Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2)
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Eleven wants to choose a new name for herself. As a bunch of geeks, her friends suggested an algorithm to choose a name for her. Eleven wants her name to have exactly n characters.

Her friend suggested that her name should only consist of uppercase and lowercase letters 'O'. More precisely, they suggested that the i-th letter of her name should be 'O' (uppercase) if i is a member of Fibonacci sequence, and 'o' (lowercase) otherwise. The letters in the name are numbered from 1 to n. Fibonacci sequence is the sequence f where
- f1 = 1,
- f2 = 1,
- fn = fn - 2 + fn - 1 (n > 2).
As her friends are too young to know what Fibonacci sequence is, they asked you to help Eleven determine her new name.
The first and only line of input contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000).
Print Eleven's new name on the first and only line of output.
8
OOOoOooO
15
OOOoOooOooooOoo
是菲波那切数列的数输出O,否则输出o,只要15项就行了(脑残了把房间的那个hack
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[],f[],n;
int main()
{
f[]=,f[]=;
for(int i=;f[i]<=;i++)
f[i+]=f[i]+f[i-],a[f[i]]=;
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(a[i]==)cout<<"O";
else cout<<"o";
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
As the guys fried the radio station facilities, the school principal gave them tasks as a punishment. Dustin's task was to add comments to nginx configuration for school's website. The school has n servers. Each server has a name and an ip (names aren't necessarily unique, but ips are). Dustin knows the ip and name of each server. For simplicity, we'll assume that an nginx command is of form "command ip;" where command is a string consisting of English lowercase letter only, and ip is the ip of one of school servers.

Each ip is of form "a.b.c.d" where a, b, c and d are non-negative integers less than or equal to 255 (with no leading zeros). The nginx configuration file Dustin has to add comments to has m commands. Nobody ever memorizes the ips of servers, so to understand the configuration better, Dustin has to comment the name of server that the ip belongs to at the end of each line (after each command). More formally, if a line is "command ip;" Dustin has to replace it with "command ip; #name" where name is the name of the server with ip equal to ip.
Dustin doesn't know anything about nginx, so he panicked again and his friends asked you to do his task for him.
The first line of input contains two integers n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 1000).
The next n lines contain the names and ips of the servers. Each line contains a string name, name of the server and a string ip, ip of the server, separated by space (1 ≤ |name| ≤ 10, name only consists of English lowercase letters). It is guaranteed that all ip are distinct.
The next m lines contain the commands in the configuration file. Each line is of form "command ip;" (1 ≤ |command| ≤ 10, commandonly consists of English lowercase letters). It is guaranteed that ip belongs to one of the n school servers.
Print m lines, the commands in the configuration file after Dustin did his task.
2 2
main 192.168.0.2
replica 192.168.0.1
block 192.168.0.1;
proxy 192.168.0.2;
block 192.168.0.1; #replica
proxy 192.168.0.2; #main
3 5
google 8.8.8.8
codeforces 212.193.33.27
server 138.197.64.57
redirect 138.197.64.57;
block 8.8.8.8;
cf 212.193.33.27;
unblock 8.8.8.8;
check 138.197.64.57;
redirect 138.197.64.57; #server
block 8.8.8.8; #google
cf 212.193.33.27; #codeforces
unblock 8.8.8.8; #google
check 138.197.64.57; #server
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
map<string,string>M;
string s,c;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
cin>>s>>c;
M[c]=s;
}
for(int i=;i<m;i++)
{
cin>>s>>c;
cout<<s<<" "<<c<<" #"<<M[c.substr(,c.length()-)]<<"\n";
}
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
As Will is stuck in the Upside Down, he can still communicate with his mom, Joyce, through the Christmas lights (he can turn them on and off with his mind). He can't directly tell his mom where he is, because the monster that took him to the Upside Down will know and relocate him.

Thus, he came up with a puzzle to tell his mom his coordinates. His coordinates are the answer to the following problem.
A string consisting only of parentheses ('(' and ')') is called a bracket sequence. Some bracket sequence are called correct bracket sequences. More formally:
- Empty string is a correct bracket sequence.
- if s is a correct bracket sequence, then (s) is also a correct bracket sequence.
- if s and t are correct bracket sequences, then st (concatenation of s and t) is also a correct bracket sequence.
A string consisting of parentheses and question marks ('?') is called pretty if and only if there's a way to replace each question mark with either '(' or ')' such that the resulting string is a non-empty correct bracket sequence.
Will gave his mom a string s consisting of parentheses and question marks (using Morse code through the lights) and his coordinates are the number of pairs of integers (l, r) such that 1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ |s| and the string slsl + 1... sr is pretty, where si is i-th character of s.
Joyce doesn't know anything about bracket sequences, so she asked for your help.
The first and only line of input contains string s, consisting only of characters '(', ')' and '?' (2 ≤ |s| ≤ 5000).
Print the answer to Will's puzzle in the first and only line of output.
((?))
4
??()??
7
For the first sample testcase, the pretty substrings of s are:
- "(?" which can be transformed to "()".
- "?)" which can be transformed to "()".
- "((?)" which can be transformed to "(())".
- "(?))" which can be transformed to "(())".
For the second sample testcase, the pretty substrings of s are:
- "??" which can be transformed to "()".
- "()".
- "??()" which can be transformed to "()()".
- "?()?" which can be transformed to "(())".
- "??" which can be transformed to "()".
- "()??" which can be transformed to "()()".
- "??()??" which can be transformed to "()()()".
?可以填(),然后判断这个括号序列是不是合法
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
int ans=;
for(int i=;s[i];i++)
{
int l=,r=;
for(int j=i;s[j];j++)
{
if(s[j]=='(')l++,r++;
else if(s[j]==')')l--,r--;
else l--,r++;
if(l<)l+=;
if(r<)break;
if(!l)ans++;
}
}
cout<<ans;
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
As we all know, Max is the best video game player among her friends. Her friends were so jealous of hers, that they created an actual game just to prove that she's not the best at games. The game is played on a directed acyclic graph (a DAG) with n vertices and m edges. There's a character written on each edge, a lowercase English letter.

Max and Lucas are playing the game. Max goes first, then Lucas, then Max again and so on. Each player has a marble, initially located at some vertex. Each player in his/her turn should move his/her marble along some edge (a player can move the marble from vertex v to vertex u if there's an outgoing edge from v to u). If the player moves his/her marble from vertex v to vertex u, the "character" of that round is the character written on the edge from v to u. There's one additional rule; the ASCII code of character of round i should be greater than or equal to the ASCII code of character of round i - 1 (for i > 1). The rounds are numbered for both players together, i. e. Max goes in odd numbers, Lucas goes in even numbers. The player that can't make a move loses the game. The marbles may be at the same vertex at the same time.
Since the game could take a while and Lucas and Max have to focus on finding Dart, they don't have time to play. So they asked you, if they both play optimally, who wins the game?
You have to determine the winner of the game for all initial positions of the marbles.
The first line of input contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 100, 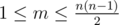 ).
).
The next m lines contain the edges. Each line contains two integers v, u and a lowercase English letter c, meaning there's an edge from vto u written c on it (1 ≤ v, u ≤ n, v ≠ u). There's at most one edge between any pair of vertices. It is guaranteed that the graph is acyclic.
Print n lines, a string of length n in each one. The j-th character in i-th line should be 'A' if Max will win the game in case her marble is initially at vertex i and Lucas's marble is initially at vertex j, and 'B' otherwise.
4 4
1 2 b
1 3 a
2 4 c
3 4 b
BAAA
ABAA
BBBA
BBBB
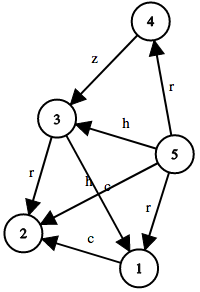
5 8
5 3 h
1 2 c
3 1 c
3 2 r
5 1 r
4 3 z
5 4 r
5 2 h
BABBB
BBBBB
AABBB
AAABA
AAAAB
Here's the graph in the first sample test case:
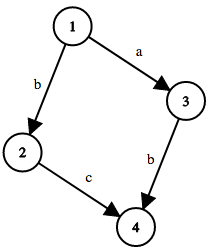
Here's the graph in the second sample test case:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=;
int SG[][][];
int head[],nxt[],to[],f[];
int tot;
int DFS(int i,int j,int k)
{
if(SG[i][j][k])return SG[i][j][k];
for(int p=head[i]; p; p=nxt[p])
if(f[p]>=k&&!DFS(j,to[p],f[p]))SG[i][j][k]=;
return SG[i][j][k];
}
void add(int u,int v,int w)
{
nxt[++tot]=head[u],head[u]=tot,to[tot]=v,f[tot]=w;
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
char c;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=,u,v; i<=m; i++)cin>>u>>v>>c,add(u,v,c-'a');
for(int i=; i<=n; i++)
{
for(int j=; j<=n; j++)
if(DFS(i,j,))cout<<'A';
else cout <<'B';
cout<<"\n";
}
return ;
}
Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2)的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2) D. MADMAX DFS+博弈
D. MADMAX time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input outp ...
- Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2):D. MADMAX(记忆化搜索+博弈论)
D. MADMAX time limit per test1 second memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Description As we a ...
- Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2):B. Radio Station
B. Radio Station time limit per test2 seconds memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Dsecription ...
- Codeforces Round #459 Div. 1
C:显然可以设f[i][S]为当前考虑到第i位,[i,i+k)的状态为S的最小能量消耗,这样直接dp是O(nC(k,x))的.考虑矩阵快速幂,构造min+转移矩阵即可,每次转移到下一个特殊点然后暴力处 ...
- Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2)-A. Eleven
A. Eleven time limit per test1 second memory limit per test256 megabytes Problem Description Eleven ...
- Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2):D. MADMAX(记忆化搜索+博弈论)
题意 在一个有向无环图上,两个人分别从一个点出发,两人轮流从当前点沿着某条边移动,要求经过的边权不小于上一轮对方经过的边权(ASCII码),如果一方不能移动,则判负.两人都采取最优策略,求两人分别从每 ...
- Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2)The Monster[匹配问题]
题意 给一个序列,包含(,),?,?可以被当做(或者),问你这个序列有多少合法的子序列. 分析 n^2枚举每一个子序列,暂时将每个?都当做右括号,在枚举右端点的时候同时记录两个信息:当前左括号多余多少 ...
- Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2)C. The Monster
C. The Monster time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- 【Codeforces Round #459 (Div. 2) B】 Radio Station
[链接] 我是链接,点我呀:) [题意] 在这里输入题意 [题解] 用map模拟一下映射就好了. [代码] #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace ...
随机推荐
- python3操作mysql数据库表01(封装查询单条、多条数据)
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding:UTF-8 -*- import pymysql# import os'''封装查询单条.多条数据'''# os.environ[' ...
- HDU 4734 F(x) (数位DP,基础)
题意: 一个非负整数的十进制位是这样的 (AnAn-1An-2 ... A2A1),定义F(x) = An * 2n-1 + An-1 * 2n-2 + ... + A2 * 2 + A1 * 1. ...
- 清理winsxs文件夹(系统更新文件)的第三方工具
工具名称(第三方): Windows Update Clean Tool 下载地址: http://www.xiazaiba.com/html/24145.html http://dx5.xiazai ...
- 为了少点击几次,自己写了一个Chrome插件
缘由 chrome应用商店有三款二维码插件,自己一直使用的第一款.这三款插件有且只有一个功能就是生成当前页面的URL的二维码. 其实这个功能基本上满足了需要移动端开发在微信里打开页面进行调试的情况. ...
- Maven settings.xml配置详解
首先:Maven中央仓库的搜索全部公共jar包的地址是,http://search.maven.org/ ===Maven基础-默认中央仓库============================== ...
- rcnn,sppnet,fast rcnn,ohem,faster rcnn,rfcn
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/21412911 rcnn需要固定图片的大小,fast rcnn不需要 rcnn,sppnet,fast rcnn,ohem,faster r ...
- Python -- 函数之推导式
5.12 推导式 l = [] for i in range(1,11): l.append(i) print(l) # 用列表推导式 (一行搞定) l = [i for i in range(1,1 ...
- 01_2_Servlet简介
01_2_Servlet简介 1. Servlet简介 Servlet是服务器小应用程序 用来完成B/S架构下,客户端请求的响应处理 平台独立,性能优良,能以线程方式运行 Servlet API为Se ...
- dSYM文件
来到新公司后,前段时间就一直在忙,前不久 项目 终于成功发布上线了,最近就在给项目做优化,并排除一些线上软件的 bug,因为项目中使用了友盟统计,所以在友盟给出的错误信息统计中能比较方便的找出客户端异 ...
- 如何在vue项目中引用Iview
iview 安装 npm install iview --save 引入iview import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import route ...
