C++(实验三)
Part 1 画布小球试验
程序源码
#include <iostream>
#include "canvas.h"
#include "ball.h" int main() {
Canvas canvas; //创建默认画布,黑底绿色 Ball ball1(,);
system("pause"); ball1.left();
system("pause"); ball1.up();
system("pause"); canvas.changeCanvasFg("E"); // 更新画布前景色
system("pause"); canvas.changeCanvasBg("D"); // 更新画布背景色
system("pause"); return ;
}
main.cpp
#ifndef CANVAS_H
#define CANVAS_H #include <string>
using std::string; class Canvas {
public:
Canvas(string bg0="", string fg0="A");
void changeCanvasBg(string bg0);
void changeCanvasFg(string fg0);
void changeCanvasColor(string bg0, string fg0);
private:
string bg; // background color
string fg; // foreground color
}; #endif
canvas.h
#include "canvas.h"
#include <cstdlib>
Canvas::Canvas(string bg0, string fg0):bg(bg0), fg(fg0) {
string color = "color ";
color += bg0;
color += fg0;
system(color.c_str());
}
void Canvas::changeCanvasBg(string bg0) {
bg = bg0; // 更新画布背景色
string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str());
}
void Canvas::changeCanvasFg(string fg0) {
fg = fg0; // 更新画布前景色
string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str());
}
void Canvas::changeCanvasColor(string bg0, string fg0){
bg = bg0; // 更新画布背景色
fg = fg0; // 更新画布前景色
string color = "color ";
color += bg;
color += fg;
system(color.c_str());
}
canvas.cpp
#ifndef BALL_H
#define BALL_H class Ball {
public:
Ball(int x0=, int y0=); // 在坐标(x,y)处构造一个小球(小球用字符O表示)
void left(int step=); // 左移step
void right(int step=); // 右移step
void up(int step=); // 上移step
void down(int step=); // 下移step
private:
int x; // x坐标
int y; // y坐标 };
#endif
ball.h
#include "ball.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib> // 因为使用了system("cls"); 所以需要包含这个头文件 using std::cout;
using std::endl; const int SIZE_X=; // 小球x轴移动范围0~SIZE_X
const int SIZE_Y=; // 小球y轴移动范围0~SIZE_Y Ball::Ball(int x0, int y0):x(x0), y(y0) { // 打印y0-1行空行
for(int line=; line <= y0-; line++)
cout << endl;
// 打印x0-1个空格
for(int col=; col <= x0-; col++)
cout << " "; // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl;
} void Ball::left(int step) {
x = x-step;
if(x <= )
x=;
// 清屏 system("cls");
// 打印y-1行空行
for(int line=; line <= y-; line++)
cout << endl;
// 打印x-1个空格
for(int col=; col <= x-; col++)
cout << " "; // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl;
} void Ball::right(int step) {
x = x+step;
if(x >= SIZE_X)
x=SIZE_X; // 清屏
system("cls");
// 打印y-1行空行
for(int line=; line <= y-; line++)
cout << endl;
// 打印x-1个空格
for(int col=; col <= x-; col++)
cout << " "; // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl;
} void Ball::up(int step) {
y = y-step;
if(y <= )
y=; // 清屏
system("cls");
// 打印y-1行空行
for(int line=; line <= y-; line++)
cout << endl;
// 打印x-1个空格
for(int col=; col <= x-; col++)
cout << " "; // 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl;
} void Ball::down(int step) {
y = y+step;
if(y >= SIZE_Y)
y = SIZE_Y; // 清屏
system("cls");
// 打印y-1行空行
for(int line=; line <= y-; line++)
cout << endl;
// 打印x-1个空格
for(int col=; col <= x-; col++)
cout << " ";
// 打印小球
cout << "O" << endl;
}
ball.cpp
运行截图

PS:system()在Xcode中运行并不是动画,而且不会改变前景色和背景色,也没有清屏,如图,还在研究中
Part 2 GRAGH
程序源码
#include <iostream>
#include "graph.h"
using namespace std; int main() { Graph graph1('*',);
graph1.draw(); system("pause");
system("cls"); Graph graph2('$',);
graph2.draw(); return ;
}
main.cpp
#ifndef GRAPH_H
#define GRAPH_H class Graph {
public:
Graph(char ch, int n);
void draw();
private:
char symbol;
int size;
}; #endif
graph.h
// 类graph的实现
#include "graph.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; // 带参数的构造函数的实现
Graph::Graph(char ch, int n): symbol(ch), size(n) {
} // 成员函数draw()的实现
// 功能:绘制size行,显示字符为symbol的指定图形样式
void Graph::draw() {
int i,j,k;
for(i=;i<=size;i++) //利用行数控制
{ for(j=size-i;j>=;j--) //控制空格的输入
cout<<" ";
for(k=;k<=*i-;k++) //控制graph的输入
cout<<symbol;
cout<<endl;
}
}
graph.cpp
运行截图

PS:依旧和上个程序一样system()的问题
Part 3 Fraction 类
程序源码
#include <iostream>
#include "Fraction.hpp"
using namespace std; int main(){
Fraction a;
printf("a:");
a.printFraction();
a.compareFraction(, );
a.addFraction(,);
a.printFraction();
cout<<endl<<"b:";
Fraction b(,);
b.printFraction();
b.compareFraction(, );
b.divideFraction(, );
b.printFraction();
cout<<endl<<"c:";
Fraction c();
c.printFraction();
c.compareFraction(, );
c.minusFraction(,);
c.printFraction();
cout<<endl<<"d:";
Fraction d(,);
d.printFraction();
d.compareFraction(, );
d.timeFraction(, );
d.printFraction();
cout<<endl<<"e:";
Fraction e(,);
e.printFraction();
e.compareFraction(, );
e.addFraction(, );
e.printFraction();
return ;
}
main.cpp
#ifndef Fraction_hpp
#define Fraction_hpp #include <stdio.h>
class Fraction{
public:
Fraction(int x0=,int y0=);
void addFraction(int x1,int y1); //两分数相加
void minusFraction(int x1,int y1); //两分数相减
void timeFraction(int x1,int y1); //两分数相乘
void divideFraction(int x1,int y1); //两分数相除
void printFraction(); //输出分数
void compareFraction(int x1,int y1); //两分数相比较
private:
int top;
int bottom; };
#endif /* Fraction_hpp */
fraction.h
#include "Fraction.hpp"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; Fraction::Fraction(int x0,int y0):top(x0),bottom(y0){
} void Fraction::addFraction(int x1,int y1){
int m,n,r,t;
if(y1==) //控制分母为零的情况
cout<<"error!"<<endl;
else
{
if(bottom==y1) //将分数化为最简形式
{ top=top+x1;
if(top%bottom==)
{ top=top/bottom;
bottom=;}
else
{ m=top;
n=bottom;
t=;
r=;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
top=top/n;
bottom=bottom/n;
}
}
else
{ top=top*y1;
x1=x1*bottom;
top=top+x1;
bottom=bottom*y1;
m=top;
n=bottom;
t=;
r=;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
top=top/n;
bottom=bottom/n;
}
}
} void Fraction::minusFraction(int x1,int y1){
int m,n,r,t;
if(y1==) //控制分母为零的情况
cout<<"error!"<<endl;
else{
if(bottom==y1) //将分数化为最简形式
{ top=top-x1;
if(top%bottom==)
{ top=top/bottom;
bottom=;}
else
{ m=top;
n=bottom;
t=;
r=;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
top=top/n;
bottom=bottom/n;
}
}
else
{ top=top*y1;
x1=x1*bottom;
top=top-x1;
bottom=bottom*y1;
m=top;
n=bottom;
t=;
r=;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
top=top/n;
bottom=bottom/n;
}
}
} void Fraction::timeFraction(int x1,int y1){
if(y1==) //控制分母为零的情况
cout<<"error!"<<endl;
else{
int m,n,r,t;
top=top*x1;
bottom=bottom*y1;
if(top%bottom==) //将分数化为最简形式
{ top=top/bottom;
bottom=;}
else
{
m=top;
n=bottom;
t=;
r=;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
top=top/n;
bottom=bottom/n;
}
}
} void Fraction::divideFraction(int x1,int y1){
int m,n,r,t;
if(y1==) //控制分母为零的情况
cout<<"error!"<<endl;
else{
top=top*y1;
bottom=bottom*x1;
if(top%bottom==) //将分数化为最简形式
{ top=top/bottom;
bottom=;}
else
{
m=top;
n=bottom;
t=;
r=;
if(m<n)
{t=m;m=n;n=t;}
r=m%n;
while(r!=)
{m=n;n=r;r=m%n;}
top=top/n;
bottom=bottom/n;
}
}
} void Fraction::printFraction(){
if(bottom==) //控制分母为零的情况
cout<<"error!"<<endl;
else
cout<<top<<"/"<<bottom<<endl;
} void Fraction::compareFraction(int x1,int y1){
double x,y;
if(y1==) //控制分母为零的情况
cout<<"error!"<<endl;
else{
x=top*1.0/bottom;
y=x1*1.0/y1;
if(x>y)
cout<<top<<"/"<<bottom<<" > "<<x1<<"/"<<y1<<endl;
else if(x<y)
cout<<top<<"/"<<bottom<<" < "<<x1<<"/"<<y1<<endl;
else cout<<top<<"/"<<bottom<<" = "<<x1<<"/"<<y1<<endl;
}
}
fraction.cpp
运行截图
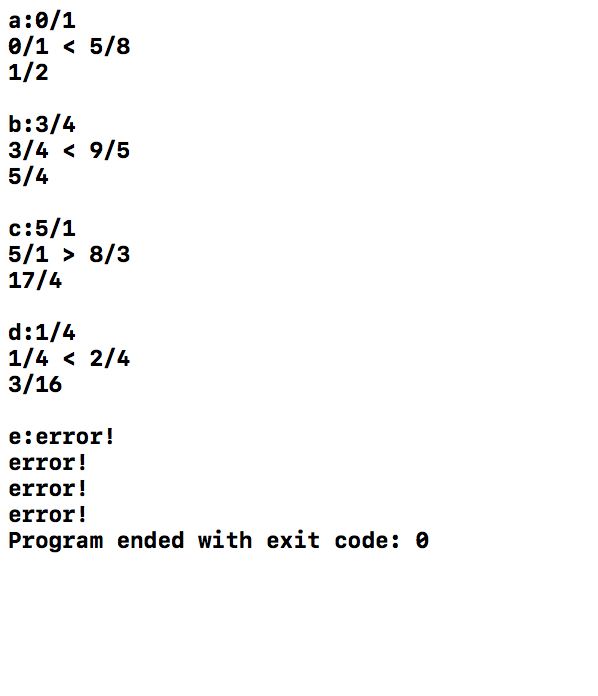
实验总结与体会
1.学会运用多文件结构,将类的定义、实现、使用部分分开,便于错误排查,使得程序更加便于管理。
2.了解了system("pause),system("color ××")函数的使用,但在Xcode中貌似有点问题,还在研究中,待完善。
3.C与C++的一些语法规则有些混淆了,说明对C++的基础语法规则掌握的还不熟练,需多敲多练。
实验二评论链接
https://www.cnblogs.com/zuiyankh/p/10587674.html#4219118
https://www.cnblogs.com/qsxsc/p/10583875.html#4219112
https://www.cnblogs.com/yfwg/p/10594280.html#4219099
C++(实验三)的更多相关文章
- FPGA与simulink联合实时环路系列——实验三 按键key
实验三 按键key 实验内容 在FPGA的实验中,经常涉及到按键的使用,按键是必不可少的人机交互的器件之一,在这些实验中,有时将按键的键值读取显示到数码管.LCD或者是通过串口传送到PC的串口助手上进 ...
- Java实验三
20145113 20145102实验三 实验步骤 编码标准 编程标准包含:具有说明性的名字.清晰的表达式.直截了当的控制流.可读的代码和注释,以及在追求这些内容时一致地使用某些规则和惯用法的重要性 ...
- Verilog HDL那些事_建模篇笔记(实验三:按键消抖)
实验三:按键消抖 首先将按键消抖功能分成了两个模块,电平检查模块和10ms延迟模块.电平检测模块用来检测按键信号的变化(是否被按下),10ms延迟模块用来稳定电平检查模块的输入,进而稳定按键信号,防止 ...
- 20145229&20145316 《信息安全系统设计基础》实验三 实时系统的移植
实验封面 实验内容 1.安装ADS(安装文件在00-ads1.2目录下,破解方法00-ads1.2\Crack目录下) 2.安装GIVEIO驱动(安装文件在01-GIVEIO目录下) 3.把整个GIV ...
- 20145301&20145321&20145335实验三
20145301&20145321&20145335实验三 这次实验我的组员为:20145301赵嘉鑫.20145321曾子誉.20145335郝昊 实验内容详见:实验三
- 20145212 实验三《敏捷开发与XP实践》
20145212 实验三<敏捷开发与XP实践> 实验内容 使用git上传代码 与20145223同学一组,使用git相互更改代码 同组实验报告链接:http://www.cnblogs.c ...
- 20145213《Java程序设计》实验三敏捷开发与XP实践
20145213<Java程序设计>实验三敏捷开发与XP实践 实验要求 1.XP基础 2.XP核心实践 3.相关工具 实验内容 1.敏捷开发与XP 软件工程是把系统的.有序的.可量化的方法 ...
- 20145206《Java程序设计》实验三实验报告
20145206<Java程序设计>实验三实验报告 实验内容 XP基础 XP核心实践 相关工具 实验步骤 (一)敏捷开发与XP 软件工程是把系统的.有序的.可量化的方法应用到软件的开发.运 ...
- 20145308刘昊阳 《Java程序设计》实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验报告
20145308刘昊阳 <Java程序设计>实验三 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验报告 实验名称 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验内容 XP基础 XP核心实践 相关工具 统计的PSP(Personal ...
- 20145337实验三实验报告——敏捷开发与XP实践
20145337实验三实验报告--敏捷开发与XP实践 实验名称 敏捷开发与XP实践 实验内容 XP基础 XP核心实践 相关工具 ** 实验步骤**### 敏捷开发与XP 软件工程包括下列领域:软件需求 ...
随机推荐
- 【论文速读】Cong_Yao_CVPR2017_EAST_An_Efficient_and_Accurate_Scene_Text_Detector
Cong_Yao_CVPR2017_EAST_An_Efficient_and_Accurate_Scene_Text_Detector 作者和代码 非官方版tensorflow实现 非官方版kera ...
- Shrinking images on Linux
When creating images from existing ISOs you often need to allocate a number of MB for the image to a ...
- CSS制作渐变背景色
<style type="text/css"> #grad1 { background: -webkit-linear-gradient(#C2F2F0,#); /* ...
- 解决ssh连接问题1
某天服务器A与B,互相ping没问题,telnet 22端口没问题 ssh -v a@10.80.97.241 OpenSSH_6.6.1, OpenSSL 1.0.1k-fips 8 Jan 201 ...
- Centos7 Docker 安装笔记
1. docker官方文档地址:https://docs.docker.com/ 2. centos版本号查看命令:uname -a centos7.3版本 3. 直接yum -install ...
- Python3 tkinter基础 Scrollbar pack 创建靠右、充满Y轴的垂直滚动条
Python : 3.7.0 OS : Ubuntu 18.04.1 LTS IDE : PyCharm 2018.2.4 Conda ...
- continue #结束本次循环,继续下一次代码
for i in range(10): if i <5: continue print(i) for j in range(10): pr ...
- SQL中IN与EXISTS的区别
1.IN子句中的子查询只能返回一个字段,不允许返回多个字段,而EXISTS可以返回多个字段 2.IN返回的是某字段的值,而EXISTS返回的则是True或False,EXISTS子句存在符合条件的结果 ...
- (转)How Transformers Work --- The Neural Network used by Open AI and DeepMind
How Transformers Work --- The Neural Network used by Open AI and DeepMind Original English Version l ...
- 何给域名配置https证书
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/ymwang/p/6893105.html http和https的区别就是,后者在网络传输过程中会很安全,原因就是给http安装了SSL证书. ...
