左倾堆(二)之 C++的实现
概要
上一章介绍了左倾堆的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了左倾堆。本章是左倾堆的C++实现。
目录
1. 左倾堆的介绍
2. 左倾堆的图文解析
3. 左倾堆的C++实现(完整源码)
4. 左倾堆的C++测试程序
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3638342.html
更多内容:数据结构与算法系列 目录
(01) 左倾堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
(02) 左倾堆(二)之 C++的实现
(03) 左倾堆(三)之 Java的实现
左倾堆的介绍
左倾堆(leftist tree 或 leftist heap),又被成为左偏树、左偏堆,最左堆等。
它和二叉堆一样,都是优先队列实现方式。当优先队列中涉及到"对两个优先队列进行合并"的问题时,二叉堆的效率就无法令人满意了,而本文介绍的左倾堆,则可以很好地解决这类问题。
左倾堆的定义
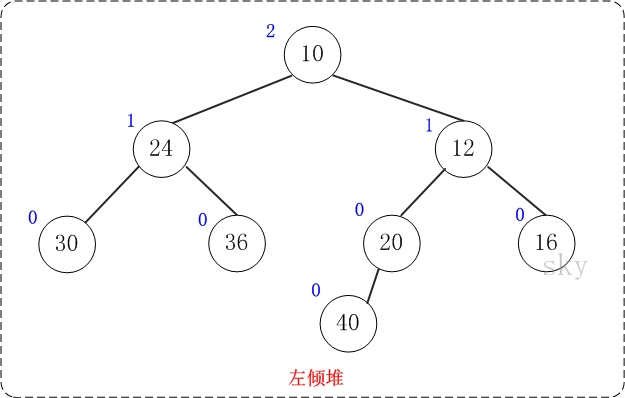
上图是一颗左倾树,它的节点除了和二叉树的节点一样具有左右子树指针外,还有两个属性:键值和零距离。
(01) 键值的作用是来比较节点的大小,从而对节点进行排序。
(02) 零距离(英文名NPL,即Null Path Length)则是从一个节点到一个"最近的不满节点"的路径长度。不满节点是指该该节点的左右孩子至少有有一个为NULL。叶节点的NPL为0,NULL节点的NPL为-1。
左倾堆有以下几个基本性质:
[性质1] 节点的键值小于或等于它的左右子节点的键值。
[性质2] 节点的左孩子的NPL >= 右孩子的NPL。
[性质3] 节点的NPL = 它的右孩子的NPL + 1。
左倾堆的图文解析
合并操作是左倾堆的重点。合并两个左倾堆的基本思想如下:
(01) 如果一个空左倾堆与一个非空左倾堆合并,返回非空左倾堆。
(02) 如果两个左倾堆都非空,那么比较两个根节点,取较小堆的根节点为新的根节点。将"较小堆的根节点的右孩子"和"较大堆"进行合并。
(03) 如果新堆的右孩子的NPL > 左孩子的NPL,则交换左右孩子。
(04) 设置新堆的根节点的NPL = 右子堆NPL + 1
下面通过图文演示合并以下两个堆的过程。
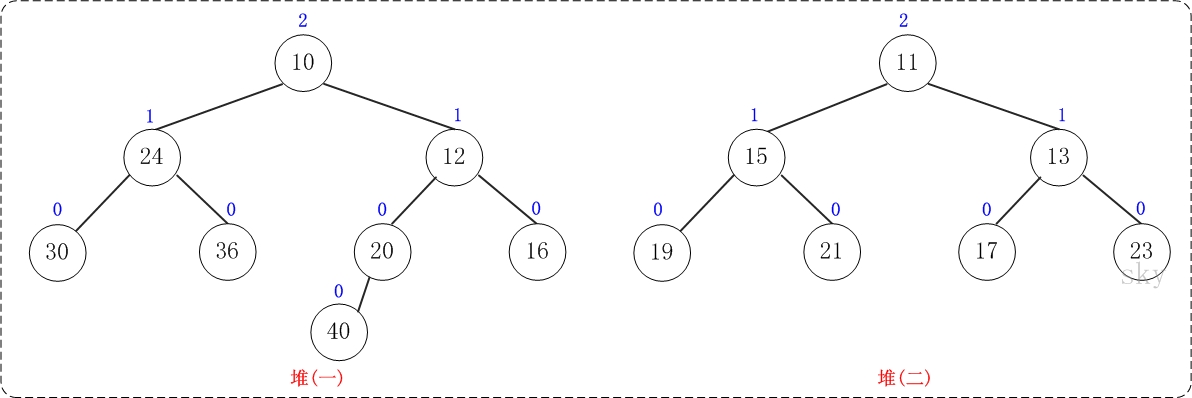
提示:这两个堆的合并过程和测试程序相对应!
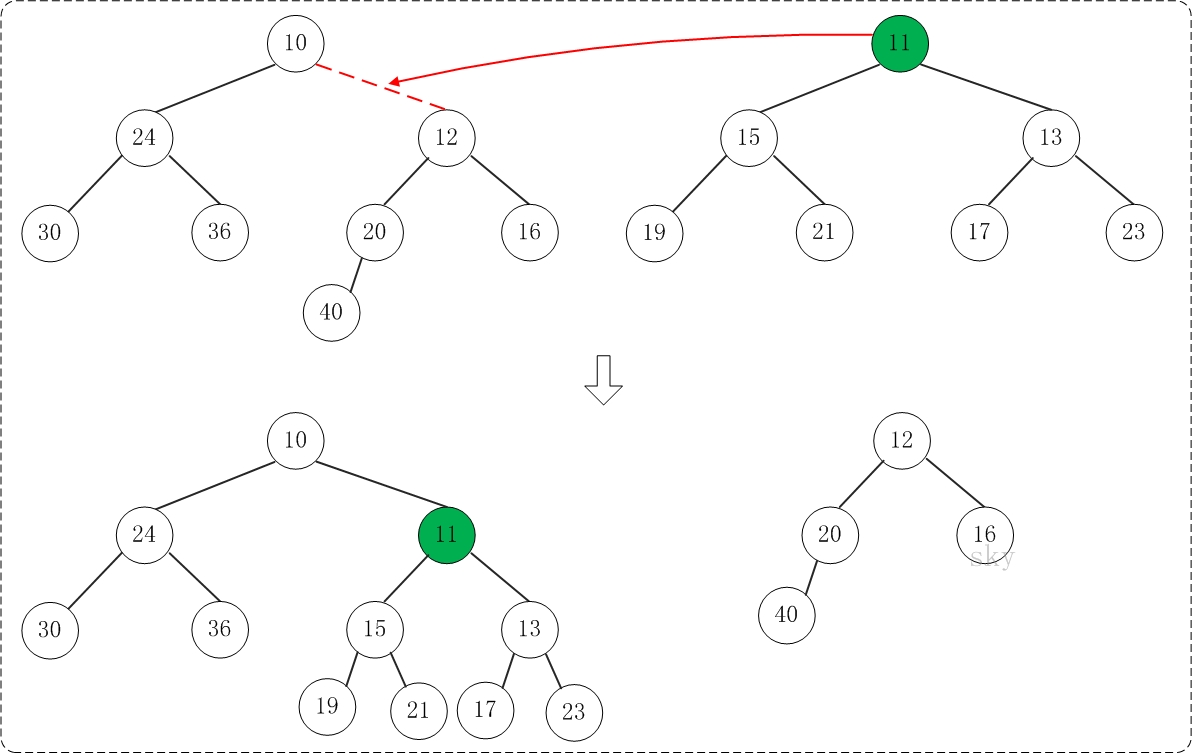
第1步:将"较小堆(根为10)的右孩子"和"较大堆(根为11)"进行合并。
合并的结果,相当于将"较大堆"设置"较小堆"的右孩子,如下图所示:
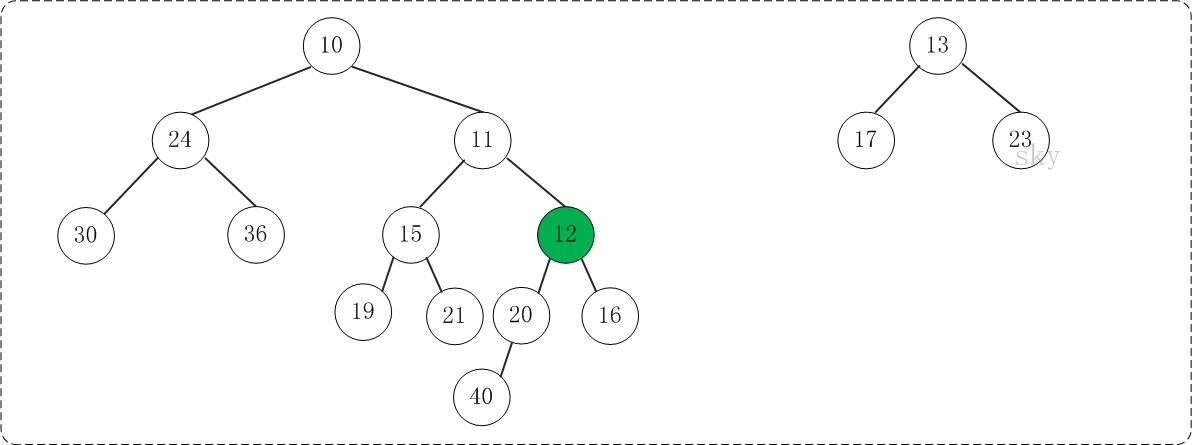
第2步:将上一步得到的"根11的右子树"和"根为12的树"进行合并,得到的结果如下:
第3步:将上一步得到的"根12的右子树"和"根为13的树"进行合并,得到的结果如下:

第4步:将上一步得到的"根13的右子树"和"根为16的树"进行合并,得到的结果如下:

第5步:将上一步得到的"根16的右子树"和"根为23的树"进行合并,得到的结果如下:
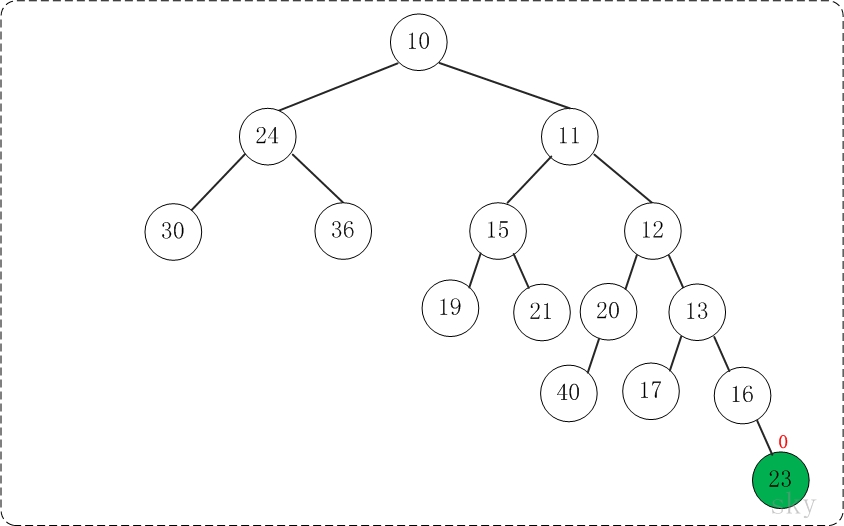
至此,已经成功的将两棵树合并成为一棵树了。接下来,对新生成的树进行调节。
第6步:上一步得到的"树16的右孩子的NPL > 左孩子的NPL",因此交换左右孩子。得到的结果如下:
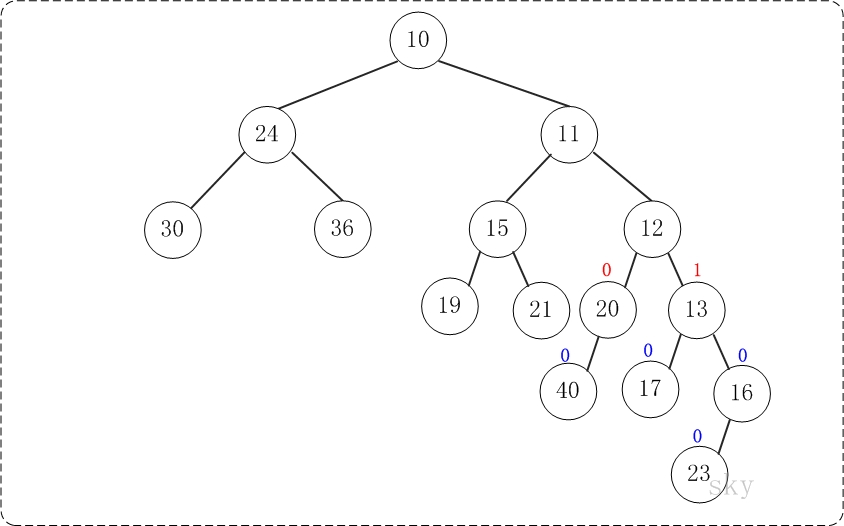
第7步:上一步得到的"树12的右孩子的NPL > 左孩子的NPL",因此交换左右孩子。得到的结果如下:

第8步:上一步得到的"树10的右孩子的NPL > 左孩子的NPL",因此交换左右孩子。得到的结果如下:
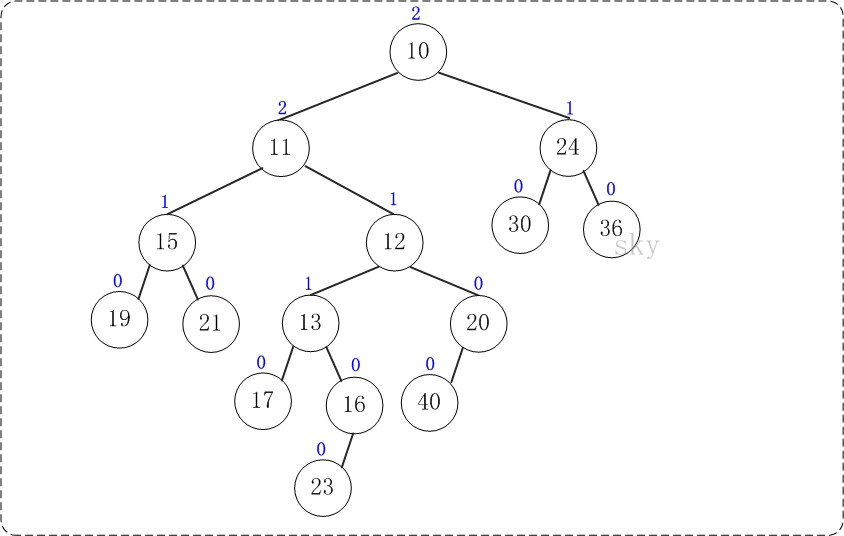
至此,合并完毕。上面就是合并得到的左倾堆!
下面看看左倾堆的基本操作的代码
1. 基本定义
template <class T>
class LeftistNode{
public:
T key; // 关键字(键值)
int npl; // 零路经长度(Null Path Length)
LeftistNode *left; // 左孩子
LeftistNode *right; // 右孩子 LeftistNode(T value, LeftistNode *l, LeftistNode *r):
key(value), npl(), left(l),right(r) {}
};
LeftistNode是左倾堆对应的节点类。
template <class T>
class LeftistHeap {
private:
LeftistNode<T> *mRoot; // 根结点 public:
LeftistHeap();
~LeftistHeap(); // 前序遍历"左倾堆"
void preOrder();
// 中序遍历"左倾堆"
void inOrder();
// 后序遍历"左倾堆"
void postOrder(); // 将other的左倾堆合并到this中。
void merge(LeftistHeap<T>* other);
// 将结点(key为节点键值)插入到左倾堆中
void insert(T key);
// 删除结点(key为节点键值)
void remove(); // 销毁左倾堆
void destroy(); // 打印左倾堆
void print();
private: // 前序遍历"左倾堆"
void preOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const;
// 中序遍历"左倾堆"
void inOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const;
// 后序遍历"左倾堆"
void postOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const; // 交换节点x和节点y
void swapNode(LeftistNode<T> *&x, LeftistNode<T> *&y);
// 合并"左倾堆x"和"左倾堆y"
LeftistNode<T>* merge(LeftistNode<T>* &x, LeftistNode<T>* &y);
// 将结点(z)插入到左倾堆(heap)中
LeftistNode<T>* insert(LeftistNode<T>* &heap, T key);
// 删除左倾堆(heap)中的结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
LeftistNode<T>* remove(LeftistNode<T>* &heap); // 销毁左倾堆
void destroy(LeftistNode<T>* &heap); // 打印左倾堆
void print(LeftistNode<T>* heap, T key, int direction);
};
LeftistHeap是左倾堆类,它包含了左倾堆的根节点,以及左倾堆的操作。
2. 合并
/*
* 合并"左倾堆x"和"左倾堆y"
*/
template <class T>
LeftistNode<T>* LeftistHeap<T>::merge(LeftistNode<T>* &x, LeftistNode<T>* &y)
{
if(x == NULL)
return y;
if(y == NULL)
return x; // 合并x和y时,将x作为合并后的树的根;
// 这里的操作是保证: x的key < y的key
if(x->key > y->key)
swapNode(x, y); // 将x的右孩子和y合并,"合并后的树的根"是x的右孩子。
x->right = merge(x->right, y); // 如果"x的左孩子为空" 或者 "x的左孩子的npl<右孩子的npl"
// 则,交换x和y
if(x->left == NULL || x->left->npl < x->right->npl)
{
LeftistNode<T> *tmp = x->left;
x->left = x->right;
x->right = tmp;
}
// 设置合并后的新树(x)的npl
if (x->right == NULL || x->left == NULL)
x->npl = ;
else
x->npl = (x->left->npl > x->right->npl) ? (x->right->npl + ) : (x->left->npl + ); return x;
} /*
* 将other的左倾堆合并到this中。
*/
template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::merge(LeftistHeap<T>* other)
{
mRoot = merge(mRoot, other->mRoot);
}
merge(x, y)是内部接口,作用是合并x和y这两个左倾堆,并返回得到的新堆的根节点。
merge(other)是外部接口,作用是将other合并到当前堆中。
3. 添加
/*
* 将结点插入到左倾堆中,并返回根节点
*
* 参数说明:
* heap 左倾堆的根结点
* key 插入的结点的键值
* 返回值:
* 根节点
*/
template <class T>
LeftistNode<T>* LeftistHeap<T>::insert(LeftistNode<T>* &heap, T key)
{
LeftistNode<T> *node; // 新建结点 // 新建节点
node = new LeftistNode<T>(key, NULL, NULL);
if (node==NULL)
{
cout << "ERROR: create node failed!" << endl;
return heap;
} return merge(mRoot, node);
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::insert(T key)
{
mRoot = insert(mRoot, key);
}
insert(heap, key)是内部接口,它是以节点为操作对象的。
insert(key)是外部接口,它的作用是新建键值为key的节点,并将其加入到当前左倾堆中。
4. 删除
/*
* 删除结点,返回根节点
*
* 参数说明:
* heap 左倾堆的根结点
* 返回值:
* 根节点
*/
template <class T>
LeftistNode<T>* LeftistHeap<T>::remove(LeftistNode<T>* &heap)
{
if (heap == NULL)
return NULL; LeftistNode<T> *l = heap->left;
LeftistNode<T> *r = heap->right; // 删除根节点
delete heap; return merge(l, r); // 返回左右子树合并后的新树
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::remove()
{
mRoot = remove(mRoot);
}
remove(heap)是内部接口,它是以节点为操作对象的。
remove()是外部接口,它的作用是删除左倾堆的最小节点。
注意:关于左倾堆的"前序遍历"、"中序遍历"、"后序遍历"、"打印"、"销毁"等接口就不再单独介绍了。后文的源码中有给出它们的实现代码,Please RTFSC(Read The Fucking Source Code)!
左倾堆的C++实现(完整源码)
左倾堆的实现文件(LeftistHeap.h)
/**
* C++: 左倾堆
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2014/03/31
*/ #ifndef _LEFTIST_TREE_HPP_
#define _LEFTIST_TREE_HPP_ #include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; template <class T>
class LeftistNode{
public:
T key; // 关键字(键值)
int npl; // 零路经长度(Null Path Length)
LeftistNode *left; // 左孩子
LeftistNode *right; // 右孩子 LeftistNode(T value, LeftistNode *l, LeftistNode *r):
key(value), npl(), left(l),right(r) {}
}; template <class T>
class LeftistHeap {
private:
LeftistNode<T> *mRoot; // 根结点 public:
LeftistHeap();
~LeftistHeap(); // 前序遍历"左倾堆"
void preOrder();
// 中序遍历"左倾堆"
void inOrder();
// 后序遍历"左倾堆"
void postOrder(); // 将other的左倾堆合并到this中。
void merge(LeftistHeap<T>* other);
// 将结点(key为节点键值)插入到左倾堆中
void insert(T key);
// 删除结点(key为节点键值)
void remove(); // 销毁左倾堆
void destroy(); // 打印左倾堆
void print();
private: // 前序遍历"左倾堆"
void preOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const;
// 中序遍历"左倾堆"
void inOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const;
// 后序遍历"左倾堆"
void postOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const; // 交换节点x和节点y
void swapNode(LeftistNode<T> *&x, LeftistNode<T> *&y);
// 合并"左倾堆x"和"左倾堆y"
LeftistNode<T>* merge(LeftistNode<T>* &x, LeftistNode<T>* &y);
// 将结点(z)插入到左倾堆(heap)中
LeftistNode<T>* insert(LeftistNode<T>* &heap, T key);
// 删除左倾堆(heap)中的结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
LeftistNode<T>* remove(LeftistNode<T>* &heap); // 销毁左倾堆
void destroy(LeftistNode<T>* &heap); // 打印左倾堆
void print(LeftistNode<T>* heap, T key, int direction);
}; /*
* 构造函数
*/
template <class T>
LeftistHeap<T>::LeftistHeap():mRoot(NULL)
{
} /*
* 析构函数
*/
template <class T>
LeftistHeap<T>::~LeftistHeap()
{
destroy(mRoot);
} /*
* 前序遍历"左倾堆"
*/
template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::preOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const
{
if(heap != NULL)
{
cout<< heap->key << " " ;
preOrder(heap->left);
preOrder(heap->right);
}
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::preOrder()
{
preOrder(mRoot);
} /*
* 中序遍历"左倾堆"
*/
template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::inOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const
{
if(heap != NULL)
{
inOrder(heap->left);
cout<< heap->key << " " ;
inOrder(heap->right);
}
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::inOrder()
{
inOrder(mRoot);
} /*
* 后序遍历"左倾堆"
*/
template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::postOrder(LeftistNode<T>* heap) const
{
if(heap != NULL)
{
postOrder(heap->left);
postOrder(heap->right);
cout<< heap->key << " " ;
}
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::postOrder()
{
postOrder(mRoot);
} /*
* 交换两个节点的内容
*/
template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::swapNode(LeftistNode<T> *&x, LeftistNode<T> *&y)
{
LeftistNode<T> *tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
} /*
* 合并"左倾堆x"和"左倾堆y"
*/
template <class T>
LeftistNode<T>* LeftistHeap<T>::merge(LeftistNode<T>* &x, LeftistNode<T>* &y)
{
if(x == NULL)
return y;
if(y == NULL)
return x; // 合并x和y时,将x作为合并后的树的根;
// 这里的操作是保证: x的key < y的key
if(x->key > y->key)
swapNode(x, y); // 将x的右孩子和y合并,"合并后的树的根"是x的右孩子。
x->right = merge(x->right, y); // 如果"x的左孩子为空" 或者 "x的左孩子的npl<右孩子的npl"
// 则,交换x和y
if(x->left == NULL || x->left->npl < x->right->npl)
{
LeftistNode<T> *tmp = x->left;
x->left = x->right;
x->right = tmp;
}
// 设置合并后的新树(x)的npl
if (x->right == NULL || x->left == NULL)
x->npl = ;
else
x->npl = (x->left->npl > x->right->npl) ? (x->right->npl + ) : (x->left->npl + ); return x;
} /*
* 将other的左倾堆合并到this中。
*/
template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::merge(LeftistHeap<T>* other)
{
mRoot = merge(mRoot, other->mRoot);
} /*
* 将结点插入到左倾堆中,并返回根节点
*
* 参数说明:
* heap 左倾堆的根结点
* key 插入的结点的键值
* 返回值:
* 根节点
*/
template <class T>
LeftistNode<T>* LeftistHeap<T>::insert(LeftistNode<T>* &heap, T key)
{
LeftistNode<T> *node; // 新建结点 // 新建节点
node = new LeftistNode<T>(key, NULL, NULL);
if (node==NULL)
{
cout << "ERROR: create node failed!" << endl;
return heap;
} return merge(mRoot, node);
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::insert(T key)
{
mRoot = insert(mRoot, key);
} /*
* 删除结点,返回根节点
*
* 参数说明:
* heap 左倾堆的根结点
* 返回值:
* 根节点
*/
template <class T>
LeftistNode<T>* LeftistHeap<T>::remove(LeftistNode<T>* &heap)
{
if (heap == NULL)
return NULL; LeftistNode<T> *l = heap->left;
LeftistNode<T> *r = heap->right; // 删除根节点
delete heap; return merge(l, r); // 返回左右子树合并后的新树
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::remove()
{
mRoot = remove(mRoot);
} /*
* 销毁左倾堆
*/
template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::destroy(LeftistNode<T>* &heap)
{
if (heap==NULL)
return ; if (heap->left != NULL)
destroy(heap->left);
if (heap->right != NULL)
destroy(heap->right); delete heap;
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::destroy()
{
destroy(mRoot);
} /*
* 打印"二叉查找树"
*
* key -- 节点的键值
* direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点;
* -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子;
* 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。
*/
template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::print(LeftistNode<T>* heap, T key, int direction)
{
if(heap != NULL)
{
if(direction==) // heap是根节点
cout << setw() << heap->key << "(" << heap->npl << ") is root" << endl;
else // heap是分支节点
cout << setw() << heap->key << "(" << heap->npl << ") is " << setw() << key << "'s " << setw() << (direction==?"right child" : "left child") << endl; print(heap->left, heap->key, -);
print(heap->right,heap->key, );
}
} template <class T>
void LeftistHeap<T>::print()
{
if (mRoot != NULL)
print(mRoot, mRoot->key, );
}
#endif
左倾堆的测试程序(LeftistHeapTest.cpp)
/**
* C 语言: 左倾堆
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2013/11/07
*/ #include <iostream>
#include "LeftistHeap.h"
using namespace std; int main()
{
int i;
int a[]= {,,,,,,,};
int b[]= {,,,,,,};
int alen=sizeof(a)/sizeof(a[]);
int blen=sizeof(b)/sizeof(b[]);
LeftistHeap<int>* ha=new LeftistHeap<int>();
LeftistHeap<int>* hb=new LeftistHeap<int>(); cout << "== 左倾堆(ha)中依次添加: ";
for(i=; i<alen; i++)
{
cout << a[i] <<" ";
ha->insert(a[i]);
}
cout << "\n== 左倾堆(ha)的详细信息: " << endl;
ha->print(); cout << "\n== 左倾堆(hb)中依次添加: ";
for(i=; i<blen; i++)
{
cout << b[i] <<" ";
hb->insert(b[i]);
}
cout << "\n== 左倾堆(hb)的详细信息: " << endl;
hb->print(); // 将"左倾堆hb"合并到"左倾堆ha"中。
ha->merge(hb);
cout << "\n== 合并ha和hb后的详细信息: " << endl;
ha->print(); // 销毁
ha->destroy(); return ;
}
左倾堆的C++测试程序
左倾堆的测试程序已经包含在它的实现文件(LeftistHeapTest.cpp)中了,这里仅给出它的运行结果:
== 左倾堆(ha)中依次添加:
== 左倾堆(ha)的详细信息:
() is root
() is 's left child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child
() is 's right child
() is 's left child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child == 左倾堆(hb)中依次添加:
== 左倾堆(hb)的详细信息:
() is root
() is 's left child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child
() is 's right child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child == 合并ha和hb后的详细信息:
() is root
() is 's left child
() is 's left child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child
() is 's right child
() is 's left child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child
() is 's left child
() is 's right child
左倾堆(二)之 C++的实现的更多相关文章
- 左倾堆(一)之 图文解析 和 C语言的实现
概要 本章介绍左倾堆,它和二叉堆一样,都是堆结构中的一员.和以往一样,本文会先对左倾堆的理论知识进行简单介绍,然后给出C语言的实现.后续再分别给出C++和Java版本的实现:实现的语言虽不同,但是原理 ...
- 左倾堆(三)之 Java的实现
概要 前面分别通过C和C++实现了左倾堆,本章给出左倾堆的Java版本.还是那句老话,三种实现的原理一样,择其一了解即可. 目录1. 左倾堆的介绍2. 左倾堆的图文解析3. 左倾堆的Java实现(完整 ...
- 纸上谈兵:左倾堆(leftist heap)
作者:Vamei 出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/vamei 欢迎转载,也请保留这段声明.谢谢! 我们之前讲解了堆(heap)的概念.堆是一个优先队列.每次从堆中取出的元素都是堆中 ...
- 二项堆(二)之 C++的实现
概要 上一章介绍了二项堆的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了二项堆.本章是二项堆的C++实现. 目录1. 二项树的介绍2. 二项堆的介绍3. 二项堆的基本操作4. 二项堆的C++实现(完整源码)5. 二项堆 ...
- 二叉堆(二)之 C++的实现
概要 上一章介绍了堆和二叉堆的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了二叉堆.本章是二叉堆的C++实现. 目录1. 二叉堆的介绍2. 二叉堆的图文解析3. 二叉堆的C++实现(完整源码)4. 二叉堆的C++测试程 ...
- 斜堆(二)之 C++的实现
概要 上一章介绍了斜堆的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了斜堆.本章是斜堆的C++实现. 目录1. 斜堆的介绍2. 斜堆的基本操作3. 斜堆的C++实现(完整源码)4. 斜堆的C++测试程序 转载请注明出处 ...
- 斐波那契堆(二)之 C++的实现
概要 上一章介绍了斐波那契堆的基本概念,并通过C语言实现了斐波那契堆.本章是斐波那契堆的C++实现. 目录1. 斐波那契堆的介绍2. 斐波那契堆的基本操作3. 斐波那契堆的C++实现(完整源码)4. ...
- 《数据结构与算法分析:C语言描述》复习——第五章“堆”——二叉堆
2014.06.15 22:14 简介: 堆是一种非常实用的数据结构,其中以二叉堆最为常用.二叉堆可以看作一棵完全二叉树,每个节点的键值都大于(小于)其子节点,但左右孩子之间不需要有序.我们关心的通常 ...
- 笔试算法题(46):简介 - 二叉堆 & 二项树 & 二项堆 & 斐波那契堆
二叉堆(Binary Heap) 二叉堆是完全二叉树(或者近似完全二叉树):其满足堆的特性:父节点的值>=(<=)任何一个子节点的键值,并且每个左子树或者右子树都是一 个二叉堆(最小堆或者 ...
随机推荐
- Java并发包中Lock的实现原理
1. Lock 的简介及使用 Lock是java 1.5中引入的线程同步工具,它主要用于多线程下共享资源的控制.本质上Lock仅仅是一个接口(位于源码包中的java\util\concurrent\l ...
- EnumHelper枚举常用操作类
在项目中需要把枚举填充到下拉框中,所以使用统一的方法实现,测试代码如下: namespace CutPictureTest.Comm { public class EnumHelper { publi ...
- Spring3 整合Hibernate3.5 动态切换SessionFactory (切换数据库方言)
一.缘由 上一篇文章Spring3.3 整合 Hibernate3.MyBatis3.2 配置多数据源/动态切换数据源 方法介绍到了怎么样在Sping.MyBatis.Hibernate整合的应用中动 ...
- 隐藏nginx 版本号信息
为了安全,想将http请求响应头里的nginx版本号信息隐藏掉: 1. nginx配置文件里增加 server_tokens off; server_tokens作用域是http server loc ...
- mycat初探
1:安装客户端 yum install mysql 2:安装服务端 yum install mysql-server 3:mycat要求不区分大小写 my.cnf(/etc/my.cnf)的[mysq ...
- Java蛇形数组的简单实现代码
上周五和朋友聊天谈到个蛇形数组的java实现办法,命题是:假设一个二维数组宽w高h,从1开始蛇形输出. int[][] numberMatric = new int[w][h]; 当时午睡过头脑袋不清 ...
- 恶心的hadoop集群
具体配置:网上一堆,我说一下我的问题好了! “完全” 分布式集群 注意地方有三点: 1.你的"master" dfs目录中的某个Id不一致,具体位置,有空我再找找.(经过我找了一下 ...
- 调用axis2开发的接口遇到的问题
第1个异常 [org.apache.struts.actions.DispatchAction] – Dispatch[/myservice/NgCallServiceInfo] to method ...
- [Lua]50行代码的解释器,用来演示lambda calculus
嗯,来写写经过: 在知乎上看见用Belleve牛用javascript写了一个精简的lisp解释器 => 我也想写一个,用lua写,能多简单呢? => 写了一个阉割的scheme解释器,包 ...
- EXCELL中怎么将两列数据对比,找出相同的和不同的数据?
假设你要从B列中找出A列里没有的数据,那你就在C1单元格里输入“=IF(ISNA(VLOOKUP(B1,A:A,1,0)),"F","T")”显示T就表示有,F ...
