组合模式(c++实现)
组合模式
定义
将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构。组合模式是的用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。
动机
当你发现需求中是体现部分与整体层次的结构时,以及你希望用户可以忽略组合对象与单个对象的不同,统一的使用组合对象结构中的所有对象时,就应该考虑用组合模式了。
UML类图
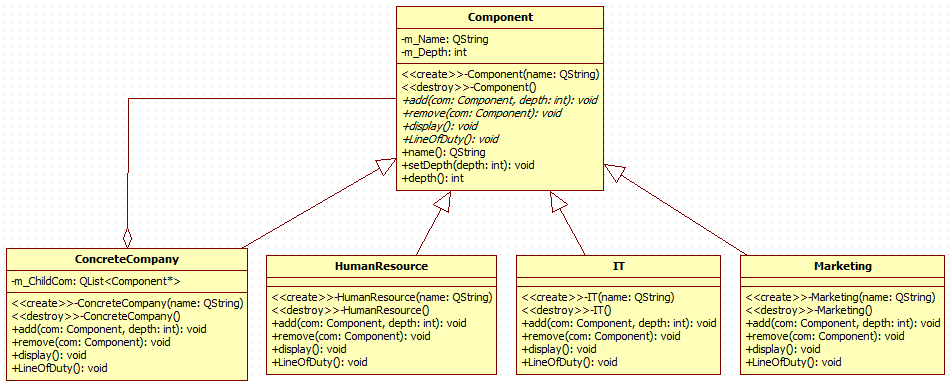
场景拆解
以一个大型公司为需求背景,组织我们的代码。一个北京总公司,下面有郑州和西安两个分公司。然后每个公司不管是总公司还是分公司都有自己的人力资源部,IT部和市场部。
源码实现
- component.h
#ifndef COMPONENT_H
#define COMPONENT_H
#include <QList>
class Component
{
public:
Component(QString name);
virtual ~Component();
virtual void add(Component* com, int depth = 0) = 0;
virtual void remove(Component* com) = 0;
virtual void display() = 0;
virtual void LineOfDuty() = 0;
QString name();
void setDepth(int depth);
int depth();
private:
QString m_Name;
int m_Depth;
};
class ConcreteCompany : public Component
{
public:
ConcreteCompany(QString name);
virtual ~ConcreteCompany();
virtual void add(Component* com, int depth = 0);
virtual void remove(Component* com);
virtual void display();
virtual void LineOfDuty();
private:
QList<Component*> m_ChildCom;
};
class HumanResource : public Component
{
public:
HumanResource(QString name);
virtual ~HumanResource();
virtual void add(Component* com, int depth = 0);
virtual void remove(Component* com);
virtual void display();
virtual void LineOfDuty();
};
class IT : public Component
{
public:
IT(QString name);
virtual ~IT();
virtual void add(Component* com, int depth = 0);
virtual void remove(Component* com);
virtual void display();
virtual void LineOfDuty();
};
class Marketing : public Component
{
public:
Marketing(QString name);
virtual ~Marketing();
virtual void add(Component* com, int depth = 0);
virtual void remove(Component* com);
virtual void display();
virtual void LineOfDuty();
};
#endif // COMPONENT_H
- component.cpp
/************************************
* @brief : 安排一下故事背景:有一个王者农药全国总公司在深圳,现在想要在全国开办事处
* 1.北京办事处- 招聘部,研发部,市场部
* 2.郑州办事处- 招聘部,研发部,市场部
* 3.西安办事处- 招聘部,研发部,市场部
* and so on...
* @author : wzx
* @date : 2020-05-11
* @project : Composite
*************************************/
#include <QDebug>
#include "component.h"
#define DELETEOBJECT(x) if(x) { delete x; x = nullptr; }
Component::Component(QString name):m_Name(name) {}
Component::~Component(){}
QString Component::name()
{
return m_Name;
}
void Component::setDepth(int depth)
{
m_Depth = depth;
}
int Component::depth()
{
return m_Depth;
}
ConcreteCompany::ConcreteCompany(QString name)
: Component(name)
{
}
ConcreteCompany::~ConcreteCompany()
{
for(auto com : m_ChildCom)
{
DELETEOBJECT(com);
}
m_ChildCom.clear();
}
void ConcreteCompany::add(Component* com, int depth)
{
com->setDepth(depth);
m_ChildCom.append(com);
}
void ConcreteCompany:: remove(Component* com)
{
m_ChildCom.removeOne(com);
}
void ConcreteCompany::display()
{
QString str;
for(int n = 0; n < depth(); ++n)
str += "--";
qDebug() << qPrintable(str) << (name());
for(auto com : m_ChildCom)
{
com->display();
}
}
void ConcreteCompany::LineOfDuty()
{
}
HumanResource::HumanResource(QString name)
: Component(name)
{
}
HumanResource::~HumanResource()
{
}
void HumanResource::add(Component* com, int depth)
{
com->setDepth(depth);
}
void HumanResource::remove(Component* com)
{
}
void HumanResource::display()
{
QString str;
for(int n = 0; n < depth(); ++n)
str += "--";
qDebug() << qPrintable(str) << (name());
}
void HumanResource::LineOfDuty()
{
qDebug() << "人力资源部,负责招聘";
}
IT::IT(QString name)
: Component(name)
{
}
IT::~IT()
{
}
void IT::add(Component* com, int depth)
{
com->setDepth(depth);
}
void IT::remove(Component* com)
{
}
void IT::display()
{
QString str;
for(int n = 0; n < depth(); ++n)
str += "--";
qDebug() << qPrintable(str) << (name());
}
void IT::LineOfDuty()
{
qDebug() << "IT部门,负责写代码";
}
Marketing::Marketing(QString name)
: Component(name)
{
}
Marketing::~Marketing()
{
}
void Marketing::add(Component* com, int depth)
{
com->setDepth(depth);
}
void Marketing::remove(Component* com)
{
}
void Marketing::display()
{
QString str;
for(int n = 0; n < depth(); ++n)
str += "--";
qDebug() << qPrintable(str) << name();
}
void Marketing::LineOfDuty()
{
qDebug() << "市场部门,负责市场推广";
}
- main.cpp
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include <QDebug>
#include "component.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);
Component* root = new ConcreteCompany("北京总部");
root->setDepth(0);
root->add(new HumanResource("人力资源部门"), 1);
root->add(new IT("IT部门"), 1);
root->add(new Marketing("市场部门"), 1);
Component* zz = new ConcreteCompany("郑州办事处");
zz->add(new HumanResource("人力资源部门"), 2);
zz->add(new IT("IT部门"), 2);
zz->add(new Marketing("市场部门"), 2);
root->add(zz, 1);
Component* xa = new ConcreteCompany("西安办事处");
xa->add(new HumanResource("人力资源部门"), 2);
xa->add(new IT("IT部门"), 2);
xa->add(new Marketing("市场部门"), 2);
root->add(xa, 1);
root->display();
return a.exec();
}
- 运行结果
"北京总部"
-- "人力资源部门"
-- "IT部门"
-- "市场部门"
-- "郑州办事处"
---- "人力资源部门"
---- "IT部门"
---- "市场部门"
-- "西安办事处"
---- "人力资源部门"
---- "IT部门"
---- "市场部门"
优点
组合模式定义了包含基本对象和组合对象的类层次结构。基本对象可以组合成更复杂的组合对象,而这个组合对象又可以被组合,这样不断的递归下去,客户代码中,任何用到基本对象的地方都可以使用组合对象了。
缺点
参考《大化设计模式》
组合模式(c++实现)的更多相关文章
- ComponentPattern (组合模式)
import java.util.LinkedList; /** * 组合模式 * * @author TMAC-J 主要用于树状结构,用于部分和整体区别无区别的场景 想象一下,假设有一批连锁的理发店 ...
- 设计模式(十一):从文Finder中认识"组合模式"(Composite Pattern)
上一篇博客中我们从从电影院中认识了"迭代器模式"(Iterator Pattern),今天我们就从文件系统中来认识一下“组合模式”(Composite Pattern).说到组合模 ...
- 设计模式(十)组合模式(Composite Pattern)
一.引言 在软件开发过程中,我们经常会遇到处理简单对象和复合对象的情况,例如对操作系统中目录的处理就是这样的一个例子,因为目录可以包括单独的文件,也可以包括文件夹,文件夹又是由文件组成的,由于简单对象 ...
- 设计模式--组合模式Composite(结构型)
一.概念 组合模式允许你将对象组合成树形结构来表现"整体/部分"层次结构.组合能让客户以一致的方式处理个别对象以及对象组合. 二.UML图 1.Component(对象接口),定义 ...
- 组合模式/composite模式/对象结构型模式
组合模式/composite模式/对象结构型 意图 将对象组合成树形结构以表示"整体--部分"的层次结构.Composite使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性. 动机 C ...
- c#设计模式-组合模式
在软件开发过程中,我们经常会遇到处理简单对象和复合对象的情况,例如对操作系统中目录的处理就是这样的一个例子,因为目录可以包括单独的文件,也可以包括文件夹,文件夹又是由文件组成的,由于简单对象和复合对象 ...
- C#设计模式系列:组合模式(Composite)
1.组合模式简介 1.1>.定义 组合模式主要用来处理一类具有“容器特征”的对象——即它们在充当对象的同时,又可以作为容器包含其他多个对象. 1.2>.使用频率 中高 2.组合模式结构图 ...
- php实现设计模式之 组合模式
<?php /** * 组合模式 * * 将对象组合成树形结构以表示"部分-整体"的层次结构,使得客户对单个对象和复合对象的使用具有一致性 * * * 1) 抽象构件角色Co ...
- 轻松掌握:JavaScript组合模式
组合模式 组合模式:将一组对象组合成树形结构,并统一对待组合对象和叶对象,忽略它们之间的不同(因为叶对象也可以也可以包含叶对象而成为组合对象),组合模式中的对象只能是一对多的关系,不能出现多对一. 基 ...
- java设计模式之组合模式
组合模式 组合模式,将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构,组合模式使得用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性.掌握组合模式的重点是要理解清楚 “部分/整体” 还有 ”单个对象“ 与 & ...
随机推荐
- D - Catch That Cow BFS
农夫知道一头牛的位置,想要抓住它.农夫和牛都于数轴上 ,农夫起始位于点 N(0<=N<=100000) ,牛位于点 K(0<=K<=100000) .农夫有两种移动方式: 1. ...
- 谁说 Vim 不好用?送你一个五彩斑斓的编辑器!
相信大家在使用各种各样强大的 IDE 写代码时都会注意到,代码中各种类型的关键字会用独特的颜色标记出来,然后形成一套语法高亮规则.这样不仅美观,而且方便代码的阅读. 而在上古神器 Vim 中,我们通常 ...
- PHP常量:JSON_UNESCAPED_UNICODE
函数: json_encode() - 对变量进行 JSON 编码 说明: json_encode ( mixed $value [, int $options = 0 [, int $depth = ...
- 详解 List接口
本篇博文所讲解的这两个类,都是泛型类(关于泛型,本人在之前的博文中提到过),我们在学习C语言时,对于数据的存储,用的差不多都是数组和链表. 但是,在Java中,链表就相对地失去了它的存在价值,因为Ja ...
- python之elasticsearch查询
下载所需模块 python安装好的情况下,通过pip install elasticsearch进行es模块的安装 安装完成后通过pip list命中查询 导入模块 from elasticsearc ...
- 数据源管理 | PostgreSQL环境整合,JSON类型应用
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里 一.PostgreSQL简介 1.和MySQL的比较 PostgreSQL是一个功能强大的且开源关系型数据库系统,在网上PostgreSQL和 ...
- serialize和json_encode 区别
(1)serialize主要用于php的序列化,存储到文件或者数据库中,json_encode 也是序列化,但是 主要用于与其他语言比如js进行交互使用,对于传输来说,json有许多优点. (2)在显 ...
- 阿里云有奖调查结果公布,赠送10个阿里巴巴logo胸针
...
4月17日,我们发起了"阿里云有奖调查!赠10个阿里巴巴logo胸针"活动,现经过随机抽奖机抽选出10名幸运同学,每人赠送一枚阿里巴巴胸针.现把获奖同学ID公布如下,请如下同学私信 ...
- Netty随记之ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter、SimpleChannelInboundHandler
ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter是ChannelInboundHandler的一个简单实现,默认情况下不会做任何处理, ...
- 日日算法:Dijkstra算法
介绍 Dijistra算法作为一种最短路径算法,可以用来计算一个节点到图上其他节点的最短距离. 主要是通过启发式的思想,由中心节点层层向外拓展,直到找到中点. 适用于无向图和有向图. 算法思想 假设我 ...
