Spring ( 五 )Spring之数据访问与事务管理
个人博客网:https://wushaopei.github.io/ (你想要这里多有)
一、Spring之数据访问
1、Spring数据访问工程环境搭建

jdbc.properties配置文件:
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.password=root
jdbc.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/jdbctemplateapplicationContext.xml配置文件:
<!-- 加载jdbc.properties配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
</bean>
<!-- jdbcTempalte是一个工具类,专门用来执行sql语句 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>测试代码:
@Test
public void testDataSource() throws Exception {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) applicationContext.getBean("dataSource");
System.out.println( dataSource.getConnection() );
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate"));
}2、Spring之JdbcTemplate使用
在Spring中提供了对jdbc的封装类叫JdbcTemplate。它可以很方便的帮我们执行sql语句,操作数据库。
先准备单表的数据库数据
drop database if exists jdbctemplate;
create database jdbctemplate;
use jdbctemplate;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int(11) primary key AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`salary` decimal(11,2) DEFAULT NULL
);
insert into `employee`(`id`,`name`,`salary`)
values (1,'李三',5000.23),(2,'李四',4234.77),(3,'王五',9034.51),
(4,'赵六',8054.33),(5,'孔七',6039.11),(6,'曹八',7714.11);
select * from employee;
创建一个与数据库表对应的javaBean类

3、将id=5的记录的salary字段更新为1300.00
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class JdbcTempalteTest {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
// 实验2:将id=5的记录的salary字段更新为1300.00
String sql = "update employee set salary = ? where id = ?";
System.out.println( jdbcTemplate.update(sql, new BigDecimal(1300),5) );
}
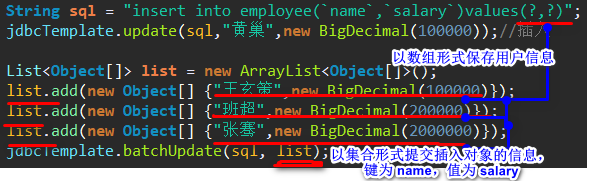
}4、批量插入
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
String sql = "insert into employee(`name`,`salary`) values(?,?)";
// jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "尚硅谷94V587",new BigDecimal(100000)); //插入一条
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<Object[]>();
batchArgs.add(new Object[] {"新来的1",new BigDecimal(30000)});
batchArgs.add(new Object[] {"新来的2",new BigDecimal(40000)});
batchArgs.add(new Object[] {"新来的3",new BigDecimal(50000)});
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
}分析图解:
数据库结果:
5、查询id=5的数据库记录,封装为一个Java对象返回
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception {
String sql = "select id,name,salary from employee where id = ?";
// rowMapper是将查询到的ResultSet的每一行记录转换成为一个javaBean对象
Employee employee = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Employee>(Employee.class), 5);
System.out.println( employee );
}
6、查询salary>4000的数据库记录,封装为List集合返回
public void test5() throws Exception {
// QueryRunner
// update() ====>>>> insert、update、delete
// 到底是查一条,还是查多条记录,由ResultSetHandler决定
// Jdbctempalte
// update() ====>>>> insert、update、delete
// queryForObject 查一个对象
// query 查多个对象
String sql = "select id,name,salary from employee where salary > ?";
List<Employee> employees = jdbcTemplate.query(sql,
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Employee>(Employee.class), new BigDecimal(4000));
employees.forEach(System.out::println);
}7、查询最大salary
@Test
public void test6() throws Exception {
String sql = "select max(salary) from employee";
BigDecimal maxSalary = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, BigDecimal.class);
System.out.println( maxSalary );
}8、使用带有具名参数的SQL语句插入一条员工记录,并以Map形式传入参数值
配置NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
<!-- 配置可以解析执行具名参数的sql的JdbcTemplate -->
<bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
Test中添加以下注解,用于注入xml中解析执行具名参数所用

@Test
public void test7() throws Exception {
/**
* :name 就是占位符,参数。名是name。 一起,就是具名参数
*/
String sql = "insert into employee(`name`,`salary`) values(:name,:salary)";
Map<String, Object>paramMap = new HashMap<>();
paramMap.put("name", "这是具名参数的name");
paramMap.put("salary", new BigDecimal(100000));
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, paramMap);
}Mysql 结果:

9、重复8,以SqlParameterSource形式传入参数值
@Test
public void test8() throws Exception {
/**
* :name 就是占位符,参数。名是name。 一起,就是具名参数
*/
String sql = "insert into employee(`name`,`salary`) values(:name,:salary)";
Employee employee = new Employee(null, "新插入的帅哥", new BigDecimal(3000));
namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql, new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(employee));
}10、创建Dao,自动装配JdbcTemplate对象
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public Employee queryEmployeeById(Integer id) {
String sql = "select id,name,salary from employee where id = ?";
Employee employee = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Employee>(Employee.class), id);
return employee;
}
}配置内容:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.webcode"></context:component-scan>测试代码:
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class JdbcTempalteTest {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
NamedParameterJdbcTemplate namedParameterJdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
EmployeeDao employeeDao;
@Test
public void test9() throws Exception {
System.out.println( employeeDao.queryEmployeeById(1) );
}
}11、通过继承JdbcDaoSupport创建JdbcTemplate的Dao
@Repository
public class EmployeeDao extends JdbcDaoSupport {
// @Autowired
// private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public Employee queryEmployeeById(Integer id) {
String sql = "select id,name,salary from employee where id = ?";
Employee employee = getJdbcTemplate().queryForObject(sql,
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Employee>(Employee.class), id);
return employee;
}
@Autowired
public void setJdbcTemplate2(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
setJdbcTemplate(jdbcTemplate);
}
}源码分析方法实现与调用过程:

二、声明式事务
事务分为声明式和编程式两种:
声明式事务:声明式事务是指通过注解(和xml配置)的形式对事务的各种特性进行控制和管理。
编码式(编程式)事务:指的是通过编码的方式实现事务的声明。
1、编码方式实现事务:

2、声明式事务环境搭建
2.1、准备测试数据库
##创建tx数据库
drop database if exists `tx`;
CREATE database `tx`;
##切换tx数据库
USE `tx`;
##删除用户表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `user`;
##创建用户表
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`username` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
`money` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
);
##插入数据
insert into `user`(`username`,`money`) values ('张三',1000),('李四',1000);
##删除图书表
drop table if exists `book`;
##创建图书表
create table `book`(
`id` int primary key auto_increment,
`name` varchar(500) not null,
`stock` int
);
##插入数据
insert into book(`name`,`stock`) values('java编程思想',100),('C++编程思想',100);
##查看数据
select * from book;
select * from user;2.2、创建一个Java工程,导入Jar包
@Repository
public class UserDao {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void updateUser() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update user set username = '用户表被修改了'");
}
}
@Repository
public class BookDao {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void updateBook() {
jdbcTemplate.update("update book set name = '图书表被修改了'");
}
}Service
@Service
public class TransactionService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
public void multiUpdate() {
userDao.updateUser();
int i = 12 / 0 ;
bookDao.updateBook();
}
}3、测试Service的默认事务
【1】测试service服务层的默认事务
默认一个sql一个事务
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
public class SpringTest {
@Autowired
TransactionService transactionService;
@Test
public void testMultiUpdate() throws Exception {
transactionService.multiUpdate();
}
}异常的演示


Spring事务引入的分析------PlatformTransactionManager类简单介绍


4、使用Spring的注解声明事务管制
【1】测试Spring的声明式事务
TransactionService中的修改
/**
* @Transactional表示当前方法有事务管理
*/
@Transactional
public void multiUpdate() {
userDao.updateUser();
// int i = 12 / 0 ;
bookDao.updateBook();
}配置文件中的内容:
<!--
配置事务管理===等价于切面
-->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<!-- dataSource一定要是操作数据库的数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<!--
开启事务的注解支持==做aop
transaction-manager="transactionManager" 使用哪个事务管理器来管理事务
如果事务管理器的id就叫transactionManager,
则:属性transaction-manager可以省略
-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
5、noRollbackFor和noRollbackForClassName测试不回滚的异常
【1】noRollbackFor和noRollbackForClassName测试不回滚的异常
/**
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @Transactional表示当前方法有事务管理<br/>
* Spring底层默认是回滚运行时异常,以运行时子异常<br/>
* noRollbackFor设置哪些异常不回滚事务<br/>
* noRollbackForClassName设置哪些类型的异常不回滚事务<br/>
*/
@Transactional(noRollbackForClassName="java.lang.ArithmeticException")
public void multiUpdate() throws FileNotFoundException {
userDao.updateUser();
int i = 12 / 0 ;
bookDao.updateBook();
}运行时异常回滚

编译异常:不回滚

6、自定义设置回滚异常
【1】rollbackFor和rollbackForClassName回滚的异常
/**
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @Transactional表示当前方法有事务管理<br/>
* Spring底层默认是回滚运行时异常,以运行时子异常<br/>
* rollbackFor是设置哪个异常回滚事务<br/>
* rollbackForClassName是设置哪个异常类名也会回滚事务<br/>
*/
@Transactional()
public void multiUpdate() throws FileNotFoundException {
userDao.updateUser();
// int i = 12 / 0 ;
int i = 12 ;
if (i == 12) {
throw new FileNotFoundException("asdf");
}
bookDao.updateBook();
}7、事务的只读属性
实验4:测试readOnly只读属性
/**
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @Transactional表示当前方法有事务管理<br/>
* Spring底层默认是回滚运行时异常,以运行时子异常<br/>
* readOnly 设置当前执行的sql语句是不是只是select查询
* 如果设置为false就允许执行insert,delete、update
*/
@Transactional(readOnly=true)
public void multiUpdate() throws FileNotFoundException {
userDao.updateUser();
bookDao.updateBook();
}
8、事务超时属性timeout(秒为单位)
/**
* @throws FileNotFoundException
* @throws InterruptedException
* @Transactional表示当前方法有事务管理<br/>
* Spring底层默认是回滚运行时异常,以运行时子异常<br/>
* timeout设置连接的超时属性。
* timeout=3表示3秒后不允许再执行sql语句
*/
@Transactional(timeout=3)
public void multiUpdate() throws InterruptedException {
userDao.updateUser();
Thread.sleep(4000);
bookDao.updateBook();
}
10、事务的传播特性propagation
什么是事务的传播行为:
当事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,必须指定事务应该如何传播。例如:方法可能继续在现有事务中运行,也可能开启一个新事务,并在自己的事务中运行。
事务的传播行为可以由传播属性指定。Spring定义了7种类传播行为。
事务的传播特性,有以下几种类型:

11、注解演示事物传播特性
UserService
BookService
TransactionService
实验1:大小事务传播特性都是REQUIRED
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void multiTransaction() {
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void updateBook() {
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void updateUser() {
实验2:大小事务传播特性都是REQUIRES_NEW
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void multiTransaction()
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void updateBook()
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void updateUser()

实验3:大事务是REQUIRED,小事务都是REQUIRES_NEW
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void multiTransaction()
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void updateBook()
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void updateUser()实验3跟实验2一样。
实验4:大事务是REQUIRED,小1REQUIRED,小2REQUIRES_NEW
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void multiTransaction()
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void updateBook()
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void updateUser()
三、xml配置式事务声明
去掉。所有@Transactional的注解。
配置文件内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.webcode"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 加载jdbc.properties配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}" />
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}" />
</bean>
<!-- jdbcTempalte是一个工具类,专门用来执行sql语句 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager"
class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 配置事务特性 -->
<tx:advice id="tx_advice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!--
配置一个或多个方法的特性
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
name表示方法名
save*表示方法名以save打头的方法都算
propagation="REQUIRED"表示必须要有事务
-->
<tx:method name="save*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="update*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<!--
精确匹配方法名
精确匹配优先 ===>>> 半模糊(update*) ====>>>> *
-->
<tx:method name="multiTransaction" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="updateUser" propagation="REQUIRES_NEW"/>
<!--
*表示剩下的方法
read-only="true"会做一些优化
-->
<tx:method name="*" read-only="true"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--
配置代理
-->
<aop:config>
<!-- advisor是配置切面 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="tx_advice"
pointcut="execution(public * com.webcode.service..*Service*.*(..))"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
四、Spring整合Web
1、在web工程中添加Spring的jar包
Spring的核心包
spring-beans-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-context-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-core-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-expression-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
aop包
spring-aop-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-aspects-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
com.springsource.org.aopalliance-1.0.0.jar
com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar
JDBC-ORM包
spring-jdbc-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-orm-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-tx-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
Spring的web整合包
spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
测试包
spring-test-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
- ServletContext在web工程启动的时候创建
- 在Web工程停止的时候销毁
整合Spring和Web容器分两个步骤:
1、导入spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
2、在web.xml配置文件中配置org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener监听器监听ServletContext的初始化
3、在web.xml配置文件中配置contextConfigLocation上下文参数。配置Spring配置文件的位置,以用于初始化Spring容器
在web.xml中配置
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
获取WebApplicationContext上下文对象的方法如下:
方法一(推荐):
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext())
方法二(不推荐):
getServletContext().getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
Spring ( 五 )Spring之数据访问与事务管理的更多相关文章
- Spring 4 官方文档学习(九)数据访问之事务管理
说明:未整理版,未完待续,请绕行 本部分的重点是数据访问以及数据访问层与业务层之间的交互. 1.Spring框架的事务管理 介绍 http://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/c ...
- Spring数据访问和事务
1.模型 2.解耦 3.实现 3.1 核心接口 3.2 代码分析 3.2.1 事务管理 3.2.2 数据访问 4.使用 4.1 编程模式 4.2 配置模式 4.2.1 声明式配置方式 4.2.2 注解 ...
- Solon Web 开发,五、数据访问、事务与缓存应用
Solon Web 开发 一.开始 二.开发知识准备 三.打包与运行 四.请求上下文 五.数据访问.事务与缓存应用 六.过滤器.处理.拦截器 七.视图模板与Mvc注解 八.校验.及定制与扩展 九.跨域 ...
- SpringBoot之数据访问和事务-专题三
SpringBoot之数据访问和事务-专题三 四.数据访问 4.1.springboot整合使用JdbcTemplate 4.1.1 pom文件引入 <parent> <groupI ...
- Spring Boot 2.x基础教程:事务管理入门
什么是事务? 我们在开发企业应用时,通常业务人员的一个操作实际上是对数据库读写的多步操作的结合.由于数据操作在顺序执行的过程中,任何一步操作都有可能发生异常,异常会导致后续操作无法完成,此时由于业务逻 ...
- Spring整合Hibernate 二 - 声明式的事务管理
Spring大战Hibernate之声明式的事务管理 Spring配置文件: 添加事务管理类的bean: <bean id="txManager" class="o ...
- 程序员笔记|Spring IoC、面向切面编程、事务管理等Spring基本概念详解
一.Spring IoC 1.1 重要概念 1)控制反转(Inversion of control) 控制反转是一种通过描述(在java中通过xml或者注解)并通过第三方去产生或获取特定对象的方式. ...
- Spring Boot 中使用 @Transactional 注解配置事务管理
事务管理是应用系统开发中必不可少的一部分.Spring 为事务管理提供了丰富的功能支持.Spring 事务管理分为编程式和声明式的两种方式.编程式事务指的是通过编码方式实现事务:声明式事务基于 AOP ...
- Spring Boot中使用@Transactional注解配置事务管理
事务管理是应用系统开发中必不可少的一部分.Spring 为事务管理提供了丰富的功能支持.Spring 事务管理分为编程式和声明式的两种方式.编程式事务指的是通过编码方式实现事务:声明式事务基于 AOP ...
随机推荐
- JS实现显示来访者的停留时间
显示来访者的停留时间 <script language="javascript"> var ap_name = navigator.appName; var ap_vi ...
- 【Spark】部署流程的深度了解
文章目录 Spark核心组件 Driver Executor Spark通用运行流程图 Standalone模式运行机制 Client模式流程图 Cluster模式流程图 On-Yarn模式运行机制 ...
- 【FreeRTOS学习05】深度解剖FreeRTOSConfig.h实现对系统的自定义剪裁
ROM/RAM太小,因此要对系统进行剪裁: 相关文章 [FreeRTOS实战汇总]小白博主的RTOS学习实战快速进阶之路(持续更新) 文章目录 相关文章 1 系统的剪裁 2 FreeRTOSConfi ...
- [hdu5521 Meeting]最短路
题意:有N个点,给定M个集合,集合Si里面的点两两之间的距离都为Ti,集合里面的所有点数之和<=1e6.有两个人分别在1和N处,求1个点使得两个人到这一点距离的最大值最小 思路:这题是裸的最短路 ...
- [codeforces525D]BFS
题目大意: 给定一个包含'.'和'*'的地图,每次操作可以把'*'->'.',用最少的操作使得新图满足条件:所有的连通块为矩形('.'为可达点) 解法: 用bfs来模拟操作的过程,对于一个2*2 ...
- flink流处理从0到1
一.DataStream API之Data Sources(消费者之数据源) 介绍: source是程序的数据源输入,你可以通过StreamExecutionEnvironment.addSource ...
- 可能会导致.NET内存泄露的8种行为
原文连接:https://michaelscodingspot.com/ways-to-cause-memory-leaks-in-dotnet/作者 Michael Shpilt.授权翻译,转载请保 ...
- ScrollView 内嵌百度地图问题解决
在ScrollView上内嵌百度地图遇到两个问题 事件冲突,移动地图的时候屏幕滚动了 移动ScrollView的时候,百度地图出现黑边 问题1的处理就有各种办法了,核心都是拦截事件,我使用的办法是加一 ...
- 这或许是最详细的JUC多线程并发总结
多线程进阶---JUC并发编程 完整代码传送门,见文章末尾 1.Lock锁(重点) 传统 Synchronizd package com.godfrey.demo01; /** * descripti ...
- codeforces Gym - 101485 D Debugging (2015-2016 Northwestern European Regional Contest (NWERC 2015))
题目描述: 点击打开链接 这题题意其实很不好理解,你有一个n行的程序,现在程序运行了r时间之后停止了运行,证明此处有一个bug,现在你需要在程序中加printf来调试找到bug所在的位置,你每次加一个 ...
