Android调用JNI本地方法经过有点改变
方法注册好后要经过哪些路
Android一个异常捕获项目 https://github.com/xroche/coffeecatch
coffeecatch
CoffeeCatch, a tiny native POSIX signal catcher (especially useful for JNI code on Android/Dalvik, but it can be used in non-Java projects)
It allows to "gracefully" recover from a signal (SIGSEGV, SIGBUS...) as if it was an exception. It will not gracefully recover from allocator/mutexes corruption etc., however, but at least "most" gentle crashes (null pointer dereferencing, integer division, stack overflow etc.) should be handled without too much troubles.
/** Enter protected section. **/
COFFEE_TRY() {
/** Try to call 'call_some_native_function'. **/
call_some_protected_function();
} COFFEE_CATCH() {
/** Caught a signal: throw Java exception. **/
/** In pure C projects, you may print an error message (coffeecatch_get_message()). **/
coffeecatch_throw_exception(env);
} COFFEE_END();
You may read the corresponding discussion about this project.
The handler is thread-safe, but client must have exclusive control on the signal handlers (ie. the library is installing its own signal handlers on top of the existing ones).
Libraries
If you want to get useful stack traces, you should build all your libraries with -funwind-tables (this adds unwinding information). On ARM, you may also use the --no-merge-exidx-entries linker switch, to solve certain issues with unwinding (the switch is possibly not needed anymore). On Android, this can be achieved by using this line in the Android.mk file in each library block:
LOCAL_CFLAGS := -funwind-tables -Wl,--no-merge-exidx-entries
Example
- Inside JNI (typically, Android)
First, build the library, or just add the two files in the list of local files to be built:
LOCAL_SRC_FILES += coffeecatch.c coffeejni.c
then, use the COFFEE_TRY_JNI() macro to protect your call(s):
/** The potentially dangerous function. **/
jint call_dangerous_function(JNIEnv* env, jobject object) {
// ... do dangerous things!
return 42;
} /** Protected function stub. **/
void foo_protected(JNIEnv* env, jobject object, jint *retcode) {
/* Try to call 'call_dangerous_function', and raise proper Java Error upon
* fatal error (SEGV, etc.). **/
COFFEE_TRY_JNI(env, *retcode = call_dangerous_function(env, object));
} /** Regular JNI entry point. **/
jint Java_com_example_android_MyNative_foo(JNIEnv* env, jobject object) {
jint retcode = 0;
foo_protected(env, object, &retcode);
return retcode;
}
and, in case of crash, get something like this (note: the last Exception with native backtrace is produced on Android >= 4.1.1):
FATAL EXCEPTION: AsyncTask #5
java.lang.RuntimeException: An error occured while executing doInBackground()
at android.os.AsyncTask$3.done(AsyncTask.java:299)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.finishCompletion(FutureTask.java:352)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.setException(FutureTask.java:219)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:239)
at android.os.AsyncTask$SerialExecutor$1.run(AsyncTask.java:230)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1080)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:573)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:841)
Caused by: java.lang.Error: signal 11 (Address not mapped to object) at address 0x42 [at libexample.so:0xa024]
at com.example.jni.ExampleLib.main(Native Method)
at com.example.ExampleActivity$Runner.runInternal(ExampleActivity.java:998)
at com.example.ExampleActivity$Runner.doInBackground(ExampleActivity.java:919)
at com.example.ExampleActivity$Runner.doInBackground(ExampleActivity.java:1)
at android.os.AsyncTask$2.call(AsyncTask.java:287)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:234)
... 4 more
Caused by: java.lang.Error: signal 11 (Address not mapped to object) at address 0x42 [at libexample.so:0xa024]
at data.app_lib.com_example.libexample_so.0xa024(Native Method)
at data.app_lib.com_example.libexample_so.0x705fc(hts_main2:0x8f74:0)
at data.app_lib.com_example.libexamplejni_so.0x4cc8(ExampleLib_main:0xf8:0)
at data.app_lib.com_example.libexamplejni_so.0x52d8(Java_com_example_jni_ExampleLib_main:0x64:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x1dc4c(dvmPlatformInvoke:0x70:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x4dcab(dvmCallJNIMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0x18a:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x385e1(dvmCheckCallJNIMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0x8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x4f699(dvmResolveNativeMethod(unsigned int const*, JValue*, Method const*, Thread*):0xb8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x27060(Native Method)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x2b580(dvmInterpret(Thread*, Method const*, JValue*):0xb8:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x5fcbd(dvmCallMethodV(Thread*, Method const*, Object*, bool, JValue*, std::__va_list):0x124:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x5fce7(dvmCallMethod(Thread*, Method const*, Object*, JValue*, ...):0x14:0)
at system.lib.libdvm_so.0x54a6f(Native Method)
at system.lib.libc_so.0xca58(__thread_entry:0x48:0)
at system.lib.libc_so.0xcbd4(pthread_create:0xd0:0)
- Outside JNI code
The COFFEE_TRY()/COFFEE_CATCH()/COFFEE_END() syntax can be used:
void my_function() {
COFFEE_TRY() {
/** Try to call 'call_some_native_function'. **/
call_some_native_function();
} COFFEE_CATCH() {
/** Caught a signal. **/
const char*const message = coffeecatch_get_message();
fprintf(stderr, "**FATAL ERROR: %s\n", message);
} COFFEE_END();
}
- Hints
If you wish to catch signals and continue running your program rather than ending it (this may be dangerous, especially if a crash was spotted within a C library function, such as malloc()), use thecoffeecatch_cancel_pending_alarm() function to cancel the default pending alarm triggered to avoid deadlocks.
JNI方法调用改变
dvmCallJNIMethod_general不知从哪个版本就没了,但从http://androidxref.com/这里看,Gingerbread - 2.3.7还有,ICS - 4.0.3就没了。
这里模拟器里导出的libdvm.so,符号,只有dvmCallJNIMethod,如下(4.4.2_API19):
File: /cygdrive/d/Developer/sdk/platforms/android-19/lib/libdvm.so
Symbol table '.dynsym' contains 1713 entries:
Num: Value Size Type Bind Vis Ndx Name
0: 00000000 0 NOTYPE LOCAL DEFAULT UND
1: 00000000 0 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT UND __cxa_finalize
394: 0004dd75 664 FUNC GLOBAL DEFAULT 8 _Z16dvmCallJNIMethodPKjP6JValuePK6MethodP6Thread
//xref: 4.4.2_r2 /dalvik/vm/interp/Stack.cpp
//http://androidxref.com/4.4.2_r2/xref/dalvik/vm/interp/Stack.cpp /*
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ /*
* Stacks and their uses (e.g. native --> interpreted method calls).
*
* See the majestic ASCII art in Stack.h.
*/
#include "Dalvik.h"
#include "jni.h" #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdarg.h> #ifdef HAVE_ANDROID_OS
#include <corkscrew/backtrace.h>
#endif /*
* Initialize the interpreter stack in a new thread.
*
* Currently this doesn't do much, since we don't need to zero out the
* stack (and we really don't want to if it was created with mmap).
*/
bool dvmInitInterpStack(Thread* thread, int stackSize)
{
assert(thread->interpStackStart != NULL); assert(thread->interpSave.curFrame == NULL); return true;
} /*
* We're calling an interpreted method from an internal VM function or
* via reflection.
*
* Push a frame for an interpreted method onto the stack. This is only
* used when calling into interpreted code from native code. (The
* interpreter does its own stack frame manipulation for interp-->interp
* calls.)
*
* The size we need to reserve is the sum of parameters, local variables,
* saved goodies, and outbound parameters.
*
* We start by inserting a "break" frame, which ensures that the interpreter
* hands control back to us after the function we call returns or an
* uncaught exception is thrown.
*/
static bool dvmPushInterpFrame(Thread* self, const Method* method)
{
StackSaveArea* saveBlock;
StackSaveArea* breakSaveBlock;
int stackReq;
u1* stackPtr; assert(!dvmIsNativeMethod(method));
assert(!dvmIsAbstractMethod(method)); stackReq = method->registersSize * // params + locals
+ sizeof(StackSaveArea) * // break frame + regular frame
+ method->outsSize * ; // args to other methods if (self->interpSave.curFrame != NULL)
stackPtr = (u1*) SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame);
else
stackPtr = self->interpStackStart; if (stackPtr - stackReq < self->interpStackEnd) {
/* not enough space */
ALOGW("Stack overflow on call to interp "
"(req=%d top=%p cur=%p size=%d %s.%s)",
stackReq, self->interpStackStart, self->interpSave.curFrame,
self->interpStackSize, method->clazz->descriptor, method->name);
dvmHandleStackOverflow(self, method);
assert(dvmCheckException(self));
return false;
} /*
* Shift the stack pointer down, leaving space for the function's
* args/registers and save area.
*/
stackPtr -= sizeof(StackSaveArea);
breakSaveBlock = (StackSaveArea*)stackPtr;
stackPtr -= method->registersSize * + sizeof(StackSaveArea);
saveBlock = (StackSaveArea*) stackPtr; #if !defined(NDEBUG) && !defined(PAD_SAVE_AREA)
/* debug -- memset the new stack, unless we want valgrind's help */
memset(stackPtr - (method->outsSize*), 0xaf, stackReq);
#endif
#ifdef EASY_GDB
breakSaveBlock->prevSave =
(StackSaveArea*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(self->interpSave.curFrame);
saveBlock->prevSave = breakSaveBlock;
#endif breakSaveBlock->prevFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame;
breakSaveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required
breakSaveBlock->xtra.localRefCookie = ; // not required
breakSaveBlock->method = NULL;
saveBlock->prevFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(breakSaveBlock);
saveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required
saveBlock->xtra.currentPc = NULL; // not required?
saveBlock->method = method; LOGVV("PUSH frame: old=%p new=%p (size=%d)",
self->interpSave.curFrame, FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock),
(u1*)self->interpSave.curFrame - (u1*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock)); self->interpSave.curFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock); return true;
} /*
* We're calling a JNI native method from an internal VM fuction or
* via reflection. This is also used to create the "fake" native-method
* frames at the top of the interpreted stack.
*
* This actually pushes two frames; the first is a "break" frame.
*
* The top frame has additional space for JNI local reference tracking.
*/
bool dvmPushJNIFrame(Thread* self, const Method* method)
{
StackSaveArea* saveBlock;
StackSaveArea* breakSaveBlock;
int stackReq;
u1* stackPtr; assert(dvmIsNativeMethod(method)); stackReq = method->registersSize * // params only
+ sizeof(StackSaveArea) * ; // break frame + regular frame if (self->interpSave.curFrame != NULL)
stackPtr = (u1*) SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame);
else
stackPtr = self->interpStackStart; if (stackPtr - stackReq < self->interpStackEnd) {
/* not enough space */
ALOGW("Stack overflow on call to native "
"(req=%d top=%p cur=%p size=%d '%s')",
stackReq, self->interpStackStart, self->interpSave.curFrame,
self->interpStackSize, method->name);
dvmHandleStackOverflow(self, method);
assert(dvmCheckException(self));
return false;
} /*
* Shift the stack pointer down, leaving space for just the stack save
* area for the break frame, then shift down farther for the full frame.
* We leave space for the method args, which are copied in later.
*/
stackPtr -= sizeof(StackSaveArea);
breakSaveBlock = (StackSaveArea*)stackPtr;
stackPtr -= method->registersSize * + sizeof(StackSaveArea);
saveBlock = (StackSaveArea*) stackPtr; #if !defined(NDEBUG) && !defined(PAD_SAVE_AREA)
/* debug -- memset the new stack */
memset(stackPtr, 0xaf, stackReq);
#endif
#ifdef EASY_GDB
if (self->interpSave.curFrame == NULL)
breakSaveBlock->prevSave = NULL;
else {
void* fp = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(self->interpSave.curFrame);
breakSaveBlock->prevSave = (StackSaveArea*)fp;
}
saveBlock->prevSave = breakSaveBlock;
#endif breakSaveBlock->prevFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame;
breakSaveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required
breakSaveBlock->xtra.localRefCookie = ; // not required
breakSaveBlock->method = NULL;
saveBlock->prevFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(breakSaveBlock);
saveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required
saveBlock->xtra.localRefCookie = self->jniLocalRefTable.segmentState.all;
saveBlock->method = method; LOGVV("PUSH JNI frame: old=%p new=%p (size=%d)",
self->interpSave.curFrame, FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock),
(u1*)self->interpSave.curFrame - (u1*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock)); self->interpSave.curFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock); return true;
} /*
* This is used by the JNI PushLocalFrame call. We push a new frame onto
* the stack that has no ins, outs, or locals, and no break frame above it.
* It's strictly used for tracking JNI local refs, and will be popped off
* by dvmPopFrame if it's not removed explicitly.
*/
bool dvmPushLocalFrame(Thread* self, const Method* method)
{
StackSaveArea* saveBlock;
int stackReq;
u1* stackPtr; assert(dvmIsNativeMethod(method)); stackReq = sizeof(StackSaveArea); // regular frame assert(self->interpSave.curFrame != NULL);
stackPtr = (u1*) SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); if (stackPtr - stackReq < self->interpStackEnd) {
/* not enough space; let JNI throw the exception */
ALOGW("Stack overflow on PushLocal "
"(req=%d top=%p cur=%p size=%d '%s')",
stackReq, self->interpStackStart, self->interpSave.curFrame,
self->interpStackSize, method->name);
dvmHandleStackOverflow(self, method);
assert(dvmCheckException(self));
return false;
} /*
* Shift the stack pointer down, leaving space for just the stack save
* area for the break frame, then shift down farther for the full frame.
*/
stackPtr -= sizeof(StackSaveArea);
saveBlock = (StackSaveArea*) stackPtr; #if !defined(NDEBUG) && !defined(PAD_SAVE_AREA)
/* debug -- memset the new stack */
memset(stackPtr, 0xaf, stackReq);
#endif
#ifdef EASY_GDB
saveBlock->prevSave =
(StackSaveArea*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(self->interpSave.curFrame);
#endif saveBlock->prevFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame;
saveBlock->savedPc = NULL; // not required
saveBlock->xtra.localRefCookie = self->jniLocalRefTable.segmentState.all;
saveBlock->method = method; LOGVV("PUSH JNI local frame: old=%p new=%p (size=%d)",
self->interpSave.curFrame, FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock),
(u1*)self->interpSave.curFrame - (u1*)FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock)); self->interpSave.curFrame = FP_FROM_SAVEAREA(saveBlock); return true;
} /*
* Pop one frame pushed on by JNI PushLocalFrame.
*
* If we've gone too far, the previous frame is either a break frame or
* an interpreted frame. Either way, the method pointer won't match.
*/
bool dvmPopLocalFrame(Thread* self)
{
StackSaveArea* saveBlock = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame); assert(!dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame));
if (saveBlock->method != SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame)->method) {
/*
* The previous frame doesn't have the same method pointer -- we've
* been asked to pop too much.
*/
assert(dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)saveBlock->prevFrame) ||
!dvmIsNativeMethod(
SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame)->method));
return false;
} LOGVV("POP JNI local frame: removing %s, now %s",
saveBlock->method->name,
SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame)->method->name);
dvmPopJniLocals(self, saveBlock);
self->interpSave.curFrame = saveBlock->prevFrame; return true;
} /*
* Pop a frame we added. There should be one method frame and one break
* frame.
*
* If JNI Push/PopLocalFrame calls were mismatched, we might end up
* popping multiple method frames before we find the break.
*
* Returns "false" if there was no frame to pop.
*/
static bool dvmPopFrame(Thread* self)
{
StackSaveArea* saveBlock; if (self->interpSave.curFrame == NULL)
return false; saveBlock = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame);
assert(!dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame)); /*
* Remove everything up to the break frame. If this was a call into
* native code, pop the JNI local references table.
*/
while (saveBlock->prevFrame != NULL && saveBlock->method != NULL) {
/* probably a native->native JNI call */ if (dvmIsNativeMethod(saveBlock->method)) {
LOGVV("Popping JNI stack frame for %s.%s%s",
saveBlock->method->clazz->descriptor,
saveBlock->method->name,
(SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame)->method == NULL) ?
"" : " (JNI local)");
dvmPopJniLocals(self, saveBlock);
} saveBlock = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(saveBlock->prevFrame);
}
if (saveBlock->method != NULL) {
ALOGE("PopFrame missed the break");
assert(false);
dvmAbort(); // stack trashed -- nowhere to go in this thread
} LOGVV("POP frame: cur=%p new=%p",
self->interpSave.curFrame, saveBlock->prevFrame); self->interpSave.curFrame = saveBlock->prevFrame;
return true;
} /*
* Common code for dvmCallMethodV/A and dvmInvokeMethod.
*
* Pushes a call frame on, advancing self->interpSave.curFrame.
*/
static ClassObject* callPrep(Thread* self, const Method* method, Object* obj,
bool checkAccess)
{
ClassObject* clazz; #ifndef NDEBUG
if (self->status != THREAD_RUNNING) {
ALOGW("threadid=%d: status=%d on call to %s.%s -",
self->threadId, self->status,
method->clazz->descriptor, method->name);
}
#endif assert(self != NULL);
assert(method != NULL); if (obj != NULL)
clazz = obj->clazz;
else
clazz = method->clazz; IF_LOGVV() {
char* desc = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&method->prototype);
LOGVV("thread=%d native code calling %s.%s %s", self->threadId,
clazz->descriptor, method->name, desc);
free(desc);
} if (checkAccess) {
/* needed for java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke */
if (!dvmCheckMethodAccess(dvmGetCaller2Class(self->interpSave.curFrame),
method))
{
/* note this throws IAException, not IAError */
dvmThrowIllegalAccessException("access to method denied");
return NULL;
}
} /*
* Push a call frame on. If there isn't enough room for ins, locals,
* outs, and the saved state, it will throw an exception.
*
* This updates self->interpSave.curFrame.
*/
if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) {
/* native code calling native code the hard way */
if (!dvmPushJNIFrame(self, method)) {
assert(dvmCheckException(self));
return NULL;
}
} else {
/* native code calling interpreted code */
if (!dvmPushInterpFrame(self, method)) {
assert(dvmCheckException(self));
return NULL;
}
} return clazz;
} /*
* Issue a method call.
*
* Pass in NULL for "obj" on calls to static methods.
*
* (Note this can't be inlined because it takes a variable number of args.)
*/
void dvmCallMethod(Thread* self, const Method* method, Object* obj,
JValue* pResult, ...)
{
va_list args;
va_start(args, pResult);
dvmCallMethodV(self, method, obj, false, pResult, args);
va_end(args);
} /*
* Issue a method call with a variable number of arguments. We process
* the contents of "args" by scanning the method signature.
*
* Pass in NULL for "obj" on calls to static methods.
*
* We don't need to take the class as an argument because, in Dalvik,
* we don't need to worry about static synchronized methods.
*/
void dvmCallMethodV(Thread* self, const Method* method, Object* obj,
bool fromJni, JValue* pResult, va_list args)
{
const char* desc = &(method->shorty[]); // [0] is the return type.
int verifyCount = ;
ClassObject* clazz;
u4* ins; clazz = callPrep(self, method, obj, false);
if (clazz == NULL)
return; /* "ins" for new frame start at frame pointer plus locals */
ins = ((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame) +
(method->registersSize - method->insSize); //ALOGD(" FP is %p, INs live at >= %p", self->interpSave.curFrame, ins); /* put "this" pointer into in0 if appropriate */
if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) {
#ifdef WITH_EXTRA_OBJECT_VALIDATION
assert(obj != NULL && dvmIsHeapAddress(obj));
#endif
*ins++ = (u4) obj;
verifyCount++;
} while (*desc != '\0') {
switch (*(desc++)) {
case 'D': case 'J': {
u8 val = va_arg(args, u8);
memcpy(ins, &val, ); // EABI prevents direct store
ins += ;
verifyCount += ;
break;
}
case 'F': {
/* floats were normalized to doubles; convert back */
float f = (float) va_arg(args, double);
*ins++ = dvmFloatToU4(f);
verifyCount++;
break;
}
case 'L': { /* 'shorty' descr uses L for all refs, incl array */
void* arg = va_arg(args, void*);
assert(obj == NULL || dvmIsHeapAddress(obj));
jobject argObj = reinterpret_cast<jobject>(arg);
if (fromJni)
*ins++ = (u4) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(self, argObj);
else
*ins++ = (u4) argObj;
verifyCount++;
break;
}
default: {
/* Z B C S I -- all passed as 32-bit integers */
*ins++ = va_arg(args, u4);
verifyCount++;
break;
}
}
} #ifndef NDEBUG
if (verifyCount != method->insSize) {
ALOGE("Got vfycount=%d insSize=%d for %s.%s", verifyCount,
method->insSize, clazz->descriptor, method->name);
assert(false);
goto bail;
}
#endif //dvmDumpThreadStack(dvmThreadSelf()); if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) {
TRACE_METHOD_ENTER(self, method);
/*
* Because we leave no space for local variables, "curFrame" points
* directly at the method arguments.
*/
(*method->nativeFunc)((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame, pResult,
method, self);
TRACE_METHOD_EXIT(self, method);
} else {
dvmInterpret(self, method, pResult);
} #ifndef NDEBUG
bail:
#endif
dvmPopFrame(self);
} /*
* Issue a method call with arguments provided in an array. We process
* the contents of "args" by scanning the method signature.
*
* The values were likely placed into an uninitialized jvalue array using
* the field specifiers, which means that sub-32-bit fields (e.g. short,
* boolean) may not have 32 or 64 bits of valid data. This is different
* from the varargs invocation where the C compiler does a widening
* conversion when calling a function. As a result, we have to be a
* little more precise when pulling stuff out.
*
* "args" may be NULL if the method has no arguments.
*/
void dvmCallMethodA(Thread* self, const Method* method, Object* obj,
bool fromJni, JValue* pResult, const jvalue* args)
{
const char* desc = &(method->shorty[]); // [0] is the return type.
int verifyCount = ;
ClassObject* clazz;
u4* ins; clazz = callPrep(self, method, obj, false);
if (clazz == NULL)
return; /* "ins" for new frame start at frame pointer plus locals */
ins = ((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame) +
(method->registersSize - method->insSize); /* put "this" pointer into in0 if appropriate */
if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) {
assert(obj != NULL);
*ins++ = (u4) obj; /* obj is a "real" ref */
verifyCount++;
} while (*desc != '\0') {
switch (*desc++) {
case 'D': /* 64-bit quantity; have to use */
case 'J': /* memcpy() in case of mis-alignment */
memcpy(ins, &args->j, );
ins += ;
verifyCount++; /* this needs an extra push */
break;
case 'L': /* includes array refs */
if (fromJni)
*ins++ = (u4) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(self, args->l);
else
*ins++ = (u4) args->l;
break;
case 'F':
case 'I':
*ins++ = args->i; /* full 32 bits */
break;
case 'S':
*ins++ = args->s; /* 16 bits, sign-extended */
break;
case 'C':
*ins++ = args->c; /* 16 bits, unsigned */
break;
case 'B':
*ins++ = args->b; /* 8 bits, sign-extended */
break;
case 'Z':
*ins++ = args->z; /* 8 bits, zero or non-zero */
break;
default:
ALOGE("Invalid char %c in short signature of %s.%s",
*(desc-), clazz->descriptor, method->name);
assert(false);
goto bail;
} verifyCount++;
args++;
} #ifndef NDEBUG
if (verifyCount != method->insSize) {
ALOGE("Got vfycount=%d insSize=%d for %s.%s", verifyCount,
method->insSize, clazz->descriptor, method->name);
assert(false);
goto bail;
}
#endif if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) {
TRACE_METHOD_ENTER(self, method);
/*
* Because we leave no space for local variables, "curFrame" points
* directly at the method arguments.
*/
(*method->nativeFunc)((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame, pResult,
method, self);
TRACE_METHOD_EXIT(self, method);
} else {
dvmInterpret(self, method, pResult);
} bail:
dvmPopFrame(self);
} static void throwArgumentTypeMismatch(int argIndex, ClassObject* expected, DataObject* arg) {
std::string expectedClassName(dvmHumanReadableDescriptor(expected->descriptor));
std::string actualClassName = dvmHumanReadableType(arg);
dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exIllegalArgumentException, "argument %d should have type %s, got %s",
argIndex + , expectedClassName.c_str(), actualClassName.c_str());
} /*
* Invoke a method, using the specified arguments and return type, through
* one of the reflection interfaces. Could be a virtual or direct method
* (including constructors). Used for reflection.
*
* Deals with boxing/unboxing primitives and performs widening conversions.
*
* "invokeObj" will be null for a static method.
*
* If the invocation returns with an exception raised, we have to wrap it.
*/
Object* dvmInvokeMethod(Object* obj, const Method* method,
ArrayObject* argList, ArrayObject* params, ClassObject* returnType,
bool noAccessCheck)
{
ClassObject* clazz;
Object* retObj = NULL;
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
s4* ins;
int verifyCount, argListLength;
JValue retval;
bool needPop = false; /* verify arg count */
if (argList != NULL)
argListLength = argList->length;
else
argListLength = ;
if (argListLength != (int) params->length) {
dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exIllegalArgumentException,
"wrong number of arguments; expected %d, got %d",
params->length, argListLength);
return NULL;
} clazz = callPrep(self, method, obj, !noAccessCheck);
if (clazz == NULL)
return NULL;
needPop = true; /* "ins" for new frame start at frame pointer plus locals */
ins = ((s4*)self->interpSave.curFrame) +
(method->registersSize - method->insSize);
verifyCount = ; //ALOGD(" FP is %p, INs live at >= %p", self->interpSave.curFrame, ins); /* put "this" pointer into in0 if appropriate */
if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) {
assert(obj != NULL);
*ins++ = (s4) obj;
verifyCount++;
} /*
* Copy the args onto the stack. Primitive types are converted when
* necessary, and object types are verified.
*/
DataObject** args = (DataObject**)(void*)argList->contents;
ClassObject** types = (ClassObject**)(void*)params->contents;
for (int i = ; i < argListLength; i++) {
int width = dvmConvertArgument(*args++, *types++, ins);
if (width < ) {
dvmPopFrame(self); // throw wants to pull PC out of stack
needPop = false;
throwArgumentTypeMismatch(i, *(types-), *(args-));
goto bail;
} ins += width;
verifyCount += width;
} #ifndef NDEBUG
if (verifyCount != method->insSize) {
ALOGE("Got vfycount=%d insSize=%d for %s.%s", verifyCount,
method->insSize, clazz->descriptor, method->name);
assert(false);
goto bail;
}
#endif if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) {
TRACE_METHOD_ENTER(self, method);
/*
* Because we leave no space for local variables, "curFrame" points
* directly at the method arguments.
*/
(*method->nativeFunc)((u4*)self->interpSave.curFrame, &retval,
method, self);
TRACE_METHOD_EXIT(self, method);
} else {
dvmInterpret(self, method, &retval);
} /*
* Pop the frame immediately. The "wrap" calls below can cause
* allocations, and we don't want the GC to walk the now-dead frame.
*/
dvmPopFrame(self);
needPop = false; /*
* If an exception is raised, wrap and replace. This is necessary
* because the invoked method could have thrown a checked exception
* that the caller wasn't prepared for.
*
* We might be able to do this up in the interpreted code, but that will
* leave us with a shortened stack trace in the top-level exception.
*/
if (dvmCheckException(self)) {
dvmWrapException("Ljava/lang/reflect/InvocationTargetException;");
} else {
/*
* If this isn't a void method or constructor, convert the return type
* to an appropriate object.
*
* We don't do this when an exception is raised because the value
* in "retval" is undefined.
*/
if (returnType != NULL) {
retObj = (Object*)dvmBoxPrimitive(retval, returnType);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc(retObj, NULL);
}
} bail:
if (needPop) {
dvmPopFrame(self);
}
return retObj;
} struct LineNumFromPcContext {
u4 address;
u4 lineNum;
}; static int lineNumForPcCb(void *cnxt, u4 address, u4 lineNum)
{
LineNumFromPcContext *pContext = (LineNumFromPcContext *)cnxt; // We know that this callback will be called in
// ascending address order, so keep going until we find
// a match or we've just gone past it. if (address > pContext->address) {
// The line number from the previous positions callback
// wil be the final result.
return ;
} pContext->lineNum = lineNum; return (address == pContext->address) ? : ;
} /*
* Determine the source file line number based on the program counter.
* "pc" is an offset, in 16-bit units, from the start of the method's code.
*
* Returns -1 if no match was found (possibly because the source files were
* compiled without "-g", so no line number information is present).
* Returns -2 for native methods (as expected in exception traces).
*/
int dvmLineNumFromPC(const Method* method, u4 relPc)
{
const DexCode* pDexCode = dvmGetMethodCode(method); if (pDexCode == NULL) {
if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method) && !dvmIsAbstractMethod(method))
return -;
return -; /* can happen for abstract method stub */
} LineNumFromPcContext context;
memset(&context, , sizeof(context));
context.address = relPc;
// A method with no line number info should return -1
context.lineNum = -; dexDecodeDebugInfo(method->clazz->pDvmDex->pDexFile, pDexCode,
method->clazz->descriptor,
method->prototype.protoIdx,
method->accessFlags,
lineNumForPcCb, NULL, &context); return context.lineNum;
} /*
* Compute the frame depth.
*
* Excludes "break" frames.
*/
int dvmComputeExactFrameDepth(const void* fp)
{
int count = ; for ( ; fp != NULL; fp = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp)->prevFrame) {
if (!dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)fp))
count++;
} return count;
} /*
* Compute the "vague" frame depth, which is just a pointer subtraction.
* The result is NOT an overly generous assessment of the number of
* frames; the only meaningful use is to compare against the result of
* an earlier invocation.
*
* Useful for implementing single-step debugger modes, which may need to
* call this for every instruction.
*/
int dvmComputeVagueFrameDepth(Thread* thread, const void* fp)
{
const u1* interpStackStart = thread->interpStackStart; assert((u1*) fp >= interpStackStart - thread->interpStackSize);
assert((u1*) fp < interpStackStart);
return interpStackStart - (u1*) fp;
} /*
* Get the calling frame. Pass in the current fp.
*
* Skip "break" frames and reflection invoke frames.
*/
void* dvmGetCallerFP(const void* curFrame)
{
void* caller = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->prevFrame;
StackSaveArea* saveArea; retry:
if (dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)caller)) {
/* pop up one more */
caller = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->prevFrame;
if (caller == NULL)
return NULL; /* hit the top */ /*
* If we got here by java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(), we don't
* want to return Method's class loader. Shift up one and try
* again.
*/
saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller);
if (dvmIsReflectionMethod(saveArea->method)) {
caller = saveArea->prevFrame;
assert(caller != NULL);
goto retry;
}
} return caller;
} /*
* Get the caller's class. Pass in the current fp.
*
* This is used by e.g. java.lang.Class.
*/
ClassObject* dvmGetCallerClass(const void* curFrame)
{
void* caller; caller = dvmGetCallerFP(curFrame);
if (caller == NULL)
return NULL; return SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->method->clazz;
} /*
* Get the caller's caller's class. Pass in the current fp.
*
* This is used by e.g. java.lang.Class, which wants to know about the
* class loader of the method that called it.
*/
ClassObject* dvmGetCaller2Class(const void* curFrame)
{
void* caller = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->prevFrame;
void* callerCaller; /* at the top? */
if (dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)caller) &&
SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->prevFrame == NULL)
return NULL; /* go one more */
callerCaller = dvmGetCallerFP(caller);
if (callerCaller == NULL)
return NULL; return SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(callerCaller)->method->clazz;
} /*
* Get the caller's caller's caller's class. Pass in the current fp.
*
* This is used by e.g. java.lang.Class, which wants to know about the
* class loader of the method that called it.
*/
ClassObject* dvmGetCaller3Class(const void* curFrame)
{
void* caller = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->prevFrame;
int i; /* at the top? */
if (dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)caller) &&
SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->prevFrame == NULL)
return NULL; /* Walk up two frames if possible. */
for (i = ; i < ; i++) {
caller = dvmGetCallerFP(caller);
if (caller == NULL)
return NULL;
} return SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(caller)->method->clazz;
} /*
* Fill a flat array of methods that comprise the current interpreter
* stack trace. Pass in the current frame ptr. Break frames are
* skipped, but reflection invocations are not.
*
* The current frame will be in element 0.
*/
void dvmFillStackTraceArray(const void* fp, const Method** array, size_t length)
{
assert(fp != NULL);
assert(array != NULL);
size_t i = ;
while (fp != NULL) {
if (!dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)fp)) {
assert(i < length);
array[i++] = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp)->method;
}
fp = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp)->prevFrame;
}
} /*
* Open up the reserved area and throw an exception. The reserved area
* should only be needed to create and initialize the exception itself.
*
* If we already opened it and we're continuing to overflow, abort the VM.
*
* We have to leave the "reserved" area open until the "catch" handler has
* finished doing its processing. This is because the catch handler may
* need to resolve classes, which requires calling into the class loader if
* the classes aren't already in the "initiating loader" list.
*/
void dvmHandleStackOverflow(Thread* self, const Method* method)
{
/*
* Can we make the reserved area available?
*/
if (self->stackOverflowed) {
/*
* Already did, nothing to do but bail.
*/
ALOGE("DalvikVM: double-overflow of stack in threadid=%d; aborting",
self->threadId);
dvmDumpThread(self, false);
dvmAbort();
} /* open it up to the full range */
ALOGI("threadid=%d: stack overflow on call to %s.%s:%s",
self->threadId,
method->clazz->descriptor, method->name, method->shorty);
StackSaveArea* saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame);
ALOGI(" method requires %d+%d+%d=%d bytes, fp is %p (%d left)",
method->registersSize * , sizeof(StackSaveArea), method->outsSize * ,
(method->registersSize + method->outsSize) * + sizeof(StackSaveArea),
saveArea, (u1*) saveArea - self->interpStackEnd);
ALOGI(" expanding stack end (%p to %p)", self->interpStackEnd,
self->interpStackStart - self->interpStackSize);
//dvmDumpThread(self, false);
self->interpStackEnd = self->interpStackStart - self->interpStackSize;
self->stackOverflowed = true; /*
* If we were trying to throw an exception when the stack overflowed,
* we will blow up when doing the class lookup on StackOverflowError
* because of the pending exception. So, we clear it and make it
* the cause of the SOE.
*/
Object* excep = dvmGetException(self);
if (excep != NULL) {
ALOGW("Stack overflow while throwing exception");
dvmClearException(self);
}
dvmThrowChainedException(gDvm.exStackOverflowError, NULL, excep);
} /*
* Reduce the available stack size. By this point we should have finished
* our overflow processing.
*/
void dvmCleanupStackOverflow(Thread* self, const Object* exception)
{
const u1* newStackEnd; assert(self->stackOverflowed); if (exception->clazz != gDvm.exStackOverflowError) {
/* exception caused during SOE, not the SOE itself */
return;
} newStackEnd = (self->interpStackStart - self->interpStackSize)
+ STACK_OVERFLOW_RESERVE;
if ((u1*)self->interpSave.curFrame <= newStackEnd) {
ALOGE("Can't shrink stack: curFrame is in reserved area (%p %p)",
self->interpStackEnd, self->interpSave.curFrame);
dvmDumpThread(self, false);
dvmAbort();
} self->interpStackEnd = newStackEnd;
self->stackOverflowed = false; ALOGI("Shrank stack (to %p, curFrame is %p)", self->interpStackEnd,
self->interpSave.curFrame);
} /*
* Extract the object that is the target of a monitor-enter instruction
* in the top stack frame of "thread".
*
* The other thread might be alive, so this has to work carefully.
*
* The thread list lock must be held.
*
* Returns "true" if we successfully recover the object. "*pOwner" will
* be NULL if we can't determine the owner for some reason (e.g. race
* condition on ownership transfer).
*/
static bool extractMonitorEnterObject(Thread* thread, Object** pLockObj,
Thread** pOwner)
{
void* framePtr = thread->interpSave.curFrame; if (framePtr == NULL || dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)framePtr))
return false; const StackSaveArea* saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(framePtr);
const Method* method = saveArea->method;
const u2* currentPc = saveArea->xtra.currentPc; /* check Method* */
if (!dvmLinearAllocContains(method, sizeof(Method))) {
ALOGD("ExtrMon: method %p not valid", method);
return false;
} /* check currentPc */
u4 insnsSize = dvmGetMethodInsnsSize(method);
if (currentPc < method->insns ||
currentPc >= method->insns + insnsSize)
{
ALOGD("ExtrMon: insns %p not valid (%p - %p)",
currentPc, method->insns, method->insns + insnsSize);
return false;
} /* check the instruction */
if ((*currentPc & 0xff) != OP_MONITOR_ENTER) {
ALOGD("ExtrMon: insn at %p is not monitor-enter (0x%02x)",
currentPc, *currentPc & 0xff);
return false;
} /* get and check the register index */
unsigned int reg = *currentPc >> ;
if (reg >= method->registersSize) {
ALOGD("ExtrMon: invalid register %d (max %d)",
reg, method->registersSize);
return false;
} /* get and check the object in that register */
u4* fp = (u4*) framePtr;
Object* obj = (Object*) fp[reg];
if (obj != NULL && !dvmIsHeapAddress(obj)) {
ALOGD("ExtrMon: invalid object %p at %p[%d]", obj, fp, reg);
return false;
}
*pLockObj = obj; /*
* Try to determine the object's lock holder; it's okay if this fails.
*
* We're assuming the thread list lock is already held by this thread.
* If it's not, we may be living dangerously if we have to scan through
* the thread list to find a match. (The VM will generally be in a
* suspended state when executing here, so this is a minor concern
* unless we're dumping while threads are running, in which case there's
* a good chance of stuff blowing up anyway.)
*/
*pOwner = dvmGetObjectLockHolder(obj); return true;
} static void printWaitMessage(const DebugOutputTarget* target, const char* detail, Object* obj,
Thread* thread)
{
std::string msg(StringPrintf(" - waiting %s <%p> ", detail, obj)); if (obj->clazz != gDvm.classJavaLangClass) {
// I(16573) - waiting on <0xf5feda38> (a java.util.LinkedList)
// I(16573) - waiting on <0xf5ed54f8> (a java.lang.Class<java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue>)
msg += "(a " + dvmHumanReadableType(obj) + ")";
} if (thread != NULL) {
std::string threadName(dvmGetThreadName(thread));
StringAppendF(&msg, " held by tid=%d (%s)", thread->threadId, threadName.c_str());
} dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "%s\n", msg.c_str());
} /*
* Dump stack frames, starting from the specified frame and moving down.
*
* Each frame holds a pointer to the currently executing method, and the
* saved program counter from the caller ("previous" frame). This means
* we don't have the PC for the current method on the stack, which is
* pretty reasonable since it's in the "PC register" for the VM. Because
* exceptions need to show the correct line number we actually *do* have
* an updated version in the fame's "xtra.currentPc", but it's unreliable.
*
* Note "framePtr" could be NULL in rare circumstances.
*/
static void dumpFrames(const DebugOutputTarget* target, void* framePtr,
Thread* thread)
{
const StackSaveArea* saveArea;
const Method* method;
int checkCount = ;
const u2* currentPc = NULL;
bool first = true; /*
* We call functions that require us to be holding the thread list lock.
* It's probable that the caller has already done so, but it's not
* guaranteed. If it's not locked, lock it now.
*/
bool needThreadUnlock = dvmTryLockThreadList(); /*
* The "currentPc" is updated whenever we execute an instruction that
* might throw an exception. Show it here.
*/
if (framePtr != NULL && !dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)framePtr)) {
saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(framePtr); if (saveArea->xtra.currentPc != NULL)
currentPc = saveArea->xtra.currentPc;
} while (framePtr != NULL) {
saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(framePtr);
method = saveArea->method; if (dvmIsBreakFrame((u4*)framePtr)) {
//dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " (break frame)\n");
} else {
int relPc; if (currentPc != NULL)
relPc = currentPc - saveArea->method->insns;
else
relPc = -; std::string methodName(dvmHumanReadableMethod(method, false));
if (dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " at %s(Native Method)\n",
methodName.c_str());
} else {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " at %s(%s:%s%d)\n",
methodName.c_str(), dvmGetMethodSourceFile(method),
(relPc >= && first) ? "~" : "",
relPc < ? - : dvmLineNumFromPC(method, relPc));
} if (first) {
/*
* Decorate WAIT and MONITOR threads with some detail on
* the first frame.
*
* warning: wait status not stable, even in suspend
*/
if (thread->status == THREAD_WAIT ||
thread->status == THREAD_TIMED_WAIT)
{
Monitor* mon = thread->waitMonitor;
Object* obj = dvmGetMonitorObject(mon);
if (obj != NULL) {
Thread* joinThread = NULL;
if (obj->clazz == gDvm.classJavaLangVMThread) {
joinThread = dvmGetThreadFromThreadObject(obj);
}
if (joinThread == NULL) {
joinThread = dvmGetObjectLockHolder(obj);
}
printWaitMessage(target, "on", obj, joinThread);
}
} else if (thread->status == THREAD_MONITOR) {
Object* obj;
Thread* owner;
if (extractMonitorEnterObject(thread, &obj, &owner)) {
printWaitMessage(target, "to lock", obj, owner);
}
}
}
} /*
* Get saved PC for previous frame. There's no savedPc in a "break"
* frame, because that represents native or interpreted code
* invoked by the VM. The saved PC is sitting in the "PC register",
* a local variable on the native stack.
*/
currentPc = saveArea->savedPc; first = false; if (saveArea->prevFrame != NULL && saveArea->prevFrame <= framePtr) {
ALOGW("Warning: loop in stack trace at frame %d (%p -> %p)",
checkCount, framePtr, saveArea->prevFrame);
break;
}
framePtr = saveArea->prevFrame; checkCount++;
if (checkCount > ) {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target,
" ***** printed %d frames, not showing any more\n",
checkCount);
break;
}
} if (needThreadUnlock) {
dvmUnlockThreadList();
}
} /*
* Dump the stack for the specified thread.
*/
void dvmDumpThreadStack(const DebugOutputTarget* target, Thread* thread)
{
dumpFrames(target, thread->interpSave.curFrame, thread);
} /*
* Dump the stack for the specified thread, which is still running.
*
* This is very dangerous, because stack frames are being pushed on and
* popped off, and if the thread exits we'll be looking at freed memory.
* The plan here is to take a snapshot of the stack and then dump that
* to try to minimize the chances of catching it mid-update. This should
* work reasonably well on a single-CPU system.
*
* There is a small chance that calling here will crash the VM.
*/
void dvmDumpRunningThreadStack(const DebugOutputTarget* target, Thread* thread)
{
StackSaveArea* saveArea;
const u1* origStack;
u1* stackCopy = NULL;
int origSize, fpOffset;
void* fp;
int depthLimit = ; if (thread == NULL || thread->interpSave.curFrame == NULL) {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target,
"DumpRunning: Thread at %p has no curFrame (threadid=%d)\n",
thread, (thread != NULL) ? thread->threadId : );
return;
} /* wait for a full quantum */
sched_yield(); /* copy the info we need, then the stack itself */
origSize = thread->interpStackSize;
origStack = (const u1*) thread->interpStackStart - origSize;
stackCopy = (u1*) malloc(origSize);
fpOffset = (u1*) thread->interpSave.curFrame - origStack;
memcpy(stackCopy, origStack, origSize); /*
* Run through the stack and rewrite the "prev" pointers.
*/
//ALOGI("DR: fpOff=%d (from %p %p)",fpOffset, origStack,
// thread->interpSave.curFrame);
fp = stackCopy + fpOffset;
while (true) {
int prevOffset; if (depthLimit-- < ) {
/* we're probably screwed */
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "DumpRunning: depth limit hit\n");
dvmAbort();
}
saveArea = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp);
if (saveArea->prevFrame == NULL)
break; prevOffset = (u1*) saveArea->prevFrame - origStack;
if (prevOffset < || prevOffset > origSize) {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target,
"DumpRunning: bad offset found: %d (from %p %p)\n",
prevOffset, origStack, saveArea->prevFrame);
saveArea->prevFrame = NULL;
break;
} saveArea->prevFrame = (u4*)(stackCopy + prevOffset);
fp = saveArea->prevFrame;
} /*
* We still need to pass the Thread for some monitor wait stuff.
*/
dumpFrames(target, stackCopy + fpOffset, thread);
free(stackCopy);
} /*
* Dump the native stack for the specified thread.
*/
void dvmDumpNativeStack(const DebugOutputTarget* target, pid_t tid)
{
#ifdef HAVE_ANDROID_OS
const size_t MAX_DEPTH = ;
backtrace_frame_t backtrace[MAX_DEPTH];
ssize_t frames = unwind_backtrace_thread(tid, backtrace, , MAX_DEPTH);
if (frames > ) {
backtrace_symbol_t backtrace_symbols[MAX_DEPTH];
get_backtrace_symbols(backtrace, frames, backtrace_symbols); for (size_t i = ; i < size_t(frames); i++) {
char line[MAX_BACKTRACE_LINE_LENGTH];
format_backtrace_line(i, &backtrace[i], &backtrace_symbols[i],
line, MAX_BACKTRACE_LINE_LENGTH);
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " %s\n", line);
} free_backtrace_symbols(backtrace_symbols, frames);
} else {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " (native backtrace unavailable)\n");
}
#endif
}
Stack.cpp
//xref : /dalvik/vm/Jni.cpp
//http://androidxref.com/4.4.2_r2/xref/dalvik/vm/Jni.cpp /*
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/ /*
* Dalvik implementation of JNI interfaces.
*/
#include "Dalvik.h"
#include "JniInternal.h"
#include "Misc.h"
#include "ScopedPthreadMutexLock.h"
#include "UniquePtr.h" #include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <limits.h> /*
Native methods and interaction with the GC All JNI methods must start by changing their thread status to
THREAD_RUNNING, and finish by changing it back to THREAD_NATIVE before
returning to native code. The switch to "running" triggers a thread
suspension check. With a rudimentary GC we should be able to skip the status change for
simple functions, e.g. IsSameObject, GetJavaVM, GetStringLength, maybe
even access to fields with primitive types. Our options are more limited
with a compacting GC. For performance reasons we do as little error-checking as possible here.
For example, we don't check to make sure the correct type of Object is
passed in when setting a field, and we don't prevent you from storing
new values in a "final" field. Such things are best handled in the
"check" version. For actions that are common, dangerous, and must be
checked at runtime, such as array bounds checks, we do the tests here. General notes on local/global reference tracking JNI provides explicit control over natively-held references that the GC
needs to know about. These can be local, in which case they're released
when the native method returns into the VM, or global, which are held
until explicitly released. (There are also weak-global references,
which have the lifespan and visibility of global references, but the
object they refer to may be collected.) The references can be created with explicit JNI NewLocalRef / NewGlobalRef
calls. The former is very unusual, the latter is reasonably common
(e.g. for caching references to class objects). Local references are most often created as a side-effect of JNI functions.
For example, the AllocObject/NewObject functions must create local
references to the objects returned, because nothing else in the GC root
set has a reference to the new objects. The most common mode of operation is for a method to create zero or
more local references and return. Explicit "local delete" operations
are expected to be exceedingly rare, except when walking through an
object array, and the Push/PopLocalFrame calls are expected to be used
infrequently. For efficient operation, we want to add new local refs
with a simple store/increment operation; to avoid infinite growth in
pathological situations, we need to reclaim the space used by deleted
entries. If we just want to maintain a list for the GC root set, we can use an
expanding append-only array that compacts when objects are deleted.
In typical situations, e.g. running through an array of objects, we will
be deleting one of the most recently added entries, so we can minimize
the number of elements moved (or avoid having to move any). If we want to conceal the pointer values from native code, which is
necessary to allow the GC to move JNI-referenced objects around, then we
have to use a more complicated indirection mechanism. The spec says, "Local references are only valid in the thread in which
they are created. The native code must not pass local references from
one thread to another." Pinned objects For some large chunks of data, notably primitive arrays and String data,
JNI allows the VM to choose whether it wants to pin the array object or
make a copy. We currently pin the memory for better execution performance. TODO: we're using simple root set references to pin primitive array data,
because they have the property we need (i.e. the pointer we return is
guaranteed valid until we explicitly release it). However, if we have a
compacting GC and don't want to pin all memory held by all global refs,
we need to treat these differently. Global reference tracking There should be a small "active" set centered around the most-recently
added items. Because it's global, access to it has to be synchronized. Additions and
removals require grabbing a mutex. If the table serves as an indirection
mechanism (i.e. it's not just a list for the benefit of the garbage
collector), reference lookups may also require grabbing a mutex. The JNI spec does not define any sort of limit, so the list must be able
to expand to a reasonable size. It may be useful to log significant
increases in usage to help identify resource leaks. Weak-global reference tracking [TBD] Local reference tracking Each Thread/JNIEnv points to an IndirectRefTable. We implement Push/PopLocalFrame with actual stack frames. Before a JNI
frame gets popped, we set "nextEntry" to the "top" pointer of the current
frame, effectively releasing the references. The GC will scan all references in the table. */ static void ReportJniError() {
dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false);
dvmAbort();
} #ifdef WITH_JNI_STACK_CHECK
# define COMPUTE_STACK_SUM(_self) computeStackSum(_self);
# define CHECK_STACK_SUM(_self) checkStackSum(_self); /*
* Compute a CRC on the entire interpreted stack.
*
* Would be nice to compute it on "self" as well, but there are parts of
* the Thread that can be altered by other threads (e.g. prev/next pointers).
*/
static void computeStackSum(Thread* self) {
const u1* low = (const u1*)SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame);
u4 crc = dvmInitCrc32();
self->stackCrc = ;
crc = dvmComputeCrc32(crc, low, self->interpStackStart - low);
self->stackCrc = crc;
} /*
* Compute a CRC on the entire interpreted stack, and compare it to what
* we previously computed.
*
* We can execute JNI directly from native code without calling in from
* interpreted code during VM initialization and immediately after JNI
* thread attachment. Another opportunity exists during JNI_OnLoad. Rather
* than catching these cases we just ignore them here, which is marginally
* less accurate but reduces the amount of code we have to touch with #ifdefs.
*/
static void checkStackSum(Thread* self) {
const u1* low = (const u1*)SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(self->interpSave.curFrame);
u4 stackCrc = self->stackCrc;
self->stackCrc = ;
u4 crc = dvmInitCrc32();
crc = dvmComputeCrc32(crc, low, self->interpStackStart - low);
if (crc != stackCrc) {
const Method* meth = dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod();
if (dvmComputeExactFrameDepth(self->interpSave.curFrame) == ) {
ALOGD("JNI: bad stack CRC (0x%08x) -- okay during init", stackCrc);
} else if (strcmp(meth->name, "nativeLoad") == &&
(strcmp(meth->clazz->descriptor, "Ljava/lang/Runtime;") == )) {
ALOGD("JNI: bad stack CRC (0x%08x) -- okay during JNI_OnLoad", stackCrc);
} else {
ALOGW("JNI: bad stack CRC (%08x vs %08x)", crc, stackCrc);
ReportJniError();
}
}
self->stackCrc = (u4) -; /* make logic errors more noticeable */
} #else
# define COMPUTE_STACK_SUM(_self) ((void))
# define CHECK_STACK_SUM(_self) ((void))
#endif /*
* ===========================================================================
* Utility functions
* ===========================================================================
*/ /*
* Entry/exit processing for all JNI calls.
*
* We skip the (curiously expensive) thread-local storage lookup on our Thread*.
* If the caller has passed the wrong JNIEnv in, we're going to be accessing unsynchronized
* structures from more than one thread, and things are going to fail
* in bizarre ways. This is only sensible if the native code has been
* fully exercised with CheckJNI enabled.
*/
class ScopedJniThreadState {
public:
explicit ScopedJniThreadState(JNIEnv* env) {
mSelf = ((JNIEnvExt*) env)->self; if (UNLIKELY(gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs)) {
// When emulating direct pointers with indirect references, it's critical
// that we use the correct per-thread indirect reference table.
Thread* self = gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs ? dvmThreadSelf() : mSelf;
if (self != mSelf) {
ALOGE("JNI ERROR: env->self != thread-self (%p vs. %p); auto-correcting", mSelf, self);
mSelf = self;
}
} CHECK_STACK_SUM(mSelf);
dvmChangeStatus(mSelf, THREAD_RUNNING);
} ~ScopedJniThreadState() {
dvmChangeStatus(mSelf, THREAD_NATIVE);
COMPUTE_STACK_SUM(mSelf);
} inline Thread* self() {
return mSelf;
} private:
Thread* mSelf; // Disallow copy and assignment.
ScopedJniThreadState(const ScopedJniThreadState&);
void operator=(const ScopedJniThreadState&);
}; #define kGlobalRefsTableInitialSize 512
#define kGlobalRefsTableMaxSize 51200 /* arbitrary, must be < 64K */ #define kWeakGlobalRefsTableInitialSize 16 #define kPinTableInitialSize 16
#define kPinTableMaxSize 1024
#define kPinComplainThreshold 10 bool dvmJniStartup() {
if (!gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.init(kGlobalRefsTableInitialSize,
kGlobalRefsTableMaxSize,
kIndirectKindGlobal)) {
return false;
}
if (!gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable.init(kWeakGlobalRefsTableInitialSize,
kGlobalRefsTableMaxSize,
kIndirectKindWeakGlobal)) {
return false;
} dvmInitMutex(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock);
dvmInitMutex(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock); if (!dvmInitReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, kPinTableInitialSize, kPinTableMaxSize)) {
return false;
} dvmInitMutex(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock); return true;
} void dvmJniShutdown() {
gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.destroy();
gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable.destroy();
dvmClearReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable);
} bool dvmIsBadJniVersion(int version) {
// We don't support JNI_VERSION_1_1. These are the only other valid versions.
return version != JNI_VERSION_1_2 && version != JNI_VERSION_1_4 && version != JNI_VERSION_1_6;
} /*
* Find the JNIEnv associated with the current thread.
*
* Currently stored in the Thread struct. Could also just drop this into
* thread-local storage.
*/
JNIEnvExt* dvmGetJNIEnvForThread() {
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
if (self == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
return (JNIEnvExt*) dvmGetThreadJNIEnv(self);
} /*
* Convert an indirect reference to an Object reference. The indirect
* reference may be local, global, or weak-global.
*
* If "jobj" is NULL, or is a weak global reference whose reference has
* been cleared, this returns NULL. If jobj is an invalid indirect
* reference, kInvalidIndirectRefObject is returned.
*
* Note "env" may be NULL when decoding global references.
*/
Object* dvmDecodeIndirectRef(Thread* self, jobject jobj) {
if (jobj == NULL) {
return NULL;
} switch (indirectRefKind(jobj)) {
case kIndirectKindLocal:
{
Object* result = self->jniLocalRefTable.get(jobj);
if (UNLIKELY(result == NULL)) {
ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): use of deleted local reference (%p)", jobj);
ReportJniError();
}
return result;
}
case kIndirectKindGlobal:
{
// TODO: find a way to avoid the mutex activity here
IndirectRefTable* pRefTable = &gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable;
ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock);
Object* result = pRefTable->get(jobj);
if (UNLIKELY(result == NULL)) {
ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): use of deleted global reference (%p)", jobj);
ReportJniError();
}
return result;
}
case kIndirectKindWeakGlobal:
{
// TODO: find a way to avoid the mutex activity here
IndirectRefTable* pRefTable = &gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable;
ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock);
Object* result = pRefTable->get(jobj);
if (result == kClearedJniWeakGlobal) {
result = NULL;
} else if (UNLIKELY(result == NULL)) {
ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): use of deleted weak global reference (%p)", jobj);
ReportJniError();
}
return result;
}
case kIndirectKindInvalid:
default:
if (UNLIKELY(gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs)) {
// Assume an invalid local reference is actually a direct pointer.
return reinterpret_cast<Object*>(jobj);
}
ALOGW("Invalid indirect reference %p in decodeIndirectRef", jobj);
ReportJniError();
return kInvalidIndirectRefObject;
}
} static void AddLocalReferenceFailure(IndirectRefTable* pRefTable) {
pRefTable->dump("JNI local");
ALOGE("Failed adding to JNI local ref table (has %zd entries)", pRefTable->capacity());
ReportJniError(); // spec says call FatalError; this is equivalent
} /*
* Add a local reference for an object to the current stack frame. When
* the native function returns, the reference will be discarded.
*
* We need to allow the same reference to be added multiple times.
*
* This will be called on otherwise unreferenced objects. We cannot do
* GC allocations here, and it's best if we don't grab a mutex.
*/
static inline jobject addLocalReference(Thread* self, Object* obj) {
if (obj == NULL) {
return NULL;
} IndirectRefTable* pRefTable = &self->jniLocalRefTable;
void* curFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame;
u4 cookie = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->xtra.localRefCookie;
jobject jobj = (jobject) pRefTable->add(cookie, obj);
if (UNLIKELY(jobj == NULL)) {
AddLocalReferenceFailure(pRefTable);
} if (UNLIKELY(gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs)) {
// Hand out direct pointers to support broken old apps.
return reinterpret_cast<jobject>(obj);
}
return jobj;
} /*
* Ensure that at least "capacity" references can be held in the local
* refs table of the current thread.
*/
static bool ensureLocalCapacity(Thread* self, int capacity) {
int numEntries = self->jniLocalRefTable.capacity();
// TODO: this isn't quite right, since "numEntries" includes holes
return ((kJniLocalRefMax - numEntries) >= capacity);
} /*
* Explicitly delete a reference from the local list.
*/
static void deleteLocalReference(Thread* self, jobject jobj) {
if (jobj == NULL) {
return;
} IndirectRefTable* pRefTable = &self->jniLocalRefTable;
void* curFrame = self->interpSave.curFrame;
u4 cookie = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(curFrame)->xtra.localRefCookie;
if (!pRefTable->remove(cookie, jobj)) {
/*
* Attempting to delete a local reference that is not in the
* topmost local reference frame is a no-op. DeleteLocalRef returns
* void and doesn't throw any exceptions, but we should probably
* complain about it so the user will notice that things aren't
* going quite the way they expect.
*/
ALOGW("JNI WARNING: DeleteLocalRef(%p) failed to find entry", jobj);
}
} /*
* Add a global reference for an object.
*
* We may add the same object more than once. Add/remove calls are paired,
* so it needs to appear on the list multiple times.
*/
static jobject addGlobalReference(Object* obj) {
if (obj == NULL) {
return NULL;
} //ALOGI("adding obj=%p", obj);
//dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false); if (false && dvmIsClassObject((Object*)obj)) {
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) obj;
ALOGI("-------");
ALOGI("Adding global ref on class %s", clazz->descriptor);
dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false);
}
if (false && ((Object*)obj)->clazz == gDvm.classJavaLangString) {
StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) obj;
char* str = dvmCreateCstrFromString(strObj);
if (strcmp(str, "sync-response") == ) {
ALOGI("-------");
ALOGI("Adding global ref on string '%s'", str);
dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false);
//dvmAbort();
}
free(str);
}
if (false && ((Object*)obj)->clazz == gDvm.classArrayByte) {
ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) obj;
if (arrayObj->length == /*&&
dvmReferenceTableEntries(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable) > 400*/)
{
ALOGI("Adding global ref on byte array %p (len=%d)",
arrayObj, arrayObj->length);
dvmDumpThread(dvmThreadSelf(), false);
}
} ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock); /*
* Throwing an exception on failure is problematic, because JNI code
* may not be expecting an exception, and things sort of cascade. We
* want to have a hard limit to catch leaks during debugging, but this
* otherwise needs to expand until memory is consumed. As a practical
* matter, if we have many thousands of global references, chances are
* we're either leaking global ref table entries or we're going to
* run out of space in the GC heap.
*/
jobject jobj = (jobject) gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.add(IRT_FIRST_SEGMENT, obj);
if (jobj == NULL) {
gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.dump("JNI global");
ALOGE("Failed adding to JNI global ref table (%zd entries)",
gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.capacity());
ReportJniError();
} LOGVV("GREF add %p (%s.%s)", obj,
dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod()->clazz->descriptor,
dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod()->name); return jobj;
} static jobject addWeakGlobalReference(Object* obj) {
if (obj == NULL) {
return NULL;
} ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock);
IndirectRefTable *table = &gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable;
jobject jobj = (jobject) table->add(IRT_FIRST_SEGMENT, obj);
if (jobj == NULL) {
gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable.dump("JNI weak global");
ALOGE("Failed adding to JNI weak global ref table (%zd entries)", table->capacity());
ReportJniError();
}
return jobj;
} static void deleteWeakGlobalReference(jobject jobj) {
if (jobj == NULL) {
return;
} ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock);
IndirectRefTable *table = &gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable;
if (!table->remove(IRT_FIRST_SEGMENT, jobj)) {
ALOGW("JNI: DeleteWeakGlobalRef(%p) failed to find entry", jobj);
}
} /*
* Remove a global reference. In most cases it's the entry most recently
* added, which makes this pretty quick.
*
* Thought: if it's not the most recent entry, just null it out. When we
* fill up, do a compaction pass before we expand the list.
*/
static void deleteGlobalReference(jobject jobj) {
if (jobj == NULL) {
return;
} ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock);
if (!gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.remove(IRT_FIRST_SEGMENT, jobj)) {
ALOGW("JNI: DeleteGlobalRef(%p) failed to find entry", jobj);
return;
}
} /*
* Objects don't currently move, so we just need to create a reference
* that will ensure the array object isn't collected.
*
* We use a separate reference table, which is part of the GC root set.
*/
static void pinPrimitiveArray(ArrayObject* arrayObj) {
if (arrayObj == NULL) {
return;
} ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock); if (!dvmAddToReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, (Object*)arrayObj)) {
dvmDumpReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, "JNI pinned array");
ALOGE("Failed adding to JNI pinned array ref table (%d entries)",
(int) dvmReferenceTableEntries(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable));
ReportJniError();
} /*
* The total number of pinned primitive arrays should be pretty small.
* A single array should not be pinned more than once or twice; any
* more than that is a strong indicator that a Release function is
* not being called.
*/
int count = ;
Object** ppObj = gDvm.jniPinRefTable.table;
while (ppObj < gDvm.jniPinRefTable.nextEntry) {
if (*ppObj++ == (Object*) arrayObj) {
count++;
}
} if (count > kPinComplainThreshold) {
ALOGW("JNI: pin count on array %p (%s) is now %d",
arrayObj, arrayObj->clazz->descriptor, count);
/* keep going */
}
} /*
* Un-pin the array object. If an object was pinned twice, it must be
* unpinned twice before it's free to move.
*/
static void unpinPrimitiveArray(ArrayObject* arrayObj) {
if (arrayObj == NULL) {
return;
} ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock);
if (!dvmRemoveFromReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable,
gDvm.jniPinRefTable.table, (Object*) arrayObj))
{
ALOGW("JNI: unpinPrimitiveArray(%p) failed to find entry (valid=%d)",
arrayObj, dvmIsHeapAddress((Object*) arrayObj));
return;
}
} /*
* Dump the contents of the JNI reference tables to the log file.
*
* We only dump the local refs associated with the current thread.
*/
void dvmDumpJniReferenceTables() {
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
self->jniLocalRefTable.dump("JNI local");
gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.dump("JNI global");
dvmDumpReferenceTable(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable, "JNI pinned array");
} void dvmDumpJniStats(DebugOutputTarget* target) {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "JNI: CheckJNI is %s", gDvmJni.useCheckJni ? "on" : "off");
if (gDvmJni.forceCopy) {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " (with forcecopy)");
}
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "; workarounds are %s", gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs ? "on" : "off"); dvmLockMutex(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock);
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "; pins=%d", dvmReferenceTableEntries(&gDvm.jniPinRefTable));
dvmUnlockMutex(&gDvm.jniPinRefLock); dvmLockMutex(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock);
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "; globals=%d", gDvm.jniGlobalRefTable.capacity());
dvmUnlockMutex(&gDvm.jniGlobalRefLock); dvmLockMutex(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock);
size_t weaks = gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefTable.capacity();
if (weaks > ) {
dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, " (plus %d weak)", weaks);
}
dvmUnlockMutex(&gDvm.jniWeakGlobalRefLock); dvmPrintDebugMessage(target, "\n\n");
} /*
* Verify that a reference passed in from native code is one that the
* code is allowed to have.
*
* It's okay for native code to pass us a reference that:
* - was passed in as an argument when invoked by native code (and hence
* is in the JNI local refs table)
* - was returned to it from JNI (and is now in the local refs table)
* - is present in the JNI global refs table
*
* Used by -Xcheck:jni and GetObjectRefType.
*/
jobjectRefType dvmGetJNIRefType(Thread* self, jobject jobj) {
/*
* IndirectRefKind is currently defined as an exact match of
* jobjectRefType, so this is easy. We have to decode it to determine
* if it's a valid reference and not merely valid-looking.
*/
assert(jobj != NULL); Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(self, jobj);
if (obj == reinterpret_cast<Object*>(jobj) && gDvmJni.workAroundAppJniBugs) {
// If we're handing out direct pointers, check whether 'jobj' is a direct reference
// to a local reference.
return self->jniLocalRefTable.contains(obj) ? JNILocalRefType : JNIInvalidRefType;
} else if (obj == kInvalidIndirectRefObject) {
return JNIInvalidRefType;
} else {
return (jobjectRefType) indirectRefKind(jobj);
}
} static void dumpMethods(Method* methods, size_t methodCount, const char* name) {
size_t i;
for (i = ; i < methodCount; ++i) {
Method* method = &methods[i];
if (strcmp(name, method->name) == ) {
char* desc = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&method->prototype);
ALOGE("Candidate: %s.%s:%s", method->clazz->descriptor, name, desc);
free(desc);
}
}
} static void dumpCandidateMethods(ClassObject* clazz, const char* methodName, const char* signature) {
ALOGE("ERROR: couldn't find native method");
ALOGE("Requested: %s.%s:%s", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature);
dumpMethods(clazz->virtualMethods, clazz->virtualMethodCount, methodName);
dumpMethods(clazz->directMethods, clazz->directMethodCount, methodName);
} static void throwNoSuchMethodError(ClassObject* c, const char* name, const char* sig, const char* kind) {
std::string msg(StringPrintf("no %s method \"%s.%s%s\"", kind, c->descriptor, name, sig));
dvmThrowNoSuchMethodError(msg.c_str());
} /*
* Register a method that uses JNI calling conventions.
*/
static bool dvmRegisterJNIMethod(ClassObject* clazz, const char* methodName,
const char* signature, void* fnPtr)
{
if (fnPtr == NULL) {
return false;
} // If a signature starts with a '!', we take that as a sign that the native code doesn't
// need the extra JNI arguments (the JNIEnv* and the jclass).
bool fastJni = false;
if (*signature == '!') {
fastJni = true;
++signature;
ALOGV("fast JNI method %s.%s:%s detected", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature);
} Method* method = dvmFindDirectMethodByDescriptor(clazz, methodName, signature);
if (method == NULL) {
method = dvmFindVirtualMethodByDescriptor(clazz, methodName, signature);
}
if (method == NULL) {
dumpCandidateMethods(clazz, methodName, signature);
throwNoSuchMethodError(clazz, methodName, signature, "static or non-static");
return false;
} if (!dvmIsNativeMethod(method)) {
ALOGW("Unable to register: not native: %s.%s:%s", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature);
throwNoSuchMethodError(clazz, methodName, signature, "native");
return false;
} if (fastJni) {
// In this case, we have extra constraints to check...
if (dvmIsSynchronizedMethod(method)) {
// Synchronization is usually provided by the JNI bridge,
// but we won't have one.
ALOGE("fast JNI method %s.%s:%s cannot be synchronized",
clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature);
return false;
}
if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) {
// There's no real reason for this constraint, but since we won't
// be supplying a JNIEnv* or a jobject 'this', you're effectively
// static anyway, so it seems clearer to say so.
ALOGE("fast JNI method %s.%s:%s cannot be non-static",
clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature);
return false;
}
} if (method->nativeFunc != dvmResolveNativeMethod) {
/* this is allowed, but unusual */
ALOGV("Note: %s.%s:%s was already registered", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature);
} method->fastJni = fastJni;
dvmUseJNIBridge(method, fnPtr); ALOGV("JNI-registered %s.%s:%s", clazz->descriptor, methodName, signature);
return true;
} static const char* builtInPrefixes[] = {
"Landroid/",
"Lcom/android/",
"Lcom/google/android/",
"Ldalvik/",
"Ljava/",
"Ljavax/",
"Llibcore/",
"Lorg/apache/harmony/",
}; static bool shouldTrace(Method* method) {
const char* className = method->clazz->descriptor;
// Return true if the -Xjnitrace setting implies we should trace 'method'.
if (gDvm.jniTrace && strstr(className, gDvm.jniTrace)) {
return true;
}
// Return true if we're trying to log all third-party JNI activity and 'method' doesn't look
// like part of Android.
if (gDvmJni.logThirdPartyJni) {
for (size_t i = ; i < NELEM(builtInPrefixes); ++i) {
if (strstr(className, builtInPrefixes[i]) == className) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
} /*
* Point "method->nativeFunc" at the JNI bridge, and overload "method->insns"
* to point at the actual function.
*/
void dvmUseJNIBridge(Method* method, void* func) {
method->shouldTrace = shouldTrace(method); // Does the method take any reference arguments?
method->noRef = true;
const char* cp = method->shorty;
while (*++cp != '\0') { // Pre-increment to skip return type.
if (*cp == 'L') {
method->noRef = false;
break;
}
} DalvikBridgeFunc bridge = gDvmJni.useCheckJni ? dvmCheckCallJNIMethod : dvmCallJNIMethod;
dvmSetNativeFunc(method, bridge, (const u2*) func);
} // TODO: rewrite this to share code with CheckJNI's tracing...
static void appendValue(char type, const JValue value, char* buf, size_t n, bool appendComma)
{
size_t len = strlen(buf);
if (len >= n - ) { // 32 should be longer than anything we could append.
buf[len - ] = '.';
buf[len - ] = '.';
buf[len - ] = '.';
return;
}
char* p = buf + len;
switch (type) {
case 'B':
if (value.b >= && value.b < ) {
sprintf(p, "%d", value.b);
} else {
sprintf(p, "%#x (%d)", value.b, value.b);
}
break;
case 'C':
if (value.c < 0x7f && value.c >= ' ') {
sprintf(p, "U+%x ('%c')", value.c, value.c);
} else {
sprintf(p, "U+%x", value.c);
}
break;
case 'D':
sprintf(p, "%g", value.d);
break;
case 'F':
sprintf(p, "%g", value.f);
break;
case 'I':
sprintf(p, "%d", value.i);
break;
case 'L':
sprintf(p, "%#x", value.i);
break;
case 'J':
sprintf(p, "%lld", value.j);
break;
case 'S':
sprintf(p, "%d", value.s);
break;
case 'V':
strcpy(p, "void");
break;
case 'Z':
strcpy(p, value.z ? "true" : "false");
break;
default:
sprintf(p, "unknown type '%c'", type);
break;
} if (appendComma) {
strcat(p, ", ");
}
} static void logNativeMethodEntry(const Method* method, const u4* args)
{
char thisString[] = { };
const u4* sp = args;
if (!dvmIsStaticMethod(method)) {
sprintf(thisString, "this=0x%08x ", *sp++);
} char argsString[]= { };
const char* desc = &method->shorty[];
while (*desc != '\0') {
char argType = *desc++;
JValue value;
if (argType == 'D' || argType == 'J') {
value.j = dvmGetArgLong(sp, );
sp += ;
} else {
value.i = *sp++;
}
appendValue(argType, value, argsString, sizeof(argsString),
*desc != '\0');
} std::string className(dvmHumanReadableDescriptor(method->clazz->descriptor));
char* signature = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&method->prototype);
ALOGI("-> %s %s%s %s(%s)", className.c_str(), method->name, signature, thisString, argsString);
free(signature);
} static void logNativeMethodExit(const Method* method, Thread* self, const JValue returnValue)
{
std::string className(dvmHumanReadableDescriptor(method->clazz->descriptor));
char* signature = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&method->prototype);
if (dvmCheckException(self)) {
Object* exception = dvmGetException(self);
std::string exceptionClassName(dvmHumanReadableDescriptor(exception->clazz->descriptor));
ALOGI("<- %s %s%s threw %s", className.c_str(),
method->name, signature, exceptionClassName.c_str());
} else {
char returnValueString[] = { };
char returnType = method->shorty[];
appendValue(returnType, returnValue, returnValueString, sizeof(returnValueString), false);
ALOGI("<- %s %s%s returned %s", className.c_str(),
method->name, signature, returnValueString);
}
free(signature);
} /*
* Get the method currently being executed by examining the interp stack.
*/
const Method* dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod() {
assert(dvmThreadSelf() != NULL); void* fp = dvmThreadSelf()->interpSave.curFrame;
const Method* meth = SAVEAREA_FROM_FP(fp)->method; assert(meth != NULL);
assert(dvmIsNativeMethod(meth));
return meth;
} /*
* Track a JNI MonitorEnter in the current thread.
*
* The goal is to be able to "implicitly" release all JNI-held monitors
* when the thread detaches.
*
* Monitors may be entered multiple times, so we add a new entry for each
* enter call. It would be more efficient to keep a counter. At present
* there's no real motivation to improve this however.
*/
static void trackMonitorEnter(Thread* self, Object* obj) {
static const int kInitialSize = ;
ReferenceTable* refTable = &self->jniMonitorRefTable; /* init table on first use */
if (refTable->table == NULL) {
assert(refTable->maxEntries == ); if (!dvmInitReferenceTable(refTable, kInitialSize, INT_MAX)) {
ALOGE("Unable to initialize monitor tracking table");
ReportJniError();
}
} if (!dvmAddToReferenceTable(refTable, obj)) {
/* ran out of memory? could throw exception instead */
ALOGE("Unable to add entry to monitor tracking table");
ReportJniError();
} else {
LOGVV("--- added monitor %p", obj);
}
} /*
* Track a JNI MonitorExit in the current thread.
*/
static void trackMonitorExit(Thread* self, Object* obj) {
ReferenceTable* pRefTable = &self->jniMonitorRefTable; if (!dvmRemoveFromReferenceTable(pRefTable, pRefTable->table, obj)) {
ALOGE("JNI monitor %p not found in tracking list", obj);
/* keep going? */
} else {
LOGVV("--- removed monitor %p", obj);
}
} /*
* Release all monitors held by the jniMonitorRefTable list.
*/
void dvmReleaseJniMonitors(Thread* self) {
ReferenceTable* pRefTable = &self->jniMonitorRefTable;
Object** top = pRefTable->table; if (top == NULL) {
return;
}
Object** ptr = pRefTable->nextEntry;
while (--ptr >= top) {
if (!dvmUnlockObject(self, *ptr)) {
ALOGW("Unable to unlock monitor %p at thread detach", *ptr);
} else {
LOGVV("--- detach-releasing monitor %p", *ptr);
}
} /* zap it */
pRefTable->nextEntry = pRefTable->table;
} /*
* Determine if the specified class can be instantiated from JNI. This
* is used by AllocObject / NewObject, which are documented as throwing
* an exception for abstract and interface classes, and not accepting
* array classes. We also want to reject attempts to create new Class
* objects, since only DefineClass should do that.
*/
static bool canAllocClass(ClassObject* clazz) {
if (dvmIsAbstractClass(clazz) || dvmIsInterfaceClass(clazz)) {
/* JNI spec defines what this throws */
dvmThrowInstantiationException(clazz, "abstract class or interface");
return false;
} else if (dvmIsArrayClass(clazz) || dvmIsTheClassClass(clazz)) {
/* spec says "must not" for arrays, ignores Class */
dvmThrowInstantiationException(clazz, "wrong JNI function");
return false;
}
return true;
} /*
* ===========================================================================
* JNI call bridge
* ===========================================================================
*/ /*
* The functions here form a bridge between interpreted code and JNI native
* functions. The basic task is to convert an array of primitives and
* references into C-style function arguments. This is architecture-specific
* and usually requires help from assembly code.
*
* The bridge takes four arguments: the array of parameters, a place to
* store the function result (if any), the method to call, and a pointer
* to the current thread.
*
* These functions aren't called directly from elsewhere in the VM.
* A pointer in the Method struct points to one of these, and when a native
* method is invoked the interpreter jumps to it.
*
* (The "internal native" methods are invoked the same way, but instead
* of calling through a bridge, the target method is called directly.)
*
* The "args" array should not be modified, but we do so anyway for
* performance reasons. We know that it points to the "outs" area on
* the current method's interpreted stack. This area is ignored by the
* precise GC, because there is no register map for a native method (for
* an interpreted method the args would be listed in the argument set).
* We know all of the values exist elsewhere on the interpreted stack,
* because the method call setup copies them right before making the call,
* so we don't have to worry about concealing stuff from the GC.
*
* If we don't want to modify "args", we either have to create a local
* copy and modify it before calling dvmPlatformInvoke, or we have to do
* the local reference replacement within dvmPlatformInvoke. The latter
* has some performance advantages, though if we can inline the local
* reference adds we may win when there's a lot of reference args (unless
* we want to code up some local ref table manipulation in assembly.
*/ /*
* If necessary, convert the value in pResult from a local/global reference
* to an object pointer.
*
* If the returned reference is invalid, kInvalidIndirectRefObject will
* be returned in pResult.
*/
static inline void convertReferenceResult(JNIEnv* env, JValue* pResult,
const Method* method, Thread* self)
{
if (method->shorty[] == 'L' && !dvmCheckException(self) && pResult->l != NULL) {
pResult->l = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(self, (jobject) pResult->l);
}
} /*
* General form, handles all cases.
*/
void dvmCallJNIMethod(const u4* args, JValue* pResult, const Method* method, Thread* self) {
u4* modArgs = (u4*) args;
jclass staticMethodClass = NULL; u4 accessFlags = method->accessFlags;
bool isSynchronized = (accessFlags & ACC_SYNCHRONIZED) != ; //ALOGI("JNI calling %p (%s.%s:%s):", method->insns,
// method->clazz->descriptor, method->name, method->shorty); /*
* Walk the argument list, creating local references for appropriate
* arguments.
*/
int idx = ;
Object* lockObj;
if ((accessFlags & ACC_STATIC) != ) {
lockObj = (Object*) method->clazz;
/* add the class object we pass in */
staticMethodClass = (jclass) addLocalReference(self, (Object*) method->clazz);
} else {
lockObj = (Object*) args[];
/* add "this" */
modArgs[idx++] = (u4) addLocalReference(self, (Object*) modArgs[]);
} if (!method->noRef) {
const char* shorty = &method->shorty[]; /* skip return type */
while (*shorty != '\0') {
switch (*shorty++) {
case 'L':
//ALOGI(" local %d: 0x%08x", idx, modArgs[idx]);
if (modArgs[idx] != ) {
modArgs[idx] = (u4) addLocalReference(self, (Object*) modArgs[idx]);
}
break;
case 'D':
case 'J':
idx++;
break;
default:
/* Z B C S I -- do nothing */
break;
}
idx++;
}
} if (UNLIKELY(method->shouldTrace)) {
logNativeMethodEntry(method, args);
}
if (UNLIKELY(isSynchronized)) {
dvmLockObject(self, lockObj);
} ThreadStatus oldStatus = dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_NATIVE); ANDROID_MEMBAR_FULL(); /* guarantee ordering on method->insns */
assert(method->insns != NULL); JNIEnv* env = self->jniEnv;
COMPUTE_STACK_SUM(self);
dvmPlatformInvoke(env,
(ClassObject*) staticMethodClass,
method->jniArgInfo, method->insSize, modArgs, method->shorty,
(void*) method->insns, pResult);
CHECK_STACK_SUM(self); dvmChangeStatus(self, oldStatus); convertReferenceResult(env, pResult, method, self); if (UNLIKELY(isSynchronized)) {
dvmUnlockObject(self, lockObj);
}
if (UNLIKELY(method->shouldTrace)) {
logNativeMethodExit(method, self, *pResult);
}
} /*
* ===========================================================================
* JNI implementation
* ===========================================================================
*/ /*
* Return the version of the native method interface.
*/
static jint GetVersion(JNIEnv* env) {
/*
* There is absolutely no need to toggle the mode for correct behavior.
* However, it does provide native code with a simple "suspend self
* if necessary" call.
*/
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
return JNI_VERSION_1_6;
} /*
* Create a new class from a bag of bytes.
*
* This is not currently supported within Dalvik.
*/
static jclass DefineClass(JNIEnv* env, const char *name, jobject loader,
const jbyte* buf, jsize bufLen)
{
UNUSED_PARAMETER(name);
UNUSED_PARAMETER(loader);
UNUSED_PARAMETER(buf);
UNUSED_PARAMETER(bufLen); ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ALOGW("JNI DefineClass is not supported");
return NULL;
} /*
* Find a class by name.
*
* We have to use the "no init" version of FindClass here, because we might
* be getting the class prior to registering native methods that will be
* used in <clinit>.
*
* We need to get the class loader associated with the current native
* method. If there is no native method, e.g. we're calling this from native
* code right after creating the VM, the spec says we need to use the class
* loader returned by "ClassLoader.getBaseClassLoader". There is no such
* method, but it's likely they meant ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader.
* We can't get that until after the VM has initialized though.
*/
static jclass FindClass(JNIEnv* env, const char* name) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); const Method* thisMethod = dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod();
assert(thisMethod != NULL); Object* loader;
Object* trackedLoader = NULL;
if (ts.self()->classLoaderOverride != NULL) {
/* hack for JNI_OnLoad */
assert(strcmp(thisMethod->name, "nativeLoad") == );
loader = ts.self()->classLoaderOverride;
} else if (thisMethod == gDvm.methDalvikSystemNativeStart_main ||
thisMethod == gDvm.methDalvikSystemNativeStart_run) {
/* start point of invocation interface */
if (!gDvm.initializing) {
loader = trackedLoader = dvmGetSystemClassLoader();
} else {
loader = NULL;
}
} else {
loader = thisMethod->clazz->classLoader;
} char* descriptor = dvmNameToDescriptor(name);
if (descriptor == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
ClassObject* clazz = dvmFindClassNoInit(descriptor, loader);
free(descriptor); jclass jclazz = (jclass) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) clazz);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc(trackedLoader, ts.self());
return jclazz;
} /*
* Return the superclass of a class.
*/
static jclass GetSuperclass(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz);
return (jclass) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*)clazz->super);
} /*
* Determine whether an object of clazz1 can be safely cast to clazz2.
*
* Like IsInstanceOf, but with a pair of class objects instead of obj+class.
*/
static jboolean IsAssignableFrom(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz1, jclass jclazz2) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ClassObject* clazz1 = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz1);
ClassObject* clazz2 = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz2);
return dvmInstanceof(clazz1, clazz2);
} /*
* Given a java.lang.reflect.Method or .Constructor, return a methodID.
*/
static jmethodID FromReflectedMethod(JNIEnv* env, jobject jmethod) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* method = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jmethod);
return (jmethodID) dvmGetMethodFromReflectObj(method);
} /*
* Given a java.lang.reflect.Field, return a fieldID.
*/
static jfieldID FromReflectedField(JNIEnv* env, jobject jfield) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* field = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jfield);
return (jfieldID) dvmGetFieldFromReflectObj(field);
} /*
* Convert a methodID to a java.lang.reflect.Method or .Constructor.
*
* (The "isStatic" field does not appear in the spec.)
*
* Throws OutOfMemory and returns NULL on failure.
*/
static jobject ToReflectedMethod(JNIEnv* env, jclass jcls, jmethodID methodID, jboolean isStatic) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jcls);
Object* obj = dvmCreateReflectObjForMethod(clazz, (Method*) methodID);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc(obj, NULL);
return addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj);
} /*
* Convert a fieldID to a java.lang.reflect.Field.
*
* (The "isStatic" field does not appear in the spec.)
*
* Throws OutOfMemory and returns NULL on failure.
*/
static jobject ToReflectedField(JNIEnv* env, jclass jcls, jfieldID fieldID, jboolean isStatic) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jcls);
Object* obj = dvmCreateReflectObjForField(clazz, (Field*) fieldID);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc(obj, NULL);
return addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj);
} /*
* Take this exception and throw it.
*/
static jint Throw(JNIEnv* env, jthrowable jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
if (jobj != NULL) {
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj);
dvmSetException(ts.self(), obj);
return JNI_OK;
}
return JNI_ERR;
} /*
* Constructs an exception object from the specified class with the message
* specified by "message", and throws it.
*/
static jint ThrowNew(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* message) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz);
dvmThrowException(clazz, message);
// TODO: should return failure if this didn't work (e.g. OOM)
return JNI_OK;
} /*
* If an exception is being thrown, return the exception object. Otherwise,
* return NULL.
*
* TODO: if there is no pending exception, we should be able to skip the
* enter/exit checks. If we find one, we need to enter and then re-fetch
* the exception (in case it got moved by a compacting GC).
*/
static jthrowable ExceptionOccurred(JNIEnv* env) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* exception = dvmGetException(ts.self());
jthrowable localException = (jthrowable) addLocalReference(ts.self(), exception);
if (localException == NULL && exception != NULL) {
/*
* We were unable to add a new local reference, and threw a new
* exception. We can't return "exception", because it's not a
* local reference. So we have to return NULL, indicating that
* there was no exception, even though it's pretty much raining
* exceptions in here.
*/
ALOGW("JNI WARNING: addLocal/exception combo");
}
return localException;
} /*
* Print an exception and stack trace to stderr.
*/
static void ExceptionDescribe(JNIEnv* env) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* exception = dvmGetException(ts.self());
if (exception != NULL) {
dvmPrintExceptionStackTrace();
} else {
ALOGI("Odd: ExceptionDescribe called, but no exception pending");
}
} /*
* Clear the exception currently being thrown.
*
* TODO: we should be able to skip the enter/exit stuff.
*/
static void ExceptionClear(JNIEnv* env) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
dvmClearException(ts.self());
} /*
* Kill the VM. This function does not return.
*/
static void FatalError(JNIEnv* env, const char* msg) {
//dvmChangeStatus(NULL, THREAD_RUNNING);
ALOGE("JNI posting fatal error: %s", msg);
ReportJniError();
} /*
* Push a new JNI frame on the stack, with a new set of locals.
*
* The new frame must have the same method pointer. (If for no other
* reason than FindClass needs it to get the appropriate class loader.)
*/
static jint PushLocalFrame(JNIEnv* env, jint capacity) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
if (!ensureLocalCapacity(ts.self(), capacity) ||
!dvmPushLocalFrame(ts.self(), dvmGetCurrentJNIMethod()))
{
/* yes, OutOfMemoryError, not StackOverflowError */
dvmClearException(ts.self());
dvmThrowOutOfMemoryError("out of stack in JNI PushLocalFrame");
return JNI_ERR;
}
return JNI_OK;
} /*
* Pop the local frame off. If "jresult" is not null, add it as a
* local reference on the now-current frame.
*/
static jobject PopLocalFrame(JNIEnv* env, jobject jresult) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* result = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jresult);
if (!dvmPopLocalFrame(ts.self())) {
ALOGW("JNI WARNING: too many PopLocalFrame calls");
dvmClearException(ts.self());
dvmThrowRuntimeException("too many PopLocalFrame calls");
}
return addLocalReference(ts.self(), result);
} /*
* Add a reference to the global list.
*/
static jobject NewGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj);
return addGlobalReference(obj);
} /*
* Delete a reference from the global list.
*/
static void DeleteGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jglobalRef) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
deleteGlobalReference(jglobalRef);
} /*
* Add a reference to the local list.
*/
static jobject NewLocalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj);
return addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj);
} /*
* Delete a reference from the local list.
*/
static void DeleteLocalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jlocalRef) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
deleteLocalReference(ts.self(), jlocalRef);
} /*
* Ensure that the local references table can hold at least this many
* references.
*/
static jint EnsureLocalCapacity(JNIEnv* env, jint capacity) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
bool okay = ensureLocalCapacity(ts.self(), capacity);
if (!okay) {
dvmThrowOutOfMemoryError("can't ensure local reference capacity");
}
return okay ? : -;
} /*
* Determine whether two Object references refer to the same underlying object.
*/
static jboolean IsSameObject(JNIEnv* env, jobject jref1, jobject jref2) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* obj1 = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jref1);
Object* obj2 = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jref2);
return (obj1 == obj2);
} /*
* Allocate a new object without invoking any constructors.
*/
static jobject AllocObject(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz);
if (!canAllocClass(clazz) ||
(!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)))
{
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
return NULL;
} Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(clazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK);
return addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj);
} /*
* Allocate a new object and invoke the supplied constructor.
*/
static jobject NewObject(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, ...) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); if (!canAllocClass(clazz) || (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz))) {
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
return NULL;
} Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(clazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK);
jobject result = addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj);
if (newObj != NULL) {
JValue unused;
va_list args;
va_start(args, methodID);
dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), (Method*) methodID, newObj, true, &unused, args);
va_end(args);
}
return result;
} static jobject NewObjectV(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, va_list args) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); if (!canAllocClass(clazz) || (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz))) {
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
return NULL;
} Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(clazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK);
jobject result = addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj);
if (newObj != NULL) {
JValue unused;
dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), (Method*) methodID, newObj, true, &unused, args);
}
return result;
} static jobject NewObjectA(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); if (!canAllocClass(clazz) || (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz))) {
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
return NULL;
} Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(clazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK);
jobject result = addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj);
if (newObj != NULL) {
JValue unused;
dvmCallMethodA(ts.self(), (Method*) methodID, newObj, true, &unused, args);
}
return result;
} /*
* Returns the class of an object.
*
* JNI spec says: obj must not be NULL.
*/
static jclass GetObjectClass(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); assert(jobj != NULL); Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj);
return (jclass) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) obj->clazz);
} /*
* Determine whether "obj" is an instance of "clazz".
*/
static jboolean IsInstanceOf(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, jclass jclazz) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); assert(jclazz != NULL);
if (jobj == NULL) {
return true;
} Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj);
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz);
return dvmInstanceof(obj->clazz, clazz);
} /*
* Get a method ID for an instance method.
*
* While Dalvik bytecode has distinct instructions for virtual, super,
* static, direct, and interface method invocation, JNI only provides
* two functions for acquiring a method ID. This call handles everything
* but static methods.
*
* JNI defines <init> as an instance method, but Dalvik considers it a
* "direct" method, so we have to special-case it here.
*
* Dalvik also puts all private methods into the "direct" list, so we
* really need to just search both lists.
*/
static jmethodID GetMethodID(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* name, const char* sig) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz);
if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)) {
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
} else if (dvmIsInterfaceClass(clazz)) {
Method* meth = dvmFindInterfaceMethodHierByDescriptor(clazz, name, sig);
if (meth == NULL) {
dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchMethodError,
"no method with name='%s' signature='%s' in interface %s",
name, sig, clazz->descriptor);
}
return (jmethodID) meth;
}
Method* meth = dvmFindVirtualMethodHierByDescriptor(clazz, name, sig);
if (meth == NULL) {
/* search private methods and constructors; non-hierarchical */
meth = dvmFindDirectMethodByDescriptor(clazz, name, sig);
}
if (meth != NULL && dvmIsStaticMethod(meth)) {
IF_ALOGD() {
char* desc = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&meth->prototype);
ALOGD("GetMethodID: not returning static method %s.%s %s",
clazz->descriptor, meth->name, desc);
free(desc);
}
meth = NULL;
}
if (meth == NULL) {
dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchMethodError,
"no method with name='%s' signature='%s' in class %s",
name, sig, clazz->descriptor);
} else {
/*
* The method's class may not be the same as clazz, but if
* it isn't this must be a virtual method and the class must
* be a superclass (and, hence, already initialized).
*/
assert(dvmIsClassInitialized(meth->clazz) || dvmIsClassInitializing(meth->clazz));
}
return (jmethodID) meth;
} /*
* Get a field ID (instance fields).
*/
static jfieldID GetFieldID(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* name, const char* sig) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)) {
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
return NULL;
} jfieldID id = (jfieldID) dvmFindInstanceFieldHier(clazz, name, sig);
if (id == NULL) {
dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchFieldError,
"no field with name='%s' signature='%s' in class %s",
name, sig, clazz->descriptor);
}
return id;
} /*
* Get the method ID for a static method in a class.
*/
static jmethodID GetStaticMethodID(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* name, const char* sig) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz);
if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)) {
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
return NULL;
} Method* meth = dvmFindDirectMethodHierByDescriptor(clazz, name, sig); /* make sure it's static, not virtual+private */
if (meth != NULL && !dvmIsStaticMethod(meth)) {
IF_ALOGD() {
char* desc = dexProtoCopyMethodDescriptor(&meth->prototype);
ALOGD("GetStaticMethodID: not returning nonstatic method %s.%s %s",
clazz->descriptor, meth->name, desc);
free(desc);
}
meth = NULL;
} jmethodID id = (jmethodID) meth;
if (id == NULL) {
dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchMethodError,
"no static method with name='%s' signature='%s' in class %s",
name, sig, clazz->descriptor);
}
return id;
} /*
* Get a field ID (static fields).
*/
static jfieldID GetStaticFieldID(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, const char* name, const char* sig) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz);
if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(clazz) && !dvmInitClass(clazz)) {
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
return NULL;
} jfieldID id = (jfieldID) dvmFindStaticFieldHier(clazz, name, sig);
if (id == NULL) {
dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exNoSuchFieldError,
"no static field with name='%s' signature='%s' in class %s",
name, sig, clazz->descriptor);
}
return id;
} /*
* Get a static field.
*
* If we get an object reference, add it to the local refs list.
*/
#define GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(_ctype, _jname, _isref) \
static _ctype GetStatic##_jname##Field(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, \
jfieldID fieldID) \
{ \
UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
StaticField* sfield = (StaticField*) fieldID; \
_ctype value; \
if (dvmIsVolatileField(sfield)) { \
if (_isref) { /* only when _ctype==jobject */ \
Object* obj = dvmGetStaticFieldObjectVolatile(sfield); \
value = (_ctype)(u4)addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj); \
} else { \
value = (_ctype) dvmGetStaticField##_jname##Volatile(sfield);\
} \
} else { \
if (_isref) { \
Object* obj = dvmGetStaticFieldObject(sfield); \
value = (_ctype)(u4)addLocalReference(ts.self(), obj); \
} else { \
value = (_ctype) dvmGetStaticField##_jname(sfield); \
} \
} \
return value; \
}
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jobject, Object, true);
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jboolean, Boolean, false);
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jbyte, Byte, false);
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jchar, Char, false);
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jshort, Short, false);
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jint, Int, false);
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jlong, Long, false);
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jfloat, Float, false);
GET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jdouble, Double, false); /*
* Set a static field.
*/
#define SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(_ctype, _ctype2, _jname, _isref) \
static void SetStatic##_jname##Field(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, \
jfieldID fieldID, _ctype value) \
{ \
UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
StaticField* sfield = (StaticField*) fieldID; \
if (dvmIsVolatileField(sfield)) { \
if (_isref) { /* only when _ctype==jobject */ \
Object* valObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), (jobject)(u4)value); \
dvmSetStaticFieldObjectVolatile(sfield, valObj); \
} else { \
dvmSetStaticField##_jname##Volatile(sfield, (_ctype2)value);\
} \
} else { \
if (_isref) { \
Object* valObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), (jobject)(u4)value); \
dvmSetStaticFieldObject(sfield, valObj); \
} else { \
dvmSetStaticField##_jname(sfield, (_ctype2)value); \
} \
} \
}
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jobject, Object*, Object, true);
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jboolean, bool, Boolean, false);
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jbyte, s1, Byte, false);
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jchar, u2, Char, false);
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jshort, s2, Short, false);
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jint, s4, Int, false);
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jlong, s8, Long, false);
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jfloat, float, Float, false);
SET_STATIC_TYPE_FIELD(jdouble, double, Double, false); /*
* Get an instance field.
*
* If we get an object reference, add it to the local refs list.
*/
#define GET_TYPE_FIELD(_ctype, _jname, _isref) \
static _ctype Get##_jname##Field(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, \
jfieldID fieldID) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); \
InstField* field = (InstField*) fieldID; \
_ctype value; \
if (dvmIsVolatileField(field)) { \
if (_isref) { /* only when _ctype==jobject */ \
Object* valObj = \
dvmGetFieldObjectVolatile(obj, field->byteOffset); \
value = (_ctype)(u4)addLocalReference(ts.self(), valObj); \
} else { \
value = (_ctype) \
dvmGetField##_jname##Volatile(obj, field->byteOffset); \
} \
} else { \
if (_isref) { \
Object* valObj = dvmGetFieldObject(obj, field->byteOffset); \
value = (_ctype)(u4)addLocalReference(ts.self(), valObj); \
} else { \
value = (_ctype) dvmGetField##_jname(obj, field->byteOffset);\
} \
} \
return value; \
}
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jobject, Object, true);
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jboolean, Boolean, false);
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jbyte, Byte, false);
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jchar, Char, false);
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jshort, Short, false);
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jint, Int, false);
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jlong, Long, false);
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jfloat, Float, false);
GET_TYPE_FIELD(jdouble, Double, false); /*
* Set an instance field.
*/
#define SET_TYPE_FIELD(_ctype, _ctype2, _jname, _isref) \
static void Set##_jname##Field(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, \
jfieldID fieldID, _ctype value) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); \
InstField* field = (InstField*) fieldID; \
if (dvmIsVolatileField(field)) { \
if (_isref) { /* only when _ctype==jobject */ \
Object* valObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), (jobject)(u4)value); \
dvmSetFieldObjectVolatile(obj, field->byteOffset, valObj); \
} else { \
dvmSetField##_jname##Volatile(obj, \
field->byteOffset, (_ctype2)value); \
} \
} else { \
if (_isref) { \
Object* valObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), (jobject)(u4)value); \
dvmSetFieldObject(obj, field->byteOffset, valObj); \
} else { \
dvmSetField##_jname(obj, \
field->byteOffset, (_ctype2)value); \
} \
} \
}
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jobject, Object*, Object, true);
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jboolean, bool, Boolean, false);
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jbyte, s1, Byte, false);
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jchar, u2, Char, false);
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jshort, s2, Short, false);
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jint, s4, Int, false);
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jlong, s8, Long, false);
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jfloat, float, Float, false);
SET_TYPE_FIELD(jdouble, double, Double, false); /*
* Make a virtual method call.
*
* Three versions (..., va_list, jvalue[]) for each return type. If we're
* returning an Object, we have to add it to the local references table.
*/
#define CALL_VIRTUAL(_ctype, _jname, _retfail, _retok, _isref) \
static _ctype Call##_jname##Method(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, \
jmethodID methodID, ...) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); \
const Method* meth; \
va_list args; \
JValue result; \
meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(obj->clazz, (Method*)methodID); \
if (meth == NULL) { \
return _retfail; \
} \
va_start(args, methodID); \
dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); \
va_end(args); \
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
return _retok; \
} \
static _ctype Call##_jname##MethodV(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, \
jmethodID methodID, va_list args) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); \
const Method* meth; \
JValue result; \
meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(obj->clazz, (Method*)methodID); \
if (meth == NULL) { \
return _retfail; \
} \
dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); \
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
return _retok; \
} \
static _ctype Call##_jname##MethodA(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, \
jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); \
const Method* meth; \
JValue result; \
meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(obj->clazz, (Method*)methodID); \
if (meth == NULL) { \
return _retfail; \
} \
dvmCallMethodA(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); \
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
return _retok; \
}
CALL_VIRTUAL(jobject, Object, NULL, (jobject) result.l, true);
CALL_VIRTUAL(jboolean, Boolean, , result.z, false);
CALL_VIRTUAL(jbyte, Byte, , result.b, false);
CALL_VIRTUAL(jchar, Char, , result.c, false);
CALL_VIRTUAL(jshort, Short, , result.s, false);
CALL_VIRTUAL(jint, Int, , result.i, false);
CALL_VIRTUAL(jlong, Long, , result.j, false);
CALL_VIRTUAL(jfloat, Float, 0.0f, result.f, false);
CALL_VIRTUAL(jdouble, Double, 0.0, result.d, false);
CALL_VIRTUAL(void, Void, , , false); /*
* Make a "non-virtual" method call. We're still calling a virtual method,
* but this time we're not doing an indirection through the object's vtable.
* The "clazz" parameter defines which implementation of a method we want.
*
* Three versions (..., va_list, jvalue[]) for each return type.
*/
#define CALL_NONVIRTUAL(_ctype, _jname, _retfail, _retok, _isref) \
static _ctype CallNonvirtual##_jname##Method(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj, \
jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, ...) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); \
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); \
const Method* meth; \
va_list args; \
JValue result; \
meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(clazz, (Method*)methodID); \
if (meth == NULL) { \
return _retfail; \
} \
va_start(args, methodID); \
dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); \
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
va_end(args); \
return _retok; \
} \
static _ctype CallNonvirtual##_jname##MethodV(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj,\
jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, va_list args) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); \
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); \
const Method* meth; \
JValue result; \
meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(clazz, (Method*)methodID); \
if (meth == NULL) { \
return _retfail; \
} \
dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); \
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
return _retok; \
} \
static _ctype CallNonvirtual##_jname##MethodA(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj,\
jclass jclazz, jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); \
ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); \
const Method* meth; \
JValue result; \
meth = dvmGetVirtualizedMethod(clazz, (Method*)methodID); \
if (meth == NULL) { \
return _retfail; \
} \
dvmCallMethodA(ts.self(), meth, obj, true, &result, args); \
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
return _retok; \
}
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jobject, Object, NULL, (jobject) result.l, true);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jboolean, Boolean, , result.z, false);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jbyte, Byte, , result.b, false);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jchar, Char, , result.c, false);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jshort, Short, , result.s, false);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jint, Int, , result.i, false);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jlong, Long, , result.j, false);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jfloat, Float, 0.0f, result.f, false);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(jdouble, Double, 0.0, result.d, false);
CALL_NONVIRTUAL(void, Void, , , false); /*
* Call a static method.
*/
#define CALL_STATIC(_ctype, _jname, _retfail, _retok, _isref) \
static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##Method(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, \
jmethodID methodID, ...) \
{ \
UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
JValue result; \
va_list args; \
va_start(args, methodID); \
dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);\
va_end(args); \
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
return _retok; \
} \
static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##MethodV(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, \
jmethodID methodID, va_list args) \
{ \
UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
JValue result; \
dvmCallMethodV(ts.self(), (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);\
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
return _retok; \
} \
static _ctype CallStatic##_jname##MethodA(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz, \
jmethodID methodID, jvalue* args) \
{ \
UNUSED_PARAMETER(jclazz); \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
JValue result; \
dvmCallMethodA(ts.self(), (Method*)methodID, NULL, true, &result, args);\
if (_isref && !dvmCheckException(ts.self())) \
result.l = (Object*)addLocalReference(ts.self(), result.l); \
return _retok; \
}
CALL_STATIC(jobject, Object, NULL, (jobject) result.l, true);
CALL_STATIC(jboolean, Boolean, , result.z, false);
CALL_STATIC(jbyte, Byte, , result.b, false);
CALL_STATIC(jchar, Char, , result.c, false);
CALL_STATIC(jshort, Short, , result.s, false);
CALL_STATIC(jint, Int, , result.i, false);
CALL_STATIC(jlong, Long, , result.j, false);
CALL_STATIC(jfloat, Float, 0.0f, result.f, false);
CALL_STATIC(jdouble, Double, 0.0, result.d, false);
CALL_STATIC(void, Void, , , false); /*
* Create a new String from Unicode data.
*
* If "len" is zero, we will return an empty string even if "unicodeChars"
* is NULL. (The JNI spec is vague here.)
*/
static jstring NewString(JNIEnv* env, const jchar* unicodeChars, jsize len) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
StringObject* jstr = dvmCreateStringFromUnicode(unicodeChars, len);
if (jstr == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) jstr, NULL);
return (jstring) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) jstr);
} /*
* Return the length of a String in Unicode character units.
*/
static jsize GetStringLength(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
return strObj->length();
} /*
* Get a string's character data.
*
* The result is guaranteed to be valid until ReleaseStringChars is
* called, which means we have to pin it or return a copy.
*/
static const jchar* GetStringChars(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jboolean* isCopy) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
ArrayObject* strChars = strObj->array(); pinPrimitiveArray(strChars); const u2* data = strObj->chars();
if (isCopy != NULL) {
*isCopy = JNI_FALSE;
}
return (jchar*) data;
} /*
* Release our grip on some characters from a string.
*/
static void ReleaseStringChars(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, const jchar* chars) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
ArrayObject* strChars = strObj->array();
unpinPrimitiveArray(strChars);
} /*
* Create a new java.lang.String object from chars in modified UTF-8 form.
*
* The spec doesn't say how to handle a NULL string. Popular desktop VMs
* accept it and return a NULL pointer in response.
*/
static jstring NewStringUTF(JNIEnv* env, const char* bytes) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
if (bytes == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
/* note newStr could come back NULL on OOM */
StringObject* newStr = dvmCreateStringFromCstr(bytes);
jstring result = (jstring) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) newStr);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*)newStr, NULL);
return result;
} /*
* Return the length in bytes of the modified UTF-8 form of the string.
*/
static jsize GetStringUTFLength(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
if (strObj == NULL) {
return ; // Should we throw something or assert?
}
return strObj->utfLength();
} /*
* Convert "string" to modified UTF-8 and return a pointer. The returned
* value must be released with ReleaseStringUTFChars.
*
* According to the JNI reference, "Returns a pointer to a UTF-8 string,
* or NULL if the operation fails. Returns NULL if and only if an invocation
* of this function has thrown an exception."
*
* The behavior here currently follows that of other open-source VMs, which
* quietly return NULL if "string" is NULL. We should consider throwing an
* NPE. (The CheckJNI code blows up if you try to pass in a NULL string,
* which should catch this sort of thing during development.) Certain other
* VMs will crash with a segmentation fault.
*/
static const char* GetStringUTFChars(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jboolean* isCopy) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
if (jstr == NULL) {
/* this shouldn't happen; throw NPE? */
return NULL;
}
if (isCopy != NULL) {
*isCopy = JNI_TRUE;
}
StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
char* newStr = dvmCreateCstrFromString(strObj);
if (newStr == NULL) {
/* assume memory failure */
dvmThrowOutOfMemoryError("native heap string alloc failed");
}
return newStr;
} /*
* Release a string created by GetStringUTFChars().
*/
static void ReleaseStringUTFChars(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, const char* utf) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
free((char*) utf);
} /*
* Return the capacity of the array.
*/
static jsize GetArrayLength(JNIEnv* env, jarray jarr) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ArrayObject* arrObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr);
return arrObj->length;
} /*
* Construct a new array that holds objects from class "elementClass".
*/
static jobjectArray NewObjectArray(JNIEnv* env, jsize length,
jclass jelementClass, jobject jinitialElement)
{
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); if (jelementClass == NULL) {
dvmThrowNullPointerException("JNI NewObjectArray elementClass == NULL");
return NULL;
} ClassObject* elemClassObj = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jelementClass);
ClassObject* arrayClass = dvmFindArrayClassForElement(elemClassObj);
ArrayObject* newObj = dvmAllocArrayByClass(arrayClass, length, ALLOC_DEFAULT);
if (newObj == NULL) {
assert(dvmCheckException(ts.self()));
return NULL;
}
jobjectArray newArray = (jobjectArray) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) newObj);
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) newObj, NULL); /*
* Initialize the array.
*/
if (jinitialElement != NULL) {
Object* initialElement = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jinitialElement);
Object** arrayData = (Object**) (void*) newObj->contents;
for (jsize i = ; i < length; ++i) {
arrayData[i] = initialElement;
}
} return newArray;
} static bool checkArrayElementBounds(ArrayObject* arrayObj, jsize index) {
assert(arrayObj != NULL);
if (index < || index >= (int) arrayObj->length) {
dvmThrowArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(arrayObj->length, index);
return false;
}
return true;
} /*
* Get one element of an Object array.
*
* Add the object to the local references table in case the array goes away.
*/
static jobject GetObjectArrayElement(JNIEnv* env, jobjectArray jarr, jsize index) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr);
if (!checkArrayElementBounds(arrayObj, index)) {
return NULL;
} Object* value = ((Object**) (void*) arrayObj->contents)[index];
return addLocalReference(ts.self(), value);
} /*
* Set one element of an Object array.
*/
static void SetObjectArrayElement(JNIEnv* env, jobjectArray jarr, jsize index, jobject jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr);
if (!checkArrayElementBounds(arrayObj, index)) {
return;
} Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj); if (obj != NULL && !dvmCanPutArrayElement(obj->clazz, arrayObj->clazz)) {
ALOGV("Can't put a '%s'(%p) into array type='%s'(%p)",
obj->clazz->descriptor, obj,
arrayObj->clazz->descriptor, arrayObj);
dvmThrowArrayStoreExceptionIncompatibleElement(obj->clazz, arrayObj->clazz);
return;
} //ALOGV("JNI: set element %d in array %p to %p", index, array, value); dvmSetObjectArrayElement(arrayObj, index, obj);
} /*
* Create a new array of primitive elements.
*/
#define NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(_artype, _jname, _typechar) \
static _artype New##_jname##Array(JNIEnv* env, jsize length) { \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
ArrayObject* arrayObj = dvmAllocPrimitiveArray(_typechar, length, ALLOC_DEFAULT); \
if (arrayObj == NULL) { \
return NULL; \
} \
_artype result = (_artype) addLocalReference(ts.self(), (Object*) arrayObj); \
dvmReleaseTrackedAlloc((Object*) arrayObj, NULL); \
return result; \
}
NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jbooleanArray, Boolean, 'Z');
NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jbyteArray, Byte, 'B');
NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jcharArray, Char, 'C');
NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jshortArray, Short, 'S');
NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jintArray, Int, 'I');
NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jlongArray, Long, 'J');
NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jfloatArray, Float, 'F');
NEW_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY(jdoubleArray, Double, 'D'); /*
* Get a pointer to a C array of primitive elements from an array object
* of the matching type.
*
* In a compacting GC, we either need to return a copy of the elements or
* "pin" the memory. Otherwise we run the risk of native code using the
* buffer as the destination of e.g. a blocking read() call that wakes up
* during a GC.
*/
#define GET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(_ctype, _jname) \
static _ctype* Get##_jname##ArrayElements(JNIEnv* env, \
_ctype##Array jarr, jboolean* isCopy) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); \
pinPrimitiveArray(arrayObj); \
_ctype* data = (_ctype*) (void*) arrayObj->contents; \
if (isCopy != NULL) { \
*isCopy = JNI_FALSE; \
} \
return data; \
} /*
* Release the storage locked down by the "get" function.
*
* The spec says, "'mode' has no effect if 'elems' is not a copy of the
* elements in 'array'." They apparently did not anticipate the need to
* un-pin memory.
*/
#define RELEASE_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(_ctype, _jname) \
static void Release##_jname##ArrayElements(JNIEnv* env, \
_ctype##Array jarr, _ctype* elems, jint mode) \
{ \
UNUSED_PARAMETER(elems); \
if (mode != JNI_COMMIT) { \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); \
unpinPrimitiveArray(arrayObj); \
} \
} static void throwArrayRegionOutOfBounds(ArrayObject* arrayObj, jsize start,
jsize len, const char* arrayIdentifier)
{
dvmThrowExceptionFmt(gDvm.exArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException,
"%s offset=%d length=%d %s.length=%d",
arrayObj->clazz->descriptor, start, len, arrayIdentifier,
arrayObj->length);
} /*
* Copy a section of a primitive array to a buffer.
*/
#define GET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_REGION(_ctype, _jname) \
static void Get##_jname##ArrayRegion(JNIEnv* env, \
_ctype##Array jarr, jsize start, jsize len, _ctype* buf) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); \
_ctype* data = (_ctype*) (void*) arrayObj->contents; \
if (start < || len < || start + len > (int) arrayObj->length) { \
throwArrayRegionOutOfBounds(arrayObj, start, len, "src"); \
} else { \
memcpy(buf, data + start, len * sizeof(_ctype)); \
} \
} /*
* Copy a section of a primitive array from a buffer.
*/
#define SET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_REGION(_ctype, _jname) \
static void Set##_jname##ArrayRegion(JNIEnv* env, \
_ctype##Array jarr, jsize start, jsize len, const _ctype* buf) \
{ \
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); \
ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr); \
_ctype* data = (_ctype*) (void*) arrayObj->contents; \
if (start < || len < || start + len > (int) arrayObj->length) { \
throwArrayRegionOutOfBounds(arrayObj, start, len, "dst"); \
} else { \
memcpy(data + start, buf, len * sizeof(_ctype)); \
} \
} /*
* 4-in-1:
* Get<Type>ArrayElements
* Release<Type>ArrayElements
* Get<Type>ArrayRegion
* Set<Type>ArrayRegion
*/
#define PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(_ctype, _jname) \
GET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(_ctype, _jname); \
RELEASE_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_ELEMENTS(_ctype, _jname); \
GET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_REGION(_ctype, _jname); \
SET_PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_REGION(_ctype, _jname); PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jboolean, Boolean);
PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jbyte, Byte);
PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jchar, Char);
PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jshort, Short);
PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jint, Int);
PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jlong, Long);
PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jfloat, Float);
PRIMITIVE_ARRAY_FUNCTIONS(jdouble, Double); /*
* Register one or more native functions in one class.
*
* This can be called multiple times on the same method, allowing the
* caller to redefine the method implementation at will.
*/
static jint RegisterNatives(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz,
const JNINativeMethod* methods, jint nMethods)
{
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz); if (gDvm.verboseJni) {
ALOGI("[Registering JNI native methods for class %s]",
clazz->descriptor);
} for (int i = ; i < nMethods; i++) {
if (!dvmRegisterJNIMethod(clazz, methods[i].name,
methods[i].signature, methods[i].fnPtr))
{
return JNI_ERR;
}
}
return JNI_OK;
} /*
* Un-register all native methods associated with the class.
*
* The JNI docs refer to this as a way to reload/relink native libraries,
* and say it "should not be used in normal native code". In particular,
* there is no need to do this during shutdown, and you do not need to do
* this before redefining a method implementation with RegisterNatives.
*
* It's chiefly useful for a native "plugin"-style library that wasn't
* loaded with System.loadLibrary() (since there's no way to unload those).
* For example, the library could upgrade itself by:
*
* 1. call UnregisterNatives to unbind the old methods
* 2. ensure that no code is still executing inside it (somehow)
* 3. dlclose() the library
* 4. dlopen() the new library
* 5. use RegisterNatives to bind the methods from the new library
*
* The above can work correctly without the UnregisterNatives call, but
* creates a window of opportunity in which somebody might try to call a
* method that is pointing at unmapped memory, crashing the VM. In theory
* the same guards that prevent dlclose() from unmapping executing code could
* prevent that anyway, but with this we can be more thorough and also deal
* with methods that only exist in the old or new form of the library (maybe
* the lib wants to try the call and catch the UnsatisfiedLinkError).
*/
static jint UnregisterNatives(JNIEnv* env, jclass jclazz) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); ClassObject* clazz = (ClassObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jclazz);
if (gDvm.verboseJni) {
ALOGI("[Unregistering JNI native methods for class %s]",
clazz->descriptor);
}
dvmUnregisterJNINativeMethods(clazz);
return JNI_OK;
} /*
* Lock the monitor.
*
* We have to track all monitor enters and exits, so that we can undo any
* outstanding synchronization before the thread exits.
*/
static jint MonitorEnter(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj);
dvmLockObject(ts.self(), obj);
trackMonitorEnter(ts.self(), obj);
return JNI_OK;
} /*
* Unlock the monitor.
*
* Throws an IllegalMonitorStateException if the current thread
* doesn't own the monitor. (dvmUnlockObject() takes care of the throw.)
*
* According to the 1.6 spec, it's legal to call here with an exception
* pending. If this fails, we'll stomp the original exception.
*/
static jint MonitorExit(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object* obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj);
bool success = dvmUnlockObject(ts.self(), obj);
if (success) {
trackMonitorExit(ts.self(), obj);
}
return success ? JNI_OK : JNI_ERR;
} /*
* Return the JavaVM interface associated with the current thread.
*/
static jint GetJavaVM(JNIEnv* env, JavaVM** vm) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
*vm = gDvmJni.jniVm;
return (*vm == NULL) ? JNI_ERR : JNI_OK;
} /*
* Copies "len" Unicode characters, from offset "start".
*/
static void GetStringRegion(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jsize start, jsize len, jchar* buf) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
int strLen = strObj->length();
if (((start|len) < ) || (start + len > strLen)) {
dvmThrowStringIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionWithRegion(strLen, start, len);
return;
}
memcpy(buf, strObj->chars() + start, len * sizeof(u2));
} /*
* Translates "len" Unicode characters, from offset "start", into
* modified UTF-8 encoding.
*/
static void GetStringUTFRegion(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jsize start, jsize len, char* buf) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
int strLen = strObj->length();
if (((start|len) < ) || (start + len > strLen)) {
dvmThrowStringIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionWithRegion(strLen, start, len);
return;
}
dvmGetStringUtfRegion(strObj, start, len, buf);
} /*
* Get a raw pointer to array data.
*
* The caller is expected to call "release" before doing any JNI calls
* or blocking I/O operations.
*
* We need to pin the memory or block GC.
*/
static void* GetPrimitiveArrayCritical(JNIEnv* env, jarray jarr, jboolean* isCopy) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr);
pinPrimitiveArray(arrayObj);
void* data = arrayObj->contents;
if (UNLIKELY(isCopy != NULL)) {
*isCopy = JNI_FALSE;
}
return data;
} /*
* Release an array obtained with GetPrimitiveArrayCritical.
*/
static void ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical(JNIEnv* env, jarray jarr, void* carray, jint mode) {
if (mode != JNI_COMMIT) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
ArrayObject* arrayObj = (ArrayObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jarr);
unpinPrimitiveArray(arrayObj);
}
} /*
* Like GetStringChars, but with restricted use.
*/
static const jchar* GetStringCritical(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, jboolean* isCopy) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
ArrayObject* strChars = strObj->array(); pinPrimitiveArray(strChars); const u2* data = strObj->chars();
if (isCopy != NULL) {
*isCopy = JNI_FALSE;
}
return (jchar*) data;
} /*
* Like ReleaseStringChars, but with restricted use.
*/
static void ReleaseStringCritical(JNIEnv* env, jstring jstr, const jchar* carray) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
StringObject* strObj = (StringObject*) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jstr);
ArrayObject* strChars = strObj->array();
unpinPrimitiveArray(strChars);
} /*
* Create a new weak global reference.
*/
static jweak NewWeakGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
Object *obj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jobj);
return (jweak) addWeakGlobalReference(obj);
} /*
* Delete the specified weak global reference.
*/
static void DeleteWeakGlobalRef(JNIEnv* env, jweak wref) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
deleteWeakGlobalReference(wref);
} /*
* Quick check for pending exceptions.
*
* TODO: we should be able to skip the enter/exit macros here.
*/
static jboolean ExceptionCheck(JNIEnv* env) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
return dvmCheckException(ts.self());
} /*
* Returns the type of the object referred to by "obj". It can be local,
* global, or weak global.
*
* In the current implementation, references can be global and local at
* the same time, so while the return value is accurate it may not tell
* the whole story.
*/
static jobjectRefType GetObjectRefType(JNIEnv* env, jobject jobj) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env);
return dvmGetJNIRefType(ts.self(), jobj);
} /*
* Allocate and return a new java.nio.ByteBuffer for this block of memory.
*/
static jobject NewDirectByteBuffer(JNIEnv* env, void* address, jlong capacity) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); if (capacity < ) {
ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): negative buffer capacity: %lld", capacity);
ReportJniError();
}
if (address == NULL && capacity != ) {
ALOGE("JNI ERROR (app bug): non-zero capacity for NULL pointer: %lld", capacity);
ReportJniError();
} /* create an instance of java.nio.DirectByteBuffer */
ClassObject* bufferClazz = gDvm.classJavaNioDirectByteBuffer;
if (!dvmIsClassInitialized(bufferClazz) && !dvmInitClass(bufferClazz)) {
return NULL;
}
Object* newObj = dvmAllocObject(bufferClazz, ALLOC_DONT_TRACK);
if (newObj == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
/* call the constructor */
jobject result = addLocalReference(ts.self(), newObj);
JValue unused;
dvmCallMethod(ts.self(), gDvm.methJavaNioDirectByteBuffer_init,
newObj, &unused, (jlong) address, (jint) capacity);
if (dvmGetException(ts.self()) != NULL) {
deleteLocalReference(ts.self(), result);
return NULL;
}
return result;
} /*
* Get the starting address of the buffer for the specified java.nio.Buffer.
*
* If this is not a "direct" buffer, we return NULL.
*/
static void* GetDirectBufferAddress(JNIEnv* env, jobject jbuf) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); // All Buffer objects have an effectiveDirectAddress field.
Object* bufObj = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jbuf);
return (void*) dvmGetFieldLong(bufObj, gDvm.offJavaNioBuffer_effectiveDirectAddress);
} /*
* Get the capacity of the buffer for the specified java.nio.Buffer.
*
* Returns -1 if the object is not a direct buffer. (We actually skip
* this check, since it's expensive to determine, and just return the
* capacity regardless.)
*/
static jlong GetDirectBufferCapacity(JNIEnv* env, jobject jbuf) {
ScopedJniThreadState ts(env); /*
* The capacity is always in the Buffer.capacity field.
*
* (The "check" version should verify that this is actually a Buffer,
* but we're not required to do so here.)
*/
Object* buf = dvmDecodeIndirectRef(ts.self(), jbuf);
return dvmGetFieldInt(buf, gDvm.offJavaNioBuffer_capacity);
} /*
* ===========================================================================
* JNI invocation functions
* ===========================================================================
*/ /*
* Handle AttachCurrentThread{AsDaemon}.
*
* We need to make sure the VM is actually running. For example, if we start
* up, issue an Attach, and the VM exits almost immediately, by the time the
* attaching happens the VM could already be shutting down.
*
* It's hard to avoid a race condition here because we don't want to hold
* a lock across the entire operation. What we can do is temporarily
* increment the thread count to prevent a VM exit.
*
* This could potentially still have problems if a daemon thread calls here
* while the VM is shutting down. dvmThreadSelf() will work, since it just
* uses pthread TLS, but dereferencing "vm" could fail. Such is life when
* you shut down a VM while threads are still running inside it.
*
* Remember that some code may call this as a way to find the per-thread
* JNIEnv pointer. Don't do excess work for that case.
*/
static jint attachThread(JavaVM* vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* thr_args, bool isDaemon) {
JavaVMAttachArgs* args = (JavaVMAttachArgs*) thr_args; /*
* Return immediately if we're already one with the VM.
*/
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
if (self != NULL) {
*p_env = self->jniEnv;
return JNI_OK;
} /*
* No threads allowed in zygote mode.
*/
if (gDvm.zygote) {
return JNI_ERR;
} /* increment the count to keep the VM from bailing while we run */
dvmLockThreadList(NULL);
if (gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount == ) {
// dead or dying
ALOGV("Refusing to attach thread '%s' -- VM is shutting down",
(thr_args == NULL) ? "(unknown)" : args->name);
dvmUnlockThreadList();
return JNI_ERR;
}
gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount++;
dvmUnlockThreadList(); /* tweak the JavaVMAttachArgs as needed */
JavaVMAttachArgs argsCopy;
if (args == NULL) {
/* allow the v1.1 calling convention */
argsCopy.version = JNI_VERSION_1_2;
argsCopy.name = NULL;
argsCopy.group = (jobject) dvmGetMainThreadGroup();
} else {
if (dvmIsBadJniVersion(args->version)) {
ALOGE("Bad JNI version passed to %s: %d",
(isDaemon ? "AttachCurrentThreadAsDaemon" : "AttachCurrentThread"),
args->version);
return JNI_EVERSION;
} argsCopy.version = args->version;
argsCopy.name = args->name;
if (args->group != NULL) {
argsCopy.group = (jobject) dvmDecodeIndirectRef(NULL, args->group);
} else {
argsCopy.group = (jobject) dvmGetMainThreadGroup();
}
} bool result = dvmAttachCurrentThread(&argsCopy, isDaemon); /* restore the count */
dvmLockThreadList(NULL);
gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount--;
dvmUnlockThreadList(); /*
* Change the status to indicate that we're out in native code. This
* call is not guarded with state-change macros, so we have to do it
* by hand.
*/
if (result) {
self = dvmThreadSelf();
assert(self != NULL);
dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_NATIVE);
*p_env = self->jniEnv;
return JNI_OK;
} else {
return JNI_ERR;
}
} /*
* Attach the current thread to the VM. If the thread is already attached,
* this is a no-op.
*/
static jint AttachCurrentThread(JavaVM* vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* thr_args) {
return attachThread(vm, p_env, thr_args, false);
} /*
* Like AttachCurrentThread, but set the "daemon" flag.
*/
static jint AttachCurrentThreadAsDaemon(JavaVM* vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* thr_args)
{
return attachThread(vm, p_env, thr_args, true);
} /*
* Dissociate the current thread from the VM.
*/
static jint DetachCurrentThread(JavaVM* vm) {
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
if (self == NULL) {
/* not attached, can't do anything */
return JNI_ERR;
} /* switch to "running" to check for suspension */
dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_RUNNING); /* detach the thread */
dvmDetachCurrentThread(); /* (no need to change status back -- we have no status) */
return JNI_OK;
} /*
* If current thread is attached to VM, return the associated JNIEnv.
* Otherwise, stuff NULL in and return JNI_EDETACHED.
*
* JVMTI overloads this by specifying a magic value for "version", so we
* do want to check that here.
*/
static jint GetEnv(JavaVM* vm, void** env, jint version) {
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf(); // GetEnv also accepts JNI_VERSION_1_1, but always returns a JNIEnv*
// corresponding to the most current supported JNI version.
if (dvmIsBadJniVersion(version) && version != JNI_VERSION_1_1) {
ALOGE("Bad JNI version passed to GetEnv: %d", version);
return JNI_EVERSION;
} if (self == NULL) {
*env = NULL;
} else {
/* TODO: status change is probably unnecessary */
dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_RUNNING);
*env = (void*) dvmGetThreadJNIEnv(self);
dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_NATIVE);
}
return (*env != NULL) ? JNI_OK : JNI_EDETACHED;
} /*
* Destroy the VM. This may be called from any thread.
*
* If the current thread is attached, wait until the current thread is
* the only non-daemon user-level thread. If the current thread is not
* attached, we attach it and do the processing as usual. (If the attach
* fails, it's probably because all the non-daemon threads have already
* exited and the VM doesn't want to let us back in.)
*
* TODO: we don't really deal with the situation where more than one thread
* has called here. One thread wins, the other stays trapped waiting on
* the condition variable forever. Not sure this situation is interesting
* in real life.
*/
static jint DestroyJavaVM(JavaVM* vm) {
JavaVMExt* ext = (JavaVMExt*) vm;
if (ext == NULL) {
return JNI_ERR;
} if (gDvm.verboseShutdown) {
ALOGD("DestroyJavaVM waiting for non-daemon threads to exit");
} /*
* Sleep on a condition variable until it's okay to exit.
*/
Thread* self = dvmThreadSelf();
if (self == NULL) {
JNIEnv* tmpEnv;
if (AttachCurrentThread(vm, &tmpEnv, NULL) != JNI_OK) {
ALOGV("Unable to reattach main for Destroy; assuming VM is shutting down (count=%d)",
gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount);
goto shutdown;
} else {
ALOGV("Attached to wait for shutdown in Destroy");
}
}
dvmChangeStatus(self, THREAD_VMWAIT); dvmLockThreadList(self);
gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount--; // remove current thread from count while (gDvm.nonDaemonThreadCount > ) {
pthread_cond_wait(&gDvm.vmExitCond, &gDvm.threadListLock);
} dvmUnlockThreadList();
self = NULL; shutdown:
// TODO: call System.exit() to run any registered shutdown hooks
// (this may not return -- figure out how this should work) if (gDvm.verboseShutdown) {
ALOGD("DestroyJavaVM shutting VM down");
}
dvmShutdown(); // TODO - free resources associated with JNI-attached daemon threads
free(ext->envList);
free(ext); return JNI_OK;
} /*
* ===========================================================================
* Function tables
* ===========================================================================
*/ static const struct JNINativeInterface gNativeInterface = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL,
NULL, GetVersion, DefineClass,
FindClass, FromReflectedMethod,
FromReflectedField,
ToReflectedMethod, GetSuperclass,
IsAssignableFrom, ToReflectedField, Throw,
ThrowNew,
ExceptionOccurred,
ExceptionDescribe,
ExceptionClear,
FatalError, PushLocalFrame,
PopLocalFrame, NewGlobalRef,
DeleteGlobalRef,
DeleteLocalRef,
IsSameObject,
NewLocalRef,
EnsureLocalCapacity, AllocObject,
NewObject,
NewObjectV,
NewObjectA, GetObjectClass,
IsInstanceOf, GetMethodID, CallObjectMethod,
CallObjectMethodV,
CallObjectMethodA,
CallBooleanMethod,
CallBooleanMethodV,
CallBooleanMethodA,
CallByteMethod,
CallByteMethodV,
CallByteMethodA,
CallCharMethod,
CallCharMethodV,
CallCharMethodA,
CallShortMethod,
CallShortMethodV,
CallShortMethodA,
CallIntMethod,
CallIntMethodV,
CallIntMethodA,
CallLongMethod,
CallLongMethodV,
CallLongMethodA,
CallFloatMethod,
CallFloatMethodV,
CallFloatMethodA,
CallDoubleMethod,
CallDoubleMethodV,
CallDoubleMethodA,
CallVoidMethod,
CallVoidMethodV,
CallVoidMethodA, CallNonvirtualObjectMethod,
CallNonvirtualObjectMethodV,
CallNonvirtualObjectMethodA,
CallNonvirtualBooleanMethod,
CallNonvirtualBooleanMethodV,
CallNonvirtualBooleanMethodA,
CallNonvirtualByteMethod,
CallNonvirtualByteMethodV,
CallNonvirtualByteMethodA,
CallNonvirtualCharMethod,
CallNonvirtualCharMethodV,
CallNonvirtualCharMethodA,
CallNonvirtualShortMethod,
CallNonvirtualShortMethodV,
CallNonvirtualShortMethodA,
CallNonvirtualIntMethod,
CallNonvirtualIntMethodV,
CallNonvirtualIntMethodA,
CallNonvirtualLongMethod,
CallNonvirtualLongMethodV,
CallNonvirtualLongMethodA,
CallNonvirtualFloatMethod,
CallNonvirtualFloatMethodV,
CallNonvirtualFloatMethodA,
CallNonvirtualDoubleMethod,
CallNonvirtualDoubleMethodV,
CallNonvirtualDoubleMethodA,
CallNonvirtualVoidMethod,
CallNonvirtualVoidMethodV,
CallNonvirtualVoidMethodA, GetFieldID, GetObjectField,
GetBooleanField,
GetByteField,
GetCharField,
GetShortField,
GetIntField,
GetLongField,
GetFloatField,
GetDoubleField,
SetObjectField,
SetBooleanField,
SetByteField,
SetCharField,
SetShortField,
SetIntField,
SetLongField,
SetFloatField,
SetDoubleField, GetStaticMethodID, CallStaticObjectMethod,
CallStaticObjectMethodV,
CallStaticObjectMethodA,
CallStaticBooleanMethod,
CallStaticBooleanMethodV,
CallStaticBooleanMethodA,
CallStaticByteMethod,
CallStaticByteMethodV,
CallStaticByteMethodA,
CallStaticCharMethod,
CallStaticCharMethodV,
CallStaticCharMethodA,
CallStaticShortMethod,
CallStaticShortMethodV,
CallStaticShortMethodA,
CallStaticIntMethod,
CallStaticIntMethodV,
CallStaticIntMethodA,
CallStaticLongMethod,
CallStaticLongMethodV,
CallStaticLongMethodA,
CallStaticFloatMethod,
CallStaticFloatMethodV,
CallStaticFloatMethodA,
CallStaticDoubleMethod,
CallStaticDoubleMethodV,
CallStaticDoubleMethodA,
CallStaticVoidMethod,
CallStaticVoidMethodV,
CallStaticVoidMethodA, GetStaticFieldID, GetStaticObjectField,
GetStaticBooleanField,
GetStaticByteField,
GetStaticCharField,
GetStaticShortField,
GetStaticIntField,
GetStaticLongField,
GetStaticFloatField,
GetStaticDoubleField, SetStaticObjectField,
SetStaticBooleanField,
SetStaticByteField,
SetStaticCharField,
SetStaticShortField,
SetStaticIntField,
SetStaticLongField,
SetStaticFloatField,
SetStaticDoubleField, NewString, GetStringLength,
GetStringChars,
ReleaseStringChars, NewStringUTF,
GetStringUTFLength,
GetStringUTFChars,
ReleaseStringUTFChars, GetArrayLength,
NewObjectArray,
GetObjectArrayElement,
SetObjectArrayElement, NewBooleanArray,
NewByteArray,
NewCharArray,
NewShortArray,
NewIntArray,
NewLongArray,
NewFloatArray,
NewDoubleArray, GetBooleanArrayElements,
GetByteArrayElements,
GetCharArrayElements,
GetShortArrayElements,
GetIntArrayElements,
GetLongArrayElements,
GetFloatArrayElements,
GetDoubleArrayElements, ReleaseBooleanArrayElements,
ReleaseByteArrayElements,
ReleaseCharArrayElements,
ReleaseShortArrayElements,
ReleaseIntArrayElements,
ReleaseLongArrayElements,
ReleaseFloatArrayElements,
ReleaseDoubleArrayElements, GetBooleanArrayRegion,
GetByteArrayRegion,
GetCharArrayRegion,
GetShortArrayRegion,
GetIntArrayRegion,
GetLongArrayRegion,
GetFloatArrayRegion,
GetDoubleArrayRegion,
SetBooleanArrayRegion,
SetByteArrayRegion,
SetCharArrayRegion,
SetShortArrayRegion,
SetIntArrayRegion,
SetLongArrayRegion,
SetFloatArrayRegion,
SetDoubleArrayRegion, RegisterNatives,
UnregisterNatives, MonitorEnter,
MonitorExit, GetJavaVM, GetStringRegion,
GetStringUTFRegion, GetPrimitiveArrayCritical,
ReleasePrimitiveArrayCritical, GetStringCritical,
ReleaseStringCritical, NewWeakGlobalRef,
DeleteWeakGlobalRef, ExceptionCheck, NewDirectByteBuffer,
GetDirectBufferAddress,
GetDirectBufferCapacity, GetObjectRefType
}; static const struct JNIInvokeInterface gInvokeInterface = {
NULL,
NULL,
NULL, DestroyJavaVM,
AttachCurrentThread,
DetachCurrentThread, GetEnv, AttachCurrentThreadAsDaemon,
}; /*
* ===========================================================================
* VM/Env creation
* ===========================================================================
*/ /*
* Create a new JNIEnv struct and add it to the VM's list.
*
* "self" will be NULL for the main thread, since the VM hasn't started
* yet; the value will be filled in later.
*/
JNIEnv* dvmCreateJNIEnv(Thread* self) {
JavaVMExt* vm = (JavaVMExt*) gDvmJni.jniVm; //if (self != NULL)
// ALOGI("Ent CreateJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self); assert(vm != NULL); JNIEnvExt* newEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) calloc(, sizeof(JNIEnvExt));
newEnv->funcTable = &gNativeInterface;
if (self != NULL) {
dvmSetJniEnvThreadId((JNIEnv*) newEnv, self);
assert(newEnv->envThreadId != );
} else {
/* make it obvious if we fail to initialize these later */
newEnv->envThreadId = 0x77777775;
newEnv->self = (Thread*) 0x77777779;
}
if (gDvmJni.useCheckJni) {
dvmUseCheckedJniEnv(newEnv);
} ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&vm->envListLock); /* insert at head of list */
newEnv->next = vm->envList;
assert(newEnv->prev == NULL);
if (vm->envList == NULL) {
// rare, but possible
vm->envList = newEnv;
} else {
vm->envList->prev = newEnv;
}
vm->envList = newEnv; //if (self != NULL)
// ALOGI("Xit CreateJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self);
return (JNIEnv*) newEnv;
} /*
* Remove a JNIEnv struct from the list and free it.
*/
void dvmDestroyJNIEnv(JNIEnv* env) {
if (env == NULL) {
return;
} //ALOGI("Ent DestroyJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self); JNIEnvExt* extEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) env;
JavaVMExt* vm = (JavaVMExt*) gDvmJni.jniVm; ScopedPthreadMutexLock lock(&vm->envListLock); if (extEnv == vm->envList) {
assert(extEnv->prev == NULL);
vm->envList = extEnv->next;
} else {
assert(extEnv->prev != NULL);
extEnv->prev->next = extEnv->next;
}
if (extEnv->next != NULL) {
extEnv->next->prev = extEnv->prev;
} free(env);
//ALOGI("Xit DestroyJNIEnv: threadid=%d %p", self->threadId, self);
} /*
* Enable "checked JNI" after the VM has partially started. This must
* only be called in "zygote" mode, when we have one thread running.
*
* This doesn't attempt to rewrite the JNI call bridge associated with
* native methods, so we won't get those checks for any methods that have
* already been resolved.
*/
void dvmLateEnableCheckedJni() {
JNIEnvExt* extEnv = dvmGetJNIEnvForThread();
if (extEnv == NULL) {
ALOGE("dvmLateEnableCheckedJni: thread has no JNIEnv");
return;
}
JavaVMExt* extVm = (JavaVMExt*) gDvmJni.jniVm;
assert(extVm != NULL); if (!gDvmJni.useCheckJni) {
ALOGD("Late-enabling CheckJNI");
dvmUseCheckedJniVm(extVm);
dvmUseCheckedJniEnv(extEnv);
} else {
ALOGD("Not late-enabling CheckJNI (already on)");
}
} /*
* Not supported.
*/
jint JNI_GetDefaultJavaVMInitArgs(void* vm_args) {
return JNI_ERR;
} /*
* Return a buffer full of created VMs.
*
* We always have zero or one.
*/
jint JNI_GetCreatedJavaVMs(JavaVM** vmBuf, jsize bufLen, jsize* nVMs) {
if (gDvmJni.jniVm != NULL) {
*nVMs = ;
if (bufLen > ) {
*vmBuf++ = gDvmJni.jniVm;
}
} else {
*nVMs = ;
}
return JNI_OK;
} /*
* Create a new VM instance.
*
* The current thread becomes the main VM thread. We return immediately,
* which effectively means the caller is executing in a native method.
*/
jint JNI_CreateJavaVM(JavaVM** p_vm, JNIEnv** p_env, void* vm_args) {
const JavaVMInitArgs* args = (JavaVMInitArgs*) vm_args;
if (dvmIsBadJniVersion(args->version)) {
ALOGE("Bad JNI version passed to CreateJavaVM: %d", args->version);
return JNI_EVERSION;
} // TODO: don't allow creation of multiple VMs -- one per customer for now /* zero globals; not strictly necessary the first time a VM is started */
memset(&gDvm, , sizeof(gDvm)); /*
* Set up structures for JNIEnv and VM.
*/
JavaVMExt* pVM = (JavaVMExt*) calloc(, sizeof(JavaVMExt));
pVM->funcTable = &gInvokeInterface;
pVM->envList = NULL;
dvmInitMutex(&pVM->envListLock); UniquePtr<const char*[]> argv(new const char*[args->nOptions]);
memset(argv.get(), , sizeof(char*) * (args->nOptions)); /*
* Convert JNI args to argv.
*
* We have to pull out vfprintf/exit/abort, because they use the
* "extraInfo" field to pass function pointer "hooks" in. We also
* look for the -Xcheck:jni stuff here.
*/
int argc = ;
for (int i = ; i < args->nOptions; i++) {
const char* optStr = args->options[i].optionString;
if (optStr == NULL) {
dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: CreateJavaVM failed: argument %d was NULL\n", i);
return JNI_ERR;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "vfprintf") == ) {
gDvm.vfprintfHook = (int (*)(FILE *, const char*, va_list))args->options[i].extraInfo;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "exit") == ) {
gDvm.exitHook = (void (*)(int)) args->options[i].extraInfo;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "abort") == ) {
gDvm.abortHook = (void (*)(void))args->options[i].extraInfo;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "sensitiveThread") == ) {
gDvm.isSensitiveThreadHook = (bool (*)(void))args->options[i].extraInfo;
} else if (strcmp(optStr, "-Xcheck:jni") == ) {
gDvmJni.useCheckJni = true;
} else if (strncmp(optStr, "-Xjniopts:", ) == ) {
char* jniOpts = strdup(optStr + );
size_t jniOptCount = ;
for (char* p = jniOpts; *p != ; ++p) {
if (*p == ',') {
++jniOptCount;
*p = ;
}
}
char* jniOpt = jniOpts;
for (size_t i = ; i < jniOptCount; ++i) {
if (strcmp(jniOpt, "warnonly") == ) {
gDvmJni.warnOnly = true;
} else if (strcmp(jniOpt, "forcecopy") == ) {
gDvmJni.forceCopy = true;
} else if (strcmp(jniOpt, "logThirdPartyJni") == ) {
gDvmJni.logThirdPartyJni = true;
} else {
dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: CreateJavaVM failed: unknown -Xjniopts option '%s'\n",
jniOpt);
free(pVM);
free(jniOpts);
return JNI_ERR;
}
jniOpt += strlen(jniOpt) + ;
}
free(jniOpts);
} else {
/* regular option */
argv[argc++] = optStr;
}
} if (gDvmJni.useCheckJni) {
dvmUseCheckedJniVm(pVM);
} if (gDvmJni.jniVm != NULL) {
dvmFprintf(stderr, "ERROR: Dalvik only supports one VM per process\n");
free(pVM);
return JNI_ERR;
}
gDvmJni.jniVm = (JavaVM*) pVM; /*
* Create a JNIEnv for the main thread. We need to have something set up
* here because some of the class initialization we do when starting
* up the VM will call into native code.
*/
JNIEnvExt* pEnv = (JNIEnvExt*) dvmCreateJNIEnv(NULL); /* Initialize VM. */
gDvm.initializing = true;
std::string status =
dvmStartup(argc, argv.get(), args->ignoreUnrecognized, (JNIEnv*)pEnv);
gDvm.initializing = false; if (!status.empty()) {
free(pEnv);
free(pVM);
ALOGW("CreateJavaVM failed: %s", status.c_str());
return JNI_ERR;
} /*
* Success! Return stuff to caller.
*/
dvmChangeStatus(NULL, THREAD_NATIVE);
*p_env = (JNIEnv*) pEnv;
*p_vm = (JavaVM*) pVM;
ALOGV("CreateJavaVM succeeded");
return JNI_OK;
}
Jni.cpp
拿2.3.3的
print(GetString(R1,-1, ASCSTR_C)),使用0 * print(GetString(DbgDword(R2+0x10),-1, ASCSTR_C)) 跟踪而不断下来,虽然文档说'void' means that function returns no meaningful value (always 0),但是还会段下来,乘以0就不一样,即运行语句又判断值。
IDA的帮助文档
// Print variables in the message window
// This function print text representation of all its arguments to the output window.
// This function can be used to debug IDC scripts void print (...);
Alphabetical list of IDC functions
The following conventions are used in the function descriptions:
'ea' is a linear address
'success' is 0 if a function fails, 1 otherwise
'void' means that function returns no meaningful value (always 0)
'anyvalue' means that function may return value of any type
下面一个截图跟踪方法调用,最后到我们的jni方法。
看这里http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/8923483,了解到注册jni方法以后再调用jni方法需要经过最直接看出的就是第一二参数变量等准备,这个来自注册时由Dalvik虚拟机的启动选项来为即将要注册的JNI选择一个合适的Bridge函数。以后通过这个Bridge函数(DalvikBridgeFunc)调用你的jni方法。但是这里有2类,每类4个。一般只有能选择1类,则对于jni方法调用存在4种调用过程。正如前面描述,从哪个版本开始就不会出现了,已经只有 一个了。
Dalvik虚拟机提供的Bridge函数主要是分为两类。第一类Bridge函数在调用完成JNI方法之后,会检查该JNI方法的返回结果是否与声明的一致,这是因为一个声明返回String的JNI方法在执行时返回的可能会是一个Byte Array。如果不一致,取决于Dalvik虚拟机的启动选项,它可能会停机。第二类Bridge函数不对JNI方法的返回结果进行上述检查。选择哪一类Bridge函数可以通过-Xcheck:jni选项来决定。不过由于检查一个JNI方法的返回结果是否与声明的一致是很耗时的,因此,我们一般都不会使用第一类Bridge函数。
此外,每一类Bridge函数又分为四个子类:Genernal、Sync、VirtualNoRef和StaticNoRef,它们的选择规则为:
1. 一个JNI方法的参数列表中如果包含有引用类型的参数,那么对应的Bridge函数就是Genernal类型的,即为dvmCallJNIMethod_general或者dvmCheckCallJNIMethod_general。
2. 一个JNI方法如果声明为同步方法,即带有synchronized修饰符,那么对应的Bridge函数就是Sync类型的,即为dvmCallJNIMethod_synchronized或者dvmCheckCallJNIMethod_synchronized。
3. 一个JNI方法的参数列表中如果不包含有引用类型的参数,并且它是一个虚成员函数,那么对应的Bridge函数就是kJNIVirtualNoRef类型的,即为dvmCallJNIMethod_virtualNoRef或者dvmCheckCallJNIMethod_virtualNoRef。
4. 一个JNI方法的参数列表中如果不包含有引用类型的参数,并且它是一个静态成员函数,那么对应的Bridge函数就是StaticNoRef类型的,即为dvmCallJNIMethod_staticNoRef或者dvmCheckCallJNIMethod_staticNoRef。
每一类Bridge函数之所以要划分为上述四个子类,是因为每一个子类的Bridge函数在调用真正的JNI方法之前,所要进行的准备工作是不一样的。例如,Genernal类型的Bridge函数需要为引用类型的参数增加一个本地引用,避免它在JNI方法执行的过程中被回收。又如,Sync类型的Bridge函数在调用JNI方法之前,需要执行同步原始,以避免多线程访问的竞争问题。
void dvmCallJNIMethod_general(const u4* args, JValue* pResult, const Method* method, Thread* self)
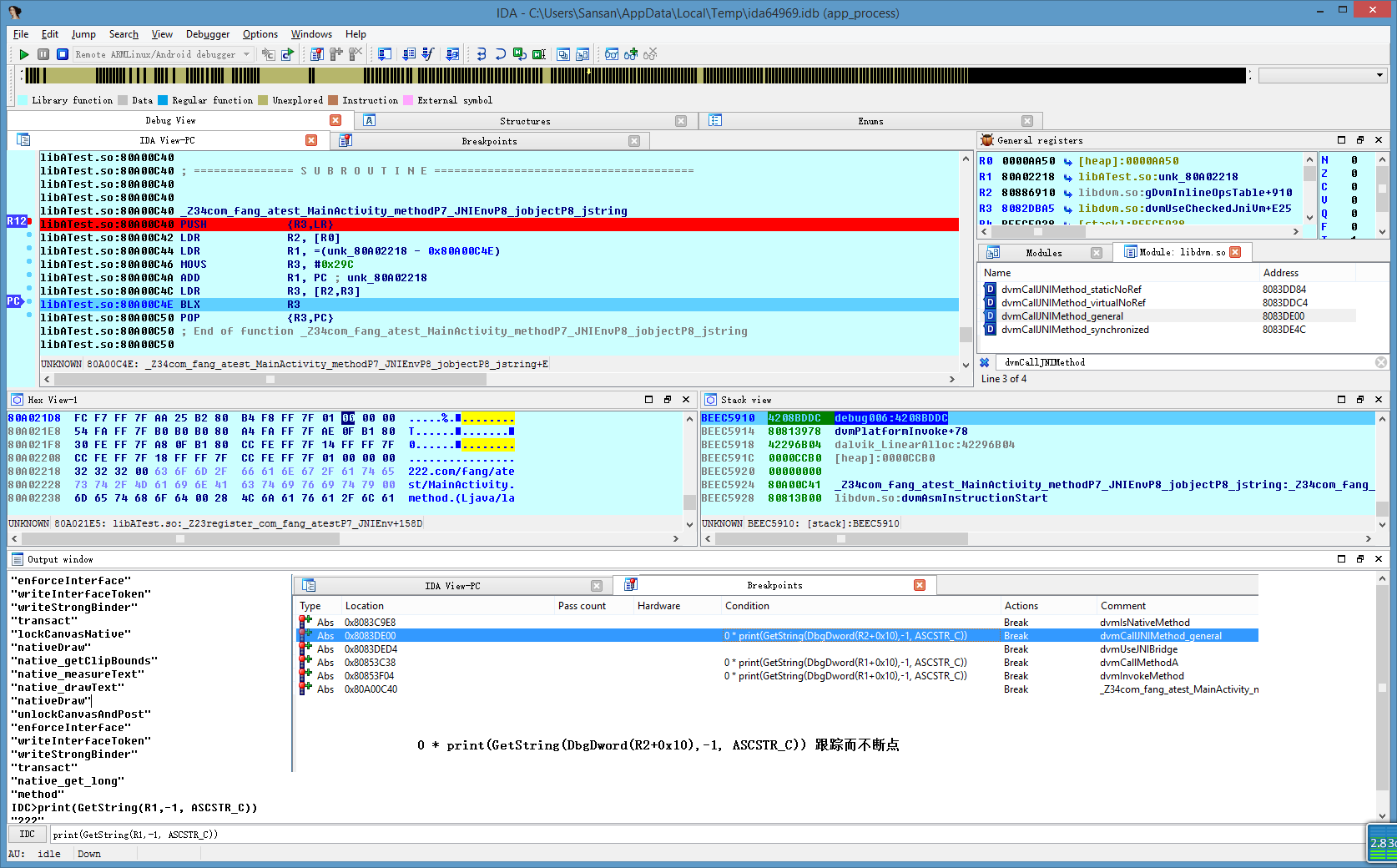
这样是不是说根据"method" == GetString(DbgDword(R2+0x10),-1, ASCSTR_C)条件断点,找到调用的函数地址。
额外说下:
// Convert address value to a string string atoa (long ea); // returns address in
// the form 'seg000:1234'
// (the same as in line prefixes)
Android下返回值:
system@framework@framework.jar@classes.dex:434C3D54 = 1108165232
system@framework@framework.jar@classes.dex:434C2475 = 1108271444
//2.3.3不自带grep,所以不能adb shell "ps | grep crackme",而使用windows的findstr,使用
adb shell ps | findstr crackme
strstr(DbgDword(R2+0x10);
D:\Developer\sdk\platform-tools>adb shell
# cat /proc//
cat /proc//
/proc//: invalid length
//这个头可以选择VC++编译器直接导入到ida里 typedef void ClassObject;
typedef void DexFile;
typedef void JValue;
typedef void RegisterMap;
typedef int u4 ;
typedef short u2; //xref: KitKat 4.4.2_r2 /dalvik/libdex/DexProto.h
/*
* Method prototype structure, which refers to a protoIdx in a
* particular DexFile.
*/
struct DexProto {
const DexFile* dexFile; /* file the idx refers to */
u4 protoIdx; /* index into proto_ids table of dexFile */
}; /*
* Native function pointer type.
*
* "args[0]" holds the "this" pointer for virtual methods.
*
* The "Bridge" form is a super-set of the "Native" form; in many places
* they are used interchangeably. Currently, all functions have all
* arguments passed in, but some functions only care about the first two.
* Passing extra arguments to a C function is (mostly) harmless.
*/
typedef void (*DalvikBridgeFunc)(const u4* args, JValue* pResult,
const Method* method, void* self); /*
* A method. We create one of these for every method in every class
* we load, so try to keep the size to a minimum.
*
* Much of this comes from and could be accessed in the data held in shared
* memory. We hold it all together here for speed. Everything but the
* pointers could be held in a shared table generated by the optimizer;
* if we're willing to convert them to offsets and take the performance
* hit (e.g. "meth->insns" becomes "baseAddr + meth->insnsOffset") we
* could move everything but "nativeFunc".
*/
struct Method {
/* the class we are a part of */
ClassObject* clazz; /* access flags; low 16 bits are defined by spec (could be u2?) */
u4 accessFlags; /*
* For concrete virtual methods, this is the offset of the method
* in "vtable".
*
* For abstract methods in an interface class, this is the offset
* of the method in "iftable[n]->methodIndexArray".
*/
u2 methodIndex; /*
* Method bounds; not needed for an abstract method.
*
* For a native method, we compute the size of the argument list, and
* set "insSize" and "registerSize" equal to it.
*/
u2 registersSize; /* ins + locals */
u2 outsSize;
u2 insSize; /* method name, e.g. "<init>" or "eatLunch" */
const char* name; /*
* Method prototype descriptor string (return and argument types).
*
* TODO: This currently must specify the DexFile as well as the proto_ids
* index, because generated Proxy classes don't have a DexFile. We can
* remove the DexFile* and reduce the size of this struct if we generate
* a DEX for proxies.
*/
DexProto prototype; /* short-form method descriptor string */
const char* shorty; /*
* The remaining items are not used for abstract or native methods.
* (JNI is currently hijacking "insns" as a function pointer, set
* after the first call. For internal-native this stays null.)
*/ /* the actual code */
const u2* insns; /* instructions, in memory-mapped .dex */ /* JNI: cached argument and return-type hints */
int jniArgInfo; /*
* JNI: native method ptr; could be actual function or a JNI bridge. We
* don't currently discriminate between DalvikBridgeFunc and
* DalvikNativeFunc; the former takes an argument superset (i.e. two
* extra args) which will be ignored. If necessary we can use
* insns==NULL to detect JNI bridge vs. internal native.
*/
DalvikBridgeFunc nativeFunc; /*
* JNI: true if this static non-synchronized native method (that has no
* reference arguments) needs a JNIEnv* and jclass/jobject. Libcore
* uses this.
*/
bool fastJni; /*
* JNI: true if this method has no reference arguments. This lets the JNI
* bridge avoid scanning the shorty for direct pointers that need to be
* converted to local references.
*
* TODO: replace this with a list of indexes of the reference arguments.
*/
bool noRef; /*
* JNI: true if we should log entry and exit. This is the only way
* developers can log the local references that are passed into their code.
* Used for debugging JNI problems in third-party code.
*/
bool shouldTrace; /*
* Register map data, if available. This will point into the DEX file
* if the data was computed during pre-verification, or into the
* linear alloc area if not.
*/
const RegisterMap* registerMap; /* set if method was called during method profiling */
bool inProfile;
};
DexProto.h
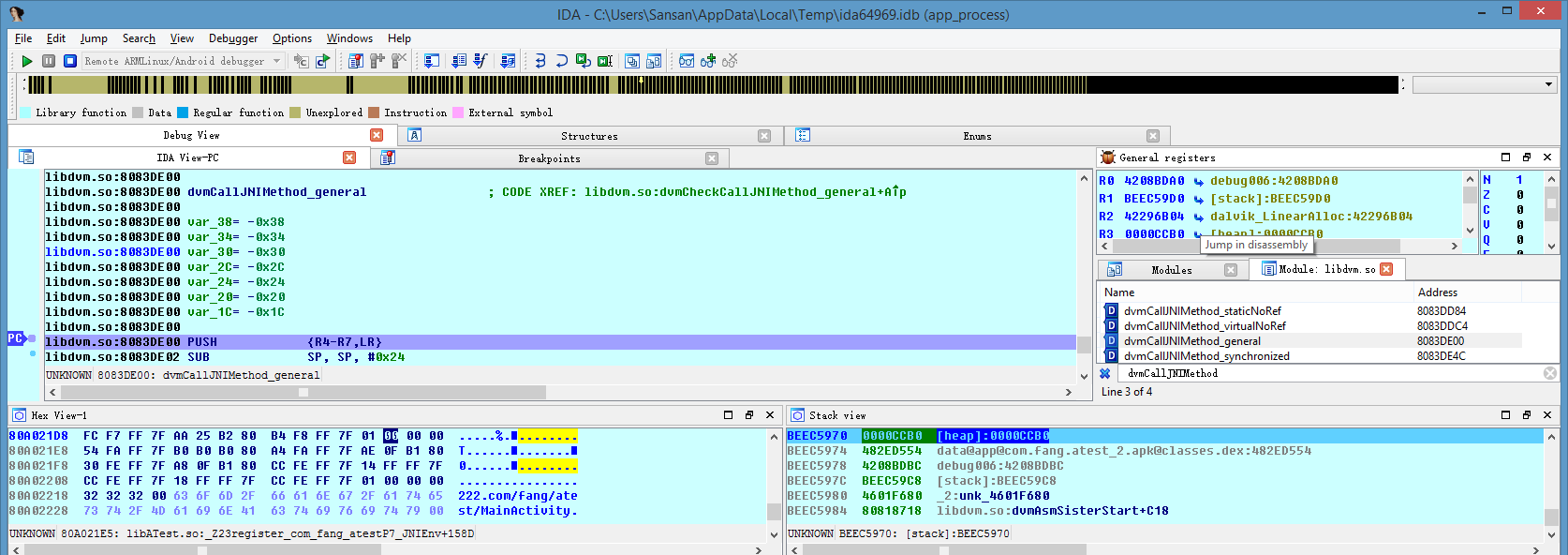
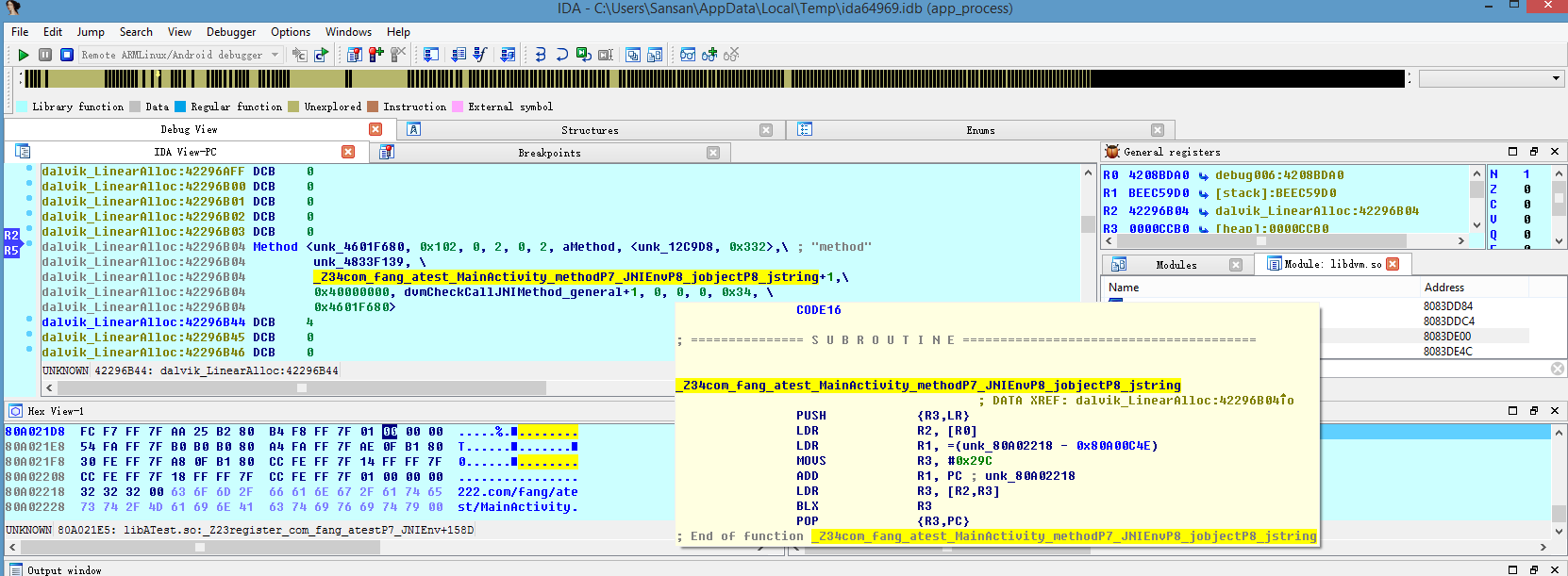
如果方法太多,如界面上的可能会无响应对话框
"unlockCanvasAndPost"
"native_computeBounds"
"lockCanvasNative"
"nativeDraw"
"native_getClipBounds"
"native_drawText"
"nativeDraw"
"unlockCanvasAndPost"
"native_computeBounds"
"lockCanvasNative"
"nativeDraw"
"native_getClipBounds"
"native_drawText"
"nativeDraw"
....
或者打印地址语句
0 * Message("%s = %d\n", GetString(DbgDword(R2+0x10),-1, ASCSTR_C), R2+0x20)
结果
enforceInterface = 1108147904
writeInterfaceToken = 1108151492
writeStrongBinder = 1108152272
transact = 1108144564
lockCanvasNative = 1108185020
nativeDraw = 1108271444
native_getClipBounds = 1108165440
native_measureText = 1108172200
native_drawText = 1108165180
nativeDraw = 1108271444
unlockCanvasAndPost = 1108186532
enforceInterface = 1108147904
writeInterfaceToken = 1108151492
writeStrongBinder = 1108152272
transact = 1108144564
native_get_long = 1108308360
method = 1110009932
native_measureText = 1108172200
getFontMetricsInt = 1108173712
native_measureText = 1108172200
native_measureText = 1108172200
lockCanvasNative = 1108185020
drawText = 1108168304
nativeDraw = 1108271444
native_getClipBounds = 1108165440
native_measureText = 1108172200
native_drawText = 1108165180
nativeDraw = 1108271444
native_getClipBounds = 1108165440
native_measureText = 1108172200
native_drawText = 1108165180
nativeDraw = 1108271444
unlockCanvasAndPost = 1108186532
#include <jni.h> jstring com_fang_atest_MainActivity_method(JNIEnv *pEnv, jobject o, jstring param)
{ return pEnv->NewStringUTF("");
}
/*
* 由于gMethods[]是一个<名称,函数指针>对照表,在程序执行时,
* 可多次调用registerNativeMethods()函数来更换本地函数的指针,
* 从而达到弹性调用本地函数的目的。
*/
static JNINativeMethod gMethods[] =
{
/* name, signature, funcPtr */
{ "method", "(Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;",
(void*) com_fang_atest_MainActivity_method }, }; static const char* const className = "com/fang/atest/MainActivity"; //在native 注册的时候首先保存java的调用方法:以便事件回调而不必每次获取,即在native里调用java对象,方法等。
int register_com_fang_atest(JNIEnv* pEnv)
{
jclass clazz; //ALOGI(TAG, "Registering %s natives\n", className);
clazz = pEnv->FindClass(className);
if (clazz == )
{
//ALOGE("Native registration unable to find class '%s'\n", className);
return -;
}
if (pEnv->RegisterNatives(clazz, gMethods, ) < )
{
//ALOGE("RegisterNatives failed for '%s'\n", className);
return -;
}
return ;
} // Set some test stuff up.
//Used by WithFramework to register native functions.
//Returns the JNI version on success, -1 on failure.
//Dalvik虚拟机加载C库时,第一件事是调用JNI_OnLoad()函数
extern "C" jint JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM* vm, void* reserved)
{
JNIEnv* env = ; /*JavaVM::GetEnv 原型为 jint (*GetEnv)(JavaVM*, void**, jint);
* GetEnv()函数返回的 Jni 环境对每个线程来说是不同的,
* 由于Dalvik虚拟机通常是Multi-threading的。每一个线程调用JNI_OnLoad()时,
* 所用的JNI Env是不同的,因此我们必须在每次进入函数时都要通过vm->GetEnv重新获取
*/
//得到JNI Env
if (vm->GetEnv(reinterpret_cast<void**>(&env), JNI_VERSION_1_4) != JNI_OK)
{
return JNI_ERR;
}
// Get jclass with env->FindClass.
// Register methods with env->RegisterNatives
//assert(env != NULL);
register_com_fang_atest(env);
// success -- return valid version number
return JNI_VERSION_1_4;
}
package com.fang.atest; import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.StringWriter;
import java.io.Writer; import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity extends Activity { /*
* static { // load library: libADemo.so try { System.loadLibrary("ATest");
* } catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError ule) {
* System.err.println("WARNING: Could not load library!"); }
*
* }
*/ private native String method(String paramString1); TextView tv; @Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv = (TextView) MainActivity.this.findViewById(R.id.textView1);
Button btnCall = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
btnCall.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub try {
tv.setText(method("888"));
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError ule) {
tv.setText(getStackTrace(ule));
ule.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
Button btnLoad = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2);
btnLoad.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
try {
System.loadLibrary("ATest");
} catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError ule) {
tv.setText(getStackTrace(ule));
System.err.println("WARNING: Could not load library!");
}
}
});
/*
* Button btnUnLoad = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
* btnLoad.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
*
* @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method
* stub try { System.loadLibrary("ATest"); } catch (UnsatisfiedLinkError
* ule) { System.err.println("WARNING: Could not load library!"); } }
* });
*/
} /**
* 将异常堆栈转换为字符串
*
* @param aThrowable
* 异常
* @return String
*/
public static String getStackTrace(Throwable aThrowable) {
final Writer result = new StringWriter();
final PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(result);
aThrowable.printStackTrace(printWriter);
return result.toString();
}
}
Android调用JNI本地方法经过有点改变的更多相关文章
- Android调用JNI本地方法跟踪目标代码
正如Android调用JNI本地方法经过有点改变章所说跟踪代码是可行的,但是跟踪某些代码会出现anr,点击取消,还是不好运,有提高办法吗?回答是有(gdb还没试过,本文只讨论ida). 下面是我使用 ...
- Android Java访问本地方法(JNI)
当功能需要本地代码实现的时候,Java 代码就需要调用本地代码. 在调用本地代码时,首先要保证本地代码被加载到 Java 执行环境中并与 Java 代码连接在一起,这样 Java 代码在调用本地方法时 ...
- 【我的Android进阶之旅】Android调用JNI出错 java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: No implementation found for的解决方法
错误描述 今天使用第三方的so库时候,调用JNI方法时出现了错误.报错如下所示: 11-01 16:39:20.979 4669-4669/com.netease.xtc.cloudmusic E/a ...
- WebView js 调用Java本地方法
webView = (WebView) this.findViewById(R.id.webview); WebSettings webSettings = webView.getSettings() ...
- JNI学习2:android 调用C语言方法与C语言调用android方法
#include <jni.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <jni.h> #in ...
- Android之——jni通用工具方法
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/l1028386804/article/details/47002207 1.将java字符串转化为c++字符串 /** *工具方法 *将ja ...
- Android调用Jni,非常简单的一个Demo
step1:创建一个android项目 Project Name:jnitest Build Target: Android 1.6 Application Nam ...
- Android与JNI(二) ---- Java调用C++ 动态调用
目录: 1. 简介 2. JNI 组件的入口函数 3. 使用 registerNativeMethods 方法 4. 测试 5. JNI 帮助方法 6. 参考资料 1. 简介 Android与JNI( ...
- JNI系列——C文件中的方法调用Java中方法
1.创建xxx.jni包并在该包下实现一些Java的方法,和要调用的本地方法 2.实现MainActivity中的按钮点击事件-即点击按钮调用本地的方法 3.在C文件中的方法中回调Java的方法 3. ...
随机推荐
- npm link & run npm script
npm link & run npm script https://blog.csdn.net/juhaotian/article/details/78672390 npm link命令可以将 ...
- Luogu【P1725】琪露诺(单调队列,DP)
本文是笔者第二篇解题报告.从现在开始,会将练的一些题发到博客上并归类到"解题报告"标签中. 琪露诺是这样一道题 这道题可以用纯DP做,但是据说会超时.(为什么?看起来过河这题比它数 ...
- ACM程序设计选修课——1024: 末位零(求末尾0的方法+可有可无的快速幂)
1024: 末位零 Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 32 MB Submit: 60 Solved: 11 [Submit][Status][Web Board] ...
- .sh 和 .ksh —— 三种主要的 Shell简介(Korn shell)
和现在的开发语言一样,语法上有些差异! 三种主要的 Shell 与其分身 在大部份的UNIX系统,三种著名且广被支持的shell 是Bourne shell(AT&T shell,在 Linu ...
- java面试题之spring aop中jdk和cglib哪个动态代理的性能更好?
在jdk6和jdk7的时候,jdk比cglib要慢: 在jdk8的时候,jdk性能得到提升比cglib要快很多: 结论出自:https://www.cnblogs.com/xuliugen/p/104 ...
- 移动web端使用rem实现自适应原理
1.先获取到物理像素和实际像素的像素比 var pixclPatio = 1 / window.devicePixelRatio; 2.viewport视口设置为像素比大小 document.writ ...
- 博彩游戏(tyvj 1519)
背景 Bob最近迷上了一个博彩游戏…… 描述 这个游戏的规则是这样的:每花一块钱可以得到一个随机数R,花上N块钱就可以得到一个随机序列:有M个序列,如果某个序列是产生的随机序列的子串,那么就中奖了,否 ...
- java并发框架Executor介绍
Executor框架是指java 5中引入的一系列并发库中与executor相关的一些功能类,其中包括线程池,Executor,Executors,ExecutorService,Completion ...
- Docker 架构详解
Docker 的核心组件包括: Docker 客户端 - Client Docker 服务器 - Docker daemon Docker 镜像 - Image Registry Docker 容器 ...
- 快充 IC BQ25896 的 常用參數
一: POWER-PATH MANAGEMENT (有接 adapter) 1:Vbat > Vsysmin,Isys = 0A, BATFET disable Vsys = Vbat + 50 ...
