你可能不知道的shell、bash二三事(Centos 7)
个人.bashrc:
~/.bashrc:
# .bashrc # User specific aliases and functions alias rm='rm -i'
alias cp='cp -i'
alias mv='mv -i' # Source global definitions
if [ -f /etc/bashrc ]; then
. /etc/bashrc
fi
全局bashrc:
/etc/bashrc:
# /etc/bashrc # System wide functions and aliases
# Environment stuff goes in /etc/profile # It's NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you
# are doing. It's much better to create a custom.sh shell script in
# /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this
# will prevent the need for merging in future updates. # are we an interactive shell?
if [ "$PS1" ]; then
if [ -z "$PROMPT_COMMAND" ]; then
case $TERM in
xterm*|vte*)
if [ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-xterm
elif [ "${VTE_VERSION:-0}" -ge ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND="__vte_prompt_command"
else
PROMPT_COMMAND='printf "\033]0;%s@%s:%s\007" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"'
fi
;;
screen*)
if [ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-screen ]; then
PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-screen
else
PROMPT_COMMAND='printf "\033k%s@%s:%s\033\\" "${USER}" "${HOSTNAME%%.*}" "${PWD/#$HOME/~}"'
fi
;;
*)
[ -e /etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-default ] && PROMPT_COMMAND=/etc/sysconfig/bash-prompt-default
;;
esac
fi
# Turn on parallel history
shopt -s histappend
history -a
# Turn on checkwinsize
shopt -s checkwinsize
[ "$PS1" = "\\s-\\v\\\$ " ] && PS1="[\u@\h \W]\\$ "
# You might want to have e.g. tty in prompt (e.g. more virtual machines)
# and console windows
# If you want to do so, just add e.g.
# if [ "$PS1" ]; then
# PS1="[\u@\h:\l \W]\\$ "
# fi
# to your custom modification shell script in /etc/profile.d/ directory
fi if ! shopt -q login_shell ; then # We're not a login shell
# Need to redefine pathmunge, it get's undefined at the end of /etc/profile
pathmunge () {
case ":${PATH}:" in
*:"$1":*)
;;
*)
if [ "$2" = "after" ] ; then
PATH=$PATH:$
else
PATH=$:$PATH
fi
esac
}
# By default, we want umask to get set. This sets it for non-login shell.
# Current threshold for system reserved uid/gids is
# You could check uidgid reservation validity in
# /usr/share/doc/setup-*/uidgid file
if [ $UID -gt ] && [ "`/usr/bin/id -gn`" = "`/usr/bin/id -un`" ]; then
umask
else
umask
fi SHELL=/bin/bash
# Only display echos from profile.d scripts if we are no login shell
# and interactive - otherwise just process them to set envvars
for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "$PS1" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null
fi
fi
done unset i
unset -f pathmunge
fi
# vim:ts=4:sw=4
用户的bashprofile:
~/.bash_profile
# .bash_profile # Get the aliases and functions
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
fi # User specific environment and startup programs PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin export PATH
[root@ckl1 bashtest]# echo $HOME
/root
全局profile:
"/etc/profile"
# /etc/profile # System wide environment and startup programs, for login setup
# Functions and aliases go in /etc/bashrc # It's NOT a good idea to change this file unless you know what you
# are doing. It's much better to create a custom.sh shell script in
# /etc/profile.d/ to make custom changes to your environment, as this
# will prevent the need for merging in future updates. pathmunge () {
case ":${PATH}:" in
*:"$1":*)
;;
*)
if [ "$2" = "after" ] ; then
PATH=$PATH:$
else
PATH=$:$PATH
fi
esac
} if [ -x /usr/bin/id ]; then
if [ -z "$EUID" ]; then
# ksh workaround
EUID=`/usr/bin/id -u`
UID=`/usr/bin/id -ru`
fi
USER="`/usr/bin/id -un`"
LOGNAME=$USER
MAIL="/var/spool/mail/$USER"
fi # Path manipulation
if [ "$EUID" = "" ]; then
pathmunge /usr/sbin
pathmunge /usr/local/sbin
else
pathmunge /usr/local/sbin after
pathmunge /usr/sbin after
fi HOSTNAME=`/usr/bin/hostname >/dev/null`
HISTSIZE=
if [ "$HISTCONTROL" = "ignorespace" ] ; then
export HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
else
export HISTCONTROL=ignoredups
fi export PATH USER LOGNAME MAIL HOSTNAME HISTSIZE HISTCONTROL # By default, we want umask to get set. This sets it for login shell
# Current threshold for system reserved uid/gids is
# You could check uidgid reservation validity in
# /usr/share/doc/setup-*/uidgid file
if [ $UID -gt ] && [ "`/usr/bin/id -gn`" = "`/usr/bin/id -un`" ]; then
umask
else
umask
fi for i in /etc/profile.d/*.sh ; do
if [ -r "$i" ]; then
if [ "${-#*i}" != "$-" ]; then
. "$i"
else
. "$i" >/dev/null
fi
fi
done unset i
unset -f pathmunge #java environment
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk1.8.0_161
export CLASSPATH=.:${JAVA_HOME}/jre/lib/rt.jar:${JAVA_HOME}/lib/dt.jar:${JAVA_HOME}/lib/tools.jar
export PATH=$PATH:${JAVA_HOME}/bin
关于别名:
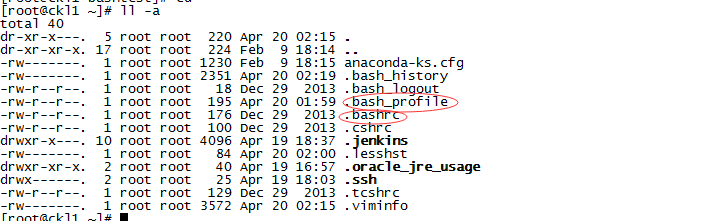
别名,典型的如ll,是ls -l 的别名,那么这个别名定义在哪呢,其实是在/etc/profile.d/colorls.sh 中,也就是我在上面几个文件中,标红的部分。
colorls.sh:
# color-ls initialization # Skip all for noninteractive shells.
[ ! -t ] && return #when USER_LS_COLORS defined do not override user LS_COLORS, but use them.
if [ -z "$USER_LS_COLORS" ]; then alias ll='ls -l' >/dev/null
alias l.='ls -d .*' >/dev/null INCLUDE=
COLORS= for colors in "$HOME/.dir_colors.$TERM" "$HOME/.dircolors.$TERM" \
"$HOME/.dir_colors" "$HOME/.dircolors"; do
[ -e "$colors" ] && COLORS="$colors" && \
INCLUDE="`/usr/bin/cat "$COLORS" | /usr/bin/grep '^INCLUDE' | /usr/bin/cut -d ' ' -f2-`" && \
break
done [ -z "$COLORS" ] && [ -e "/etc/DIR_COLORS.$TERM" ] && \
COLORS="/etc/DIR_COLORS.$TERM" [ -z "$COLORS" ] && [ -e "/etc/DIR_COLORS.256color" ] && \
[ "x`/usr/bin/tty -s && /usr/bin/tput colors 2>/dev/null`" = "x256" ] && \
COLORS="/etc/DIR_COLORS.256color" [ -z "$COLORS" ] && [ -e "/etc/DIR_COLORS" ] && \
COLORS="/etc/DIR_COLORS" # Existence of $COLORS already checked above.
[ -n "$COLORS" ] || return if [ -e "$INCLUDE" ];
then
TMP="`/usr/bin/mktemp .colorlsXXX -q --tmpdir=/tmp`"
[ -z "$TMP" ] && return /usr/bin/cat "$INCLUDE" >> $TMP
/usr/bin/grep -v '^INCLUDE' "$COLORS" >> $TMP eval "`/usr/bin/dircolors --sh $TMP 2>/dev/null`"
/usr/bin/rm -f $TMP
else
eval "`/usr/bin/dircolors --sh $COLORS 2>/dev/null`"
fi [ -z "$LS_COLORS" ] && return
/usr/bin/grep -qi "^COLOR.*none" $COLORS >/dev/null >/dev/null && return
fi unset TMP COLORS INCLUDE alias ll='ls -l --color=auto' >/dev/null
alias l.='ls -d .* --color=auto' >/dev/null
alias ls='ls --color=auto' >/dev/null
(END)
所以,什么情况下可以执行别名呢:
1:执行了/etc/profile
2:执行了~/.bashrc,~/.bashrc中引用了 /etc/bashrc(在该文件中,执行了ll别名所在的colorls.sh文件)
3:执行了~/.bash_profile,因为该文件中判断是否存在~/.bashrc,存在的话,会去执行~/.bashrc;根据上一步的结论,自然也就可以执行别名。
ok。那么,进一步,什么情况会执行上述的两种情况:
第一种情况(/etc/profile):
查阅了man bash后,发现:
1.交互的登录shell,或者--login选项的非交互shell。
When bash is invoked as an interactive login shell, or as a non-interactive shell with the --login option, it first reads and executes
commands from the file /etc/profile, if that file exists. After reading that file, it looks for ~/.bash_profile, ~/.bash_login, and ~/.profile,
in that order, and reads and executes commands from the first one that exists and is readable.
The --noprofile option may be used when the shell is started to inhibit this behavior.
不过在我的centos7中,~/.profile不存在。
第二种情况(~/.bashrc):
1.交互的,但不是登录的shell。
When an interactive shell that is not a login shell is started, bash reads and executes commands from ~/.bashrc, if that file exists.
This may be inhibited by using the --norc option. The --rcfile file option will force bash to read and execute commands from file instead of ~/.bashrc.
第三种情况(~/.bash_profile):
同情况1。
Shell的几种类型:
ok。那么看了上面两种还是很蒙,那么我们再科普下什么是交互shell、非交互shell、登录shell和非登录shell。
我是参考了这里:https://blog.csdn.net/wisgood/article/details/52043522
我的理解:
登录shell:
ssh登录的,就是登录shell,登录shell要退出的话,是执行logout。比如我们用的putty、securtCRT。
非登录shell:
登录成功了之后,或者并没有进行远程登录,直接就在本机的(VMVARE的虚拟机中的shell都不能算,可采用下面的方法测试)ubuntu打开终端,这种,我理解的就是非登录shell。
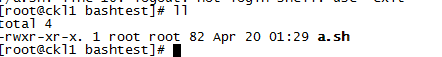
我做了个小实验,我是secureCRT远程到该服务器的,在/home/upload/bashtest/a.sh中,我写了句logout:
[root@ckl1 bashtest]# less a.sh
#/bin/bash logout
执行该脚本:
[root@ckl1 bashtest]# ./a.sh
结果:
./a.sh: line 3: logout: not login shell: use `exit'
区分登录与非登录shell的好办法:
(https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/38175/difference-between-login-shell-and-non-login-shell)
1.通过echo $0,如果结果是-bash,那就是login shell。否则不是。

2.如果可以执行logout命令,那么就是login shell;否则不是。
交互shell:
就是我们不管是用SecurtCRT这样的工具进入远程服务器也好,或者本机打开终端也好,都可以执行各种命令
在执行这些命令时,shell是可以和我们互动的,比如要求我们输入东西,比如按Tab可以提示,等等。
非交互Shell:
shell脚本执行,一般来说就是非交互的,我们写好了脚本,只要交给shell执行就好,期间不需要和我们交互。命令输入错了,会直接提示并退出。
以上两种,其实是不同维度,可以两两组合
| 交互 | 非交互 | |
| 登录 | 远程登录ssh,调用的文件包括:/etc/profile,~/.bash_profile,~/.bash_login,~/.profile | 较少见,可能读/etc/profile , ~/.profile。也可能不读。依然请参考第一个答案:https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/38175/difference-between-login-shell-and-non-login-shell |
| 非登录 | 本机打开终端,调用文件包括:~/.bashrc | 执行shell脚本,调用文件包括:BASH_ENV 指定的文件 |
非交互shell中,怎么才能使用别名:
参考:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1615877/why-aliases-in-a-non-interactive-bash-shell-do-not-work
方式1:
shopt -s expand_aliases
不过我的centos 7,未生效。
方式2:
source their .bashrc at the end of their profile。
也就是在~/.bash_profile中新增一行:source ~/.bashrc
但是我这边依然没生效。
方式3:
直接脚本中增加:source ~/.bashrc
#/bin/bash
ls -l echo "ll "
source ~/.bashrc ll
ok。可以正常工作。
ssh执行远程命令时,怎么才能使用别名:
1.
首先修改远程主机的~/.bashrc,新增一行:
shopt -s expand_aliasesssh -t @host ll
2.
ssh @host 'bash -ci ll'
参考:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1615877/why-aliases-in-a-non-interactive-bash-shell-do-not-work
你可能不知道的shell、bash二三事(Centos 7)的更多相关文章
- 你可能不知道的Shell
Shell也叫做命令行界面,它是*nix操作系统下用户和计算机的交互界面.Shell这个词是指操作系统中提供访问内核服务的程序. 这篇文章向大家介绍Shell一些非广为人知.但却实用有趣的知识,权当品 ...
- JavaScript中你所不知道的Object(二)--Function篇
上一篇(JavaScript中你所不知道的Object(一))说到,Object对象有大量的内部属性,而其中多数和外部属性的操作有关.最后留了个悬念,就是Boolean.Date.Number.Str ...
- 你能知道的或者不知道的shell变量都在这里
第2章 shell变量讲解 2.1 shell中的变量讲解 2.1.1 什么是shell变量 变量的本质就是内存中的一块区域 变量名 位置 变量是脚本中经常会使用的内容信息 变量可以在脚本中直接使用 ...
- 【转】你可能不知道的Shell
本文转自http://coolshell.cn/articles/8619.html,只摘取了其中的一部分. 再分享一些可能你不知道的shell用法和脚本,简单&强大! 在阅读以下部分前,强烈 ...
- 关于JavaScript对象,你所不知道的事(二)- 再说属性
说完了对象那些不常用的冷知识,是时候来看看JavaScript中对象属性有哪些有意思的东西了. 不出你所料,对象属性自然也有其相应的特征属性,但是这个话题有点复杂,让我们先从简单的说起,对象属性的分类 ...
- Spring中你可能不知道的事(二)
在上一节中,我介绍了Spring中极为重要的BeanPostProcessor BeanFactoryPostProcessor Import ImportSelector,还介绍了一些其他的零碎知识 ...
- 你需要知道的Nginx配置二三事
做服务端开发的,工作中难免会遇到处理Nginx配置相关问题.在配置Nginx时,我一直本着“照葫芦画瓢”的原则,复制已有的配置代码,自己修修改改然后完成配置需求,当有人问起Nginx相关问题时,其实仍 ...
- c++ --> 你可能不知道的c++
你可能不知道的c++ 你可能不知道的 C++(一) 你可能不知道的 C++(二)
- 你所不知道的linq(二)
上一篇说了from in select的本质,具体参见你所不知道的linq.本篇说下from...in... from... in... select 首先上一段代码,猜猜结果是什么? class P ...
随机推荐
- 浪漫程序员 HTML5爱心表白动画
我们程序员在追求爱情方面也是非常浪漫的,下面是一位同学利用自己所学的HTML5知识自制的HTML5爱心表白动画,画面非常温馨甜蜜,这样的创意很容易打动女孩,如果你是单身的程序员,也赶紧来制作自己的爱心 ...
- 共享锁(S锁)和排它锁(X锁)
释义 共享锁:(读取)操作创建的锁.其他用户可以并发读取数据,但任何事物都不能获取数据上的排它锁,直到已释放所有共享锁. 共享锁(S锁)又称为读锁,若事务T对数据对象A加上S锁,则事务T只能读A:其他 ...
- Linux 下 Nginx + JDK + Tomcat + MySQL 安装指南
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/smartbetter/article/details/52026342 Nginx 是一款高性能的 http 服务器/反向代理服务器/电子邮 ...
- C语言中的数组问题
数组默认最后一位是 结束符 占一位, 假如是7个字节大小的数组 实际输入为6个字节,最后一个字节为'\0' 这样写 char password_set[7]={"123456"}; ...
- [Err] 1231 - Variable 'sql_mode' can't be set to the value of 'NULL
在MYSQL还原语句的时候,报: [Err] - Variable 'sql_mode' can't be set to the value of 'NULL 解决办法:打开SQL语句,把里面的注释给 ...
- git branch 命令
1.git init 该命令执行之后并没有创建branch 2.git add 添加文件,这时branch 也还没生成.git branch name也没用 3.git commit 提交到git r ...
- Linux服务器部署 Elasticsearch 成功,本机却访问不了
Elasticsearch版本: elasticsearch- 服务器版本: CentOS release 6.8 (Final) 问题: Linux服务器上部署了 Elasticsearch 5.5 ...
- PostgreSQL分布式架构之——PL/Proxy
1. PL/Proxy的介绍 1.1 PL/Proxy概述 PL/Proxy是一款能在PostgreSQL数据库实现数据库水平拆分的软件:可以理解分布式架构(shared nothing);但是不是真 ...
- Ruby Tutorial
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/ruby/ruby_quick_guide.htm http://www.cnblogs.com/PurpleCow/archive/201 ...
- 流媒体服务器+EasyDarwin+EasyPusher+VLC+Red5+OBS+Unity+RTSP+RTMP+FFMPEG
最近有个需求在Unity中直播桌面,着用到了视频流. ------------------------------ VLC自身有流服务器功能,但是非常慢非常慢,还是用VLC拉流吧,好像大家也是这么做的 ...
