django高级之爬虫基础
目录:
- 爬虫原理
- requests模块
- beautifulsoup模块
- 爬虫自动登陆示例
一、爬虫原理
Python非常适合用来开发网页爬虫,理由如下:
1、抓取网页本身的接口
相比与其他静态编程语言,如java,c#,c++,python抓取网页文档的接口更简洁;相比其他动态脚本语言,如perl,shell,python的urllib包提供了较为完整的访问网页文档的API。(当然ruby也是很好的选择)
此外,抓取网页有时候需要模拟浏览器的行为,很多网站对于生硬的爬虫抓取都是封杀的。这是我们需要模拟user agent的行为构造合适的请求,譬如模拟用户登陆、模拟session/cookie的存储和设置。在python里都有非常优秀的第三方包帮你搞定,如Requests,mechanize
2、网页抓取后的处理
抓取的网页通常需要处理,比如过滤html标签,提取文本等。python的beautifulsoap提供了简洁的文档处理功能,能用极短的代码完成大部分文档的处理。
其实以上功能很多语言和工具都能做,但是用python能够干得最快,最干净。
3、爬虫架构
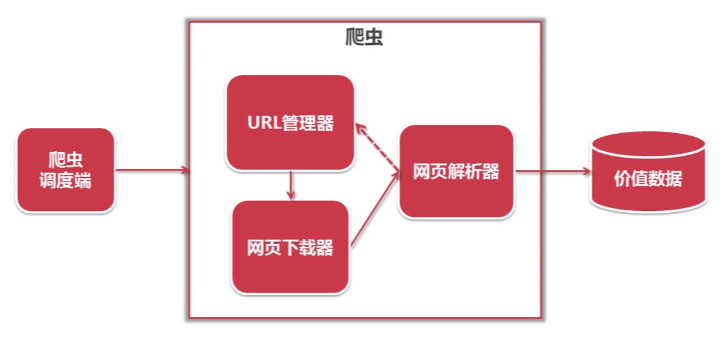
URL管理器:管理待爬取的url集合和已爬取的url集合,传送待爬取的url给网页下载器。
网页下载器(urllib、requests):爬取url对应的网页,存储成字符串或文件,传送给网页解析器。
网页解析器(BeautifulSoup):解析出有价值的数据,存储下来,同时补充url到URL管理器。
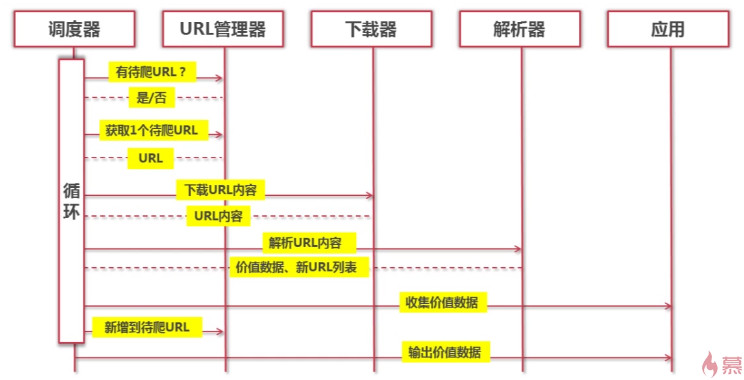
4、运行流程
5、HTTP请求内容
GET:
http GET /index.html?p=1 http1.1\r\nhost:oldboyedu.com\r\n....\r\n\r\
默认请求头:Content-Type:text/html; charset=utf-8
无请求体
POST:
http POST / http1.1\r\nhost:oldboyedu.com\r\n....\r\n\r\nname=alex&age=18
默认请求头:content-type:application/url-from
请求体:\r\n\r\nname=alex&age=18
http POST / http1.1\r\nhost:oldboyedu.com\r\n....\r\n\r\n{"name": "alex", "age": 18}
默认请求头:content-type:application/json
请求体:\r\n\r\n{"name": "alex", "age": 18}
ps.响应:
- 响应:
响应头
- 浏览器读取
响应体
- 看到的内容
6、提高爬虫性能
【协程】异步非阻塞,并在网页解析器(BeautifulSoup)使用lxml模块(为c语言写的规则模块,效率高)解析。
7、待补充:
二、requests模块
Python标准库中提供了:urllib、urllib2、httplib等模块以供Http请求,但是,它的 API 太渣了。它是为另一个时代、另一个互联网所创建的。它需要巨量的工作,甚至包括各种方法覆盖,来完成最简单的任务。
Requests 是使用 Apache2 Licensed 许可证的 基于Python开发的HTTP 库,其在Python内置模块的基础上进行了高度的封装,从而使得Pythoner进行网络请求时,变得美好了许多,使用Requests可以轻而易举的完成浏览器可有的任何操作。
1、get请求:
# 1、无参数实例
import requests
ret = requests.get('https://github.com/timeline.json')
print ret.url
print ret.text
# 2、有参数实例
import requests
payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
ret = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/get", params=payload)
print ret.url
print ret.text
2、POST请求
# 1、基本POST实例
import requests
payload = {'key1': 'value1', 'key2': 'value2'}
ret = requests.post("http://httpbin.org/post", data=payload)
print ret.text
# 2、发送请求头和数据实例
import requests
import json
url = 'https://api.github.com/some/endpoint'
payload = {'some': 'data'}
headers = {'content-type': 'application/json'}
ret = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(payload), headers=headers) # 等价于request.post(url,json=payload)
print ret.text
print ret.cookies
3、其他请求
requests.get(url, params=None, **kwargs)
requests.post(url, data=None, json=None, **kwargs)
requests.put(url, data=None, **kwargs)
requests.head(url, **kwargs)
requests.delete(url, **kwargs)
requests.patch(url, data=None, **kwargs)
requests.options(url, **kwargs) # 以上方法均是在此方法的基础上构建
requests.request(method, url, **kwargs)
4、更多参数
method:请求类型(GET、POST、delete、put、head、patch、options)
url:访问地址
Params:在 QueryString、Form、Server Variable 以及 Cookies 找数据,他首先在 QueryString 集合查找数据,如果在 QueryString 找到数据,就返回数据,如果没有找到就去 Form 集合中查找数据,找到就返回,否则在往下一下个集合查找数据。是所有post和get传过来的值的集合
data(json): POST类型所带参数,声名发送请求体的格式
headers:定制头部信息
cookies:定制cookies信息
files:文件处理
(optional) Dictionary of ``'name': file-like-objects`` (or ``{'name': file-tuple}``) for multipart encoding upload.
``file-tuple`` can be a 2-tuple ``('filename', fileobj)``, 3-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type')``
or a 4-tuple ``('filename', fileobj, 'content_type', custom_headers)``, where ``'content-type'`` is a string
defining the content type of the given file and ``custom_headers`` a dict-like object containing additional headers
to add for the file.
auth:登陆使用,适用于类似ftp之类封装好的简单登陆验证。
(optional) Auth tuple to enable Basic/Digest/Custom HTTP Auth.
timeout:请求等待响应多长时间,数据发送多长时间。 仅对连接过程有效,与响应体的下载无关。
(optional) How long to wait for the server to send data
before giving up, as a float, or a :ref:`(connect timeout, read
timeout) <timeouts>` tuple.
allow_redirects:网络请求中可能会遇到重定向,我们需要一次处理一个请求,可以把重定向禁止。模拟打开
(optional) Boolean. Set to True if POST/PUT/DELETE redirect following is allowed.
proxies:代理访问配置。
(optional) Dictionary mapping protocol to the URL of the proxy.
verify:https是否访问开启,配合cert的CA证书使用
(optional) whether the SSL cert will be verified. A CA_BUNDLE path can also be provided. Defaults to ``True``.
stream:(optional) if ``False``, the response content will be immediately downloaded.
块编码请求
对于出去和进来的请求,Requests 也支持分块传输编码。要发送一个块编码的请求,仅需为你的请求体提供一个生成器(或任意没有具体长度的迭代器): def gen():
yield 'hi'
yield 'there' requests.post('http://some.url/chunked', data=gen())
对于分块的编码请求,我们最好使用 Response.iter_content() 对其数据进行迭代。在理想情况下,你的 request 会设置 stream=True,这样你就可以通过调用 iter_content 并将分块大小参数设为 None,从而进行分块的迭代。如果你要设置分块的最大体积,你可以把分块大小参数设为任意整数。
cert:私有证书配置。
(optional) if String, path to ssl client cert file (.pem). If Tuple, ('cert', 'key') pair.
使用方法:
def param_method_url():
# requests.request(method='get', url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/')
# requests.request(method='post', url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/')
pass def param_param():
# - 可以是字典
# - 可以是字符串
# - 可以是字节(ascii编码以内) # requests.request(method='get',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# params={'k1': 'v1', 'k2': '水电费'}) # requests.request(method='get',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# params="k1=v1&k2=水电费&k3=v3&k3=vv3") # requests.request(method='get',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# params=bytes("k1=v1&k2=k2&k3=v3&k3=vv3", encoding='utf8')) # 错误
# requests.request(method='get',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# params=bytes("k1=v1&k2=水电费&k3=v3&k3=vv3", encoding='utf8'))
pass def param_data():
# 可以是字典
# 可以是字符串
# 可以是字节
# 可以是文件对象 # requests.request(method='POST',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# data={'k1': 'v1', 'k2': '水电费'}) # requests.request(method='POST',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# data="k1=v1; k2=v2; k3=v3; k3=v4"
# ) # requests.request(method='POST',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# data="k1=v1;k2=v2;k3=v3;k3=v4",
# headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
# ) # requests.request(method='POST',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# data=open('data_file.py', mode='r', encoding='utf-8'), # 文件内容是:k1=v1;k2=v2;k3=v3;k3=v4
# headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
# )
pass def param_json():
# 将json中对应的数据进行序列化成一个字符串,json.dumps(...)
# 然后发送到服务器端的body中,并且Content-Type是 {'Content-Type': 'application/json'}
requests.request(method='POST',
url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
json={'k1': 'v1', 'k2': '水电费'}) def param_headers():
# 发送请求头到服务器端
requests.request(method='POST',
url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
json={'k1': 'v1', 'k2': '水电费'},
headers={'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'}
) def param_cookies():
# 发送Cookie到服务器端
requests.request(method='POST',
url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
data={'k1': 'v1', 'k2': 'v2'},
cookies={'cook1': 'value1'},
)
# 也可以使用CookieJar(字典形式就是在此基础上封装)
from http.cookiejar import CookieJar
from http.cookiejar import Cookie obj = CookieJar()
obj.set_cookie(Cookie(version=0, name='c1', value='v1', port=None, domain='', path='/', secure=False, expires=None,
discard=True, comment=None, comment_url=None, rest={'HttpOnly': None}, rfc2109=False,
port_specified=False, domain_specified=False, domain_initial_dot=False, path_specified=False)
)
requests.request(method='POST',
url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
data={'k1': 'v1', 'k2': 'v2'},
cookies=obj) def param_files():
# 发送文件
# file_dict = {
# 'f1': open('readme', 'rb')
# }
# requests.request(method='POST',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# files=file_dict) # 发送文件,定制文件名
# file_dict = {
# 'f1': ('test.txt', open('readme', 'rb'))
# }
# requests.request(method='POST',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# files=file_dict) # 发送文件,定制文件名
# file_dict = {
# 'f1': ('test.txt', "hahsfaksfa9kasdjflaksdjf")
# }
# requests.request(method='POST',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# files=file_dict) # 发送文件,定制文件名
# file_dict = {
# 'f1': ('test.txt', "hahsfaksfa9kasdjflaksdjf", 'application/text', {'k1': '0'})
# }
# requests.request(method='POST',
# url='http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/',
# files=file_dict) pass def param_auth():
from requests.auth import HTTPBasicAuth, HTTPDigestAuth ret = requests.get('https://api.github.com/user', auth=HTTPBasicAuth('wupeiqi', 'sdfasdfasdf'))
print(ret.text) # ret = requests.get('http://192.168.1.1',
# auth=HTTPBasicAuth('admin', 'admin'))
# ret.encoding = 'gbk'
# print(ret.text) # ret = requests.get('http://httpbin.org/digest-auth/auth/user/pass', auth=HTTPDigestAuth('user', 'pass'))
# print(ret)
# def param_timeout():
# ret = requests.get('http://google.com/', timeout=1)
# print(ret) # ret = requests.get('http://google.com/', timeout=(5, 1))
# print(ret)
pass def param_allow_redirects():
ret = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/', allow_redirects=False)
print(ret.text) def param_proxies():
# proxies = {
# "http": "61.172.249.96:80",
# "https": "http://61.185.219.126:3128",
# } # proxies = {'http://10.20.1.128': 'http://10.10.1.10:5323'} # ret = requests.get("http://www.proxy360.cn/Proxy", proxies=proxies)
# print(ret.headers) # from requests.auth import HTTPProxyAuth
#
# proxyDict = {
# 'http': '77.75.105.165',
# 'https': '77.75.105.165'
# }
# auth = HTTPProxyAuth('username', 'mypassword')
#
# r = requests.get("http://www.google.com", proxies=proxyDict, auth=auth)
# print(r.text) pass def param_stream():
ret = requests.get('http://127.0.0.1:8000/test/', stream=True)
print(ret.content)
ret.close() # from contextlib import closing
# with closing(requests.get('http://httpbin.org/get', stream=True)) as r:
# # 在此处理响应。
# for i in r.iter_content():
# print(i) def requests_session():
import requests session = requests.Session() ### 1、首先登陆任何页面,获取cookie i1 = session.get(url="http://dig.chouti.com/help/service") ### 2、用户登陆,携带上一次的cookie,后台对cookie中的 gpsd 进行授权
i2 = session.post(
url="http://dig.chouti.com/login",
data={
'phone': "",
'password': "xxxxxx",
'oneMonth': ""
}
) i3 = session.post(
url="http://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=8589623",
)
print(i3.text)
官方文档:http://cn.python-requests.org/zh_CN/latest/user/quickstart.html#id4
三、beautifulsoup模块
BeautifulSoup是一个模块,该模块用于接收一个HTML或XML字符串,然后将其进行格式化,之后遍可以使用他提供的方法进行快速查找指定元素,从而使得在HTML或XML中查找指定元素变得简单。
| 解析器 | 使用方法 | 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Python标准库 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “html.parser”) |
|
|
| lxml HTML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, “lxml”) |
|
|
| lxml XML 解析器 | BeautifulSoup(markup, [“lxml”, “xml”])BeautifulSoup(markup, “xml”) |
|
|
| html5lib | BeautifulSoup(markup, “html5lib”) |
|
|
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
asdf
<div class="title">
<b>The Dormouse's story总共</b>
<h1>f</h1>
</div>
<div class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister0" id="link1">Els<span>f</span>ie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</div>
ad<br/>sf
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
""" soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, features="lxml")
# 找到第一个a标签
tag1 = soup.find(name='a')
# 找到所有的a标签
tag2 = soup.find_all(name='a')
# 找到id=link2的标签
tag3 = soup.select('#link2')
1、安装
pip3 install beautifulsoup4
2、使用示例:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
...
</body>
</html>
""" soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, features="lxml")
3、name,标签名称(获取,更改)
# tag = soup.find('a')
# name = tag.name # 获取
# print(name)
# tag.name = 'span' # 设置
# print(soup)
4、attr,标签属性(获取,更改)
# tag = soup.find('a')
# attrs = tag.attrs # 获取
# print(attrs)
# tag.attrs = {'ik':123} # 设置
# tag.attrs['id'] = 'iiiii' # 设置
# print(soup)
5、children,所有子标签(获取)
# body = soup.find('body')
# v = body.children
6、children,所有子子孙孙标签(获取)
# body = soup.find('body')
# v = body.descendants
7、clear,将标签的所有子标签全部清空(保留标签名)
# tag = soup.find('body')
# tag.clear()
# print(soup)
8、decompose,递归的删除所有的标签
# body = soup.find('body')
# body.decompose()
# print(soup)
9、extract,递归的删除所有的标签,并获取删除的标签
# body = soup.find('body')
# v = body.extract()
# print(soup)
10、decode,转换为字符串(含当前标签);decode_contents(不含当前标签)
# body = soup.find('body')
# v = body.decode()
# v = body.decode_contents()
# print(v)
11、 encode,转换为字节(含当前标签);encode_contents(不含当前标签)
# body = soup.find('body')
# v = body.encode()
# v = body.encode_contents()
# print(v)
12、 find,获取匹配的第一个标签
# tag = soup.find('a')
# print(tag)
# tag = soup.find(name='a', attrs={'class': 'sister'}, recursive=True, text='Lacie')
# tag = soup.find(name='a', class_='sister', recursive=True, text='Lacie')
# print(tag)
13、find_all,获取匹配的所有标签
# tags = soup.find_all('a')
# print(tags)
# tags = soup.find_all('a',limit=1)
# print(tags)
# tags = soup.find_all(name='a', attrs={'class': 'sister'}, recursive=True, text='Lacie')
# # tags = soup.find(name='a', class_='sister', recursive=True, text='Lacie')
# print(tags)
# ####### 列表 #######
# v = soup.find_all(name=['a','div'])
# print(v)
# v = soup.find_all(class_=['sister0', 'sister'])
# print(v)
# v = soup.find_all(text=['Tillie'])
# print(v, type(v[0]))
# v = soup.find_all(id=['link1','link2'])
# print(v)
# v = soup.find_all(href=['link1','link2'])
# print(v)
# ####### 正则 #######
import re
# rep = re.compile('p')
# rep = re.compile('^p')
# v = soup.find_all(name=rep)
# print(v)
# rep = re.compile('sister.*')
# v = soup.find_all(class_=rep)
# print(v)
# rep = re.compile('http://www.oldboy.com/static/.*')
# v = soup.find_all(href=rep)
# print(v)
# ####### 方法筛选 #######
# def func(tag):
# return tag.has_attr('class') and tag.has_attr('id')
# v = soup.find_all(name=func)
# print(v)
# ## get,获取标签属性
# tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.get('id')
# print(v)
14、has_attr,检查标签是否具有该属性
# tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.has_attr('id')
# print(v)
15、 get_text,获取标签内部文本内容
# tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.get_text('id')
# print(v)
16、index,检查标签在某标签中的索引位置
# tag = soup.find('body')
# v = tag.index(tag.find('div'))
# print(v)
# tag = soup.find('body')
# for i,v in enumerate(tag):
# print(i,v)
17、is_empty_element,是否是空标签(是否可以是空)或者自闭合标签,
判断是否是如下标签:'br' , 'hr', 'input', 'img', 'meta','spacer', 'link', 'frame', 'base'
# tag = soup.find('br')
# v = tag.is_empty_element
# print(v)
18、当前的关联标签
# soup.next 下一个子元素
# soup.next_element list形式下一个子元素
# soup.next_elements list形式所有子元素
# soup.next_sibling 下一个元素的兄弟
# soup.next_siblings list形式元素的所有兄弟元素 #
# tag.previous 上一个元素
# tag.previous_element list形式上一个元素
# tag.previous_elements list形式上面所有元素
# tag.previous_sibling list形式上一个元素的所有兄弟
# tag.previous_siblings list形式上所有元素的所有兄弟 #
# tag.parent 父节点
# tag.parents 所有父节点
19、查找某标签的关联标签
# tag.find_next(...)
# tag.find_all_next(...)
# tag.find_next_sibling(...)
# tag.find_next_siblings(...) # tag.find_previous(...)
# tag.find_all_previous(...)
# tag.find_previous_sibling(...)
# tag.find_previous_siblings(...) # tag.find_parent(...)
# tag.find_parents(...) # 参数同find_all
20、 select,select_one, CSS选择器
soup.select("title")
soup.select("p nth-of-type(3)")
soup.select("body a")
soup.select("html head title")
tag = soup.select("span,a")
soup.select("head > title")
soup.select("p > a")
soup.select("p > a:nth-of-type(2)")
soup.select("p > #link1")
soup.select("body > a")
soup.select("#link1 ~ .sister")
soup.select("#link1 + .sister")
soup.select(".sister")
soup.select("[class~=sister]")
soup.select("#link1")
soup.select("a#link2")
soup.select('a[href]')
soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]')
soup.select('a[href^="http://example.com/"]')
soup.select('a[href$="tillie"]')
soup.select('a[href*=".com/el"]')
from bs4.element import Tag
def default_candidate_generator(tag):
for child in tag.descendants:
if not isinstance(child, Tag):
continue
if not child.has_attr('href'):
continue
yield child
tags = soup.find('body').select("a", _candidate_generator=default_candidate_generator)
print(type(tags), tags)
from bs4.element import Tag
def default_candidate_generator(tag):
for child in tag.descendants:
if not isinstance(child, Tag):
continue
if not child.has_attr('href'):
continue
yield child
tags = soup.find('body').select("a", _candidate_generator=default_candidate_generator, limit=1)
print(type(tags), tags)
21、标签的内容.text(只能取) .string(能取、能改)
# tag = soup.find('span')
# print(tag.string) # 获取
# tag.string = 'new content' # 设置
# print(soup)
# tag = soup.find('body')
# print(tag.string)
# tag.string = 'xxx'
# print(soup)
# tag = soup.find('body')
# v = tag.stripped_strings # 递归内部获取所有标签的文本
22.append在当前标签内部追加一个标签
# tag = soup.find('body')
# tag.append(soup.find('a'))
# print(soup)
#
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj = Tag(name='i',attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj.string = '我是一个新来的'
# tag = soup.find('body')
# tag.append(obj)
# print(soup)
23、insert在当前标签内部指定位置插入一个标签
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj = Tag(name='i', attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj.string = '我是一个新来的'
# tag = soup.find('body')
# tag.insert(2, obj)
# print(soup)
24、 insert_after,insert_before 在当前标签后面或前面插入
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj = Tag(name='i', attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj.string = '我是一个新来的'
# tag = soup.find('body')
# # tag.insert_before(obj)
# tag.insert_after(obj)
# print(soup)
25、replace_with 在当前标签替换为指定标签
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj = Tag(name='i', attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj.string = '我是一个新来的'
# tag = soup.find('div')
# tag.replace_with(obj)
# print(soup)
26、创建标签之间的关系
# tag = soup.find('div')
# a = soup.find('a')
# tag.setup(previous_sibling=a)
# print(tag.previous_sibling)
27、wrap,将指定标签把当前标签包裹起来
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj1 = Tag(name='div', attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj1.string = '我是一个新来的'
#
# tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.wrap(obj1)
# print(soup) # tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.wrap(soup.find('p'))
# print(soup)
28、unwrap,去掉当前标签,将保留其包裹的标签
# tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.unwrap()
# print(soup)
四、自动登陆爬虫示例
1、抽屉
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import requests # ############## 方式一 ##############
"""
# ## 1、首先登陆任何页面,获取cookie
i1 = requests.get(url="http://dig.chouti.com/help/service")
i1_cookies = i1.cookies.get_dict() # ## 2、用户登陆,携带上一次的cookie,后台对cookie中的 gpsd 进行授权
i2 = requests.post(
url="http://dig.chouti.com/login",
data={
'phone': "8615131255089",
'password': "xxooxxoo",
'oneMonth': ""
},
cookies=i1_cookies
) # ## 3、点赞(只需要携带已经被授权的gpsd即可)
gpsd = i1_cookies['gpsd']
i3 = requests.post(
url="http://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=8589523",
cookies={'gpsd': gpsd}
) print(i3.text)
""" # ############## 方式二 ##############
"""
import requests session = requests.Session()
i1 = session.get(url="http://dig.chouti.com/help/service")
i2 = session.post(
url="http://dig.chouti.com/login",
data={
'phone': "8615131255089",
'password': "xxooxxoo",
'oneMonth': ""
}
)
i3 = session.post(
url="http://dig.chouti.com/link/vote?linksId=8589523"
)
print(i3.text) """ 抽屉新热榜
2、github
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # ############## 方式一 ##############
#
# # 1. 访问登陆页面,获取 authenticity_token
# i1 = requests.get('https://github.com/login')
# soup1 = BeautifulSoup(i1.text, features='lxml')
# tag = soup1.find(name='input', attrs={'name': 'authenticity_token'})
# authenticity_token = tag.get('value')
# c1 = i1.cookies.get_dict()
# i1.close()
#
# # 1. 携带authenticity_token和用户名密码等信息,发送用户验证
# form_data = {
# "authenticity_token": authenticity_token,
# "utf8": "",
# "commit": "Sign in",
# "login": "wupeiqi@live.com",
# 'password': 'xxoo'
# }
#
# i2 = requests.post('https://github.com/session', data=form_data, cookies=c1)
# c2 = i2.cookies.get_dict()
# c1.update(c2)
# i3 = requests.get('https://github.com/settings/repositories', cookies=c1)
#
# soup3 = BeautifulSoup(i3.text, features='lxml')
# list_group = soup3.find(name='div', class_='listgroup')
#
# from bs4.element import Tag
#
# for child in list_group.children:
# if isinstance(child, Tag):
# project_tag = child.find(name='a', class_='mr-1')
# size_tag = child.find(name='small')
# temp = "项目:%s(%s); 项目路径:%s" % (project_tag.get('href'), size_tag.string, project_tag.string, )
# print(temp) # ############## 方式二 ##############
# session = requests.Session()
# # 1. 访问登陆页面,获取 authenticity_token
# i1 = session.get('https://github.com/login')
# soup1 = BeautifulSoup(i1.text, features='lxml')
# tag = soup1.find(name='input', attrs={'name': 'authenticity_token'})
# authenticity_token = tag.get('value')
# c1 = i1.cookies.get_dict()
# i1.close()
#
# # 1. 携带authenticity_token和用户名密码等信息,发送用户验证
# form_data = {
# "authenticity_token": authenticity_token,
# "utf8": "",
# "commit": "Sign in",
# "login": "wupeiqi@live.com",
# 'password': 'xxoo'
# }
#
# i2 = session.post('https://github.com/session', data=form_data)
# c2 = i2.cookies.get_dict()
# c1.update(c2)
# i3 = session.get('https://github.com/settings/repositories')
#
# soup3 = BeautifulSoup(i3.text, features='lxml')
# list_group = soup3.find(name='div', class_='listgroup')
#
# from bs4.element import Tag
#
# for child in list_group.children:
# if isinstance(child, Tag):
# project_tag = child.find(name='a', class_='mr-1')
# size_tag = child.find(name='small')
# temp = "项目:%s(%s); 项目路径:%s" % (project_tag.get('href'), size_tag.string, project_tag.string, )
# print(temp) github
3、知乎
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import time import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup session = requests.Session() i1 = session.get(
url='https://www.zhihu.com/#signin',
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.98 Safari/537.36',
}
) soup1 = BeautifulSoup(i1.text, 'lxml')
xsrf_tag = soup1.find(name='input', attrs={'name': '_xsrf'})
xsrf = xsrf_tag.get('value') current_time = time.time()
i2 = session.get(
url='https://www.zhihu.com/captcha.gif',
params={'r': current_time, 'type': 'login'},
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.98 Safari/537.36',
}) with open('zhihu.gif', 'wb') as f:
f.write(i2.content) captcha = input('请打开zhihu.gif文件,查看并输入验证码:')
form_data = {
"_xsrf": xsrf,
'password': 'xxooxxoo',
"captcha": 'captcha',
'email': '424662508@qq.com'
}
i3 = session.post(
url='https://www.zhihu.com/login/email',
data=form_data,
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.98 Safari/537.36',
}
) i4 = session.get(
url='https://www.zhihu.com/settings/profile',
headers={
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_10_5) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/54.0.2840.98 Safari/537.36',
}
) soup4 = BeautifulSoup(i4.text, 'lxml')
tag = soup4.find(id='rename-section')
nick_name = tag.find('span',class_='name').string
print(nick_name) 知乎
4、博客园
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import re
import json
import base64 import rsa
import requests def js_encrypt(text):
b64der = 'MIGfMA0GCSqGSIb3DQEBAQUAA4GNADCBiQKBgQCp0wHYbg/NOPO3nzMD3dndwS0MccuMeXCHgVlGOoYyFwLdS24Im2e7YyhB0wrUsyYf0/nhzCzBK8ZC9eCWqd0aHbdgOQT6CuFQBMjbyGYvlVYU2ZP7kG9Ft6YV6oc9ambuO7nPZh+bvXH0zDKfi02prknrScAKC0XhadTHT3Al0QIDAQAB'
der = base64.standard_b64decode(b64der) pk = rsa.PublicKey.load_pkcs1_openssl_der(der)
v1 = rsa.encrypt(bytes(text, 'utf8'), pk)
value = base64.encodebytes(v1).replace(b'\n', b'')
value = value.decode('utf8') return value session = requests.Session() i1 = session.get('https://passport.cnblogs.com/user/signin')
rep = re.compile("'VerificationToken': '(.*)'")
v = re.search(rep, i1.text)
verification_token = v.group(1) form_data = {
'input1': js_encrypt('wptawy'),
'input2': js_encrypt('asdfasdf'),
'remember': False
} i2 = session.post(url='https://passport.cnblogs.com/user/signin',
data=json.dumps(form_data),
headers={
'Content-Type': 'application/json; charset=UTF-8',
'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest',
'VerificationToken': verification_token}
) i3 = session.get(url='https://i.cnblogs.com/EditDiary.aspx') print(i3.text) 博客园
django高级之爬虫基础的更多相关文章
- Python爬虫基础
前言 Python非常适合用来开发网页爬虫,理由如下: 1.抓取网页本身的接口 相比与其他静态编程语言,如java,c#,c++,python抓取网页文档的接口更简洁:相比其他动态脚本语言,如perl ...
- Python基础+爬虫基础
Python基础+爬虫基础 一.python的安装: 1.建议安装Anaconda,会自己安装一些Python的类库以及自动的配置环境变量,比较方便. 二.基础介绍 1.什么是命名空间:x=1,1存在 ...
- python 3.x 爬虫基础---Urllib详解
python 3.x 爬虫基础 python 3.x 爬虫基础---http headers详解 python 3.x 爬虫基础---Urllib详解 前言 爬虫也了解了一段时间了希望在半个月的时间内 ...
- Django高级部分
Django高级部分 1.上传图片: 当Django在处理文件上传的时候,文件数据被保存在request.FILES,FILES中的每个键为<input type="file" ...
- python 3.x 爬虫基础---常用第三方库(requests,BeautifulSoup4,selenium,lxml )
python 3.x 爬虫基础 python 3.x 爬虫基础---http headers详解 python 3.x 爬虫基础---Urllib详解 python 3.x 爬虫基础---常用第三方库 ...
- java网络爬虫基础学习(三)
尝试直接请求URL获取资源 豆瓣电影 https://movie.douban.com/explore#!type=movie&tag=%E7%83%AD%E9%97%A8&sort= ...
- java网络爬虫基础学习(一)
刚开始接触java爬虫,在这里是搜索网上做一些理论知识的总结 主要参考文章:gitchat 的java 网络爬虫基础入门,好像要付费,也不贵,感觉内容对新手很友好. 一.爬虫介绍 网络爬虫是一个自动提 ...
- python从爬虫基础到爬取网络小说实例
一.爬虫基础 1.1 requests类 1.1.1 request的7个方法 requests.request() 实例化一个对象,拥有以下方法 requests.get(url, *args) r ...
- Django高级实战 开发企业级问答网站完整
资源获取链接点击这里 Django高级实战 开发企业级问答网站 从实际需求分析开始,实现当今主流知识问答应用的功能,包括动态.文章.问答.私信.消息通知.搜索.个人中心,打造企业级知识问答网站,由此全 ...
随机推荐
- 【BZOJ】1627: [Usaco2007 Dec]穿越泥地(bfs)
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1627 裸bfs不解释.. #include <cstdio> #include < ...
- 转载: crypto:start() 错误。
错误信息: Eshell V5.10.3 (abort with ^G)1> crypto:start().** exception error: undefined function cry ...
- add命令
将文件加入到索引,要使用add命令.在<file>指定加入索引的文件.用空格分割可以指定多个文件. git add demo.html test.html //添加两个文件 添加当前目录下 ...
- 【LDA】nlp
http://pythonhosted.org/lda/getting_started.html http://radimrehurek.com/gensim/
- MFC存储图片到SQL Server数据库
第一步:建立数据库表,比如:id char,pic image. 第二步:建立MFC单文档应用程序,再添加类CMyRecordset,基类选择CRecordset,导入数据库的刚建立的表. 第三步:在 ...
- VS工程目录下的ipch文件夹和.sdf文件
Visual Studio 2010工程目录下的ipch文件夹和.sdf文件 - web8 - 博客园http://www.cnblogs.com/web100/archive/2012/12/21/ ...
- SQL语句:语法错误(操作符丢失)在查询表达式中
所谓操作符丢失,应该是你在拼接SQL语句是少了关键词或者分隔符,导致系统无法识别SQL语句.建议:1.监控SQL语句,看看哪里出现问题:断点看下最后的sql到底是什么样子就知道了,另外你可以把这段sq ...
- Jquery判断某个标签 Id是否存在
query判断某个标签 Id是否存在, 如果是下面的 jQuery 代码判断一个对象是否存在,是不能用的 if($("#id")){}else{} 因为 $(“#id”) 不管对象 ...
- android高仿微信UI点击头像显示大图片效果, Android 使用ContentProvider扫描手机中的图片,仿微信显示本地图片效果
http://www.cnblogs.com/Jaylong/archive/2012/09/27/androidUI.html http://blog.csdn.net/xiaanming/arti ...
- python3个人习惯的gitignore
简介 就是普通的.gitignore # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files __pycache__/ *.py[cod] *$py.class # C ext ...
