,
completedTasks => completedTasks.Where(t => t.Status == TaskStatus.RanToCompletion).Max(t => t.Result),
CancellationToken.None)
.ContinueWith(t => Console.WriteLine("The maximum is: " + t.Result),
TaskContinuationOptions.ExecuteSynchronously).Wait(); // Wait is for testing only
这段代码才是用TaskFactory的核心,这个会等待所有工厂中的线程执行完毕(包括被取消)才会执行,还有一个方法叫ContinueWhenAny:当有一个线程结束操作就会执行。这里要注意的是:
两个方法都有带TaskContinuationOptions参数的重载,但是有那么几个是不能用的:
- NotOnRanToCompletion
- NotOnFaulted
- OnlyOnCanceled
- NotOnCanceled
- OnlyOnFaulted
- OnlyOnRanToCompletion
也就是说无论前面任务是什么状态,这个方法都会执行,所以我们必须要自己去判断:Where(t => t.Status == TaskStatus.RanToCompletion).
【C#】线程之Task的更多相关文章
- Asp.Net Core 轻松学-多线程之Task(补充)
前言 在上一章 Asp.Net Core 轻松学-多线程之Task快速上手 文章中,介绍了使用Task的各种常用场景,但是感觉有部分内容还没有完善,在这里补充一下. 1. 任务的等待 在使用 ...
- WebAPI调用笔记 ASP.NET CORE 学习之自定义异常处理 MySQL数据库查询优化建议 .NET操作XML文件之泛型集合的序列化与反序列化 Asp.Net Core 轻松学-多线程之Task快速上手 Asp.Net Core 轻松学-多线程之Task(补充)
WebAPI调用笔记 前言 即时通信项目中初次调用OA接口遇到了一些问题,因为本人从业后几乎一直做CS端项目,一个简单的WebAPI调用居然浪费了不少时间,特此记录. 接口描述 首先说明一下,基于 ...
- C# 多线程之Task资料
博客 Stephen Toub From MicroSoft Crop. Stephen Cleary Parallelism in .NET 文章 It's All About the Sync ...
- Asp.Net Core 轻松学-多线程之Task快速上手
前言 Task是从 .NET Framework 4 开始引入的一项基于队列的异步任务(TAP)模式,从 .NET Framework 4.5 开始,任何使用 async/await 进行修饰 ...
- C# 多线程之Task(任务
1.简介 为什么MS要推出Task,而不推Thread和ThreadPool,以下是我的见解: (1).Thread的Api并不靠谱,甚至MS自己都不推荐,原因,它将整个Thread类都不开放给W ...
- 20181105_线程之Task
Task是基于.net Framework3.0框架, Task使用的线程也是来自于ThreadPool 多线程的两个意义: 优化体验(常见于不卡界面), 提升运行速度(不同线程可以分担运算任务) 总 ...
- 【C#】线程之Parallel
在一些常见的编程情形中,使用任务也许能提升性能.为了简化变成,静态类System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel封装了这些常见的情形,它内部使用Task对象. Parallel.Fo ...
- Java多线程之Runnable与Thread
Java多线程之Thread与Runnable 一.Thread VS Runnable 在java中可有两种方式实现多线程,一种是继承Thread类,一种是实现Runnable接口:Thread类和 ...
- JAVA多线程之UncaughtExceptionHandler——处理非正常的线程中止
JAVA多线程之UncaughtExceptionHandler——处理非正常的线程中止 背景 当单线程的程序发生一个未捕获的异常时我们可以采用try....catch进行异常的捕获,但是在多线程环境 ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu server下搭建Maven私服Nexus
Ubuntu server下搭建Maven私服Nexus Maven私服Nexus的作用,主要是为了节省资源,在内部作为maven开发资源共享服务器来使用. 1.下载 通过root用户进去Ubuntu ...
- Ubunbu新建的用户使用SecureCrt无法Table补全、无法高亮
Check 两个地方: 1. 确保/etc/passwd中配置有/bin/bash (这个是用来控制补全). 2. 在~/.bashrc中配置, export TERM=linux (这个是用来控制 ...
- 使用 jackson 解析 json 演示样例
首先须要下载3个包,下载地址在Github FasterXML,这三个核心模块各自是: Streaming ("jackson-core") defines low-level s ...
- ASP.NET 回调技术(CallBack)
在asp.net中客户端与服务器端的交互默认都是整页面提交, 此时客户端将当前页面表单中的数据(包括一些自动生成的隐藏域)都提交到服务器端,服务器重新实例化一个当前页面类的实例响应这个请求,然后将整个 ...
- js后退一直停留在当前页面或者禁止后退
//禁用后退按钮 function stopHistoryGo() { //禁用回退 window.location.hash="no-back-button"; window.l ...
- 读写文本(.txt)文件 .NET
http://www.cnblogs.com/jx270/archive/2013/04/14/3020456.html (一) 读取文件 如果你要读取的文件内容不是很多,可以使用 File.Read ...
- Linux流量监控工具-iftop教程
Linux流量监控工具-iftop教程http://automationqa.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=2854&fromuid=2
- js 当前日期增加自然月
js 在日期不满足的情况下就会自动加1个月,比如在当前时间为3月31号,传入1,1两个参数,预期结果为2月29日,但是结果输出了3月2日.就是如果不满就会溢出到下个月,后来看了api发现了setMon ...
- notepad++插件
html插件 https://github.com/downloads/davegb3/NppTidy2/Tidy2_0.2.zip
- MTNET 自用ios网络库开源
短短两天就在https://git.oschina.net/gangwang/MTNET这里收获15个星 github 5星, 值得收藏! MTNET 自用ios网络库开源, 自用很久了,在数歀上架的 ...
